MOPITT观测的CO分布规律及与瓦里关地面观测结果的比较
Distribution of Carbon Monoxide from MOPITT of 2000—2004 and Comparisons with Surface Measurements in Mt. Waliguan Station
-
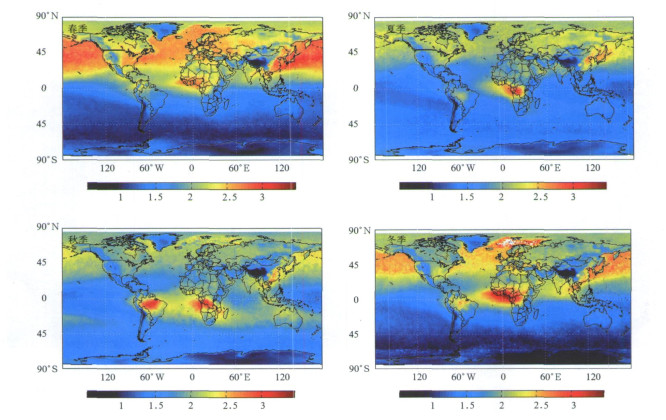
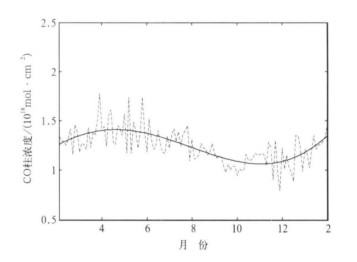
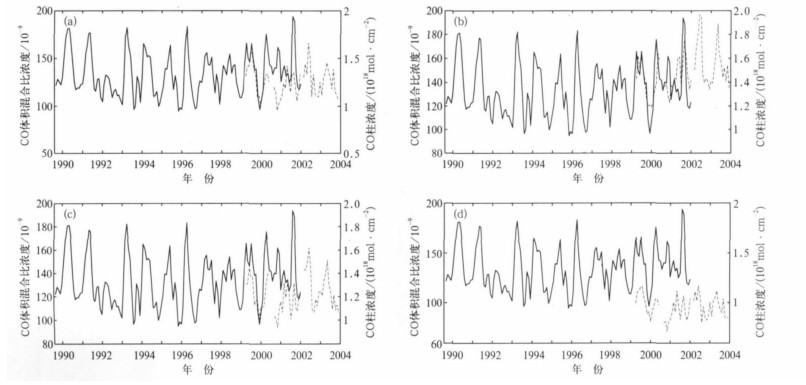
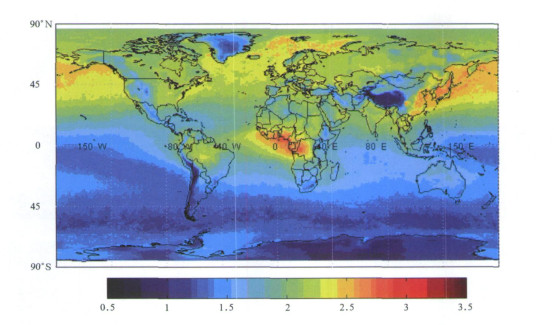
摘要: 利用TERRA/MOPITT仪器测量的2000年3月—2004年5月的CO数据, 分析了CO的时空分布特征及其变化趋势, 并且与美国国家海洋大气管理局气候监测与诊断实验室 (CMDL/NOAA) 在瓦里关站的CO观测结果进行比较和验证。结果表明: CO的高值区在北半球主要位于东亚、西欧和北美, 而在南半球主要位于非洲中西部和南美洲的赤道地区; CO的分布随季节变化显著, 春季北半球的CO浓度最高, 而秋季南半球的CO浓度偏高; 东亚的CO高值区主要是位于中国东部沿海地区和日本列岛一带。对于北京和瓦里关CO的趋势分析明表:这两个地区的CO浓度在这4年内都是呈上升趋势。结合CMDL的观测资料与卫星观测结果进行比较和检验发现, 瓦里关站卫星观测结果和CMDL的结果在时间序列的变化趋势一致, 卫星柱总量的观测数据和CMDL数据的相关性非常好。Abstract: Carbon monoxide (CO) is one of the main pollutants produced by incomplete combustion processes, such as the burning of fossil fuels in urban and industrial areas as well as by biofuel and biomass burning. CO has long been recognized for its critical role in tropospheric chemistry. Coupled with a one to three month lifetime, the wide variety and seasonal variation of sources makes CO an excellent tracer of atmospheric motions. Surface CO measurements which have generally been limited to surface or boundary layer measurements often substantially impacted by local pollution can not provided a global synoptic view of CO on a daily basis. To better understand global CO cycles, observations from the space are necessary. The Measurements of Pollution in the Troposphere (MOPITT) instrument, funded by the Canadian Space Agency and manufactured by COM DEV of Cambridge, Ontario, is launched onboard the NASA Earth Observing System (EOS) Terra satellite in December, 1999. MOPITT offers the first daily, global synoptic observations of CO since March 2000. The MOPITT data set contains CO total column amount, CO mixing ratios at six altitudes (850 hPa, 700 hPa, 500 hPa, 350 hPa, 250 hPa, 150 hPa) and the corresponding location and time along the track. Here Level 2, Version 3 MOPITT CO data are used which includes the latitude and longitude of MOPITT at nadir, the corresponding CO column and six layers of CO mixing ratio. The data are aggregated and interpolated to achieve grid data with a resolution of 1°×1° at 3-day average. Distribution properties and trend of CO from MOPITT of March 2000 to May 2004 are analyzed and comparisons with CMDL/NOAA surface CO measurements in Mt. Waliguan station are made. The results show that there is a large variation for global CO distribution. On the average, CO in Northern hemisphere is higher than that in Southern hemisphere. CO peak centers are located in East Asia, West Europe and North America in Northern hemisphere while in Middle West Africa and tropic regions of South America in Southern hemisphere. There is a significant seasonal variation for CO with a peak concentration in spring time in Northern hemisphere and in Autumn in Southern hemisphere. CO concentrations are high over coast regions of China and Japan all along a year. CO at Sichuan Basin which is located in the east of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are higher than that of its surrounding regions. Trends analysis of Beijing and Mt. Waliguan suggests that CO concentrations over these two regions increase during 2000—2004. Comparisons with CMDL/NOAA surface CO measurement in Mt. Waliguan shows that the variations of these two datasets agree well and there is a significant correlation between MOPITT CO column and CMDL surface measurements. The increasing trend for CO during 2000—2004 obtained from these two datasets is at magnitude of a few thousandth.
-
Key words:
- MOPITT;
- CO;
- CMDL;
- Mt. Waliguan station
-
表 1 北京、瓦里关2000年3月—2004年5月CO柱总量统计 (单位: mol/cm2)
Table 1 Statistic of column CO during March 2000—May 2004 at Beijing and Waliguan station (unit: mol/cm2)

-
[1] 秦瑜, 赵春生.大气化学基础.北京:气象出版社, 2003. [2] Logan J A, Prather M J, Wofsy S C, et al. Tropospheric chemistry: A global perspective. J Geophys Res, 1981, 86: 7210-7254. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC08p07210 [3] James R D. MOPITT: 12 Years of Planning and 2.5 Years of Operations. IEEE, 2002. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1025783/?reload=true&arnumber=1025783&filter%3DAND(p_IS_Number:22037) [4] Benesch W, Migeotte M, Neven L. Investigations of atmospheric CO at the Jungfraujoch. J Opt Soc Am, 1953, 43: 1119-1123. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.43.001119 [5] Edwards D P, Lamarque J F, Attie'J L, et al. Tropospheric ozone over the tropical Atlantic: A satellite perspective. J Geophys Res, 108, D8, 4237, doi: 10.1029/2002JD002927, 2003. [6] Bremer H, Kar J, Drummond F, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of MOPITT CO in Africa and South America: A comparison with SHADOZ ozone and MODIS aerosol. J Geophys Res, 109, D12304, doi:10.1029/2003JD004234, 2004. [7] Fang Yuanyuan, Zhao Chunsheng, Li Chengcai. Analysis of the distribution of carbon monoxide from MOPITT over East Asia in 2002. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Science, 2005, 29(4): 407-416. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653506012720 [8] Emmons L, Attie J L, Gille J, et al. Seasonal Variation of Asia Outflow from MOPITT CO and MOZART. Geophysical Research Abstracts, 2003, 5, 08020. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234440713_Seasonal_variation_of_Asian_outflow_from_MOPITT_CO [9] Zhao C, Peng L, Tie X X, et al. A High CO Episode of Longrange Transport Detected by MOPITT, Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. Jan 2006, Pages 1-10, DOI10.1007/s11270-006-9191-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9191-1. [10] Heald C L, Jacob D J, Fiore A M, et al. Asian outflow and transpacific transport of carbon monoxide and ozone pollution: An integrated satellite, aircraft and model perspective. J Geophys Res, 2003, 108 (D24), 4804, doi: 10.1029/2003JD003507. [11] Wang Jinxue, Merritt N D, John C G, et al. Retrieval of tropospheric carbon monoxide profiles from MOPITT: Algorithm description and retrieval simulation. J Geophys Res, 1999, 56: 219-232. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=1174810 [12] 周凌, 汤洁, Ernst M, 等.中国西部本底大气中CO的连续测量.环境科学, 2001, 22(3): 1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200103000.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: