近50 年海河流域径流的变化趋势研究
STUDY OF TRENDS IN RUNOFF FOR THE HAIHE RIVER BASIN IN RECENT 50 YEARS
-
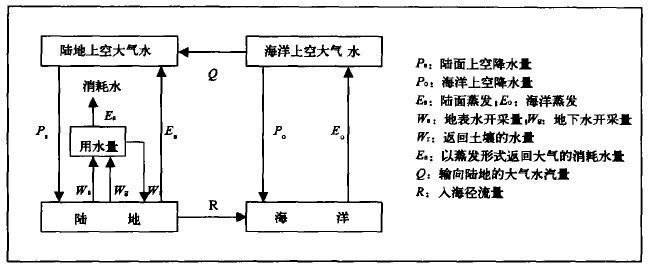
摘要: 该文用Mann-Kendall方法对近50年海河流域山区20个子流域的径流及降水的变化趋势进行了显著性检验, 结合降水, 径流及气温的年代距平值的同步分析以及径流对气候变化的敏感性研究结果, 对近50年海河流域径流的变化趋势, 提出了一个半定量分析的研究思路和方法。提出影响径流变化的三种类型:以气候暖干化为主, 人类活动为辅的径流显著衰减型;以人类活动为主, 气候暖干化为辅的径流显著衰减型;人类活动与气候变异都不明显, 径流无显著变化的类型。分析结果展示了气候、人类活动与水之间的相互作用。这种相互作用, 给径流的变化趋势分析和成因分析带来了复杂性与困难, 也给气候变化对水资源的影响研究提出了挑战。Abstract: Mann-Kendall’s test was used to identify runoff trends for 20 sub-catchments located in the mountain area of the Haihe river basin in recent 50 years. Combining the in-phase analysis the decadal changes of precipitation, runoff and air temperature, and the sensitivity analysis of runoff to climate change, a semi-quantitative analysis approach was presented. By using this analysis method, the change trend and the attribution of natural runoff for the Haihe river basin can be summarized into three patterns: 1) Annual natural runoff has decreased significantly, of which the main factor is the dry and warming trend of the climate and the secondary is the anthropogenic activities; 2) Annual natural runoff has decreased significantly, of which the main factor is the anthropogenic activities and the secondary is dry and warning climate trend; 3) Annual natural runoff has no significant change trend, for the climatic variability and anthropogenic activities are not significant. This study reflects the interaction between climate, human activities and water. The mutual interaction causes complexities and difficulties to analye the change trend and attribution of runoff, and presents challenge to the impact study of climate change to water resources as well.
-
Key words:
- Climate variability;
- Anthropogenic activities;
- Trends in runoff
-
表 1 海河流域1980年和1997年人口、灌溉面积及各种用水量比较

表 2 大清河南支代表性流域年降水量、天然年径流量及年平均气温距平的年代际变化

表 3 大清河南支代表性流域年降水量、天然年径流量及实测年径流量的年代际变化

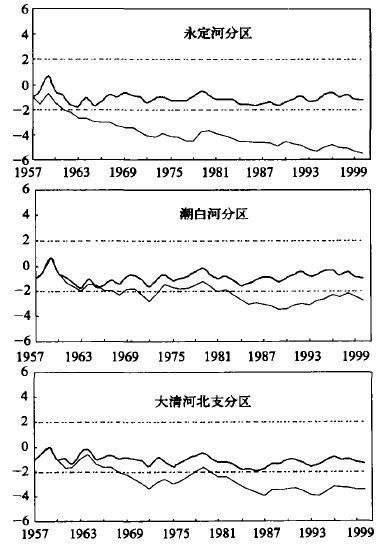
表 4 永定河分区年降水量、天然年径流量的年代际变化

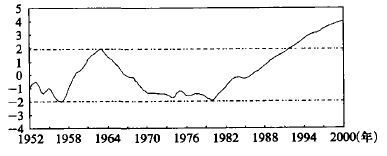
表 5 滦河桃林站年降水量、天然年径流量的年代际变化

-
[1] 贺伟程, 卢琼. 河川径流系列一致性处理办法. 水问题论坛,2002,4:18~20. [2] Mann H B. Non parametric tests against trend. Econometricn, 1945,13:245~259. doi: 10.2307/1907187 [3] Kendall M G. Rank correlation methods. Oxford Univ. Press. New York, 1975. [4] Liu Z, Todini E. Towards a comprehensive physically based rainfall-runoff model. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 2002. 6(5): 859~881. doi: 10.5194/hess-6-859-2002 [5] 刘克岩. 海河南系山区降雨径流关系的变化. 河北水利科技, 1994,4:31~34. [6] 刘昌明,陈志恺. 中国水资源现状评价和供需发展趋势分析. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. 2001. [7] 刘春蓁. 华北水文循环特征. 见: 施雅风主编. 气候变化对西北华北水资源的影响. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社. 1995. 159~177. [8] 马柱国, 魏和林,符淙斌. 中国东部区域土壤湿度的变化与气候变率的关系. 气象学报,2000,58(3): 276~287. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200003002.htm [9] 刘春蓁,英爱文,颜开. 中国水资源对气候变化的敏感性及脆弱性研究. 见: 符淙斌,严中伟主编. 全球变化与我国未来的生存环境. 北京: 气象出版社. 1996. 330~338. [10] 刘九夫,郭方,等. 气候异常对海河流域水资源评估模型研究. 水科学进展,2000,11(增刊): 27~35. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: