夏季长江中下游旱涝年季节内振荡气候特征
Climatic Features of Intraseasonal Oscillations of Summer Rainfalls over Mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in the Flood and Drought Years
-
摘要: 利用1951—2004年我国740站逐日降水资料对夏季长江中下游典型旱涝年季节内振荡周期、强度和位相等特征进行合成对比分析发现:长江中下游涝年降水季节内振荡周期较旱年长, 涝年以30~60 d周期为主, 而旱年以10~30 d周期为主。旱涝年长江中下游地区夏季降水的10~30 d振荡整体上均强于30~60 d振荡; 10~30 d及30~60 d振荡, 涝年的强度都大于旱年。季节内振荡在旱年的北传较涝年强, 能达到50°N附近; 而涝年不仅有明显的季节内振荡从低纬度地区向北传播, 同时还有弱的振荡从中高纬度地区向南传播, 两者汇合于长江流域形成强的振荡中心。影响我国低频降水的低频异常环流分布模态在旱涝年是一致的, 但涝年的低频环流强于旱年, 而这种低频环流场的差异正是造成涝年的低频降水强于旱年的原因之一。Abstract: In order to understand further climatic characters of the intraseasonal oscillation and its relationship with the interannual variation of summer rainfalls over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, the composite comparison analysis is applied to the intraseasonal oscillation in between the flood and drought years.Firstly, eight flood years and 7 drought years are identified by using 740 stations daily rainfall datasets in China from 1951 to 2004.And then differences in the period, the intensity and the phase cycle of the intraseasonal oscillation of summer rainfalls in between the drought years and the flood years over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River are discussed.The main results are as follows.The period of the intraseasonal oscillation of summer rainfalls over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River is relatively longer in the flood years, with the dominating 30 —60-day oscillation.While it is relatively shorter against a droughty interannual background, mainly being 10—30-day.Generally, the 10—30-day oscillation has greater amplitude than the 30—60-day oscillation in both flood and drought years, but the situation is opposite in certain areas over the lower Reaches of the Yangtze River or in some years.As for the intraseasonal oscillation, the amplitude is greater in the flood years than in the drought years.In the drought years, significant northward propagation can be observed to reach 50°N or so.But in the flood years, both the northward propagation from the low latitude and the weak southward propagation from the mid-high latitudes are obvious.And two branches of intraseasonal oscillations merge over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River and form strong oscillation centers.The phase composite analysis of the intraseasonal components of summer rainfalls in China and the corresponding low-level circulation show that the modes of the low-frequent anomalous circulation influencing the low-frequent summer rainfalls in China are similar in flood and drought years.However, the anomalous rainfalls and circulations on the intraseasonal scale are stronger under the flood background than the drought background, being an important cause for more rainfalls in flood years than in drought years.In conclusion, the intraseasonal oscillation has an important impact on the annual variation in aspects such as the period, the propagation, the intensity, the phase cycle and so on.
-
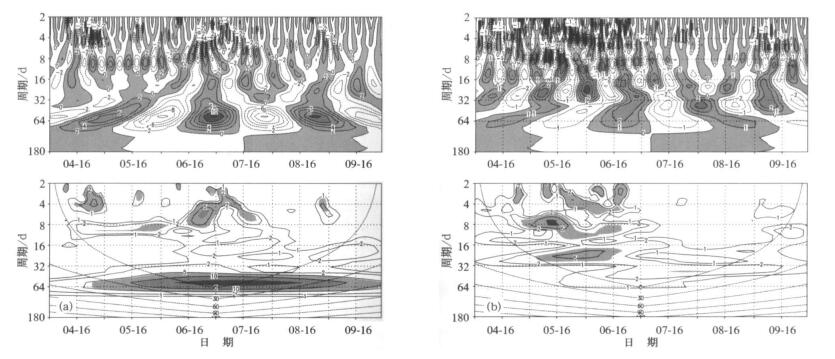
图 1 长江中下游4-9月涝年 (a) 和旱年 (b) 降水合成序列的小波分析
(上图为小波实部, 阴影区表示正值; 下图为小波标准功率谱, 阴影区表示通过90%信度检验, 虚线表示边界影响)
Fig. 1 Wavelet analysis of rainfall amounts in the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River during the period from April to September for flood years (a) and drought years (b), respectively
(the upper panels present the real parts of the wavelet, with the positive values being shaded, while the lower panels present the standard power spectrum, with the shaded areas exceeding the confidence level of 90% and the dashed lines denote the boundary effect)
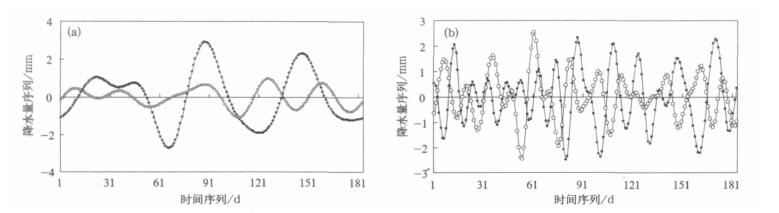
图 2 30~60 d (a) 和10~30 d (b) 滤波的旱涝年长江中下游4-9月降水量序列
(实心圆表示涝年, 空心圆表示旱年)
Fig. 2 Time series of the 30-60-day oscillation (a) and the 10-30-day oscillation (b) of rainfall amounts during the period from April to September over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River
(solid circles and hollow circles denote flood years and drought years, respectively)
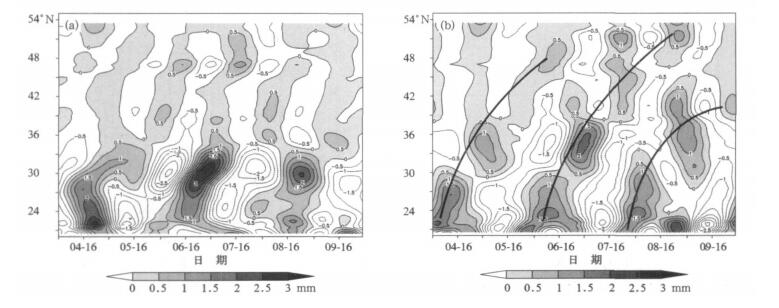
图 3 长江中下游涝年 (a) 和旱年 (b) 夏季降水量30~60 d振荡的时间-经向剖面图
(取110°~122°E平均, 阴影区表示正值, 粗实线表示30~60 d振荡的北传路径)
Fig. 3 Time-meridion section (averaged over 110°-122°E) of the 30-60-day oscillation of summer rainfalls in flood years (a) and drought years (b) over the mid-lower Reaches of the Yangtze River
(the positive values are shaded, thick solid lines denote the northward propagation of the 30-60-day oscillation)
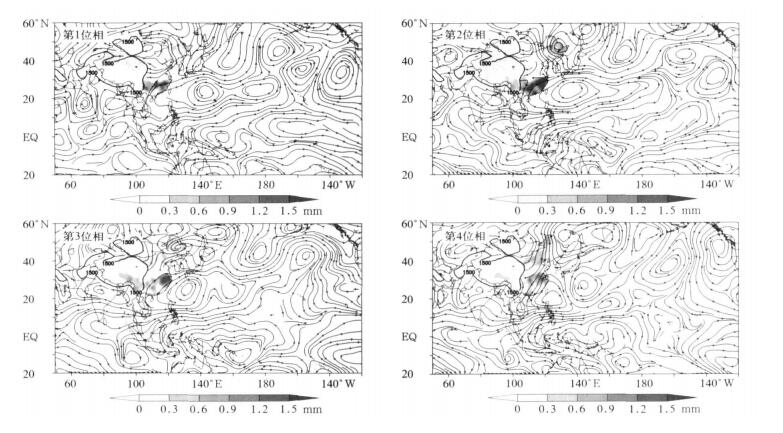
图 4 长江中下游夏季典型涝年与旱年我国降水量与850 hPa风场30~60 d振荡的位相合成差值图
(阴影区表示异常降水量, 流线表示异常低频风场)
Fig. 4 Differential distribution of the 30-60-day component of rainfalls and the wind field at 850 hPa between flood years and drought years
(shaded areas denote anomalous rainfall; streamlines denote anomalous low-frequeng wind)
-
[1] 陆日宇.华北汛期降水量变化中年代际和年际尺度的分离.大气科学, 2002, 26(5):611-624 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200205002.htm [2] 况雪源, 丁裕国, 施能.中国降水场QBO分布型态及其长期变率特征.热带气象学报, 2002, 18(4):359-367 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200204008.htm [3] 杨秋明.中国降水准2年主振荡模态与全球500hPa环流联系的年代际变化.大气科学, 2006, 30(1):131-145 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200601010.htm [4] Yang H, Li C Y. The relation between atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation and summer severe flood and drought in the Changjian-Huaihe River basin. Adv Atmos Sci, 2003, 20 (4) : 540-553 doi: 10.1007/BF02915497 [5] Li C Y, Long Z X, Zhang Q Y. Strong/weak summer monsoon activity over the South China Sea and atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation. AdvAtmos Scl, 2001, 18(6) : 1146-1160 doi: 10.1007%2Fs00376-001-0029-x [6] 周静亚, 杨大升, 黄嘉佑.夏季热带及副热带环流系统周期振荡与我国降水的功率谱分析.热带气象, 1986, 12(3):185-203 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX198603000.htm [7] 何素兰, 宋连春, 黄荣辉.黄河中下游旱涝年的低频波振荡特征.应用气象学报, 1993, 4(4):402-407 http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19930469&flag=1 [8] 黄静, 朱乾根.长江流域旱涝年低频风场分布和演变的差异.南京气象学院学报, 1996, 19(3):276-282 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX603.001.htm [9] 李崇银.华北地区汛期降水的一个分析研究.气象学报, 1992, 50(1):41-49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB199201004.htm [10] 任宏利, 张培群, 李维京, 等.西北区东部春季降水及其水汽输送的低频振荡特征.高原气象, 2006, 25(2):285-292 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200602014.htm [11] Wang B, Xu X H. Northern hemisphere summer monsoon singularities and climatological intraseasonal oscillation. J Climate, 1997, 10: 1071-1085 doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<1071:NHSMSA>2.0.CO;2 [12] 王遵娅, 丁一汇.中国雨季的气候学特征.大气科学, 2008, 32(1):1-13 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200801001.htm [13] 陶诗言.季风研究中有待解决的问题//国家自然科学基金委员会等编.现代大气科学前沿和展望.北京:气象出版社, 1996.35-36 [14] 丁一汇, 村上胜人.东亚季风.北京:气象出版社, 1994.74-92 [15] 何金海, Murakami T, Nazakawa T.1979年夏季亚洲季风区域40-50天周期振荡的环流及水汽输送场的变化.南京气象学院学报, 1984, 2:163-175 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX198402003.htm [16] 王遵娅, 丁一汇, 何金海, 等.近50年来中国气候变化特征的再分析.气象学报, 2004, 62(2):228-236 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200402009.htm [17] Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al. The NCAR/NCEP 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Arner Meteor Soc, 1996, 77: 437-471 doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2 [18] 陈丽臻, 张先恭,陈隆勋.长江流域两个典型旱, 涝年大气30—60天低频波差异的初步分析.应用气象学报, 1994, 5(4):483-488 http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940482&flag=1 [19] 王遵娅.中国夏季降水的气候变率及其可能机制研究.北京:中国科学院研究生院, 2007:116-124. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: