珠江三角洲区域大气输送和扩散的季节特征
The Seasonal Characteristics of Regional Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion over the Pearl River Delta
-
摘要: 根据1985—2004年NCEP/NCAR再分析资料,采用HYSPLIT扩散模式和虚拟源方法,模拟分析了珠江三角洲大气污染物的空间和时间分布状况,初步讨论了珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散的季节特征,及其长期变化趋势。结果表明:珠江三角洲大气的输送和扩散有明显的季节变化特征,春、夏季大气污染物汇聚区位于珠江三角洲的西北侧,秋、冬季位于偏西侧;春、夏季的汇聚区明显强于秋、冬季。春、夏季大气分别向珠江三角洲西北和偏北方向的山区输送和扩散,而秋、冬季则沿着较为平坦的粤西海岸,向西南偏西方向输送和扩散。秋、冬季大气污染物的滞留时间明显比春、夏季短。1985—2004年大气输送和扩散能力存在年际差异,其中以2004年的输送和扩散能力最弱、1996年最强。Abstract: After being emitted from the sources, air pollutants experience a series of atmospheric physical and chemical processes before reaching the receptor, in which the core process is the atmospheric transport, diffusion process and the clearance changes accompanied with them. Understanding the climatic background of atmospheric transport and diffusion of the Pearl River Delta would be helpful to determine the area affected by air pollutants, the regularity of air pollutants input, output and detention over this area, providing scientific basis for air pollution prediction, control and management. Based on the meteorological field of wind, temperature, humidity, geopotential height and precipitation from the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis for the period of 1985—2004, the HYSPLIT dispersion model and setting virtual air pollution sources approach are adopted to simulate the distribution of air pollutant, dispersive path and detention time over the Pearl River Delta, with full consideration of wet and dry removal processes. The seasonal characteristics and long term trends of atmospheric transport and diffusion process over this region are examined, and the main results are shown as follows. The significant differences of the distribution, diffusive paths and detention time of virtual air pollutants among four seasons suggest that there are remarkable seasonal variations of atmospheric transport and diffusion processes over the Pearl River Delta. In spring and summer, the air pollutant convergence zone is located at northwest side of the Pearl River Delta, while in autumn and winter it lies on the northwest side of the Pearl River Delta. Among four seasons, the convergence zone in summer is the strongest, followed by spring, autumn and winter. In spring and summer, the air pollutants are transported and dispersed to the mountainous area of the northwest and north side of the Pearl River Delta, respectively, while in autumn and winter, those are transported and dispersed along the relatively flat coast of western Guangdong to the west southwest. In autumn and winter, the atmospheric transport and diffusion rates are significantly higher than those in spring and summer. Pollutants stay over the Pearl River Delta for longer than 24 hours for 66.7% and 75.3% of all the air pollution events in spring and summer, respectively, while in autumn and winter, there are only 22.1% and 30.4%. The terrain effect is one of the possible factors that responsible for the weaker atmospheric transport and diffusion in spring and summer. For the period of 1985—2004, atmospheric transport and diffusion ability are weakest in 2004 and strongest in 1996 with significant annual differences, which may be caused by the variation of atmospheric systems.
-
引言
珠江三角洲是我国经济和工业发展最快的地区之一,自改革开放以来平均经济增长速度高达16.8%/a。2002年在占全国0.4%的国土面积上聚集了全国3%的人口,创造了占全国近9%的国内生产总值,珠江三角洲已成为我国最大的工业制造区、繁荣的都市群之一。但经济的高速发展必然要消耗大量能源,不可避免地排放出大量的大气污染物。大气污染物不仅是导致大气能见度下降、影响人类健康的直接因素[1-2],同时也是改变地气系统能量收支,导致气候变化和极端天气气候事件增多的重要原因[3-4]。
大气污染物自污染源排放后,历经各种大气过程而到达接受体,其中的核心过程是大气输送和扩散过程及其在这一过程中发生的迁移和清除变化[5]。大气输送和扩散过程中的稀释扩散与输送率的时空变化很大、支配因素复杂,不仅受到不同尺度大气系统的作用[6-7],还受到下垫面性质、地形及建筑物等下垫面状况的影响。大气污染物既可长距离输送,对远离排放源的地区造成影响[8-9],也可能形成污染物的汇聚,造成局地污染[10]。珠江三角洲位于我国华南沿海,是热带季风活动最典型地区。冬季为冬季风控制期,多受弱变性冷高压脊、静止锋、低压槽等天气系统控制;夏季为西南季风盛行期,高空由东风稳定控制,西北太平洋和南海多热带气旋活动[11]。春、秋季分别为冬-夏、夏-冬的过渡季节,控制天气系统的强弱、配置更为复杂。造成珠江三角洲大气严重污染的天气背景既有冷高压型、脊后槽前型、低压型和暖高压型等陆地天气型,也包括热带气旋等海上天气系统[12]。珠江三角洲下垫面条件复杂,北部有南岭余脉构成的粤北山地,海拔高度最高近2000m;东西两侧有高低起伏的丘陵山地,海拔多在1000 m以下。珠江三角洲一方面受来自南海暖湿气流和来自北方跨越南岭干冷气流的季节性影响,当大范围系统风较弱时,还受山谷风、城市热岛环流和海陆风等多种局地环流的复杂影响[13]。随着珠江三角洲城市化的发展,也使城市间的大气污染物相互影响和作用复杂化[14-15]。
认识大气输送和扩散的背景条件,有助于确定污染源的可能影响地区,以及污染物的区域输入、输出和滞留规律等。本文根据NCEP/NCAR再分析的风、温、湿、位势高度和降水等气象要素场资料,通过设置虚拟大气污染源,模拟分析了珠江三角洲大气污染物的水平分布区域、扩散路径以及滞留时间等,讨论了珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散过程的季节变化特征及其长期趋势。主要目的是通过模拟分析,认识和理解珠江三角洲大气输送及扩散的气候背景条件,为预测、控制和治理珠江三角洲大气污染提供科学依据。
1. 方法与资料
1.1 模式简介
HYSPLIT是由美国海洋大气局空气资源研究所 (NOAA ARL) 开发的一种拉格朗日和欧拉混合型的污染扩散模式系统[16]。模式采用地形σ坐标,平流和扩散计算采用拉格朗日方法,浓度计算采用欧拉方法,模式过程包括:平流输送、湍流扩散、干湿沉降和化学转化等。本研究考虑了大气中的输送、扩散以及干湿沉降过程,但不包括化学转化过程。本文采用HYSPLIT污染扩散模式系统模拟计算大气污染物的空间和时间分布特征。以下对模式及参数设置做简单介绍,详情可参见文献[16]。
1.1.1 平流输送
HYSPLIT平流计算采用轨迹计算方法,通过计算粒子的移动轨迹,确定粒子的空间位置。由于气象场经过线性插值处理,高阶计算方法并不能得到更高的精度[17]。本文中粒子的空间位置计算,采用了简化计算方法:

(1) 
(2) 其中,P(t) 为初始位置,V(P,t) 为P(t) 点的水平风矢量;P′(t+ △th) 为第1猜值点位置,V(P′,t+ △th) 为P′(t+ △th) 点上的内插水平风矢量;th为可变时间步长。
1.1.2 湍流扩散
湍流扩散过程通过在平均流场上迭加一湍流分量的贡献,计算粒子的湍流扩散过程:

(3) 其中,U′(t+ △t)△t和W′(t+ △t)△t分别为代表水平和垂直方向上的湍流风速分量。湍流扩散的计算比较繁杂,文献[16]给出了具体方法。
1.1.3 干、湿沉降
大气污染物的干、湿沉降采用式 (4) 计算:

(4) 其中,m为污染物质量,βdry为干沉降系数,βinc和βbel分别为粒子云内清除率和云下清除率。干沉降系数βdry=Vd/Zp, Zp表示贴地层的厚度;Vd为干沉降速率,采用VanderHoven的方法计算[18]。βinc和βbel采用Hicks的参数化方法计算[19]。
1.2 虚拟源的设定与计算
本文的主要目的是通过模拟污染物在大气驱动下的空间和时间分布特征,考察珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散过程,并非分析特定污染物烟团或烟羽的输送、扩散过程。因此,采用了设置虚拟大气污染源的方法进行模拟研究。虚拟源的设置和模拟计算过程如下:在珠江三角洲中心区设定16个面积为0.25°×0.25°的均匀面源 (图 1),每个面源每小时释放出100个粒子,连续释放20年。逐一计算粒子自面源排放后的空间位移过程,并逐小时记录其空间位置。
污染物的浓度计算采用PIC (particleincell) 方法,浓度场的网格结构独立于气象场。浓度网格以21.73°N,112.67°E为中心,水平范围取20°×20°,网格距为0.25°,垂直范围为10~10000m。若粒子被输送或扩散到模式范围以外,或超出10000m的高度限制,或发生干、湿沉降沉降将不再考虑。最后,根据粒子空间位置记录,逐时统计各浓度网格中的粒子数,计算大气污染物的浓度[20-21]。由于气象场垂直坐标的原因,本文以大气污染物的水平分布状态 (柱浓度) 为主要分析对象。
本文中,每个粒子代表的污染物质量Q取值为1kg, 即珠江三角洲区域大气污染物的源强设定为16×102kg·h-1。柱状网格中污染物的平均浓度为

(5) 式 (5) 中,C为污染物的平均浓度,单位:mg·m-3;N(t) 为每小时进入柱状网格的粒子数;Ts为统计的时间长度,V为柱状网格的体积。
1.3 气象场资料
本研究以1985-2004年水平网格2.5°×2.5°、时间间隔为6h的NCEP/NCAR再分析资料[22]作为模式的气象场。采用的要素包括:1000~10hPa17层的气温、位势高度、经向和纬向风和12层的垂直速度以及地面降水场等。与其他再分析资料集相比,NCEP/NCAR再分析资料有以下优点:输入的原始资料包括:全球探空资料、COADS全球海面资料、飞机资料、地面资料、卫星探测资料、微波探测成像的地面风资料 (SSM/I) 等一系列的探测资料,具有较好的客观性和准确性;采用了全球统一的再分析系统和统一的质量控制措施,方便不同地区之间的对比;最重要的是其可获取性,以及较好的时间和空间覆盖率。目前,NCEP/NCAR再分析资料广泛用于天气、气候诊断分析,并作为初始场、边界条件资料用于天气气候模拟和预测研究。
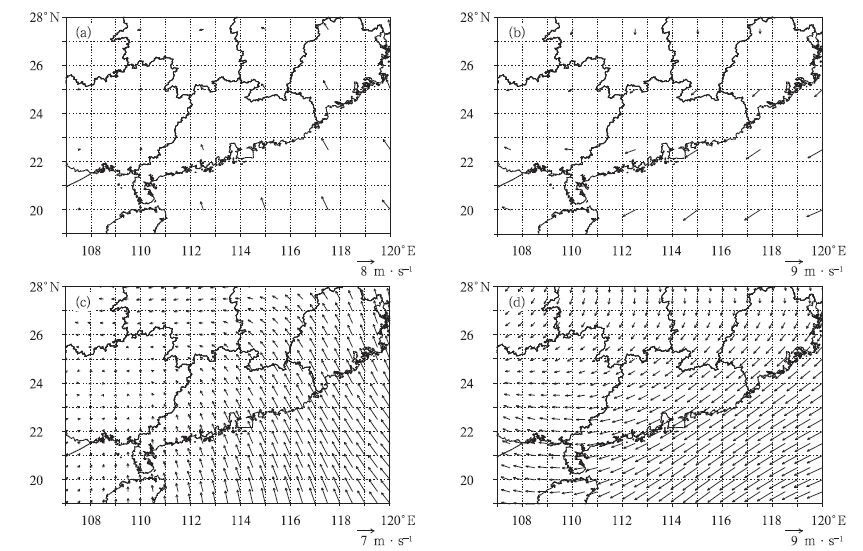
由于NCEP/NCAR2.5°×2.5°再分析资料的网格较粗,气象场需要在时间和空间上进行内插处理,以获取计算网格上的气象要素值。在本研究中,采用了双线性内插方法进行水平插值,即认为细网格上的要素值不仅在x轴方向呈线性变化,同时在y轴方向上也呈线性变化。为检验资料内插处理的合理性,选取2004年1年的粗网格资料与经过内插处理的细网格资料进行对比分析,发现细网格风场也能较好地反映该区域大气运动特征。图 2a,2b分别给出夏季、冬季各1个时次的1000hPa粗网格水平风场;图 2c,2d为粗网格经过双线性内插处理后的0.5°×0.5°细网格风场。对比图 2a,2b与图 2c,2d可知,在夏季和冬季典型的盛行风条件下,经内插处理后的风场在流场特征上与粗网格一致。近年来,一些研究也表明,经线性内插处理后的粗网格再分析资料,能够很好地反映区域大气的输送和扩散特征[23-25]。
![]() 图 2 NCEP/NCAR再分析资料的2.5°×2.5°水平风场与经过线性内插后的0.5°×0.5°水平风场(a) NCEP/NCAR夏季水平风场,(b) NCEP/NCAR冬季水平风场,(c) 经内插处理后的夏季水平风场,(d) 经内插处理后的冬季水平风场Figure 2. The original 2.5°X2.5° horizontal wind field of NCEP/NCARreanalysis and the linear-interpolated 0.5°×0.5° horizontal wind field(a) the original wind field for summer, (b) the original wind field forwinter, (c) the liner-interpolated wind field for summer, (d) the linear-interpolated wind field for winter
图 2 NCEP/NCAR再分析资料的2.5°×2.5°水平风场与经过线性内插后的0.5°×0.5°水平风场(a) NCEP/NCAR夏季水平风场,(b) NCEP/NCAR冬季水平风场,(c) 经内插处理后的夏季水平风场,(d) 经内插处理后的冬季水平风场Figure 2. The original 2.5°X2.5° horizontal wind field of NCEP/NCARreanalysis and the linear-interpolated 0.5°×0.5° horizontal wind field(a) the original wind field for summer, (b) the original wind field forwinter, (c) the liner-interpolated wind field for summer, (d) the linear-interpolated wind field for winter在本研究中,气象场最大的缺陷是NCEP/NCAR再分析资料在垂直方向上采用了气压坐标,这在下垫面条件较为复杂时,有可能对低层大气污染物的垂直分布模拟结果造成一定影响。由于这一原因,本文只对大气污染物的柱浓度进行了分析。
2. 主要结果
2.1 大气输送和扩散汇聚区
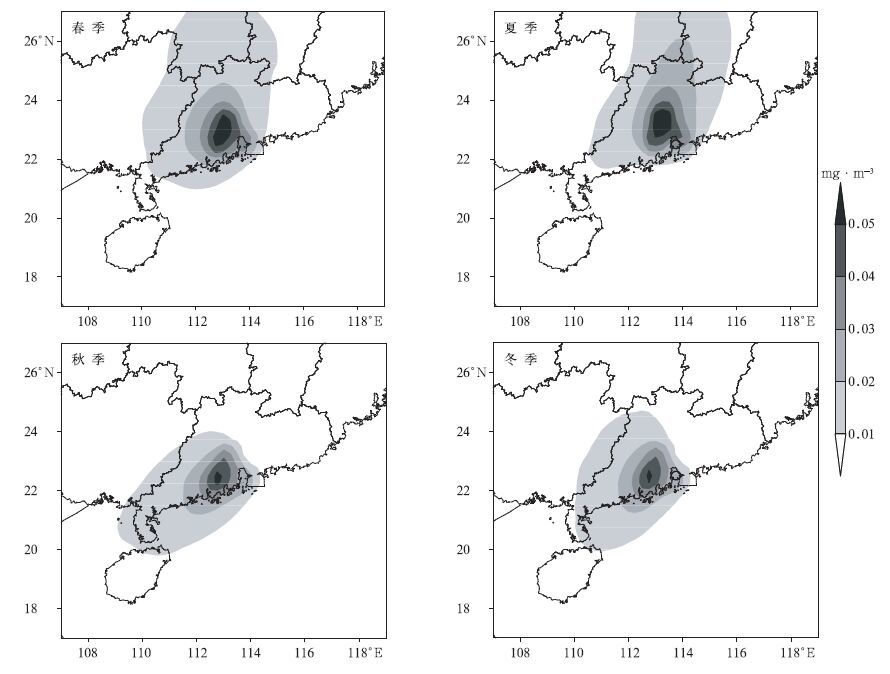
在大气输送和扩散作用下,大气污染物处于持续运动过程中,柱状网格中代表污染物浓度的粒子数也处于一种动态平均状态。根据逐小时各柱状网格中记录的粒子数,按春季 (3-5月)、夏季 (6-8月)、秋季 (9-11月) 和冬季 (12月-次年2月)4个季节,分别统计模式范围内1985-2004年20年的柱浓度平均值 (图 3)。
由图 3可见,在大气输送和扩散过程的作用下,4个季节的浓度分布状态有明显的差异。首先,由4个季节的柱浓度分布来看:春季柱浓度大值区主要分布在珠江三角洲的西北侧,中心位于佛山、肇庆和清远地区;夏季的浓度大值区分布与春季基本一致。而秋、冬两季的柱浓度大值区分布在珠江三角洲西侧,中心位于江门和阳江地区。其次,对比4个季节的柱浓度值大小也可知,春、夏季的大气污染物最为集中,柱浓度值明显要比秋、冬季的大得多。其中,以夏季的浓度值最大,春季次之,秋季和冬季最小。
珠江三角洲柱浓度的模拟结果表明:4个季节大气输送和扩散过程可导致明显的汇聚区,春、夏季汇聚区位于珠江三角洲西北侧的佛山、肇庆和清远地区,而秋、冬季位于西侧的江门和阳江地区;大气输送和扩散能力,以夏季最弱,春季稍强,秋季和冬季最强。这一结果似乎与珠江三角洲重污染事件多出现在秋、冬季的事实不符[26-27]。这里需要强调的是:上述模拟结果是大气污染物的柱浓度,而近地面层的重污染事件还与混合层厚度等条件有关;另外,上述模拟结果为大气污染物的长期平均值,与小概率的重污染事件没有直接关系。模拟结果与观测事实并不矛盾。
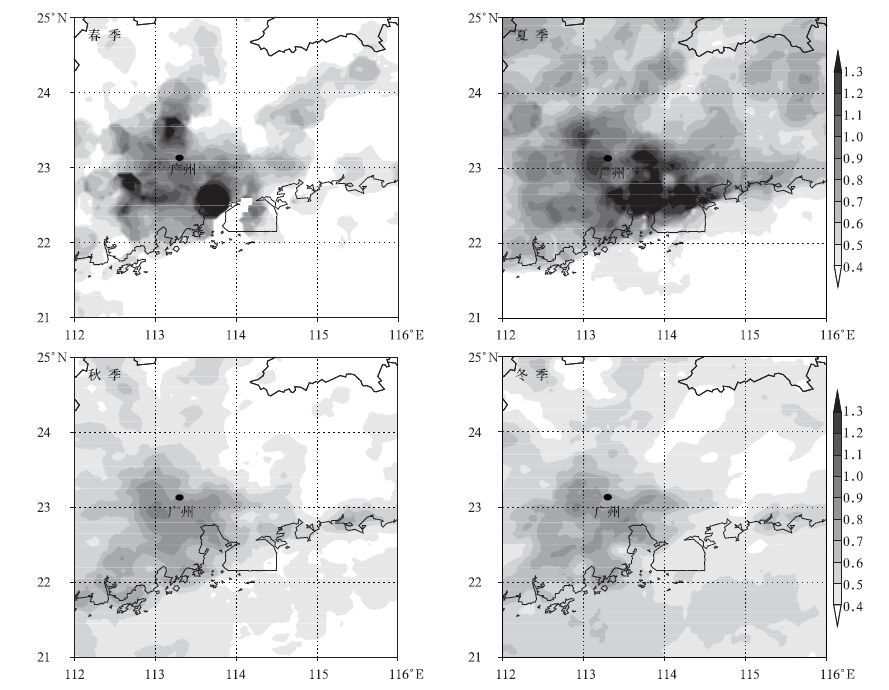
由第1章的虚拟污染源设置和资料处理可知,本研究在污染源的处理上采用了对称分布的均匀面源 (图 1);而且水平风场也能较好地反映该区域的大气流场特征 (图 2)。显然,污染源分布和风场误差并非导致污染物分布出现季节性差异的主要原因。图 4给出了2004年珠江三角洲EOS MODIS气溶胶光学厚度的季节分布状况。对比图 3和图 4可知,模拟计算的珠江三角洲大气污染物平均柱浓度值,无论是在水平分布形态上,还是在季节变化上都与MODIS气溶胶光学厚度基本一致。另外,珠江三角洲地面能见度的观测结果也可验证模拟计算结果的可靠性。能见度长期观测资料显示,在盛行风作用下,珠江三角洲东、西两侧的能见度具有明显的东高西低分布特征,东侧惠阳地区的能见度值远高于西侧肇庆、江门地区[14],这也与柱浓度高值区主要分布在珠江三角洲西侧的特征一致。由此可见,模拟计算的大气污染物季节分布特征基本反映了在特殊的气候背景和地理环境下,珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散所具有的汇聚特性。
一些研究结果认为,导致珠江三角洲春、夏季大气气溶胶光学厚度较秋、冬季偏大的原因,可能与春、夏季偏南风活跃、来自海上的海盐粒子和水汽增多有关[28-29]。本文模拟结果表明:除了海盐粒子和水汽含量增加等因素可导致气溶胶粒子散射系数增大外,大气输送和扩散过程也是造成珠江三角洲气溶胶光学厚度变化的重要因素之一。
2.2 大气输送和扩散的路径
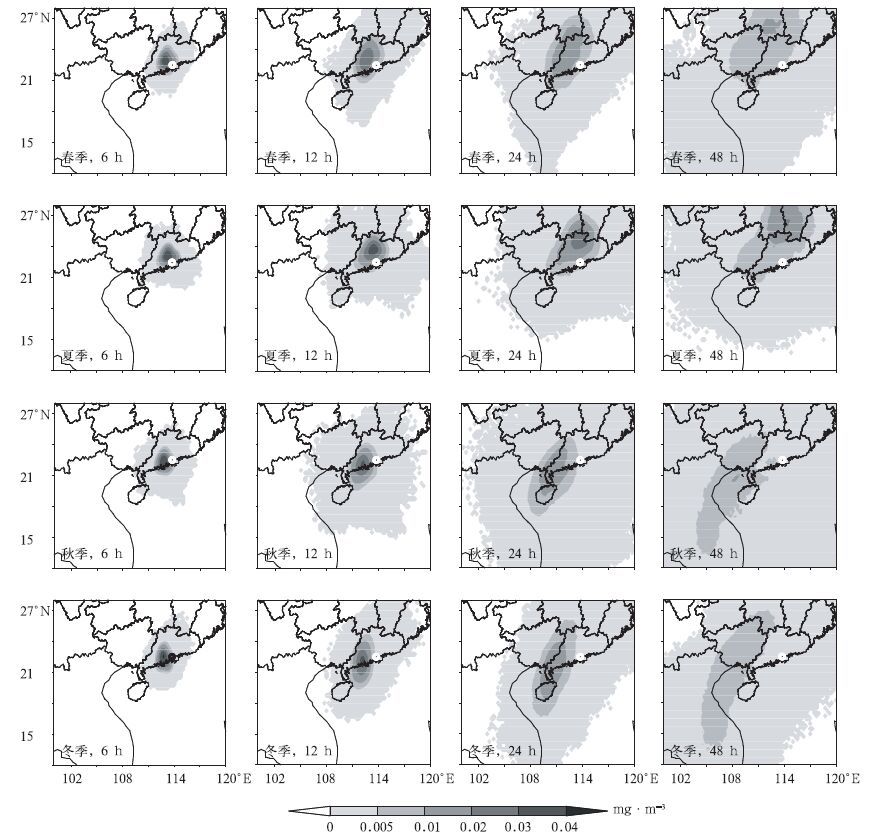
上述虚拟大气污染物的柱浓度平均结果,只能反映珠江三角洲不同季节的大气污染物静态分布特征,还无法了解其动态变化过程,及其对周边地区可能造成的影响。本文按4个季节,分别统计了虚拟大气污染物排放6h, 12h, 24h和48h后的平均柱浓度 (图 5),进一步分析大气的输送和扩散路径。
由图 5可见,春季大气污染物主要向西北方向输送和扩散。虚拟污染物排放6h后,浓度中心移到珠江三角洲的西北侧;12h后浓度中心继续向西北移动;24h后的浓度大值区移到广东与广西交界处;48h后浓度中心消失,影响范围扩大到广东、广西和湖南3省区。
与春季相比,夏季的大气污染物的移动方向略为偏北,主要向珠江三角洲的西北偏北方向输送和扩散。虚拟污染物排放6h后浓度中心位于佛山地区;12h后浓度中心移到粤北地区;24h后浓度中心到达广东与湖南交界处;48h后浓度大值区进入湖南境内,但仍可见明显的浓度中心区。
秋季大气污染物沿海岸线向西南西方向输送和扩散。虚拟污染物排放6h后的柱浓度中心位于珠江三角洲的西侧;12h后浓度中心移动到江门、阳江地区。24h后向南北方向扩散,中心区移动到粤西雷州半岛地区,48h后移到广西南部和北部湾地区。冬季大气污染物排放后的移动方向与秋季基本一致,均为沿海岸线向西南西方向移动,影响广东省西南沿海地区。
由大气输送和扩散路径可知:春季大气主要向西北方向输送和扩散,大气污染物的影响范围包括广东省西北部和广西东北部地区;夏季大气主要向偏北方向输送和扩散,大气污染物影响珠江三角洲以北的粤北地区和湖南南部地区。而秋、冬季大气基本上都是沿海岸线向西南偏西方向输送和扩散,影响广东省西部沿海地区以及广西、海南部分地区。一些研究认为,秋、冬季珠江三角洲地区是香港地区大气污染物的主要来源地[30-31]。显然,在气候意义上,珠江三角洲排放的大气污染物只在某些极特殊的风场条件下,才有可能影响中国香港地区;相反,中国香港地区排放的大气污染物,一年四季都对珠江三角洲有影响。
对比4个季节6h, 12h, 24h和48h的柱浓度大值区分布也可知:夏季大气向北的输送和扩散受到明显抑制,浓度大值区移动缓慢,并且48h后仍存在显著的浓度大值中心;春季浓度大值区向西北方向的移动速度比夏季略快,中心区的浓度值明显小于夏季;而秋、冬季浓度中心区迅速消散,移动速度明显比春、夏季加快。大气输送和扩散路径也表明,夏季大气的输送和扩散能力最弱,其次为春季;而秋季和冬季大气的输送和扩散能力明显加强。
2.3 大气输送和扩散的时间特征
虚拟大气污染物的空间分布和移动路径都表明,珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散能力存在显著的季节差异。本文在20年大气污染物空间分布的模拟基础上,设置以21.73°N,112.67°E为中心,范围为2°×2°的矩形区域 (图 1),通过模拟分析虚拟大气污染物在珠江三角洲区域内的停留时间,进一步考察大气输送和扩散过程的季节差异。本文以虚拟大气污染物由释放起,至其总数的90%或移出该区域,或已沉降到地面所需的时间,作为衡量大气输送和扩散能力的时间指标,称之为大气污染物的区域滞留时间。
图 6给出了按季节统计的滞留时间分布特征,由图 6可知,总体上大气污染物在珠江三角洲的滞留时间都不超过120h, 但4个季节的滞留时间差异明显。
由春、夏季的大气污染物滞留时间分布 (图 6a,6b) 可见,滞留时间分布在6~120h的广泛范围内,滞留时间小于24h的只占了小部分。夏季滞留时间的分布比春季更加均匀,长滞留时间的比例更大。由表 1可知,春、夏季滞留时间超过24h的分别占66.7%,75.3%;滞留时间为24~48h和48~72h所占比例接近;而滞留时间为72~120h所占比例,春季、夏季分别达到20.8%和31.9%。夏季大气污染物的滞留时间明显长于春季。由图 6c,6d可见,秋季和冬季滞留时间的峰值都出现在24h内。另外,由表 1也可知,大气污染物滞留时间超过24h的比例,秋季为22.1%,冬季也只有30.4%;冬季大气污染物的滞留时间略高于秋季。对比4个季节大气污染物的滞留时间,春、夏季大气污染物在珠江三角洲的滞留时间要比秋、冬季长得多。
表 1 4个季节大气污染物滞留时间的统计结果Table 1. The statistics of、air pollutant detention-time for four seasons
4个季节的大气污染物滞留时间表明:春、夏季不利于大气污染物的输送和扩散,大气污染物对珠江三角洲地区的影响时间更长;而秋、冬季大气的输送和扩散能力较强,大气污染物在该地区的滞留时间较短,对该地区的影响相对较小。这一结果与2.2节污染物空间分布的分析结果一致。
珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散能力的季节变化,除了与季风背景下的大尺度环流有关外,还可能受到下垫面条件的影响[32],尤其是珠江三角洲三面环山、一面临海,受喇叭口地形影响显著[12]。一方面山脉的动力效应会对气流产生阻挡作用,使得气流的速度与方向变得复杂,阻碍大气低层的输送和扩散;另一方面山脉的热力效应,也会形成山地特有的局地热力环流,降低大气的输送和扩散速度。秋、冬季大气污染物沿较为平坦的粤西海岸线向西南西方向输送,受地形影响较小;春、夏季的降水量虽然远大于秋、冬季,但大气污染物向西北和偏北方向输送和扩散,受珠江三角洲北部和西北部山脉的影响较大。地形的作用可能是春、夏季大气输送和扩散能力较弱的重要原因之一。
2.4 大气输送和扩散的长
在热带季风区,大气系统不仅有显著季节变化特征,同时也存在年际或年代际的准周期性振荡现象[33],大气系统的变化有可能对局地大气输送和扩散产生影响。根据模拟结果,本文统计了1985-2004年珠江三角洲以21.73°N,112.67°E为中心,2°×2°范围内 (见图 1) 的年平均柱浓度值,考察了珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散能力的长期变化趋势。
由图 7可见,1985-2004年珠江三角洲虚拟大气污染物浓度值,并未呈简单的上升或下降趋势,而是表现出一种不规则波动特征。其中,1985-1992年浓度值基本上呈上升趋势;1992年后浓度值下降,直到1996年达到最低;1996年后浓度又呈上升趋势,直到2004年达到最高。在20年中,1992和2004年的浓度值的水平最高,1996年最低。虚拟大气污染物浓度值长期变化趋势,反映出随着大气环流的演变、局地气象要素以及天气形势的变化,珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散的能力不仅有明显的季节变化特征,同时也存在年际变化。
大气输送和扩散能力的长期变化,对区域大气环境的变化趋势有重要影响。在区域大气污染物排放量维持不变的前提下,既有可能导致该区域空气质量在某一阶段转好,也有可能在某一阶段变差。珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散的长期变化趋势,还需要监测资料的进一步验证。
3. 结论
本文根据1985-2004年NCEP/NCAR再分析资料,在综合考虑了大气的平流输送、湍流扩散和干、湿沉降过程的基础上,采用HYSPLIT扩散模式和虚拟源方法模拟珠江三角洲大气污染物的空间和时间分布状况,对珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散过程的季节特征以及长期变化趋势做了初步分析。得到如下的初步结论:
1) 珠江三角洲不同季节的大气污染物水平分布、扩散路径以及滞留时间等都有明显的差异,大气输送和扩散过程表现出显著的季节变化特征。
2) 春、夏季大气污染物的汇聚区位于珠江三角洲西北侧的佛山、肇庆和清远地区;秋、冬季大气汇聚区位于珠江三角洲西侧的江门和阳江地区。其中,以夏季的汇聚最强,春季次之,秋季和冬季最弱。
3) 春季大气污染物主要向西北方向输送和扩散,大气污染物主要影响粤西北和广西东部地区;夏季向偏北方向输送和扩散,主要影响粤北和湖南南部地区;而秋、冬季大气污染物则沿着较为平坦的粤西海岸向西南西方向输送和扩散,影响广东省西部沿海的阳江、茂名和湛江等地区。
4) 春、夏季珠江三角洲的大气输送和扩散能力较弱,大气污染物在该区域内的滞留时间较长;而秋、冬季的大气输送和扩散能力相对较强,大气污染物的滞留时间较短。春、夏季大气污染物向西北或向北方向输送,喇叭口地形的作用可能是导致大气输送和扩散能力较弱的重要原因之一。
5) 从1985-2004年的大气污染物模拟结果来看,珠江三角洲大气输送和扩散能力存在明显的年际差异;其中以2004年的大气输送和扩散能力最弱、1996年最强。
致谢: 北京大学物理学院李成才教授提供了珠江三角洲EOS MODIS气溶胶光学厚度资料,特此鸣谢。 -
图 2 NCEP/NCAR再分析资料的2.5°×2.5°水平风场与经过线性内插后的0.5°×0.5°水平风场
(a) NCEP/NCAR夏季水平风场,(b) NCEP/NCAR冬季水平风场,(c) 经内插处理后的夏季水平风场,(d) 经内插处理后的冬季水平风场
Figure 2. The original 2.5°X2.5° horizontal wind field of NCEP/NCARreanalysis and the linear-interpolated 0.5°×0.5° horizontal wind field
(a) the original wind field for summer, (b) the original wind field forwinter, (c) the liner-interpolated wind field for summer, (d) the linear-interpolated wind field for winter
表 1 4个季节大气污染物滞留时间的统计结果
Table 1 The statistics of、air pollutant detention-time for four seasons

-
Malm W C. Characteristics and origins of haze in the continental United-States.Earth-Sci Rev, 1992, 33:1-36. DOI: 10.1016/0012-8252(92)90064-Z
Samet J M, Dominici F, Curriero F C, et al.Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 US Cities, 1987—1994.New Engl J Med, 2000, 343:1742-1749. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM200012143432401
Houghton J T, Ding Y, Griggs D J, et al.Climate Change2001:The Scientific Basis.Cambridage:Cambridge University Press, 2001.
Menon S, Hansen E J, Nazarenko L, et al.Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India.Science, 2002, 297:2250-2253. DOI: 10.1126/science.1075159
蒋维楣, 曹文俊, 蒋瑞宾.空气污染气象学教程.南京:南京大学出版社, 1993. 徐祥德.城市大气环境污染动力学理论问题.应用气象学报, 2002, 13 (增刊):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1000.htm 任阵海, 万本太, 虞统, 等.不同尺度大气系统对污染边界层的影响及其水平流场输送.环境科学研究, 2004, 17(1):7-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200401002.htm Peppler R A.ARM Southern Great Plains site observations of the smoke pall associated with the 1998 Central American fires.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2000, 81:2563-2591. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0477(2000)081<2563:ASGPSO>2.3.CO;2
Rogers C M, Bowman K P.Transport of smoke from the Central American fires of 1998.J Geophys Res, 2001, 106:28357-28368. DOI: 10.1029/2000JD000187
苏福庆, 任阵海, 高庆先, 等.北京及华北平原边界层大气中污染物的汇聚系统—边界层输送汇.环境科学研究, 2004, 17(1):21-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200401004.htm 钱光明.广东省气候业务技术手册.北京:气象出版社, 2008:281. 李琼, 李福娇, 叶燕翔, 等.珠江三角洲地区天气类型与污染潜势及污染浓度的关系.热带气象学报, 1999, 15(4):363-369. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX199904009.htm 范绍佳, 王安宇, 樊琦, 等.珠江三角洲大气边界层特征及其概念模型.中国环境科学, 2006, 26(增刊):4-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ2006S1001.htm 王淑兰, 张远航, 钟流举, 等.珠江三角洲城市间空气污染的相互影响.中国环境科学, 2005, 25(2):133-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200502002.htm 黄健, 吴兑, 黄敏辉, 等.1954-2004年珠江三角洲大气能见度变化趋势.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(1):61-70. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080111&flag=1 Draxler R.Description of the HYSPLIT-4 Modeling System.NOAA Technical Memo ERL ARL-224, 1997.
Draxler R.Trajectory optimization for balloon flight planning.Wea Forecasting, 1996, 11:111-114. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0434(1996)011<0111:TOFBFP>2.0.CO;2
Van der Hoven I.Deposition of Particles and Gases∥Slade D.Meteorology and Atomic Energy.TID-24190, NTIS, Spring-field, VA, 1968:1-445.
Hicks B B.Differences in Wet and Dry Particle Deposition Parameters Between North America and Europe∥Aerosols:Research, Risk Assessment, and Control Strategies, Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, MI, 1986:973-982.
Zannetti P.Air Pollution Modeling.New York:Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1990.
郭昱, 蔡旭晖, 刘辉志, 等.北京地区大气中尺度扩散模态和时间特征分析.北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 2002, 38(5):705-712. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200205021.htm Kalnay E and Coauthors.The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1996, 77:437-471. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
颜鹏, 黄健, DraxlerR.周边地区对北京地面SO2影响的初步研究.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(增刊):144-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2002S1015.htm Dexheimer D N, Bowman P K.Lagrangian methods for climatologic alanalysis of regional atmospheric transport.J Appl Meteor, 2004, 43:623-630. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043<0623:LMFCAO>2.0.CO;2
颜鹏, 黄健, DraxlerR.北京地区SO2污染的长期模拟及不同类型排放源影响的计算与评估.中国科学 (D辑), 2005, 35(增刊):167-176. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2005S1016.htm 刘爱君, 杜尧东, 王惠英.广州灰霾天气的气候特征分析.气象, 2004, 30(12):68-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200412015.htm 江肶, 曹春燕.2003年深圳市灰霾气候特征及影响因素.广东气象, 2004, 4:14-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDCX200404005.htm Li F, Ramanathan V.Winter to summer monsoon variation of aerosol optical depth over the tropical Indian Ocean.J Geophys Res, 2002, 107(D16), 4284, doi: 10.1029/2001JD000949.
李成才, 毛节泰, 陈介中, 等.利用MODIS研究中国东部地区气溶胶光学厚度的分布和季节变化特征.科学通报, 2003, 48(19):2094-2100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200319018.htm Chung K K, ChanJ C L, NgaC N, et al.Synoptic conditions associated with high carbon monoxide episodes at acoastal station in Hong Kong.Atmos Environ, 1999, 33:3087-3095. DOI: 10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00328-2
Lam K S, Chan L Y, Wang T, et al.Flow patterns influencing the seasonal behavior of surface ozone and carbon monoxide at a coastal site near Hong Kong.Atmos Environ, 2001, 35:3121-3135. DOI: 10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00559-8
陈燕, 蒋维楣, 郭文利, 等.珠江三角洲地区城市群发展对局地大气污染物扩散.环境科学学报, 2005, 25(5):700-710. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200505022.htm 戴念军, 谢安, 张勇.南海夏季风活动的年际和年代际特征.气候与环境研究, 2000, 5(4):363-374. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200004003.htm

 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: