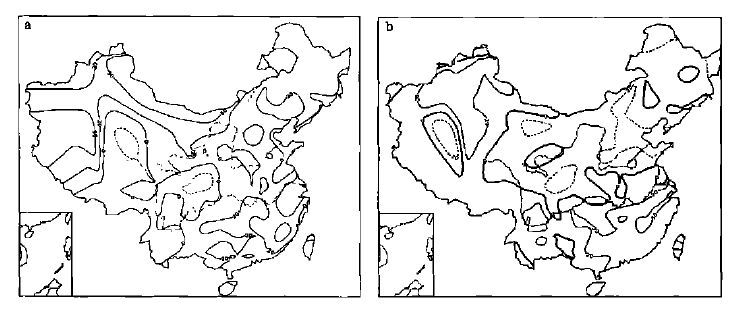
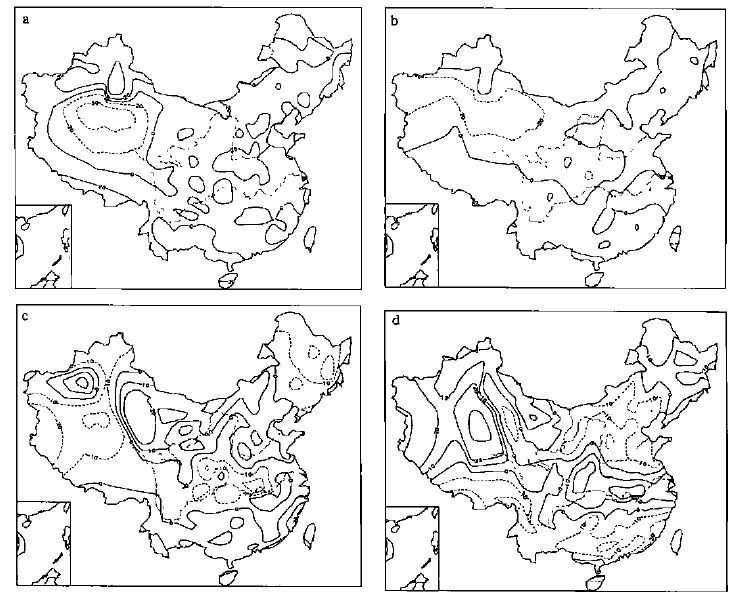
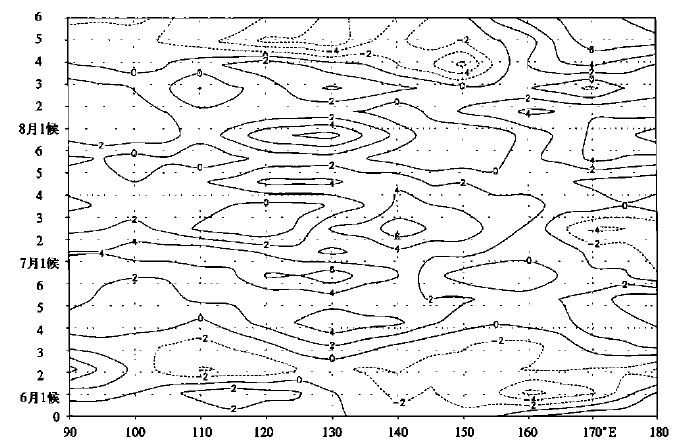
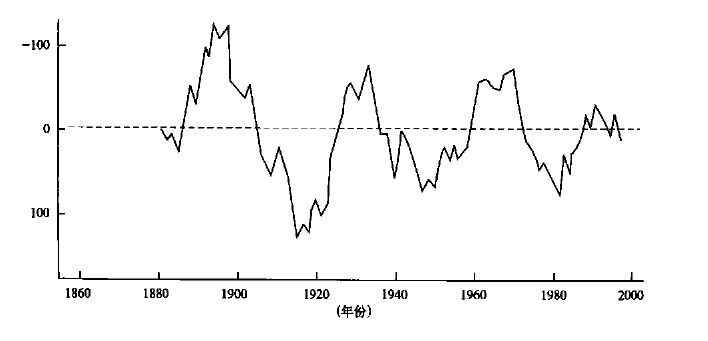
南涝北旱的年代气候特点和形成条件
DECADE CLIMATE CHARACTERS AND FORMATION CONDITION OF FLOODING IN SOUTH AND DROUGHT IN NORTH IN CHINA
-
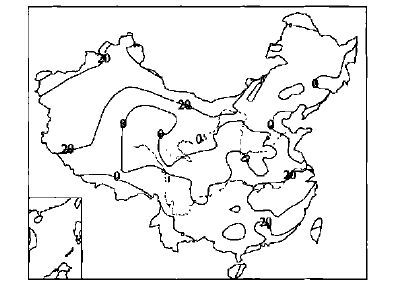
摘要: 通过研究最近50年我国夏季降水分布的年代际及年际气候变化特征,以及对20世纪90年代至今夏季旱涝趋势的对比分析,讨论了夏季主要雨带位置南移的气候趋势,以及亚洲大陆高压、ENSO事件对夏季降水的影响关系。结果表明,20世纪90年代后期开始我国夏季旱涝分布气候态发生较大的变化,这可能预示夏季进入南涝北旱的年代气候时期。这些结果对于降水的年代气候预测和短期气候预测都具有重要意义。Abstract: According to the analysis of the decade and interannual climate character variation of summer precipitation in recent fifty years and decade climate variation of continental high over Asia and ENSO event, the distribution of summer precipitation in recent years is contrasted. The result indicates that the distribution of summer precipitation had great change from the latter of the 1990s. The changeable distribution trends of flooding and drought in summer in the 1990s and the beginning of this century are analyzed. It is found that the decade climate character of summer precipitation had obvious change in recent years in our country. The main rain belt of the 1990s was in the Yangtze River to the north of Jiangnan areas. The decade climate character was that the precipitation was more than normal in the north and the south of China and less than normal in the middle areas. From the beginning of the end of last century, the main rain belt was located the south of the Yangtze River to South China, and the North probably entered into dry spell. It may come into the decade climate period of flooding in the south and drought in the north in summer. According the analysis, the climate character of precipitation change in recent summers related to the main rain belt moving trend from north to south, and it also related to the influence of the climate change of atmospheric circulation, especially East Asia continental high. The warm water of the equator Pacific also took the corresponding effect to decade climate change of summer precipitation. It is concluded that the summer precipitation will still has the climate character that the precipitation is more than normal in south and less in north, therefore the drought climate trend of the north will be more rigorous. It is highly important to predict the decade climate variation and short-term climate variation of summer precipitation.
-
表 1 20世纪各年代降水距平百分率主要多雨区纬度位置

表 2 江南多雨期和少雨期在ENSO冷暖事件年的平均降水距平

-
[1] 王绍武, 胡增臻. 气象要素场显著性检验的统计模拟方法. 见: 王绍武, 黄朝迎等主编. 长江黄河旱涝灾害发生规律及其经济影响的诊断研究. 北京: 气象出版社, 1993. 215~221. [2] 陈兴芳, 孙林海.我国年、季降水的年代际变化分析.气象, 2002, 28(7):3~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200207001.htm [3] 王绍武.现代气候学研究进展.北京:气象出版社, 2001.365~367. [4] 王绍武, 赵宗慈.长期天气预报基础.上海:上海科学技术出版社, 1987.96. [5] 陈兴芳, 赵振国.中国汛期降水预测研究及应用.北京:气象出版社, 2002.43~71. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: