平流层火山气溶胶时空传播规律及其气候效应
The Space-time Propagation Patterns of the Stratospheric Volcanic Aerosols and the Preliminary Analysis of Their Climate Effect
-
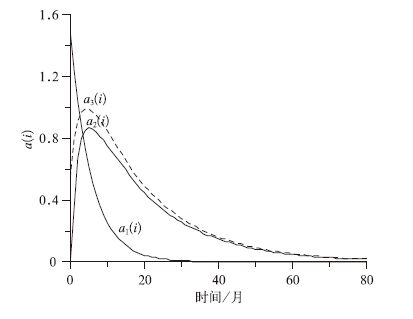
摘要: 根据平流层火山气溶胶传播规律研究,该文构建了反映火山喷发强度、平流层火山气溶胶相对浓度、火山气溶胶扩散速率和反映火山爆发地理位置并且按e指数规律衰减的火山活动指数 (VEI) 时空分布函数,进一步建立了北半球中高纬度、南北半球低纬度和南半球中高纬度3个1945—2008年逐月火山活动指数时间序列。根据3个逐月火山活动指数时间序列分别分析了北半球中高纬度、南北半球低纬度和南半球中高纬度火山活动对于相应纬度带地面气温的影响。研究表明:无论南北半球还是热带,火山活动强时地面气温下降,火山活动弱时地面气温上升,并且地面气温对于火山活动的响应明显滞后。Abstract: Based on the research of the propagation patterns of the stratospheric volcanic aerosols, the space time distribution function of Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) with the exponential decay is constructed which can reflect the volcano eruption intensity, the relative concentration, the propagation rate of the stratospheric volcanic aerosols and the volcano eruption location. Furthermore, time series of the volcanic activity indexes (1945—2008) every 3 months at middle and high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, the low latitudes of the Northern and Southern Hemisphere and the middle and high latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere are built up. Based on the time series of volcanic activity indexes, the influences of the volcano activity on the surface temperature at middle and high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, at low latitudes of the Northern and Southern Hemisphere and at middle and high latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere, are analyzed separately. The results indicate that either at the Northern and Southern hemisphere or at the tropical zone the ground layer air temperature decreases when the volcanic activity is strong, while it increases when the volcanic activity is weak. At the same time, the variations of the ground layer air temperature lag behind those of the volcanic activity.
-
Key words:
- volcanic activity;
- climate effects;
- VEI;
- time series;
- volcanic aerosols
-
表 1 1955—1958年北半球中高纬度VEI时间序列与北半球中纬度地面气温距平Δt
Table 1 The VEI time series in Northern Hemisphere in middle and high latitudes of 1955—1958 and the ground surface temperature anomaly in the middle latitudes of Northern Hemisphere

-
[1] 王绍武.全球温度变暖的检测及成因分析.应用气象学报,1993,4(2):226-233. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX199302013.htm [2] 石广玉,许黎.大气臭氧与气溶胶垂直分布的高空气球探测.大气科学,1996,20(4):401-407. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK604.002.htm [3] Mccormick M P,Thomason L W,Trepte C R.Atmospheric effects of the Mt Pinatubo eruption.Nature,1995,373:399-404. doi: 10.1038/373399a0 [4] 曲维政,赵进平,赵雪,等.火山活动对南半球平流层大气温度异常变化的影响.地学前缘,2004,11(2):144-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200402040.htm [5] 曲维政,黄菲,赵进平,等.火山活动对北半球平流层气候异常变化的影响.地球物理学进展,2006,21(2):650-659. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200602048.htm [6] Qu Weizheng,Bai Yan,Huang Fei,et al.Effect of volcanic activity on the temperature in the tropical upper atmosphere.Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2006,49(4):408-416. [7] Bluth G J,Doiron S D,Schnetzler C.et al.Global tracking of the SO2,clouds from the June 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruptions.Geophys Res Lett,1992,19(2):151-154. doi: 10.1029/91GL02792 [8] Krueger A J.Vocanic sulfur dioxide measurements from the total ozone mapping spectrometer instruments.Geophys Res Lett,1995,100,D7:14057-14076. [9] Cole-Dai J,Mosley-Thompson E,Thompson L G.Quantifying the Pinatubo volcanic in south polarsnow.Geophys Res Lett,1997,24(21):2679-2682. doi: 10.1029/97GL02734 [10] Deshler T,Hofmann D J,Johnson B J,et al.Balloonborne measurements of the Pinatubo aerosol size distribution and volatility at Laramie,Wyoming during the summer of 1991.Geophy Res Lett,1992,19(2):199-202. doi: 10.1029/91GL02787 [11] Hmelevtsov S S.Aerosol and modern climate change.Meteorology and Hydrology,1987,11:59-63. [12] Xu Qun.The assessment of volcanic dust veil index of northern temperate zone in the recent 100 years.Acta Geophysica Sinica,1985,28(6):558-568. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX198506001.htm [13] Lamoureux S F,England J H,Sharp M J,et al.A varve record of increased Little Ice Age rainfall associated with volcanic activity,Arctic Archipelabo,Canada.The Holocene,2001,11:243-249. doi: 10.1191/095968301668776315 [14] Zhang Chengyuan,Xi Daoying,Liu Xiaoyan,et al.A theoretical model for diffusion of volcanic eruptive sediment.Journal of Natural Disasters,2003,12(1):109-107. [15] Lwasaka Y,Shibata T.Lidar measuremcnts at Alaska(1991-1994)-Pinatubo volcanic effect on stratospheric aerosol layer.The Review of Laser Engineering,1995,23(2):166-170. doi: 10.2184/lsj.23.166 [16] Lambert R J,Scblesinger M E,Hammitt J K.The impact of potential abrupt climate changes on nearterm policy choices.Clim Change,1994,26:351-376. doi: 10.1007/BF01094402 [17] 胡荣明,石广玉.平流层气溶胶的辐射强迫及其气候响应的水平二维分析.大气科学,1998,22(1):18-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK801.002.htm [18] 徐晓斌,刘希文,林伟立.输送对区域本底站痕量气体浓度的影响.应用气象学报,2009,20(6):656-664. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090602&flag=1 [19] 胡婷,孙照渤,张海东.我国380 nm波长气溶胶光学厚度分布特征和演变趋势.应用气象学报,2008,19(5):513-520. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080501&flag=1 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: