交叉小波变换在区域气候分析中的应用
Application of Cross Wavelet Transformation to Analysis on Regional Climate Variations
-
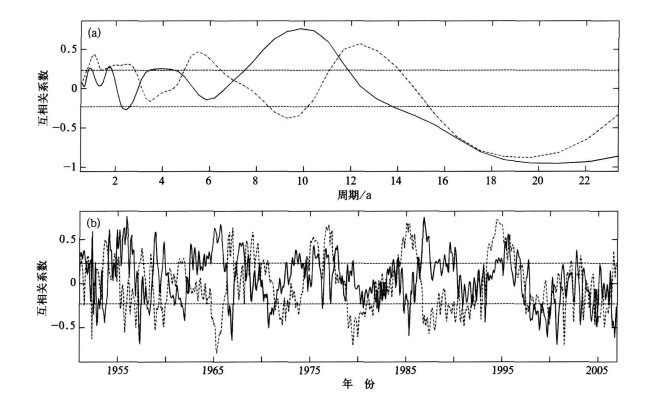
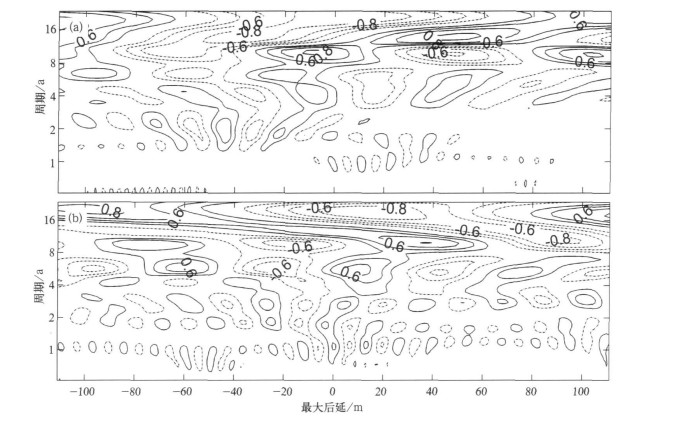
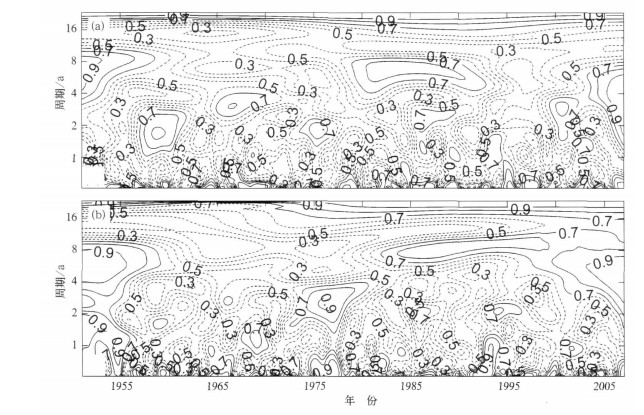
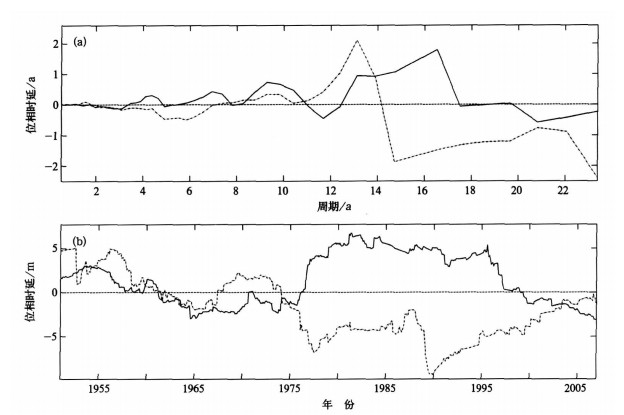
摘要: 将交叉谱与小波变换分析方法相结合,与传统的交叉谱方法相比,交叉小波变换方法用于区域气候变化与大气环流系统之间耦合振荡行为的相关分析更具优越性,不仅可以弥补经典交叉谱分析方法存在的缺陷,而且能够发挥小波变换在时频两域都具有表征气候信号局部化特征的作用;该方法具有较强的耦合信号分辨能力,便于描述耦合信号在时频域中分布状况的优点。采用交叉小波变换分析北极涛动指数(AOI)距平与河南省月平均降水量距平、气温距平序列之间的联合统计特征及其在时频域中的相关关系,根据小波互相关系数、交叉小波凝聚谱和小波位相谱分析北极涛动对河南省气候变化的可能影响。应用结果表明:河南省降水量和气温变化与AOI之间存在着多时间尺度的显著相关振荡,年代际尺度周期上的互相关系数明显大于年际尺度周期,相关程度随耦合振荡频率的增大而减小,相关显著性取决于两者的时频域联合统计特征,时域中小波互相关系数、小波凝聚谱和小波位相谱的分布具有明显的局部化特征;说明北极涛动年际和年代际异常对河南省气候变化具有显著影响。Abstract: By combining the cross spectrum with the wavelet transform, the cross wavelet transform method is adopted to analysis on variations of regional climate. Compared with the traditional cross spectrum method, more advantages for the correlation analysis of coupling oscillations between regional climate variation and atmospheric circulation system are provided by the cross wavelet transform method. Not only the limitation of the classical cross spectrum method is made up, but also the technical predominance of the wavelet transform method is exerted on displaying the localized distributing characteristics of climate signal in time and frequency space. This method possesses the ability to distinguish coupling signals of two time series and the excellence to describe the distributing of coupling signals in time-frequency space, it can be applied to diagnose and forecast the variations of regional climate in the work of provincial meteorological bureaus. As an example, this method is used to study the associated statistical characteristics and time-frequency correlations between the anomaly series of monthly Arctic Oscillation Indices (ΔIAO) and monthly precipitation (ΔR), temperature(ΔT) in Henan Province in the last 56 years. The influences of Arctic Oscillation on climate variations in Henan Province are analyzed by means of wavelet cross-correlation coefficient, wavelet coherence spectrum and wavelet phase spectrum. The results show that there are significant correlative oscillations at multi-time scales between the variations of precipitation, temperature in Henan Province and Arctic Oscillation. The wavelet cross-correlations between ΔIAO and ΔR, ΔIAO and ΔT on inter-decadal timescale are obviously higherthan on inter-annual timescale in frequency space, and the correlation measure decreases with the increasing of coupling oscillation frequencies. In time domain, positive and negative correlations between ΔIAO and ΔR, ΔIAO and ΔT display the staggered distributing characteristics, and the correlation measure varies with the inter-annual and inter-decadal timescale. It is estimated that the negative correlation between ΔIAO and ΔR, the positive correlation between ΔIAO and ΔT will be maintained for 1—2 years by the varying tendency of wavelet cross-correlation coefficients. Analysis on the wavelet coherence spectrum shows that the coherent significances depend on the associated statistical characteristics of ΔIAO and ΔR, ΔIAO and ΔT in time and frequency space. There are localized distributing characteristics of wavelet coherence and phase in time space. The significant syntonic periods between ΔIAO and ΔR are quasi-2-year, 3—5-year, 6—8-year and above 20-year timescales, interdecadal correlation distributes in all time space and inter-annual correlations presents at different stages in time space. The significant correlations between ΔIAO and ΔT are showed on the periods of about 1a, 2—4-year, 6—8-year and above 16-year, the coherent significance increases obviously after 1974 for inter-decadal correlation and it is different for inter-annual correlations at different stages in time space. The cross-wavelet phases of correlative oscillation between ΔIAO and ΔR, ΔIAO and ΔT vary with the syntonic frequencies. The phase differences of correlative oscillation on inter-decadal timescale are lager than on inter-annual timescales, and the phase variations are inphase basically before 1975 and inverted clearly after 1975 in time space.It shows that Arctic Oscillation anomalies of inter-annual and inter-decadal timescale have significant influence on climate variations in Henan Province.The relationship and coherent significance between the variations of precipitation, temperature in Henan Province and Arctic Oscillation depend on their associated statistical characteristics in time-frequency space.
-
-
[1] 魏凤英.气候统计诊断与预测方法研究进展.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):736-742. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200606122&flag=1 [2] 吴贤云, 丁一汇, 王琪, 等.近40年长江中游地区旱涝特点分析.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(1):19-28. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060103&flag=1 [3] 贾丽伟, 李维京, 陈德亮.东北地区降水与大气环流关系.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5):557-566. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060596&flag=1 [4] 孙兰东, 岳立, 刘新伟.甘肃省极端最高气温的气候特征分析.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(增刊):110-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2006S1015.htm [5] 高辉.淮河夏季降水与赤道东太平洋海温对应关系的年代际变化.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(1):1-9. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060101&flag=1 [6] 李春, 方之芳.北极涛动与东北冬季温度的联系.高原气象, 2005, 24(6):927-934. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200506011.htm [7] 解明恩, 张万诚.ENSO事件与云南冬季气温异常.应用气象学报, 2000, 11(1): 115-122. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20000117&flag=1 [8] 唐国利, 丁一汇.近44年南京温度变化的特征及其可能原因的分析.大气科学, 2006, 30(1):56-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200601004.htm [9] 马振锋, 彭骏, 高文良.近40年西南地区的气候变化事实.高原气象, 2006, 25(4):633-642. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200604009.htm [10] 章基嘉, 高学杰. 1891~1990年期间北半球大气环流和中国气候的变化.应用气象学报, 1994, 5(1): 1-10. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940103&flag=1 [11] 张元箴, 王淑静.南半球环流与西太平洋副热带高压和台风群中期活动的关系.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(1):80-87. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990136&flag=1 [12] 丁裕国, 江志红, 施能, 等.奇异交叉谱分析及其在气候诊断中的应用.大气科学, 1999, 23(1): 91-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK901.010.htm [13] 胡增臻, 石伟.小波变换在大气科学中的应用研究.大气科学, 1997, 21(1):58-72. [14] 林振山, 邓自旺.子波气候诊断技术的研究.北京:气象出版社, 1999.9-37. [15] 吴洪宝, 吴蕾.气候变率诊断和预测方法.北京:气象出版社, 2005: 181-192. [16] 陈涛, 孙卫国, 程炳岩.交叉小波变换在河南降水时频分析中的应用.南京气象学院学报, 2002, 25(5): 685-692. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX200205014.htm [17] Sun Weiguo, Cheng Bingyan, Huang Hairen. The frequency characteristics of warm and cold episodes in the Nino regions. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2005, 11(2):200-205. [18] Lonnie Hudgins, Huang Jiangping. Bivariate wavelet analysis of Asia monsoon and ENSO. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 1996, 13(3):299-312. doi: 10.1007/BF02656848 [19] Torrence C, Compo G P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1998, 79(1): 61-78. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0061:APGTWA>2.0.CO;2 [20] 丁裕国, 江志红.气象数据时间序列信号处理.北京:气象出版社, 1998: 278-283. [21] Thompson D W, Wallace J M. Regional climate impacts of the Northern Hemisphere annular mode. Science, 2001, 293:85-89. doi: 10.1126/science.1058958 [22] Gong Daoyi, Wang Shaowu, Zhu Jinghong. East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic Oscillation. Geophys Res Lett, 2001, 28(10):2073-2076. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012311 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: