北京地区酸雨特征及影响因素
Characteristics and Impact Factors of Acid Rain in Beijing
-
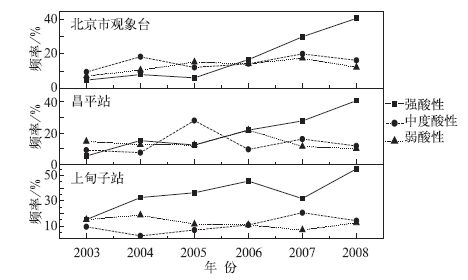
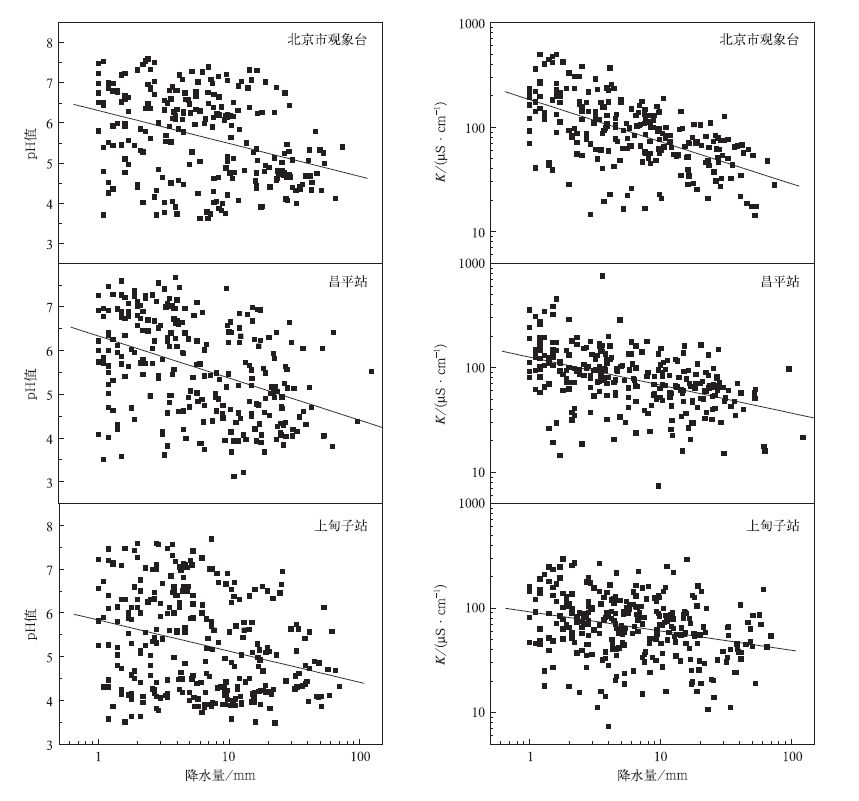
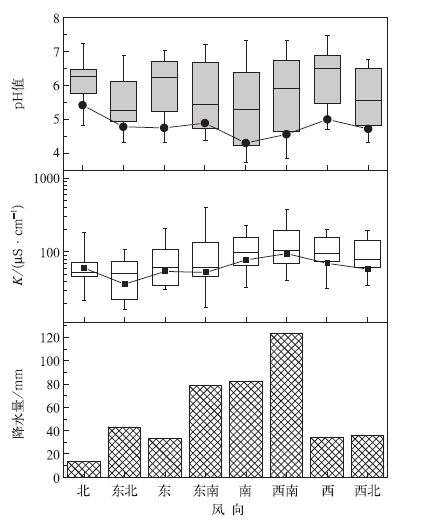
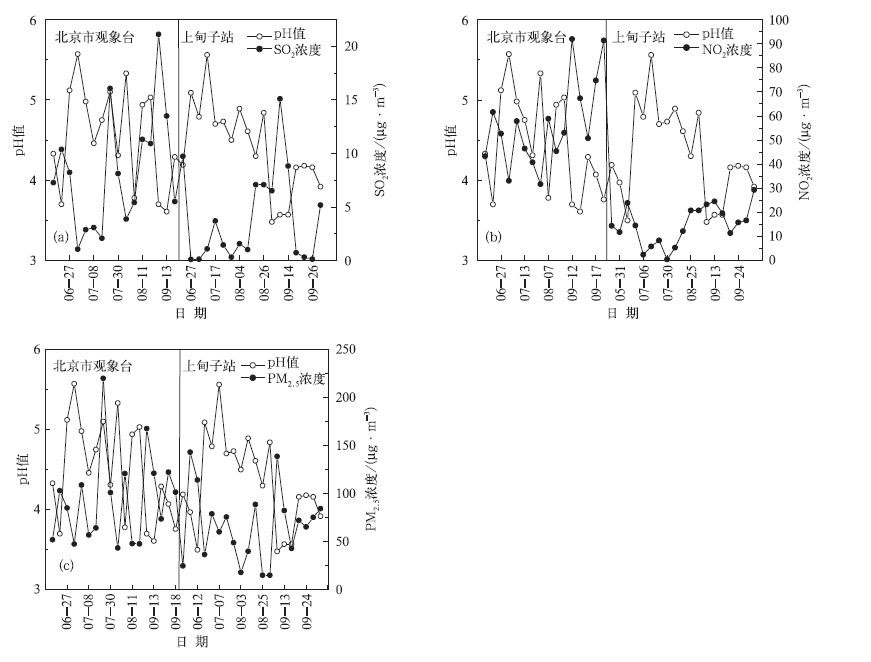
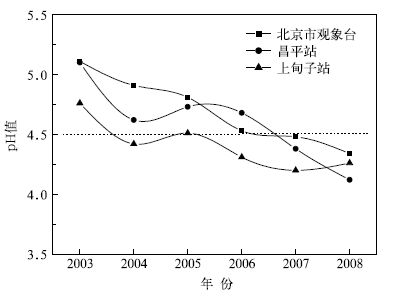
摘要: 利用2003-2008年北京地区3个酸雨观测站(北京市观象台、昌平站、上甸子站)的酸雨观测资料并结合探空及大气成分资料,分析了近年来北京地区的酸雨变化特征,研究了不同气象条件和大气污染物对酸雨的影响。结果表明:2003-2008年降水平均pH值均小于5.6, 且近6年来,降水pH值呈波动下降的趋势。北京地区夏、秋两季降水平均pH值及犓值较春、冬季节低;pH值及犓值随降水量的增大呈下降趋势,而强酸雨频率则随降水量的增大呈上升趋势;在偏南气流影响下,降水酸度增强且酸沉降量大,酸雨污染严重;当连续发生逆温状况时,酸雨出现频率增大;大气污染物SO2, NO2, PM2.5的浓度与降水pH值成负相关关系,说明近地层污染物浓度对降水酸度有重要影响。Abstract: The annual and seasonal characteristics of acid rain in Beijing during 2003-2008 and their relationships with the meteorological conditions and pollutant concentrations are investigated using data observed at Beijing Weather Observatory, Changping and Shangdianzi acid rain observation stations. The average pH of precipitation is lower than 5.6 from 2003 to 2008, and the variation in the annual average precipitation acidity displays a decreasing trend over the past 6 years. After 2007, the acid rain pollution becomes more serious in Beijing area, when the average pH of precipitation is lower than 4.5 at all the three observation stations. The annual average pH values of precipitation at Beijing Weather Observatory and Changping are higher than that at Shangdianzi Station in the past 6 years except for 2008. It shows that the acidification degree in background area is heavier than that in urban area. Seasonal and monthly variations in precipitation acidity, conductivity and the frequency of acid rain are observed in Beijing area. The average pH and K values of acid rain in summer and autumn are lower than those in spring and winter. The frequency of acid rain with pH < 4.5 and 4.5 < pH < 5.0 is highest in autumn and summer, respectively.The monthly variation of acid deposition show that the heaviest acid rain pollution occurs in summertime, espe-cially in August.The decrease tendency in the pH and K value and the increase tendency in the frequency of acid rain with pH < 4.5 are found with the increase of precipitation intensity, respectively.The higher pH and K value at Beijing Weather Observatory and Changping Station indicate that the process of below-cloud scavenging is more important in urban area, and alkaline coarse particles in the atmosphere plays an important role in neutralization.The wind direction at 1500 ml evel has significant influence on the precipi-tation acidity and conductivity value over Beijing area.The lowest pH is observed with south wind, and higher K value and heavier acid deposition are recorded with the southwest and south wind.The transport of pollutants by the southerly flow enhances the acidity of precipitation.The acid rain is also influenced by the temperature inversion.The frequency of acid rain increases when continuous inversion occurs (temper-ature inversion occurs at rainy day and the day before that).Temperature inversion occurs most frequently during autumn that leads to the increase of acid rain pollution in this season.Furthermore, pollutants in the atmosphere have important effect on the acidity of precipitation.There is a significant negative correla-tion between the concentration of atmospheric pollutants, suchas SO2, NO2 and PM2.5, and the pH of rain, suggesting that the variation of pollutant concentration in lower atmosphere layer has significant in-fluence on the acid rain.SO2 and NO2 are the important precursors of the acidic compositions and the major contributors of acidity in rainwater.The neutralization effect of fine particles (PM2.5) is very weak.On the contrary, the acid compositions of PM2.5 are partly contributed to the acidity of precipitation when they are scavenged into the rainwater.
-
Key words:
- acid rain;
- pH value;
- K value;
- frequency of acid rain;
- impact factors
-
表 1 2007年9月12—14日北京地区降水概况
Table 1 Overview of rainfall during 12-14 September 2007 in Beijing Are

-
[1] 唐孝炎, 张远航, 邵敏.大气环境化学.北京:高等教育出版社, 2006. [2] 戴树桂, 岳贵春, 王晓蓉.环境化学.北京:高等教育出版社, 1997:60-63. [3] 丁国安, 徐晓斌, 王淑凤, 等.中国气象局酸雨网基本资料数据集及初步分析.应用气象学报, 2004, 15(增刊):85-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2004S1012.htm [4] 赵艳霞, 侯青.1993-2006年中国区域酸雨变化特征及成因分析.气象学报, 2008, 66(6):1032-1042. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200806017.htm [5] 汤洁, 徐晓斌, 巴金, 等.1992 2006年我国降水酸度的变化趋势.科学通报, 2010, 55(8):705-712. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201008009.htm [6] 王文兴, 徐鹏举.中国大气降水化学研究进展.化学进展, 2009, 21(2/3):266-281. http://www.baidu.com/link?url=ioJgzzn_Fn1aIOQ5mH9CvYf-7ESzgEPyEbR-kwe3Das6mkcqiv-jGh-mR_LbF2pQ32uLu3Mv-t8FHgnXi1Ph5W6nFoUh2bZSXYH-liZLEYjKy4F0A6fpnnFBHosKVOZ238Lz3shM7CGvhBaF47LrTotqAqosbvHIJYMjEynRxdwmM6PrirF4FXwOCsa3vJWM54dGldfyGRI5zTRkcbyWb1CAcTongMdqjoEfYu407edQMSc4hV18BtfJ18EGlYR2oXGN60YhEkJkaeIdRo36jXfTWrcnV3rvBFVYxFoITDq-omY5ZCIqoERH6ft73zN7--smZYKKKluiU1_qfRGbt-f03duNlMLH6UGTiIebU1UK8hxlI8_L-W50L5y2e5l_W9mlf5VBP5XacI7HOnmDqa&wd=&eqid=89c839ff0000151b00000005587de18b [7] Kulshrestha U C, Monika J, Kulshlrestha R S, et al.Chemi-cal characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-cen-tral India.Atmospheric Environment, 2003, 37(21):3019-3026. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00266-8 [8] 徐敬, 张小玲, 徐晓斌, 等.上甸子本底站湿沉降化学成分变化与来源解析.环境科学学报, 2008, 28(5):1001-1006. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200805031.htm [9] 胡敏, 张静, 吴志军.北京降水化学组成特征及其对大气颗粒物的去除作用.中国科学 (B辑), 2005, 35(2):169-176. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK200502010.htm [10] 张维, 邵德民, 沈爱华, 等.上海梅雨季节云水和雨水的化学组分分析.应用气象学报, 1991, 2(4):375-384. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19910452&flag=1 [11] 丁国安, 郑向东, 马建中, 等.近30年大气化学和大气环境研究回顾.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):796-814. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200606128&flag=1 [12] Chate D M, Rao P S P, Naik M S, et al.Scavenging of aero-sols and their chemical species by rain.Atmospheric Environ-ment, 2003, 37(18):2477-2484. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00162-6 [13] Zimmermann F, Lux H, Maenhaut W, et al.Areview of air pollution and atmospheric deposition dynamics in southern Saxony, Germany, Central Europe.Atmospheric Environ-ment, 2003, 37(5):671-691. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00829-4 [14] 林长城, 林详明, 邹燕, 等.福州气象条件与酸雨的关系研究.热带气象学报, 2005, 21(3):330-336. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200503013.htm [15] 董惠清, 黄海洪, 高安宁, 等.南宁市酸雨频率特征分析.气象科技, 2003, 31(2):101-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ200302006.htm [16] 吴贤笃, 施松微, 吴正可.温州市酸雨特征及气象条件分析.浙江气象, 2004, 25(4):20-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJQX200404005.htm [17] 陈德林, 古淑芳, 李洪珍.降水酸度与降水物理量关系的分析.气象科学研究院院刊, 1989, 4(1):82-87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX198901011.htm [18] 杨复沫, 贺克斌, 雷宇, 等.2001 2003年间北京大气降水的化学特征.中国环境科学, 2004, 25(5):538-541. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200405007.htm [19] 汤洁, 徐晓斌, 巴金, 等.近年来京津地区酸雨形势变化的特点分析---气溶胶影响的探讨.中国科学院研究生院学报, 2007, 24(5):667-673. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB200705018.htm [20] Wang Y, Zhuang G S, Tang A, et al.The ion chemistry and the source of PM2.5 aerosol in Beijing.Atmospheric Envi-ronment, 2005, 39(21):3771-3784. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.013 [21] Yao Xiaohong, Chak K C, Ming Fang, et al.The water-sol-uble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing, China.Atmoshpheric Environment, 2002, 36(26):4223-4234. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00342-4 [22] 徐敬, 丁国安, 严鹏, 等.北京地区PM2.5的成分特征及来源分析.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5):645-654. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070599&flag=1 [23] 中国气象局.酸雨观测业务规范.北京:气象出版社, 2005:24-25. [24] 程新金, 黄美元.降水化学特性的一种分类分析方法.气候与环境研究, 1998, 3(1):82-88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH801.007.htm [25] 王文兴, 张婉华, 石泉, 等.影响我国降水酸性因素的研究.中国环境科学, 1993, 13(6):401-406. http://www.baidu.com/link?url=0Sto3RWciGvCd5Wh4s90nK7xNJOvq0yqverexN8kOFqWgiLsAU9j1d8G43YaLV3Cx-5NmN_IeC6n1RF6zLh3uuMOBC4IhHDRK5VVBNkksg0eAMjFHv54e6UtGyV64BlZhWQuSgEh4TWa1NRW7bNQKE8ZLUhX24Nnz11f0NR9dMUNMUUEKu4dEUbPaAW4OhsEMpy0A-JX-OiFlbChubM7UGVfbw08pjYBcpV2RqfABhBgDKL-iTNN-9hBbQDkD37bDI8hM7R1LLJFBmwhD2Tk-Ei9-BzltT0RBkH62ru3Qym_vjtijrnO7RhIj5A1kMw1jFm3pDcU4EdguzKQWhCFHUzPdXM220ekj-xoNoEdOivtnviOnMxY_OrHmkErHM55_dLAMJFKFo7B5Va1Rgq2l_&wd=&eqid=8cbe3fe900033ff500000005587de1f3 [26] 王玮, 王英, 苏红梅, 等.北京市沙尘暴天气大气气溶胶酸度和酸化缓冲能力.环境科学, 2001, 22(5):25-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200105005.htm [27] 王文兴.中国酸雨成因研究.中国环境科学, 1994, 14(5):323-329. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ405.001.htm [28] 张峥, 孟广礼.1988年两广地区春季酸雨观测和天气形势分析.北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 1992, 28(1):86-95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199201010.htm [29] 吴兑, 邓雪娇.环境气象学与特种气象学预报.北京:气象出版社, 2001:105-106. [30] 赵勇, 孙中党, 王飞, 等.郑州市大气酸性物质与降水酸性的相关性分析.环境科学研究, 2001, 14(6):20-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200106005.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: