杭州市区大气臭氧浓度变化及气象要素影响
The Variation of Ozone Concentrations in Urban Districts of Hangzhou and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors
-
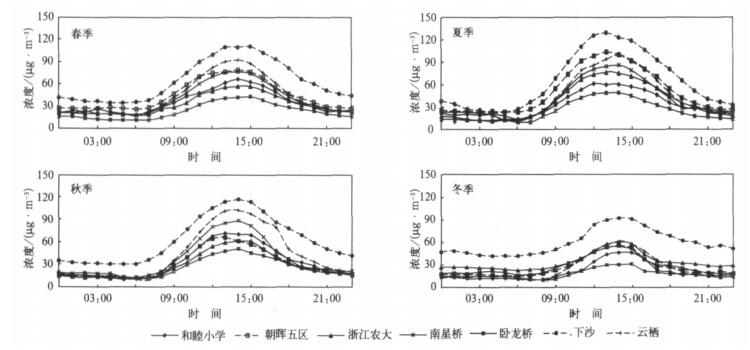
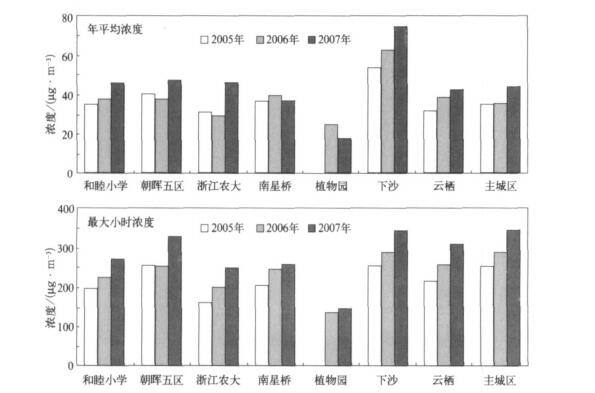
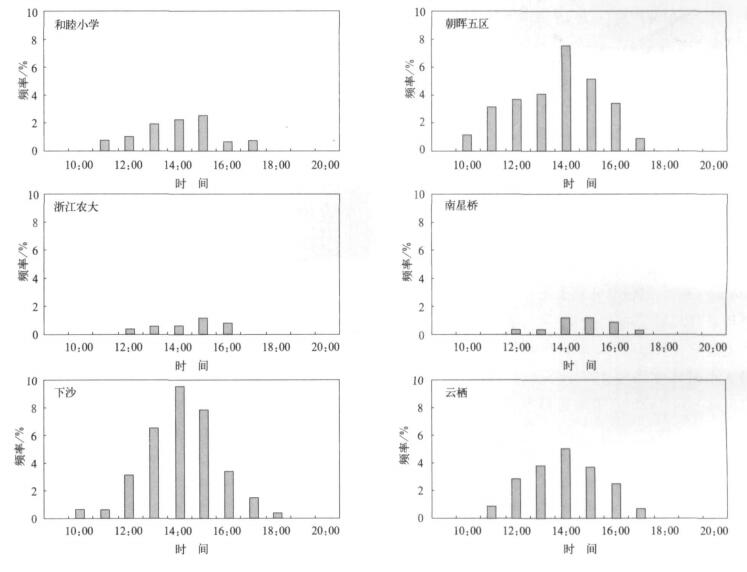
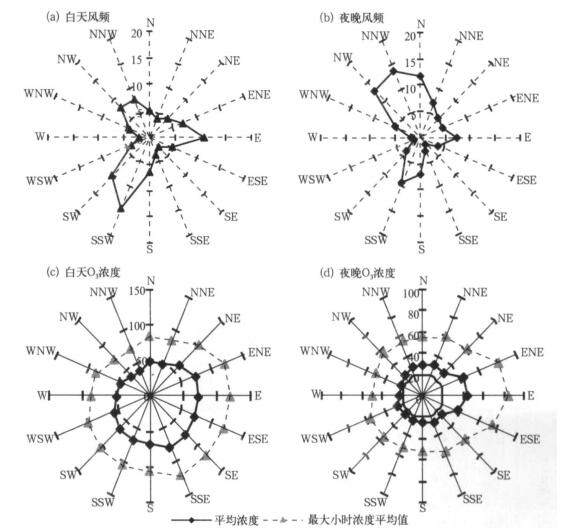
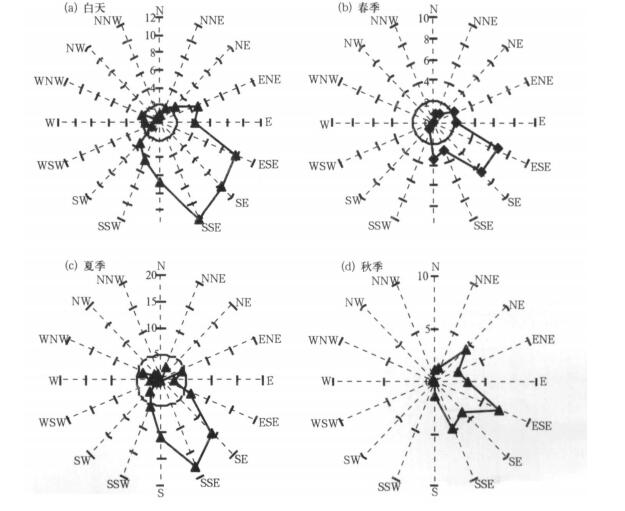
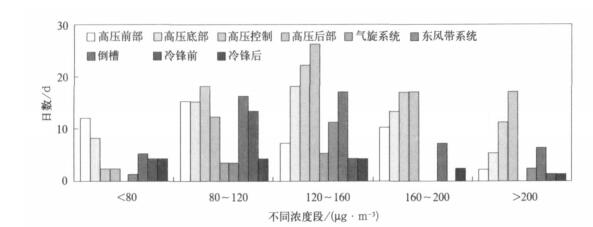
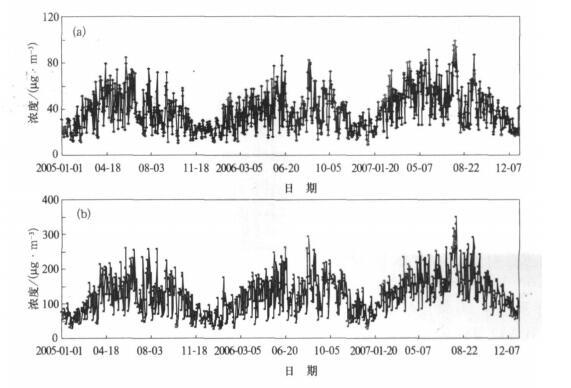
摘要: 利用2005-2007年杭州市区大气O3连续监测资料, 分析了O3浓度变化特征, 在此基础上结合气象观测资料, 分析了大气O3与天气系统间的关系, 建立了O3与气象要素间的多元回归方程。结果表明: 2007年O3平均浓度和最大小时浓度分别为44 μg.m-3和348 μg.m-3, 比上一年增加20%左右, 超标现象也越来越严重; O3浓度有明显的季节变化, 夏季高、冬季低; 大气O3浓度超标主要出现在高压后部和高压控制等天气类型。在紫外线强度较强时O3浓度也高, 二者呈显著正相关; 对O3与各种气象因子进行多元回归分析表明: O3主要受到温度、相对湿度、日照等因素影响。Abstract: Based on the observation data of near surface O3 and meteorological factors in 7 monitoring sites of Hangzhou urban area from 2005 to 2007, the O3 concentration and their temporal variation characteristics are researched. The peak hourly concentration and its nonattainment rate of Hangzhou are compared with those of other major cities at home and abroad. The variation of O3 concentration and its nonattainment rate under different weather conditions are studied, and the variation of O3 concentration with different levels of UV intense is discussed. The results show that the ozone concentration increases significantly year by year, the annual mean ozone concentration and the peak hourly concentration in 2007 are 44 μg.m-3 and 348 μg.m-3, respectively, showing a growth of about 20%from 2006. The ozone nonattainment rate in 2007 is 13.2%, about twice as high as that in 2006. The percentages of ozone nonattainment days from June to September are 75% in total nonattainment days. The appearing time of ozone nonattainment is from 10:00 to 18:00, and the most frequent appearing time of highest nonattainment concentration is around 14:00. The higher ozone nonattainment rate occurs in summer, primarily under the wind direction of SSE, lower in spring, still lower in fall, and the low est value occurs in winter, taking on a very obvious seasonal variation trend. The variation of ozone concentration in sites differs during four seasons, showing highest concentration in summer and lowest in winter where concentration are higher, but on the others sites highest value occurs in spring and lowest in winter. The diurnal mean concentration during the rainy season is low er with effects of air mass and meteorological conditions brought by summer monsoon. The diurnal variation ranges of ozone concentration are different in four seasons, showing higher peak value and low er valley in summer and fall. The concentrations of peak and valley are all low er in winter. The diurnal variation range of higher concentration sites is bigger than that of lower concentration sites. The peak hourly concentration in Hangzhou is close to the levels of Texas, US and Hong Kong, China, but the nonattainment range is higher. During the daytime, the highest ozone concentration occurs under the wind direction of SE, and during nighttime under the wind direction of E. The variation of ozone concentration changes with synoptic systems. The ozone concentrations in areas controlled by high pressure passage and high pressure systems are higher, and percentages of nonattainment days are 37.8% and 24.4% respectively. The ozone concentration is higher on the UV intense days. The ozone concentration and intensity of UV radiation are significantly correlated. The results of multiple regression analysis between ozone concentrations and various weather factors show that the temperature, relative humidity, duration of sunshine are major factors that affect ozone concentration. The ozone concentration is remarkable negatively correlated with relative humidity and visibility (P < 0.05), and is significantly positively correlated with the temperature and sunshine (P < 0.05). The cause is that higher temperature, lower relative humidity and longer time of sunshine may accelerate the rate of photochemical reaction, which has a positive impact on O3 generation, and leads to higher concentration of ozone, otherwise ozone concentration is lower.
-
-
[1] Staehelin J, Thudium J, Burhler R, et al.Trends in surface ozone concentrations at ARIS A (Switzerland).Atmos Envir, 1994, 28(1): 57-87. [2] 王春乙, 关福来. O3浓度变化对我国主要农作物产量的可能影响.应用气象学报, 1995, 6(增刊): 69-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX5S1.009.htm [3] 张远航, 邵可声, 唐孝炎.中国城市光化学烟雾污染研究.北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 1998, 34(2): 392-400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ8Z1.033.htm [4] Affre C, Carrara A, Lefebre F, et al. Aircraft measurement of ozone turbulent flu x in the atmospheric boundary layer. Atmos Environ, 1999, 33: 1561-1574. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00366-5 [5] Abdul-Wahab S A, Al-Alawi S M. Assessment and prediction of tropospheric ozone concentration levels using artificial neural net-works.Envir on Modelling Software, 2002, 17(3): 219-228. doi: 10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00077-9 [6] Canpenter L J, Clemitshaw K C, Burgess R A, et al. Investigation and evaluation of the NOx/O3 photochemical steady state.Atmos Environ, 1998, 32(19): 3353-3365. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00416-0 [7] 唐孝炎.大气环境化学 (第一版).北京:高等教育出版社, 1990: 38-41; 43-45. [8] 白建辉, 王明星.地面臭氧光化学过程规律的初步研究.气候与环境研究, 2001, 6(1): 91-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200101010.htm [9] Wang T, Cheung T F, Li Y S. Ozone and related gaseous pollutants in the boundary layer of eastern China :Overview of the rcent measurements at a rural site. Geophys Res Lett, 2001, 28: 2373-2376. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012378 [10] Xu X, Lin W, Wang T, et al.Long-term reend of surface ozone at a regional background station in eastern China 1991-2006:Enhanced variability.Atmos Chem Phys, 2008, 8: 2595-2067. doi: 10.5194/acp-8-2595-2008 [11] Lin Weili, Xu Xiaobin, Zhang Xiaoling, et al. Contributions of pollutants from North China Plain to surface ozone at the Shangdianzi GAW Station.Atmos Chem Phys Discuss, 2008, 8: 9139-9165. doi: 10.5194/acpd-8-9139-2008 [12] 马一琳, 张远航.北京市大气光化学氧化剂污染研究.环境科学研究, 2000, 13(1): 14-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200001003.htm [13] 王淑兰, 柴发合.北京市O3污染的区域特征分析.地理科学, 2002, 22(3): 360-364. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DLKX200203017.htm [14] 广东省环境保护监测中心站, 香港特别行政区环境保护署.粤港珠江三角洲区域空气监控网络2006年监测结果报告.http:∥www.gdepb. gov.cn gsgg/200710/t20071026_49978.html. [15] 广东省环境保护监测中心站, 香港特别行政区环境保护署.粤港珠江三角洲区域空气监控网络2007年监测结果报告.http:∥www. gdepb.gov.cn/gsgg/200710/t20071026_49978. html. [16] Monitor Values Report-Criteria Air Pollutants.http:∥iaspub.epa.gov/airsdata. [17] European Environment Agency. Technical Report Air Pollution by Ozone across Europe during Summer 2006.ISSN 1725-2237, 2007(5): 9. [18] European Environment Agency. Technical Report Air Pollution by Ozone across Europe during Summer 2007.ISSN 1725-2237, 2008(5): 9. [19] 安俊琳, 王跃思, 李昕, 等.北京地面紫外辐射与空气污染的关系研究.环境科学, 2008, 29(4): 1053-1058. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200804039.htm [20] 任丽红, 胡非, 王玮.北京夏季垂直分布与气象因子的相关研究.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(2): 166-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200502002.htm [21] 杨昕, 李兴生.近地面O3变化化学反应机理的数值研究.大气科学, 1999, 23(4): 427-438. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK199904005.htm [22] 丁国安, 罗超, 汤洁, 等.清洁地区气象因子与地面O3关系的初步研究.应用气象学报, 1995, 6(3): 350-355. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19950354&flag=1 [23] 郑向东, 丁国安, 孙敏峰, 等.北京冬季低层大气O3垂直分布观测结果的研究.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(特刊): 100-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1010.htm [24] Tsutsumi Y, Makino Y, Jensen J. Aircraft measurements of tropospheric ozone over the western Pacific Ocean.Atmos Environ, 1996, 30: 1763-1772. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00378-9 [25] 谈建国, 陆国良, 耿福海.上海夏季近地面臭氧浓度及其相关气象因子的分析和预报.热带气象学报, 2007, 23(5): 515-520. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200705013.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: