Cascade插值方法在GRAPES模式中的应用
Application of Cascade Interpolation to GRAPES Model
-
摘要: 基于半拉格朗日 (semi-Lagrangian) 方案的数值天气预报模式, 求解半拉格朗日轨迹上游点变量, 通常采用传统直线逐点拉格朗日多项式插值, 由已知模式格点 (欧拉网格点) 的数值插值获得。对于三维空间上游点的插值, N阶精度需要O(N3) 运算量。N增大, 运算量将大幅增加, 特别耗费计算机机时, 而采用Cascade插值法 (降阶插值法) 则只需要O(N) 运算量。它的显著特点是:用曲线代替直线, 通过一系列中间过渡网格点, 在曲线上用一维拉格朗日插值, 使得相邻拉格朗日格点或中间过渡点的插值不再是孤立的, 而且可以重复使用某些中间结果, 达到减少运算量的目的。将这种方法合理应用于GRAPES模式, 并根据模式的特点, 对Cascade插值过程中独立变量的距离分段计算, 从而有利于实现并行计算。计算结果表明Cascade插值法与传统直线逐点插值法相比, 计算效率平均提高约30%, 同时不降低精度。
-
关键词:
- 欧拉网格点;
- 拉格朗日网格点;
- Cascade插值方法;
- GRAPES模式
Abstract: For the numerical weather predicting model (NWM) based on semi-Lagrange scheme, it is not economical to apply the conventional point-by-point approach based on Cartesian product of one-dimensional Lagrange interpolation polynomials to evaluate up-stream variables at each integration time step. It takes O(N3) operations to calculate each point. The bigger the N value is, the more accurate the calculation may become. However, it involves too much calculation. When the method of a Cascade of one-dimensional interpolation of the entire data is employed, it requires only O(N) operations. The so-called Cascade method is a highly efficient means of carrying out the grid-to-grid interpolations required by a high-order semi-Lagrangian model. It goes like follows: The intersection points between the regular Eularian and curvilinear Lagrangian meshes form hybrid coordinate lines, and some variables of the intermediate points and the target point of the Lagrangian mesh can be interpolated by using one-dimensional curvilinear Lagrange interpolation method. First, the values of all intermediate points are interpolated. Then, the values of the target points are interpolated from the evaluated intermediate values step by step.The interpolation of the target points is not isolated because the adjoining target point uses shared some intermediate points. Some intermediate results can be repeatedly utilized so that it reduces the amount of computation in interpolation process.GRAPES (Global/Regional Assimilation and Prediction System) is a new generation of numerical weather prediction system of China developed by Research Center for Numerical Meteorological Prediction of CAMS (Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences) of CMA (China Meteorological Administration). It is designed based on the scheme using two time-level semi-Implicit time integration and semi-Lagrangian backward trajectories. It is also a fully compressible, non-hydrostatic grid model using latitude and longitude, as well as terrain-following height vertical coordinate. The model variables are staggered in two-dimension horizontal space in the form of an Arakawa-C grid. According to the designing principles of softw are engineering, GRAPES is a standardized, modularized, and coding infrastructure system. As far as the big numerical predicting models are concerned, the parallel computing becomes a necessary feature of them. The parallel computation of GRAPES is realized by means of decomposing zone in latitude and longitude directions. In order to parallelize Cascade interpolation code conveniently, the independent variables like distance on the curves need to be calculated in individual subsections instead of those from the start point.When the Cascade interpolation is applied in GRAPES model, predicting models are tested based on different horizontal grid resolutions such as those of 50km (720×360) and 100km (360×180). There are 31 vertical levels altogether.The timing of interpolating upstream points is monitored on the IBM-1600 cluster in CMA.The results of tests show that Cascade interpolation can significantly reduce computer running time by about 30%, compared with the conventional Cartesian interpolation, without affecting the accuracy of predicting models.-
Key words:
- Euler meshes;
- Lagrange meshes;
- Cascade interpolation;
- GRAPES mode
-
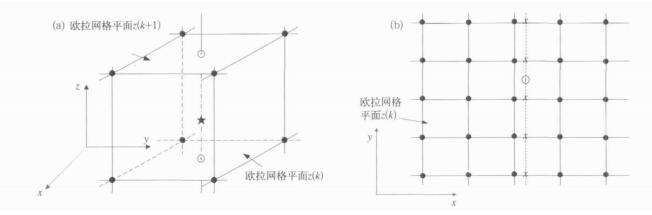
图 1 三维空间拉格朗日三次插值
(a) 三维空间单网格 (●为欧拉网格点; ★表示三维目标点; ⊙表示过★目标点直线与欧拉网格平面z(k) 垂直交叉点), (b) 二维空间水平网格 (x表示平面上过⊙直线与欧拉网格线y(j) 垂直交叉点; 计算⊙点和★点运算量分别为O(N2) 和O(N3), N=4为三次插值)
Fig. 1 The cubic interpolation schematics of a three-dimension space point using Cartesian product technique
(a) schematic illustration of a single grid in three-dimension space (●Eularian grids points; ★ the three-dimension space target points; ⊙ intersection point between line and level panel through ★ point), (b) schematic illustration of a horizontal grids in two-dimension space (x the intersection points betw een the line through ⊙ point and Eularian grid lines y(j) on level panel; the computation operation of the ⊙ and ★ points is O(N2) and O(N3), respesctively, N=4 for cubics)
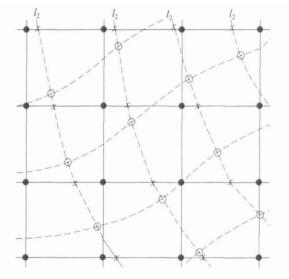
图 2 欧拉网格与拉格朗日网格
在z(n) 平面构成的网格 (实线代表欧拉网格, 虚线拉格朗日网格; ●代表欧拉网格点; x为第二类中间过渡点; ⊙为第一类中间过渡点; l2为第一类和第二类中间过渡点构成的曲线)
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of Eularian grid (solid lines) and Lagrange grid
(broken lines) at z(n) panel (● presents nodes of the Eularian grid; x is the second intersection points; the first intersection is marked by ⊙ points; l2 curves composed of the first intersection points and the second points)
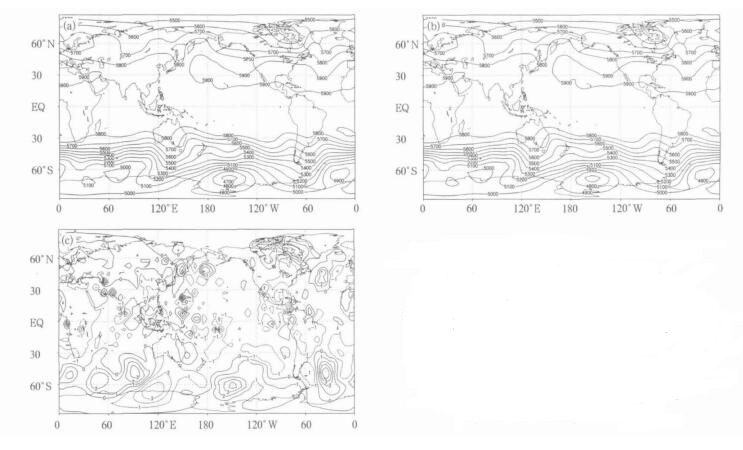
图 3 采用不同插值方法48 h预报, 500hPa位势高度及偏差 (单位:gpm)
(a) 传统Cartesian插值, (b) Cascade插值, (c) 两种插值方法预报500 hPa位势高度偏差
Fig. 3 An example of 48-hour 500hPa geo-potential height forecast using Cartesian product and Cascade interpolation technique (unit:gpm)
(a) the convention Cartesian-product interpolation, (b) the Cascade interpolation scheme, (c) the difference of 48-hour 500 hPa geo-potential height forecast using two methods
-
[1] Staniforth A, Cote J. Semi-Lagrangian integration scheme for atmospherle models-A review. Mon Wea Rev, 1991, 119:2206-2223. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1991)119<2206:SLISFA>2.0.CO;2 [2] Bermejo R, Staniforth A. The conversion of semi-Lagragian advection scheme to quasi-monotone scheme. Mon Wea Rev, 1992, 120: 2622-2632. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1992)120<2622:TCOSLA>2.0.CO;2 [3] McDonald A. Accuracy of multiply-upstream, semi-Lagrangian scheme Ⅱ. Mon Wea Rev, 1987, 115:1446-1450. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<1446:AOMUSL>2.0.CO;2 [4] Purser R J, Leslie L M. An efficient interpolation procedure for high-order three-dimensional semi-Lagrangian models. Mon Wea Rev, 1991, 119:2492-2498. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1991)119<2492:AEIPFH>2.0.CO;2 [5] Bates J R, Semazzi F H M, Higgins R W, et al. Integration of the shallow-water equations on the sphere using a vector semi Lagragian scheme with a multi-grid solver. Mon Wea Rev, 1990, 118: 1615-1627. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118<1615:IOTSWE>2.0.CO;2 [6] Purser R J, Leslie L M. An efficient semi-Lagrangian scheme using third order semi implicit time integration and forward trajectories. Mon Wea Rev, 1994, 120: 745-756. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241552573_An_Efficient_Semi-Lagrangian_Scheme_Using_Third-Order_Semi-Implicit_Time_Integration_and_Forward_Trajectories [7] Nair Ramachandran, Cote J, Staniforth Andrew. Monotonic cascade interpolation for semi-Lagrangian advection. Q J R Meteorol Soc, 1999, 125:197-212. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1477-870X [8] Rancic M. An efficient, conservative, monotone remapping for semi-lagrangian transport algorithm. Mon Wea Rev, 1995, 123: 1213-1217. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1995)123<1213:AECMRF>2.0.CO;2 [9] 陈德辉, 杨学胜, 张红亮, 等.多尺度非静力通用模式框架的设计策略.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(4):452-461. http://qk.cams.cma.gov.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030456&flag=1 [10] 杨学胜, 陈嘉滨, 胡江林, 等.全球非静力半隐式半拉格朗日模式及其极区离散处理.中国科学 (D辑):地球科学, 2007, 37(9):1267-1272. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200709015.htm [11] 陈嘉滨, 季仲贞.半隐式半拉格朗日平方守恒计算格式的构造.大气科学, 2004, 28(4):527-535. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200404004.htm [12] 薛纪善.新世纪初我国数值天气预报的科技创新研究.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5):602-610. http://qk.cams.cma.gov.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200605103&flag=1 [13] 陈德辉, 沈学顺.新一代数值预报系统GRAPES研究进展.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):773-777. http://qk.cams.cma.gov.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200606125&flag=1 [14] 胡江林, 沈学顺, 张红亮, 等.GRAPES模式动力框架的长期积分特征.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(3):276-284. http://qk.cams.cma.gov.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070349&flag=1 [15] Sun Wen-yih, Kao-san yeh. A general semi-Lagrangian advection scheme employing forward trajectories. Q J R Meteorol Soc, 1997, 123:2463-2476. doi: 10.1002/qj.v123:544 [16] 伍湘君, 金之雁, 黄丽萍, 等.GRAPES模式软件框架与实现.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(4):539-546. http://qk.cams.cma.gov.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050468&flag=1 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: