临安大气气溶胶理化特性季节变化
Seasonal Physical and Chemical Features Variation of Ambient Aerosol in Lin'an
-
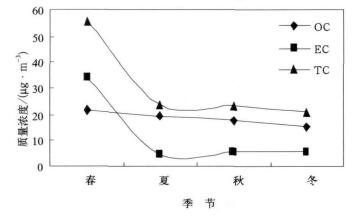
摘要: 分别利用碳成分分析仪、离子色谱仪和原子吸收光谱仪等获取浙江省临安地区大气气溶胶在春、夏、秋、冬四季的质量浓度、离子与碳成分特性,并对不同粒径气溶胶成分分布特点作了较详细分析。结果表明:气溶胶质量浓度、可溶性离子浓度以及碳成分浓度具有明显的季节变化趋势。整个尺度范围内,气溶胶质量浓度季节变化特点为春季浓度最高,达到534 μg/m3;冬季次之,质量浓度为117.21 μg/m3;夏季浓度最低,平均为65.7 μg/m3;秋季质量浓度98.6 μg/m3。可溶性离子成分在气溶胶中所占比例具有明显的季节性,其中夏季最高为49.4%,春季最低为11.3%。硫酸根离子SO42-和氨根离子NH4+和硝酸根离子NO3- 3种离子浓度之和约占离子总量的75%~83%。受温度影响,硝酸根离子NO3-浓度随季节变化幅度较大,夏季平均浓度为1.7 μg/m3, 冬季平均浓度为11.5 μg/m3,是夏季浓度的6.8倍。碳浓度分布特点显示,气溶胶中元素碳浓度春季最高,夏季最低。有机碳浓度春季最高,冬季最低。气溶胶粒度分布特点也非常明显。四季中粒径小于11 μm(PM11)的气溶胶均占气溶胶总量的90%以上,粒径小于2.1 μm(PM2.1)的气溶胶占到气溶胶总量的53%以上。可溶性离子在粒径小于2.1 μm气溶胶颗粒中,以硫酸根离子、氨根离子和硝酸根离子为主。碳成分尺度分布特征为颗粒越小,有机碳及元素碳浓度越高。Abstract: The seasonally chemical and microphysical characteristics of aerosols in Lin'an regional atmospheric pollution monitoring station is investigated. The aerosol is collected on both Teflon filters and Quartz filters at the same time which are analyzed by different methods for different purpose. The Teflon filters are prepared for analyzing the water soluble ion concentration, while the quartz filters are used for analyzing the organic carbon and element carbon. Seven sampling periods represent different seasons. The details of sampling information are listed below: from March 30, 2002 to April 8, 2002 for spring; from August 14 to 24, in 2002, from July 20 to 30, in 2003, and from August 17 to 29, in 2004 for summer; from November 7 to 23, in 2003, from November 6 to 20, in 2004 for fall, and from January 15 to February 2, 2005 for winter. The ion chromatogram analyzer is used to discuss water soluble ion concentration of aerosol. A sunset carbon analyzer is applied to measure the organic carbon and element carbon in aerosol. Not only the seasonal mass, ion and carbon concentration of ambient aerosol are studied in Lin'an, but also the size distribution characteristic of aerosol components is analyzed in detail. Generally speaking, there are obvious variations among different seasons of mass, ion and carbon concentration. For the whole size range, the mass concentration in spring is the highest with 534 μg/m3, and it is 117.21 μg/m3 in winter which is just lower than that in spring. The lowest concentration occurs in summer with 65.7 μg/m3, and 98.6 μg/m3 in fall. The ions occupy different percentage of mass in different season. In summer, the ions' concentration is 49.4% of mass concentration, and it is 11.3% in spring. At the same time, the total concentration of sulfate, ammonium and nitrate is 75%—83% of the whole ions' concentration. On the other hand, nitrate concentration varies with season greatly. The average concentration of it is only 1.7 μg/m3 in summer. The characteristic of carbon shows that the highest element carbon concentration appears in spring and the lowest appears in summer. For organic carbon, spring's concentration is the highest and winter's concentration is the lowest. Moreover, the characteristic of size distribution is also obvious. The PM11 reaches 90% of the whole mass concentration. PM2.1 also occupies 53% of the whole mass. Sulfate, ammonium and nitrate are the main ions in fine particles. The characteristic of carbon size distribution shows that the smaller the particles are, the higher the concentration reaches.
-
Key words:
- aerosol;
- mass concentration;
- ion;
- carbon;
- size distribution
-
表 1 7次采样过程质量浓度(单位: μg/m3)
Table 1 The mass concentration of 7 campaigns(unit: μg/m3)

表 2 不同季节各种离子成分占总离子成分百分比(单位: %)
Table 2 The percentage of different ions in different seasons(unit: %)

表 3 四季气溶胶可溶性离子成分相关系数
Table 3 The correlation between ions in the 4 seasons

表 4 四季粗细粒子气溶胶中各离子成分相关分析
Table 4 Correlation coefficients of different ions in four seasons

表 5 四季不同尺度气溶胶OC与EC比值比较
Table 5 The seasonal ratio of OC to EC comparison in different size stages

-
[1] 许黎, 冈田菊夫, 张鹏, 等.北京地区春末-秋初气溶胶理化特性的观测研究.大气科学, 2002, 26(3):401-411. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200203010.htm [2] 王明星.大气化学.北京:气象出版社, 1991. [3] IPCC.Climate Change 2001:The Scientific Basis.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2001:1-881. [4] Surabi Menon, James Hansen, Larissa Nazarenko, et al.Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India.Science, 2002, 297:2250-2253. doi: 10.1126/science.1075159 [5] Jacobson M Z.Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols.Nature, 2001, 409:695-697. doi: 10.1038/35055518 [6] Jacobson M Z.Control of fossil-fuel particulate black carbon plus organic matter, possibly the most effective method of slowing global warming.J Geophys Res, 2002, 107(D19), 4410, doi: 10.1029/2001JD001376. [7] 杨复沫, 贺克斌, 马永亮, 等.北京大气PM2.5中微量元素的浓度变化特征与来源.环境化学, 2003, 24(6):33-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200306004.htm [8] 杨复沫, 贺克斌, 马永亮, 等.北京PM2.5化学物种的质量平衡特征.环境化学, 2004, 23(3):326-333. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX200403017.htm [9] Shi Zongbo, Shao Longyi, Jones T P, et al.Characterization of airborne individual particles collected in an urban area, a satellite city and a clean air area in Beijing, 2001.Atmos Environ, 2003, 37:4097-4108. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00531-4 [10] 周福民, 孙庆瑞, 王美蓉, 等.北京中关村地区气溶胶的酸性测量.环境科学, 1998, 19(2):6-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ802.001.htm [11] 周秀骥.长江三角洲地层大气与生态系统相互作用研究.北京:气象出版社, 2004. [12] Xu J, Bergin M H, Yu X, et al.Measurement of aerosol chemical, physical and radiative properties in the Yangtze delta region of China.Atmos Environ, 2002, 36:161-173. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00455-1 [13] 杨东贞, 于晓岚.临安本底站微量气体浓度分布特征及其对气溶胶的影响.应用气象学报, 1995, 6(4):400-406. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19950462&flag=1 [14] 杨东贞, 颜鹏, 张养梅, 等.WMO区域本底站气溶胶特征分析.第四纪研究, 2006, 26(5):733-741. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200605007.htm [15] 颜鹏, 张养梅, 王淑凤, 等.临安夏季气溶胶离子成分尺度分布特征.气象学报, 2005, 63(6):980-987. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200506013.htm [16] 颜鹏, 杨东贞, 汤洁, 等.临安一次沙尘暴过程影响气溶胶物理化学特性演变的初步分析.第四纪研究, 2004, 24(4):437-446. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200404009.htm [17] Zhang X Y, Cao J J, Li L M, et al.Characterization of atmospheric aerosol over Xi'an in the south margin of the Loess Plateau, China.Atmos Environ, 2002, 36:4189-4199. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00347-3 [18] Ando M, Katagiri K, Tamura K, et al.Indoor and outdoor air pollution in Tokyo and Beijing supercities.Atmos Environ, 1994, 30:695-702. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223322084_Indoor_and_outdoor_air_pollution_in_Tokyo_and_Beijing_supercities [19] 时宗波, 邵龙义, 李红, 等.北京市西北城区取暖期环境大气中PM10的物理化学特征.环境科学, 2002, 23(1):31-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200201006.htm [20] Waldman J M, Lioy P J, Zelenka M, et al.Winter time measurements of aerosol acidity and trace elements in Wuhan, a city in central China.Atmos Environ, 1991, 25B:113-120. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/095712729190045G [21] Salmon L G, Christoforou C S, Cass G R, et al.Air pollutants in the Buddhist cave temples at the Yungang Grottoes, China.Environ Sci Technol, 1994, 28:805-811. doi: 10.1021/es00054a010 [22] Bergin M H, Cass G, Xu J, et al.Aerosol reactive, physical and chemical properties in Beijing during June 1999.J Geophysical Res, 2001, 106(D16):17969-17980. doi: 10.1029/2001JD900073 [23] 唐孝炎.大气环境化学.北京:高等教育出版社, 2002. [24] Admas P J, Seinfeld J H, Koch D M, et al.Global concentrations of troposphere sulfate, nitrate and ammonium aerosol simulated in a general circulation model.J Geophys Res, 1999, 104:13791-13823. doi: 10.1029/1999JD900083 [25] 刘振海.分析化学手册.北京:高等教育出版社, 2000. [26] Schaap M, Spindler G, Schulz M, et al.Artefacts in the sampling of nitrate studied in the "INTERCOMP" campaigns of EUROTRAC-aerosol.Atmos Environ, 2004, 38:6487-6496. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.08.026 [27] 数学手册编写组.数学手册.北京:高等教育出版社, 1998. [28] Turpin B J, Huntzicker J J.Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS.Atmos Environ, 1995, 29:3527-3544. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(94)00276-Q [29] Turpin B J, Lim H J.Species contribution to PM2.5 concentrations:Revising common assumption for estimating organic mass.Aerosol Sci Technol, 2001, 35:602-610. doi: 10.1080/02786820119445 [30] Turpin B J, Huntzicker J J, Larson S M, et al.Los Angeles summer midday particulate carbon:Primary and secondary aerosol.Environ Sci Technol, 1991, 25:1788-1793. doi: 10.1021/es00022a017 [31] James D A, Alfarra M R, Keith N B, et al.Quantitative sampling using an aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer 2:Measurements of fine particulate chemical composition in two U K cities.J Geophys Res, 108(D3), 4091, doi: 10.1029/2002JD002359, 2003. [32] 孙宏, 张择, 裴力民, 等.齐齐哈尔市大气气溶胶中有机碳和元素碳污染初步分析.齐齐哈尔师范学院学报(自然科学版), 1997, 17(2):57-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLKX199702020.htm [33] He Z, Kim Y J, Ogunjobi K O, et al.Carbonaceous aerosol characteristic of PM2.5 particles in northeastern Asia in summer 2002.Atmos Environ, 2004, 38:1795-1800. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.12.023 [34] Ye B, Ji X, Yang H, et al.Concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai for a 1-year period.Atmos Environ, 2003, 37:499-510. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00918-4 [35] Cao J J, Lee S C, Ho K F, et al.Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region China during 2001 winter period.Atmos Environ, 2003, 37:1451-1460. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)01002-6 [36] Zhang X Y, Wang Y Q, Wang D, et al.Charaterization and sources of regional-scale transported carbonaceous and dust aerosol from different pathways in coarstal and sandy land of China.J Geophys Res, 2005, 110:D15301. doi: 10.1029/2004JD005457 [37] Chow J C, Watson J G, Lu Z, et al.Descriptive analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 at regionally representative locations during SJVAQS/AUSPEX.Atmos Environ, 1996, 30:2079-2112. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00402-5 [38] Gray H A, Cass G R, Huntzicker J J.Characteristics of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon particle concentrations in Los Angeles.Environ Sci Technol, 1986, 20:580-589. doi: 10.1021/es00148a006 [39] Andreae M O.Soot carbon and excess fine potassium:Long range transport of combustion-derived aerosol.Science, 1983, 220:1148-1151. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4602.1148 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: