陕西秋季降水变化特征
Variation Characteristics of Autumn Precipitation in Shaanxi Province
-
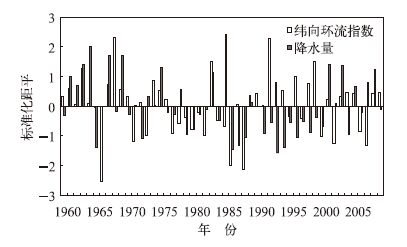
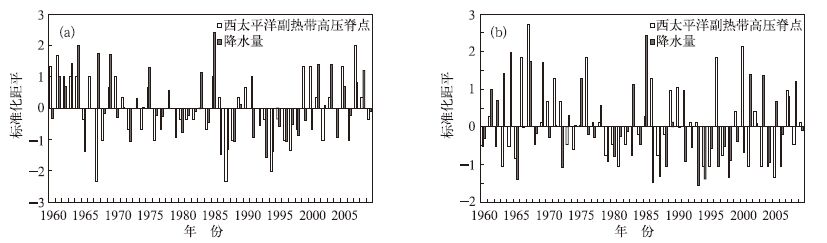
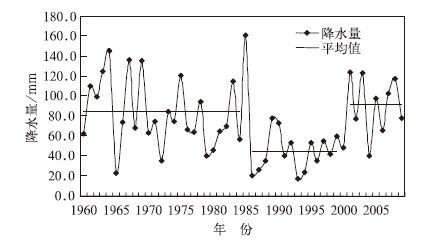
摘要: 利用1960—2009年陕西74个台站逐月降水资料和同期NCEP/NCAR再分析资料,采用Mann Kendall和REOF等方法分析了近50年陕西秋季降水变化时空分布及环流特征。研究表明:近50年来, 陕西9月降水对整个秋季降水具有决定性作用,呈现出“北少南多”和“北多南少”的空间分布特征;当西太平洋副热带高压位置偏西偏北,纬向环流指数偏弱,海平面气压场为“西低东高”的形势,850 hPa风场上西北地区东部为西太平洋副热带高压外围的东南气流控制时,陕西秋季降水空间分布多呈现“北多南少”型。Abstract: Based on monthly rainfall data of 74 stations and NCEP/NCAR reanalysis dataset from 1960 to 2009, the variation characteristics of autumn rainfall over Shaanxi Province and the main factors influence on autumn rainfall are analyzed by the methods of Mann Kendall and REOF with a horizontal resolution of 2.5°×2.5°. It shows that the rainfall of September has decisive effect on the total autumn rainfall over Shaanxi Province. The September rainfall occupies 57.3% of the total autumn rainfall from 1960 to 2009, and from 2000 to 2009 it occupies 61.5%. The September rainfall can be divided into 2 types by spatial distribution: One is fewer in the north and more in the south, the other is more in the north and fewer in the south. The first type shows no obvious decadal variations, but the second type varies obviously in these decades as it occurs a lot from 1960 to 1985, less frequently from 1986 to 2000, and then more frequently again from 2001 to 2009. Statistics on the variation of atmospheric circulation and the second type rainfall distribution indicates that when subtropical high over western Pacific (SHWP) is more northwest (northeast and southwest) to its regular position, there are 12 years (25 years) that the September rainfall over the northern Shaanxi Province is more (less) in the past 50 years. When the zonal circulation index (ZCI) is weaker (stronger), there are 14 years (16 years) that the September rainfall over the northern Shaanxi Province is more (less) in the past 50 years. The correlations between the rainfall, the SHWP and ZCI are more obvious since the 1980s. Meanwhile the sea level pressure is low in the west and high in the east in the years when September rainfall over the northern Shaanxi Province is more, because there are more low weather systems from the northwest Xinjiang. So the east part of northwest China is controlled by the subtropical high over west Pacific and the southeast winds provides sufficient water vapor.
-
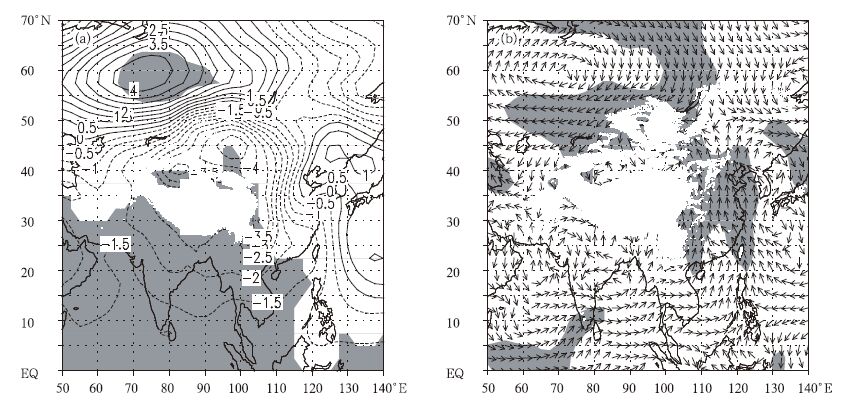
图 4 陕西北部9月降水偏多和偏少年份合成的海平面气压差值图 (单位:hPa)(a) 和850hPa风场差值图 (b)(阴影区域为通过0.05的显著性检验)
Fig. 4 The departures of seasurface pressure (unit: hPa) (a) and 850 hPa wind field (b) of the composited years in terms of the maximin and minimin of the precipitation in September over Northern Shaanxi (level exceeds 0.05 shown as shaded)
表 1 陕西北部9月降水量与纬向环流指数和西太平洋副热带高压位置关系
Table 1 The interdecadal changes of precipitation in September in Northern Shaanxi, zonal circulation index and the location of subtropical high over west Pacific

-
[1] 威廉·伯勒斯.21世纪的气候.北京:气象出版社, 2007. [2] 王遵娅, 丁一汇.中国雨季的气候学特征.大气科学, 2008, 32(1):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200801001.htm [3] 高由禧, 郭其蕴.我国的秋雨现象.气象学报, 1958, 29(4):264-273. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB195804005.htm [4] 刘富明.大气环流由夏到秋的转变及其与四川秋雨形成的关系.四川气象, 1981(2):1-6. [5] 刘天适, 周全瑞.1981年8月13-24日汉中、宝鸡地区连阴特大暴雨天气分析.陕西气象, 1983(5):13-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXQI198305004.htm [6] 白虎志, 董文杰.华西秋雨的气候特征及成因分析.高原气象, 2004, 23(6):884-889. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200406022.htm [7] 鲍媛媛, 阿布力米提, 李峰, 等.2001年华西秋雨时空分布特点及其成因分析.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(2):215-222. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030226&flag=1 [8] 方建刚, 白爱娟, 陶建玲, 等.2003年陕西秋季连阴雨降水特点及环流条件分析.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(4):509-517. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050464&flag=1 [9] 方建刚, 侯建忠, 陶建玲, 等.秦岭地区秋季降水的气候特征分析.气象科学, 2008, 24(4):416-420. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200804009.htm [10] 方建刚, 张弘, 白爱娟, 等.陕西强连阴雨天气个例的综合分析.气象科学, 2006, 26(5):578-585. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200605016.htm [11] 陈娇娜, 李国平, 黄文诗, 等.华西秋雨天气过程中GPS遥感水汽总量演变特征.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(6):753-760. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090614&flag=1 [12] 汤绪, 孙国武, 钱维宏.亚洲夏季风北边缘研究.北京:气象出版社, 2003. [13] 魏凤英.现代气候统计诊断与预测技术.北京:气象出版社, 2007. [14] 黄菲, 李栋梁, 汤绪, 等.用过程透雨量确定的东亚夏季风北边缘特征.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(5):530-538. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090503&flag=1 [15] Rossby C G.Relationship between variations in the intensity of the zonal variation and the displacement of the semi-perma-nent centers of action.Journal of Marine Research, 1939, 2:38-55. doi: 10.1357/002224039806649023 [16] 李崇银.气候动力学.北京:气象出版社, 2005. [17] 王绍武.北半球500毫巴月平均环流特征及演变规律的研究:西风指数.气象学报, 1963, 33(3):361-374. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB196303008.htm [18] 严华生, 胡娟, 范可, 等.近50年来夏季西风指数变化与中国夏季降水的关系.大气科学, 2007, 31(4):717-726. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200704015.htm [19] 冯文, 王可丽, 江灏.夏季区域西风指数对中国西北地区水汽场特征影响的对比分析.高原气象, 2004, 23(2):271-275. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200402022.htm [20] 李万莉, 王可丽, 傅慎明, 等.区域西风指数对西北地区水汽输送及收支的指示性.冰川冻土, 2008, 30(1):28-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200801005.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: