我国月降水量气候噪声的估计
THE ESTIMATION ON CLIMATE NOISE OF MONTHLY PRECIPITATION IN CHINA
-
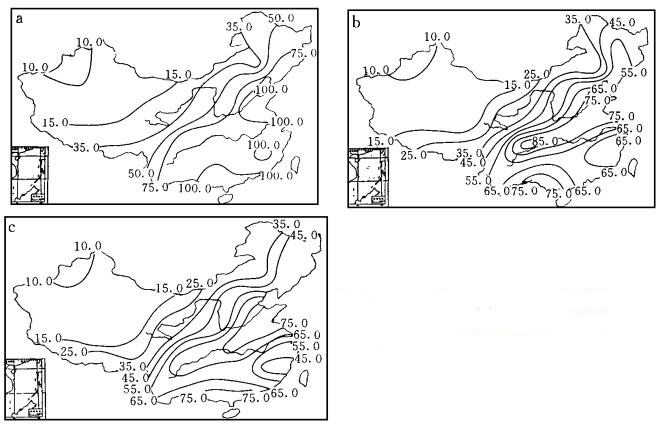
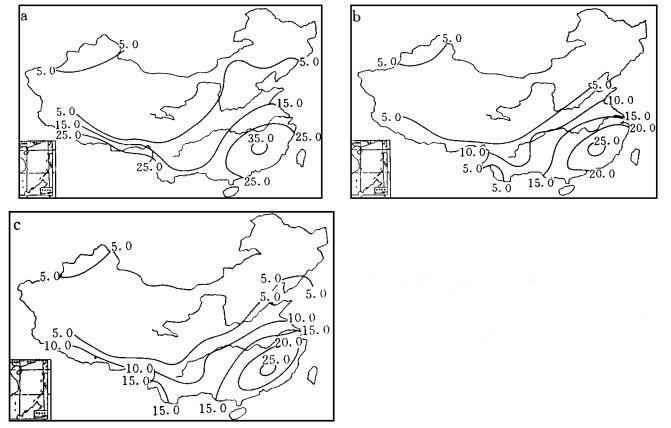
摘要: 利用我国大陆均匀分布的70个测站1961~1991年逐日降水量资料, 讨论了月降水量的气候噪声的3种估计方法, 并分别用改进后的方法估计了1、4、7、10月四个有代表性月份降水量的气候噪声.结果表明:我国月降水量的气候噪声随着降水量增加, 具有明显的季节变化, 一般夏季月份的噪声显著大于冬季月份, 秋季月份稍高于春季月份.从空间分布看, 春、夏、秋、冬全国绝大部分地区的气候噪声由南向北、由沿海向内陆明显减小.Abstract: Based on the daily precipitation data of 70 stations selected evenly over China from 1961 to 1991, three estimating methods on climate noise of monthly precipitation are discussed. The climate noises of monthly precipitation in January, April, July and October are estimated by using the improved methods. The results show that with the precipitation increasing, the climate noise of monthly precipitation would increase and has obvious seasonal change. Generally, the value of climate noise is greater in summer than in winter. In spatial distribution, the climate noise in the most areas of China decreases prominently from south to north, and from coastal areas to inland all the year round.
-
Key words:
- Monthly precipitation;
- Climate noise;
- Variance
-
表 1 1月和7月降水量噪声估计值 (mm)

-
[1] Leith C E.The Design of Statistical-dynamically Climate Model and Statistical Constraints on the Predictability of Climate.The Physical Basis of Climate and Climate Modeling, GARP.Ser, No.16, WMO-ICSU, 1975.137~141. [2] Madden R A.Estimates of the natural variability of time-averaged sea-level pressure.Mon.Wea.Rev., 1976, 104:942~952. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1976)104<0942:EOTNVO>2.0.CO;2 [3] Trenberth K E.Some effects of finite sample size and persistence on meteorological statistics: Part Ⅰautocorrelation.Mon.Wea.Rev., 1984, 112: 2359~2368. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1984)112<2359:SEOFSS>2.0.CO;2 [4] Trenberth K E.Some effects of finite sample size and persistence on meteorological statistics: Part Ⅱ potential predictability.Mon.Wea.Rev., 1984, 112: 2359~2368. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1984)112<2359:SEOFSS>2.0.CO;2 [5] Yamamoto, et al.An estimate of climate noise.J.Meteor.Soc.Japan, 1985, 63 (6): 1147~1156. [6] 马开玉, 董谢琼.我国的降水资源及其稳定性与潜在可预报性: (Ⅱ) 潜在可预报性.气象科学, 1995, 15 (1): 72~79. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD9495&filename=QXKX199501008&v=MTA5OTk4ZVgxTHV4WVM3RGgxVDNxVHJXTTFGckNVUkwyZlkrZHNGeS9sVWIvSk5EWEFkckt4RjlUTXJvOUZiSVI= [7] 吴洪宝.青海省月平均温度潜在长期可预报性的估计.南京气象学院学报, 1995, 18: 282~287. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX502.018.htm [8] Madden R A and Shea D J.Potential Long-Range Predictability of Precipitation over North America.Proceedings of the Seventh Annual Climate Diagnostics Workshop, NCAR, U.S.Department of Commerce, 1982.423~426. [9] 王绍武.气候论断与研究进展.北京:气象出版社, 1993.92~93. [10] 黄嘉佑.气象统计与预报方法.北京:气象出版社, 1992.347~348. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: