近56年我国暖冬气候事件变化
Temporal Change of Warm Winter Events over the Last 56 Years in China
-
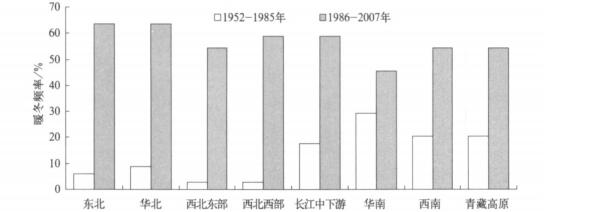
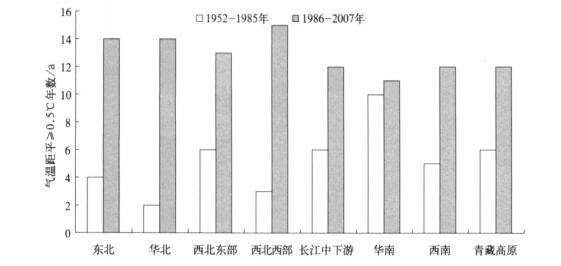
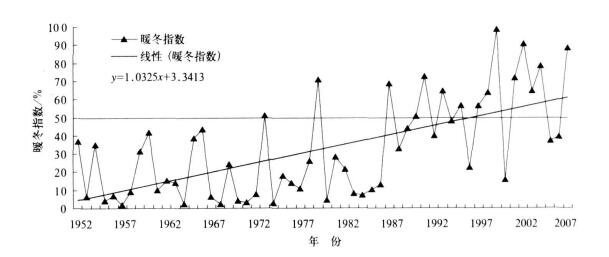
摘要: 对冬季平均气温序列采用三分位方法确定单站暖冬阈值, 并将单站暖冬分为弱和强两个等级。以此为基础, 确定区域暖冬和全国暖冬的界定方法和等级划分标准。区域暖冬采用站点相对比例确定, 全国暖冬采用暖冬面积相对比例界定。对我国1952— 2007年的暖冬事件变化特征的分析结果表明:南方暖冬频率高于北方, 强暖冬多发区出现在我国中西部地区; 北方单站暖冬指数上升幅度大于南方, 表明北方暖冬事件上升趋势更加明显; 以1986年为界, 前期 (1952— 1985年) 南、北方各区域均很少出现暖冬, 南方各区暖冬频率略高于北方各区, 后期 (1986—2007年) 各区暖冬年大为增加, 北方各区增加最明显且超过了南方; 56年中, 全国性暖冬共发生15次 (年), 其中强暖冬共有5次 (年); 全国暖冬指数呈显著上升趋势, 在有效面积不变的情况下, 暖冬面积每10年增加10%。Abstract: The climate of China is now clearly in the global warming up trend, in which the winter warming of thenorthern China is the most obvious.The influence of the warm winter upon the human society is omnibearing, including the direct or indirect impact on human health, daily life, economy activity, agriculture product and ecological environment.Generally, the warm winter means that the air temperature of winter is higher than the climatenormal values (the winter air temperature climatology value from 1971 to 2000).According to the China nationalstandard, the warm winter is classified into two groups by space and intensity grades.In the space group the warmwinter is divided into three spatial grads as sing le station warm winter, regional warm winter, and national warmwinter.In the intensity group, there are two grades as weak warm winter (warm winter) and strong warm winter.Average winter air temperature is divided into 3 probability categories to define the threshold of warm winter forsingle station and its warm winter intensity.Then the division criterions for regional and national winter warm intensity are calculated according to percentile rank of warm winter stations and areas respectively.On the basis of the new division method for warm winter, the characteristics of warm winter since 1952 in China are analyzed too.The analysis reveals that the southern China has a higher frequency of warm winter than northern China, while inmid-west China region strong warm winter occurs more frequently.The rising amplitude of warm winter index islarger in northern China than that in southern part, indicating that the warming trend in northern China is moreobvious.During 1952 to 1985, the occurrence of warm winter is rare in the nation-wide of China, when the frequency of warm winter in southern part of China is slightly higher than that happens in the northern part of China.The incidence of warm winter changes from the year of 1986.The number of warm winter year increases since1986 both in southern and northern China with that of northern part increasing significantly.The results also showthat there are 15 national warm winter years over 56 years with 5 strong warm winters.National warm winter index has an obvious rising trend at a warm winter area rate of 10%per 10 years.However, the air temperature hasgreat year -to-year variations, the possible abnormal cold winter should be properly considered even in the obviousglobal warming trend, and hence impacts of the cold winter shouldn't be neglected.
-
Key words:
- warm winter;
- division method;
- surface air temperature
-
表 1 各区不同年代暖冬频率比较 (单位:%)
Table 1 Frequency of warm winter events for regions and decades (unit :%)

表 2 区域暖冬指数趋势系数及线性趋势
Table 2 Trends of regional warm winter indices for the eight regions

-
[1] IPCC.Climate Change 2007 —The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group Ⅰ to the Third Assessment Report of the IPCC.Cambridge :Cambridge University Press, 2007 :1 -996. [2] 任国玉, 初子莹, 周雅清, 等.中国气温变化研究最新进展.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(4) : 702-716. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504001.htm [3] 唐红玉, 翟盘茂, 王振宇.1951~2002年中国平均最高、最低气温及日较差变化.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(4) : 728 -735. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504003.htm [4] 黄嘉佑, 胡永云.中国冬季气温变化的趋向性研究.气象学报, 2006, 64(5) : 614 -621. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200605007.htm [5] 翟盘茂, 潘晓华.中国北方近50年温度和降水极端事件变化.地理学报, 2003, 58(9) :1 -10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB2003S1000.htm [6] 陈隆勋, 邵永宁, 张清芬, 等.近四十年我国气候变化的初步分析.应用气象学报, 1991, 2(2) : 164 -173. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19910215&flag=1 [7] 马柱国, 符淙斌, 任小波, 等.中国北方年极端温度的变化趋势与区域增暖的联系.地理学报, 2003, 58 (9) : 11 -19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB2003S1001.htm [8] 屠其璞, 邓自旺, 周晓兰.中国气温的区域特征研究.气象学报, 2000, 58(3) : 289 -296. [9] 李栋梁, 彭素琴, 姚辉.我国西北地区冬季平均产气温的气候特征.大气科学, 1995, 19(3) : 192-199. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK502.007.htm [10] 魏凤英, 曹鸿兴, 王丽萍.20世纪80~90年代我国气候增暖进程的统计事实.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(1) :79 -86. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030109&flag=1 [11] 缪启龙, 许遐祯, 潘文卓.南京56年来冬季气温变化特征.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(5) : 620-626. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080514&flag=1 [12] 王凌, 张强, 陈峪, 等.1956 —2005年中国暖冬和冬季温度变化.气候变化研究进展, 2007, 3(1) : 26 -30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200701005.htm [13] 周自江, 王颖.中国近46年冬季气温序列变化的研究.南京气象学院学报, 2000, 23(1) : 106-112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX200001016.htm [14] 龚道溢, 王绍武.近百年我国的异常暖冬与冷冬.灾害学, 1999, 14(2) : 63 -68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU902.013.htm [15] 陈峪, 王凌, 邹旭恺, 等.GB/ T 21983 —2008暖冬等级.中华人民共和国国家标准.北京:中国标准出版社, 2008. [16] 黄嘉佑.气象统计分析与预报方法.北京:气象出版社, 2000. [17] 朱艳峰, 谭桂容, 王永光.中国冬季气温变化的空间模态及其与大尺度环流异常的联系.气候变化研究进展, 2007, 3(5) : 266 -270. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200705006.htm [18] 康丽华, 陈文, 魏科.我国冬季气温年代际变化及其与大气环流异常变化的关系.气候与环境研究, 2006, 11(3) : 330 -339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200603008.htm [19] Li Q X, Dong W J.Detecting and adjusting temporal inhomogeneity in Chines e mean surface air temperature data.Adv Atmos Sci, 2004, 21 (2) : 260 -268. doi: 10.1007/BF02915712 [20] 周雅清, 任国玉.华北地区地表气温观测中城镇化影响的检测和订正.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(4) : 743 -753. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504005.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: