CO2湍流通量误差的修正和不确定性研究进展
CORRECTION OF ERRORS AND UNCERTAINTY IN THE MEASUREMENTS OF CO2 TURBULENT FLUX
-
摘要: 目前国内外对能量和CO2涡动相关通量的测量误差的谱修正缺乏一致性,导致各测量站之间的资料对比难以进行,给全球尺度资料的合成造成很大困难。因此在强调长期CO2通量测量精度的同时,还应该注重确定对测量误差修正的首选方法和研究重点。该文主要介绍了两种用于修正测量仪器误差的谱方法;二维和三维的气流运动对通量误差的影响;资料处理中的误差;夜间CO2通量的测量问题。Abstract:
The lack of unanimous opinion in spectral correction of energy and carbon dioxide eddy covariance flux error caused the difficulties not only in intercomparison of results derived form the different experiments, but also in synthesis data for global models. Two kinds of spectral methods used to correct sensor error were introduced. The influence of two-dimension and triple–dimension air current on CO2 flux was discussed. Meanwhile, Error encountered in processing data and problems of measurement CO2 flux in nighttime were investigated.
-
Key words:
- Eddy covariance;
- Long-term flux data;
- Carbon balance
-
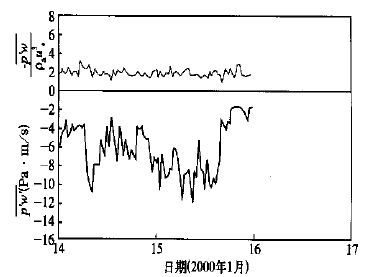
图 1 2000年1月两天



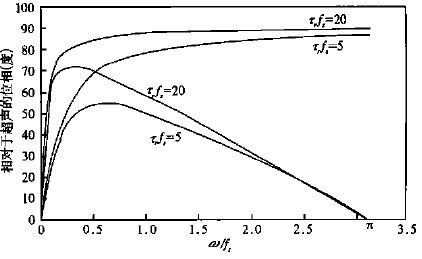
图 2 一阶滤波器和线性滤波器的位相比较[3]
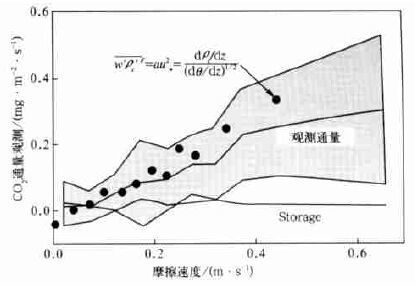
图 3 夜间观测的CO2 通量

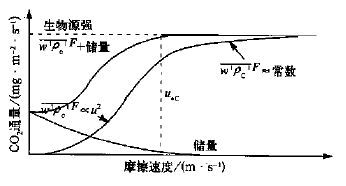
图 4 储量修正的CO2 通量与摩擦速度的关系[3]
-
[1] Wofsy S C, Hollinger D Y for the AmeriFlux science team. Scientific Plan for AmeriFlux: US Long-Term Flux Measurement Network, 1998. [2] Leuning R, King K M .Comparison of eddy-covariance measurement s of CO2 fluxes by open-and closed-path CO2 analysers .Boundary-Layer Meteorology , 1992 , 59 :297~311 . doi: 10.1007/BF00119818 [3] Massman W J, Lee X. Eddy covariance flux corrections and uncertainties in long-term studies of carbon and energy exchanges. Agriculture and Forest Meteorology, 2002, 113: 121~144. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00105-3 [4] Kaimal J C, Clifford S F, Lataitis R J. Effect of finite sampling on atmospheric spectra. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1989, 47: 337~347. doi: 10.1007/BF00122338 [5] Moncrieff J B, Mahli Y, Leuning R. The propagation of errors in long-term measurements of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon and water. Global Change Biology, 1996, 2: 231~240. doi: 10.1111/gcb.1996.2.issue-3 [6] Massman W J. Reply to comment by Rannik on A simple method for estimating frequency response corrections for eddy covariance systems. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2001,107:204~251. [7] Moore C J. Frequency response corrections for eddy correlation systems. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1986, 37: 17~35. doi: 10.1007/BF00122754 [8] Goulden M L, Munger J W, Fan S-M, et al. Measurements of carbon sequestration by long-term eddy covariance: Methods and a critical evaluation of accuracy. Global Change Biology, 1996, 2: 169~182. doi: 10.1111/gcb.1996.2.issue-3 [9] Massman W J. A simple method for estimating frequency response corrections for eddy covariance systems. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 104: 185~198. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00164-7 [10] Kaimal J C, Wyngaard J C, Izumi Y, et al. Deriving power spectra from a three-component sonic anemometer. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1972, 7: 827~837. [11] Gash J H C, Culf A D. Applying a linear detrend to eddy correlation data in real time. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1996, 79: 301~306. doi: 10.1007/BF00119443 [12] Finnigan J J, Clements R, Mahli Y. A re-evaluation of long-term flux measurement techniques. Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2003,107(1):1~48. doi: 10.1023/A:1021554900225 [13] Hgstrm U. An alternative explanation for the systematic height variation of normalized vertical velocity variance in the near-neutral surface layer. In 14th Symposium on Boundary Layer and Turbulence, 2000. 31-32, American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA. [14] McMillen R T. An eddy correlation technique with extended applicability to non-simple terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1988, 43: 231~245. doi: 10.1007/BF00128405 [15] Garrat J R. The internal boundary layer- a review. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1990, 50: 171~203. doi: 10.1007/BF00120524 [16] Finnigan J. A comment on the paper by Lee (1998): "On micrometeorological observations of surface air-exchange over tall vegetation". Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1999, 97: 55~64. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(99)00049-0 [17] Smith R B. The influence of mountain on the atmosphere. Advances in Geophysics, 1979, 21, 87~230. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60262-9 [18] Tanner C B, Thurtell G W. Anemoclinometer measurements of Reynolds stress and heat transport in the atmospheric surface layer. Dept. Of Soil Science, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, Research and Development Tech Report ECOM 66-G22-F to the US Army Electronics Command, 1969. [19] Wilczak J M, Oncley S P, Stage S A. Sonic anemometer tilt correction alforithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2000,99(1):127~150. [20] Lee X, Barr A G. Climatology of gravity waves in a forest. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1998, 124: 1403~1419. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1477-870X [21] Paw U K T, Baldocchi D D, Meyers T P, et al. Correction of eddy-covariance measurements incorporating both advective effects and density fluxes. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2000, 97: 487~511. doi: 10.1023/A:1002786702909 [22] Finnigan J. A streamline coordinate system for distorted turbulent shear flows. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1983, 130: 241~258. doi: 10.1017/S002211208300107X [23] Kristensen L. Time series analysis. Dealing with imperfect data. RisoNational Laboratory, Riso-I-1228(EN), 1998. 31. [24] Sakai R K, Fitzjarrald D R, Moore K E. Importance of low-frequency contributions to eddy fluxes observed over rough surfaces. Submitted to Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2001. [25] Leclerc M Y, Thurtell G W. Footprint prediction of scalar fluxes using a Markovian analysis. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1990, 91: 39~49. [26] Hu X, Lee X, Steven D E. A numerical study of nocturnal wavelike motion in forests. Submitted to Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2001. [27] Wyngaard J, Kosovic B. Similarity of stricture-function parameters in the stably stratified boundary-layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1994, 71: 277~296. doi: 10.1007/BF00713742 [28] Goulden M L, Munger J W, Fan S-M, et al. Measurements of carbon sequestration by long-term eddy covariance: Methods and a critical evaluation of accuracy. Global Change Biology, 1996, 2:169~182. doi: 10.1111/gcb.1996.2.issue-3 [29] Wofsy S C, Goulden M L, Munger J W, et al. Net exchange of CO2 in a midlatitude forest. Science, 1993, 260: 1314~1317. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5112.1314 [30] Aubinet M, Grelle A, Ibrom A, et al. Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: The EUROFLUX methodology. Advances in Ecological research, 2000, 30: 113~175. [31] Black T A, Chen W J, Barr A G, et al. Increased carbon sequestration by a boreal deciduous forest in years with a warm spring. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27: 1271~1274. doi: 10.1029/1999GL011234 [32] Grace J, Malhi Y, Lloyd J, et al. The use of eddy covariance to infer the net carbon dioxide uptake of Brazilian rain forest. Global Change Biology, 1996, 2: 209~217. doi: 10.1111/gcb.1996.2.issue-3 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: