北京地区雷暴过程闪电与地面降水的相关关系
Relationship Between Lightning Activities and Surface Precipitation in Thunderstorm Weather in Beijing
-
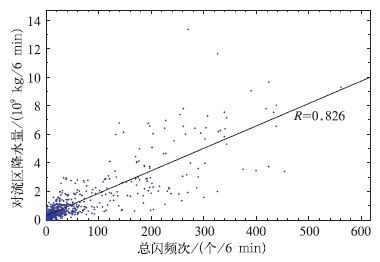
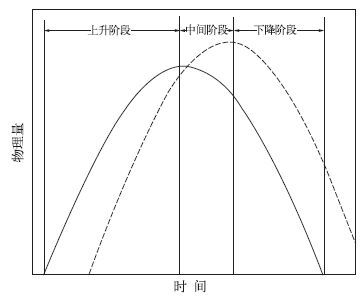
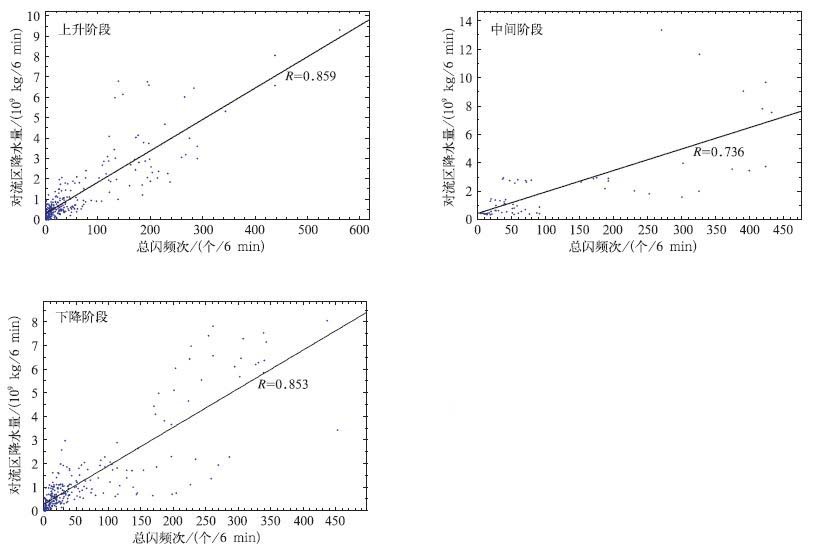
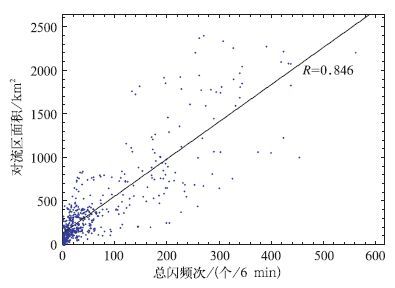
摘要: 该文选取北京地区2006年夏季的18次雷暴过程,利用SAFIR3000三维闪电定位系统观测到的总闪数据,分析了闪电与雷达反演的对流活动区降水量和对流活动区面积的相关关系,结果表明:北京地区的雷暴活动中,单个闪电所表征的降水量的范围在0.86×107~6.57×107 kg/fl之间,平均值为2.65×107 kg/fl;闪电活动与对流活动区降水量的线性相关关系显著,相关系数达到0.826;闪电活动与对流活动区面积也具有显著的线性关系,相关性系数达到0.846。文中给出了基于6 min闪电频次估算6 min对流降水量以及对流活动区面积的拟合方程。分析还发现,总闪活动与降水的关系要明显好于地闪,总闪信息的应用极大提高了分析结果的质量和可信性,分析结果对于利用闪电信息估测降水具有参考意义。Abstract: Study on the relationship between lightning activity and precipitation is valuable for estimating the rainfall based on lightning detection in the areas where other observation methods such as radar, precipitation gauge and so on are inapplicable. Therefore, 18 thunderstorm processes occurred in Beijing area are investigated based on radar observation and correlative radar algorithms, then the convective regions and stratiform regions are distinguished and the precipitation intensity of the thunderstorms is calculated. The total lightning data (intracloud (IC) lightning and cloud to ground (CG) lightning) of the thunderstorms detected by SAFIR3000 3 D total lightning location system is used in the analysis to discuss the relationship between the lightning activities and the amounts of precipitation in convective regions and the areas of convective regions. It is found that the precipitation per flash (PRF) ranges from 0.86×107 kg/fl to 6.57×107 kg/fl with the average value of 2.65×107 kg/fl. Through comparing the standard deviation of the PRF calculated based on total lightning (PRFL) and that calculated based on CG lightning (PRFCG), it shows that PRFL is more stable than PRFCG in different thunderstorms. It demonstrates that for the time series of the peaks of lightning activities and the peaks of the amounts of precipitation in convective regions and the areas of convective regions, there are three styles of situation, i.e., ahead, behindhand and synchronous, which shows the complex relationship between them. The significant linear correlations between lightning activities and the amounts of precipitation in convective regions are found in all thunderstorms. The statistics including all samples shows that the coefficient is 0.826 and the fitting equation is MCR=1.574×107FTL+2.956×108. FTL is the frequency of the total lightning in 6 min and MCR is the amount of precipitation in convective regions in 6 min with the unit of kg/6 min. According to the situation of the time series of the peaks of lightning activities and precipitation, every thunderstorm process is divided into three stages: Rising stage, intermediate stage and falling stage. The correlation between lightning activity and the precipitation is found to be the most significant during the rising stage, followed in turn by falling stage and intermediate stage, and the corresponding coefficients are 0.859, 0.853 and 0.736, respectively. The relationships between the lightning activities and the areas of convective regions are found to be outstanding in 16 thunderstorms. When all the thunderstorms are considered, the coefficient reaches 0.846 and the fitting equation is ACR=4.267FTL+130.283.ACR is the area of convective region with the unit of km2 and FTL is the frequency of the total lightning in 6 min. According to the time series of the peaks of the lightning frequencies and the areas of convective regions, the thunderstorm processes are divided into three stages in the same way. It shows that all the linear correlations for three stages are outstanding, especially for rising stage. The coefficients for rising stage, intermediate stage and falling stage are 0.862, 0.834 and 0.837, respectively. Through the analysis, it is found that the relationships between the total lightning activity and the precipitation in convective region and the area of convective region are always better than those between the CG lightning activity and the precipitation and the area, indicating that the application of the total lightning data has improved the quality and reliability of the results.
-
Key words:
- lightning activities;
- convective region;
- precipitation
-
表 1 2006年雷暴过程说明
Table 1 Analyzed thunderstorms processes in 2006

表 2 RPF值的统计 (单位:107kg/fl)
Table 2 Statistics of RPF value (unit:107kg/fl)

表 3 相关研究中单个总闪或地闪对应的降水分析
Table 3 Rainfall relevant to one lightning discharge or clout-to-ground lightning discharge in other studies

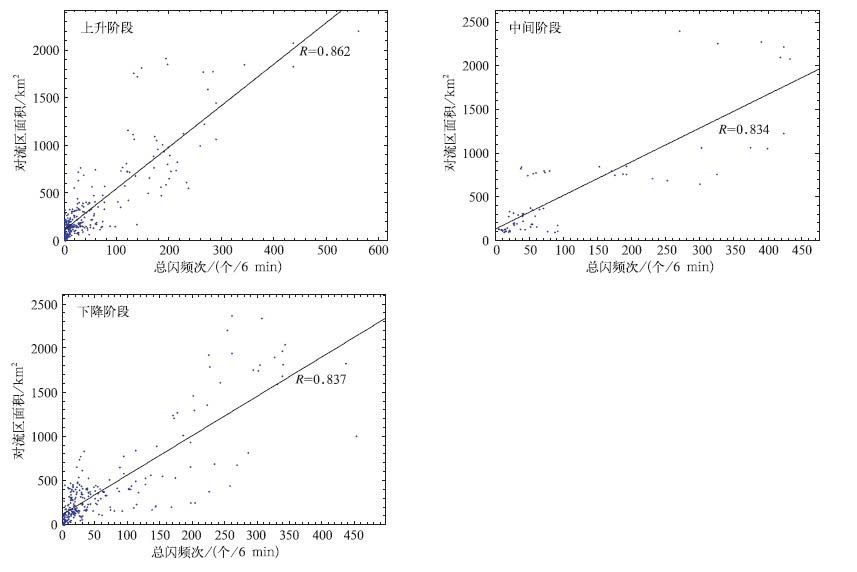
表 4 雷暴不同阶段总闪与对流区降水量的线性关系分析
Table 4 Linear correlation of different development stages of thunderstorm processes between the total lightning frequency and the rainfall mass in the convective regions

表 5 雷暴不同阶段总闪与对流活动区面积的线性关系分析
Table 5 Linear correlation of different development stages of thunderstorm processes between the total lightning frequency and the area of the convective regions

-
[1] 郑栋, 孟青, 吕伟涛, 等.北京及其周边地区夏季地闪活动时守特征分析.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(5):638-644. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050582&flag=1 [2] 王飞, 张义军, 赵均壮, 等.雷达资料在孤立单体雷电预警中的初步应用.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(2):153-160. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080228&flag=1 [3] 王飞, 董万胜, 张义军, 等.云内大粒子对闪电活动影响的个例模拟.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(5):564-570. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090507&flag=1 [4] Vonnegut B.Some facts and speculations concerning the origin and role of thunderstorms electricity.Meteorol Monogr, 1963, 5:224-241. [5] Williams E R, Weber M E, Orville R E.The relationship between lightning type and convective state of thunderclouds.J GeophysRes, 1989, 94(D11): 13213-13220. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.207.8701&rep=rep1&type=pdf [6] 张义军, 孟青, 马明, 等.闪电探测技术发展和资料应用.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5):611-620. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200605104&flag=1 [7] 张义军, 周秀骥.雷电研究的回顾和进展.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6).829-834. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200606130&flag=1 [8] Petersen W A, Rutledge S A.On the relationship between cloud-to-ground lightning and convective rainfall.J Geophys Res, 1998, 103(D12):14025-14040. doi: 10.1029/97JD02064 [9] Soriano R L, Pablo F D, Diez E G.Relationship between convective precipitation and cloud-to-ground lightning in the Iberian Peninsula.Mon Wea Rev, 2001, 129 (12):2998-3003. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129<2998:RBCPAC>2.0.CO;2 [10] Piepgrass M V, Krider E P, Moore C B.Lightning and surface rainfall during Florida thunderstorms.J Geophys Res, 1982, 87(C13):11193-11201. doi: 10.1029/JC087iC13p11193 [11] Gungle B, Krider E P.Cloud-to-ground lightning and surface rainfall in warm-season Florida thunderstorms.J Geophys Res, 2006, 111, D19203, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006802. [12] Wang K Y, Liao S A.Lightning, radar reflectivity, infrared brightness temperature, and surface rainfall during the 2-4 July 2004 severe convective system over Taiwan area.J Geophys Res, 2006, 111, D05206, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006411. [13] Chang D E, Weinman J A, Morales C A, et al.The effect of space borne microwave and ground-based continuous lightning measurements on forecasts of the 1998 Groundhog Day storm.MonWeaRe-u, 2001, 129(8): 2809-1833. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493%282001%29129%3C1809%3ATEOSMA%3E2.0.CO%3B2 [14] 周筠君, 郄秀书, 张义军, 等.地闪与对流性天气系统中降水关系的分析.气象学报, 1999, 57(1):103-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB901.008.htm [15] Zipser E J.Deep cumulonimbus cloud systems in the tropics with and without lightning.Mon Wea Rev, 1994, 122(8):1837-1851. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1994)122<1837:DCCSIT>2.0.CO;2 [16] Tapia A, Smith J A, Dixon M.Estimation of convective rainfall from lightning observations.J Appl Meteorol, 1998, 37(11):1497-1509. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1998)037<1497:EOCRFL>2.0.CO;2 [17] Alexander G D, Weinman J A, Karyampudi V et al.The effect of assimilating rain rates derived from satellites and lightning on forecasts of the 1993 superstorm.Mon Wea Rev, 1999, 127(7):1433-1457. [18] Kawasaki Z I, Yamamoto K, Matsuura K, et al.SAFIR operation and evaluation of it’s performance.Geophys Res Lett, 1994, 21(12):1133-1136. doi: 10.1029/93GL02788/references [19] Richard P, Lojou J Y.Assessment of Application of Storm Cell Electrical Activity Monitoring to Intense Precipitation Forecast//10th Int Conf on Atmospheric Electricity, Osaka, Japan, 1996:284-287. [20] Cheze J L, Sauvageot H.Area-average rainfall and lightning activity.J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(D2):1707-1715. doi: 10.1029/96JD02972 [21] Mazur V, Williams E, Boldi R, et al.Initial comparison of lightning mapping with operational time-of-arrival and interferometric systems.J Geophys Res, 1997, 102 (D10):11071-11085. doi: 10.1029/97JD00174 [22] Lee J, Wada M, Kawasaki Z I, et al.Lightning activity during winter thunderstorm season observed by SAFIR.Electr Engjpn, 2000, 132(1):30-37. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6416(20000715)132:1%3C30::AID-EEJ5%3E3.0.CO;2-%23/abstract [23] Pineda N, Bech J, Rigo T, et al.Comparison of Radar Precipitation Fields with Lightning Observations//Proceedings on the 4th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Barcelona (Spain), September, 2006. [24] Montanya J, Pineda N, March V, et al.Experimental evaluation of the Catalan Lightning Location Network//19th Int Lightning Detection Conf, Tucson, Arizona, USA, 2006. [25] Montanya J, Pineda N, Soula S, et al.Total Lightning Activity and Electrostatic Field in a Hail-bearing Thunderstorm in Catalonia//19th Int Lightning Detection Conf, Tucson, Arizona, USA, 2006. [26] Driie C, Hauf T, Finke U, et al.Comparison of a SAFIR lightning detection network in northern Germany to the operational BLIDS network.J Geophys Res, 2007, 112, D18114, doi: 10.1029/2006JD007680. [27] Zheng D, Zhang Y, Meng Q, et al.Total lightning characteristics and electric structure evolution in a hailstorm.Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2009, 23(2):233-249. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-QXXW200902010.htm [28] Cummins K L, Murphy M J, Bardo E A, et al.A combined TOA/MDF technology upgrade of the U.S.National Lightning Detection Network.J Geophys Res, 1998, 303(D8):9035-9044. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/doi?DOI=10.1029/98JD00153 [29] Wacker R S, Orville R E.Changes in measured lightning flash count and return stroke peak current after the 1994 U.S.National Lightning Detection Network upgrade, 1, Observations.J Geophys Res, 1999, 104(D2):2151-2158. doi: 10.1029/1998JD200060 [30] Wacker R S, Orville R E.Change in measured lightning flash count and return stroke peak current after the 1994 U.S.National Lightning Detection Network upgrade, 2, Theory.J Geophys Res, 1999, 104(D2):2159-2162. [31] Orville R E, Huffines G R.Clout-to-ground lightning in the United States:NLDN results in the first decade, 1989-98.MonWeaRevy 2001, 129(5):1179-1193, [32] Carey L D, Rutledge S A, Petersen W A.The relationship between Severe Storm Reports and Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Polarity in the Contiguous United States from 1989 to 1998.Mon Wea Rev, 2003, 131(7):1211-1228. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2003)131<1211:TRBSSR>2.0.CO;2 [33] Pineda N, Rigo T, Bech J, et al.Lightning and precipitation relationship in summer thunderstorms:Case studies in the North Western Mediterranea region.Atmos Res, 2007, 85 (2):159-170. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.12.004 [34] 肖艳姣, 刘黎平.三维雷达反射率资料用于层状云和对流云的识别研究.大气科学, 2007, 31(4):646-654. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200704008.htm [35] Williams E R, Rutledge S A, Geotis S G)et al, A radar and electrical study of tropical “hot towers”.J Atmos Sci, 1992, 49(15):1386-1395. [36] Kinzer G D.Cloud-to-ground lightning versus radar reflectivity in Oklahoma thunderstorms.J Atmos Sci, 1974, 31(3):787-799. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1974)031<0787:CTGLVR>2.0.CO;2 [37] Grosh R C.Lightning-Precipitation-The Life History of Isolated Thunderstorms.Conference on Cloud Physics and Atmospheric Electricity.Am Meteorol Soc, Issaquah, Wash, 1978. [38] Goodman S J, Buechler D E, Wright P D, et al.Lightning and precipitation history of a microburst-producing storm.Geophys Res Lett, 1988, 15(11):1185-1188. doi: 10.1029/GL015i011p01185 [39] Goodman S J, Buechler D E.Lightning-rainfall Relationships.16th Conference on Severe Local Storms.Am Meteorol Soc Kananaskis Park, Alberta, Canada, 1990. [40] Buechler D E, Wright P D, Goodman S J.Lightning/Rainfall Relationships During COHMEX//Preprints, 16th Conf on Severe Local Storms.Amer Meteor Soc, 1990:710-714. [41] Nielsen K E, Goodman S J, Buechler D E.Cloud-to-ground Lightning and Rainfall Volumes in Mesoscale Convective Sys-tems.16 th Conference on Severe Local Storms and Conference on Atmospheric Electricity.Am Meteorol Soc, Kananaskis, Canada, 1990. [42] Holle R L, Watson A I, Lopez R E, et al.The liefe cycle of lightning and severe weather in a 3-4 June 1985 PRE-STORM mesoscale convective system.MonWeaRev, 1994, 122(8):1798-1808. [43] Senesi S, Bougeault P, Chaze J, et al.The Vaison-La-Ro-maine flash flood:Mesoscale analysis and predictability issues.Wea Forecasting, 1996, 11(4):417-442. doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(1996)011<0417:TVLRFF>2.0.CO;2 [44] Soula S, Sauvageot H, Molinie G, et al.The CG lightning activity of a storm causing a flash flood.Geophys Res Lett, 1998, 25(8):1181-1184. doi: 10.1029/98GL00517 [45] Molinie G, Soula S, Chauzy S.Cloud-to-ground lightning activity and radar observations of storms in the Pyrenees range area.Q J R Meteorol Soc, 1999, 125(560):3103-3122. doi: 10.1002/qj.49712556015/abstract [46] Soula S, Chauzy S.Some aspects of the correlation between lightning and rain activities in thunderstorms.Atmos Res, 2001, 56(1-4):355-373. doi: 10.1016/S0169-8095(00)00086-7 [47] Zhou Y J, Qie X S, Soula S.A study of the relationship between cloud-to-ground lightning and precipitation in the convective weather system in China.Ann Geophys, 2002, 20 (1):107-113. doi: 10.5194/angeo-20-107-2002 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: