北京地区PM10浓度空间分布特征的综合变分分析
Integrated Analysis on Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM10 Concentration Based on Variational Processing Method in Beijing
-
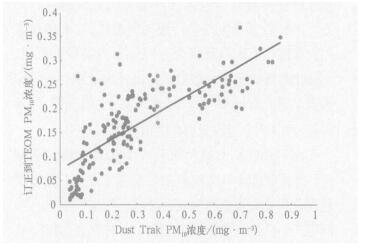
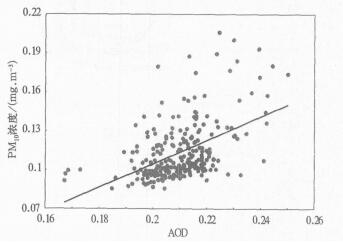
摘要: 利用2003年10月北京地区PM10浓度流动观测资料和同期MODIS AOD(Aerosol Optical Depth)高分辨率遥感资料,采用卫星遥感地面观测变分订正处理方法,综合分析了北京地区PM10浓度的空间分布特征以及机动车排放的影响效应。动态观测试验结果表明:北京城区大部分为轻污染区, 北京近郊区PM10浓度高值区沿环路呈环状分布,其中北京西南部、南部和东北部污染较严重,北京城郊街区PM10的空间分布受机动车排放的影响较大。MODIS卫星遥感资料分析表明:北京城区及近郊区AOD值较远郊区高得多,AOD空间分布场中存在虚假高值区,AOD非均匀分布特征不明显。采取点面结合综合观测研究思路,运用卫星遥感地面观测综合变分分析方法,可以取得客观订正的显著效果。经地面实测PM10浓度变分订正后的AOD变分场可以较高分辨率信息描述北京地区AOD的非均匀分布特征,弥补地面PM10浓度观测的缺陷。Abstract: A study is carried out on the spatial distribution characteristics of PM10 mass concentration and effect of pollutants from motor vehicle emissions in the main streets, the ring roads which are located in urban districts and suburbs in Beijing, based on the integrated Atmospheric Pollution Field Experiments (BECAPEX, Beijing City Atmospheric Pollution Experiment) and variational processing methods by satellite retrieval data whose horizontal resolution is 1 km. The results show that PM10 mass concentration in the majority of urban area are low, especially in ancient building communities which are located inside the Second Ring Road and in large afforestation zone. High concentration areas of PM10 in suburb distribute along ring roads, and pollutions are much serious in the southwest, the south and the northeast of the suburbs. The above mentioned fact shows that the impact of vehicle emissions on PM10 concentration is very serious in blocks which are located in urban districts and suburbs. Before satellite retrieval data are corrected by variational processing method, the value of MODIS AOD (Aerosol Optical Depth) in urban districts and suburbs are much higher than that in exurb, there are inveracious high value areas of AOD in its spatial distribution field and its unsymmetrical spatial distribution characteristics is not obvious. AOD values in most exurbs are lower than that in urban districts and suburbs, especially in the northwest of the exurb. But AOD values in the southwest and the southeast of the exurb are relatively high. The remarkable corrected effect is obtained by using a point plane integrated observation research technique and variational processing method by MODIS AOD retrieval data and corresponding observation data on the ground. AOD variational field with higher resolution information could be used to describe unsymmetrical spatial distribution characteristics in urban district and suburb detailedly, especially in exurb. This method can be used to make up the limitation of observation in exurbs. After satellite retrieval data are corrected by variational processing method, unsymmetrical spatial distribution char acteristics of AOD value are more distinct and conformed with that of PM10 concentration. Inveracious high value areas of AOD distribution are removed. Orbicular distribution of AOD in near suburb is more obvious and its unsymmetrical distribution characteristics in exurbs are also more notable. The location and intensity of the above high and low AOD value areas are stable accordingly.
-
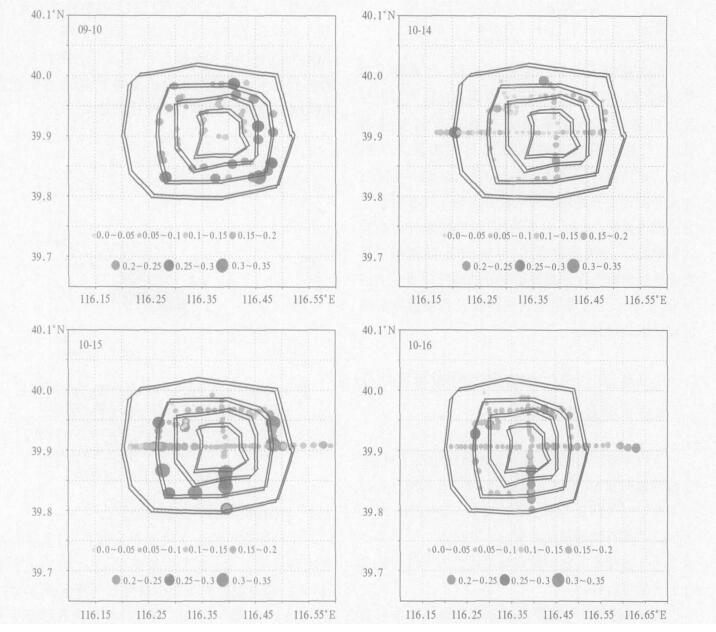
图 5 2003年9月10日和10月15日北京地区变分订正前后MODIS AOD空间分布场
(a)9月10日订正前,(b)9月10日订正后,(c)10月15日订正前,(d)10月15日订正后
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution characteristics of original AOD retrieval data and AOD value processed by variational method in Beijing on Sep 10 and Oct 15, 2003
(a)original AOD retrieval data on Sep 10,(b)AOD variational value on Sep 10,(c)original AOD retrieval data on Oct 15,(d)AOD variational value on Oct 15
表 1 2003年9月10日和10月13—16日北京市南郊观象台各时次云量
Table 1 Hourly cloud amount observed in Beijing South Observatory during 09 : 00—12 : 00, on Sep 10 and Oct 13—16, 2003

表 2 2003年9月10日, 10月14—16日北京地区实测PM10浓度超标情况
Table 2 Superscale of PM10 concentration observed in Beijing on Sep 10 and Oct 14—16, 2003

-
[1] Fuji T, Hayashi S, Hogg J C, et al.Particulate matter induces cytokine expression in human bronchial epithelial cells.American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 2001, 25(3):265-271. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.25.3.4445 [2] 魏复盛, 胡伟, 滕恩江, 等.空气污染与儿童呼吸系统患病率的相关分析.中国环境科学, 2000, 20(3):220-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200003008.htm [3] 纪飞, 苏文颖, 秦瑜.对流层光化学过程中的气粒转化研究.大气科学, 2001, 25(2):269-276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200102015.htm [4] 徐祥德.城市化环境大气污染模型动力学问题.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(增刊):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1000.htm [5] Colvile R N, Hutchinson E J, Mindell J S, et al.The transport sector as a source of air pollution.Atmos Environ, 2001, 35:1537-1565. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00551-3 [6] Chan L Y, Chan C Y, Qin Y.The effect of commuting microenvironment on commuter exposures to vehicular emission in Hong Kong.Atmos Environ, 1999, 33:1777-1787. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00338-0 [7] Cantanho A D A.Wintertime and summertime Sao Paulo aerosol source apportionment study.Atmos Environ, 2001, 35:4889-4902. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00357-0 [8] 吕萍, 袁九毅, 张文煜, 等.一个研究街道峡谷流场及浓度场特征的三维数值模式.四川环境, 2003, 2:64-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ200302020.htm [9] 贺克斌, 何东全, 唐仲洲.我国汽车排放污染现状与发展.环境科学, 1996, 17(4):80-83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ604.026.htm [10] http:∥www.cei.gov.cn/auto/doc/QCdaily/200411151693.htm. [11] 蔡旭晖, 张睿, 宋宇, 等.北京地区大气PM10和SO2的背景浓度分析.气候与环境研究, 2004, 9(3):445-453. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200403003.htm [12] 赵越, 潘钧, 张红远, 等.北京地区大气中可吸入颗粒物的污染现状分析.环境科学研究, 2004, 17(1):67-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200401015.htm [13] 毛节泰, 李成才, 张军华, 等.MODIS卫星遥感北京地区气溶胶光学厚度及其与地面光度计遥感的对比.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(增刊):127-135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1013.htm [14] 周秀骥, 徐祥德.2000年春季沙尘暴动力学特征.中国科学(D辑), 2002, 32(4):327-334. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200204007.htm [15] 徐祥德, 周秀骥, 翁永辉, 等.星载MODIS资料与地面光度计探测气溶胶变分场.科学通报, 2003, 15:1680-1685. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200315018.htm [16] 徐祥德, 许健民, 王继志, 等.大气遥感再分析场构造技术与原理.北京:气象出版社, 2003:58-91. [17] 李成才, 毛节泰, 刘启汉.利用MODIS资料遥感香港地区高分辨率气溶胶光学厚度.大气科学, 2005, 29(3):335-342. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200503000.htm [18] 李成才, 毛节泰, 刘启汉, 等.利用MODIS光学厚度遥感产品研究北京及周边地区的大气污染.大气科学, 2003, 27(5):869-879. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200305007.htm [19] 魏凤英.现代气候统计诊断与预测技术.北京:气象出版社, 1999:35-37. [20] Lee Yuet Lai, Sequeira R.Water-soluble aerosol and visibility degradation in Hong Kong during autumn and early winter, 1998.Environmental Pollution, 2002, 116:225-233. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00135-X [21] 王淑英, 张小玲.北京地区PM10污染的气象特征.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(增刊):177-184. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1019.htm [22] 王雪松, 李金龙.北京地区夏季PM10污染的数值模拟研究.北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 39(3):419-427. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200303022.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: