毫米/亚毫米波探测大气温度和湿度的通道选择
Channel Selection of Millimeter/Submillimeter Wave for Temperature and Humidity Sounding
-
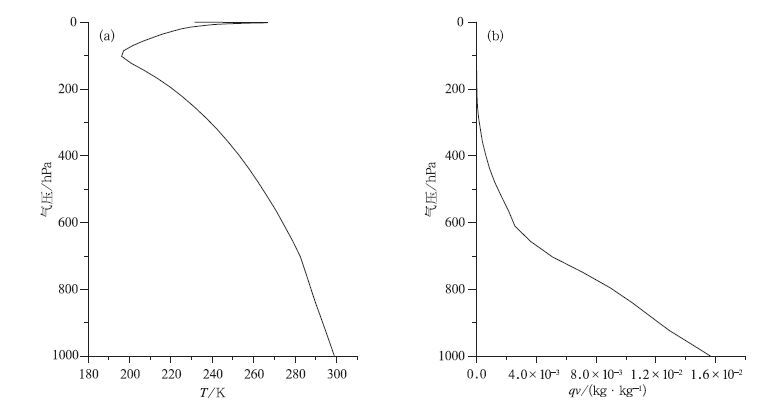
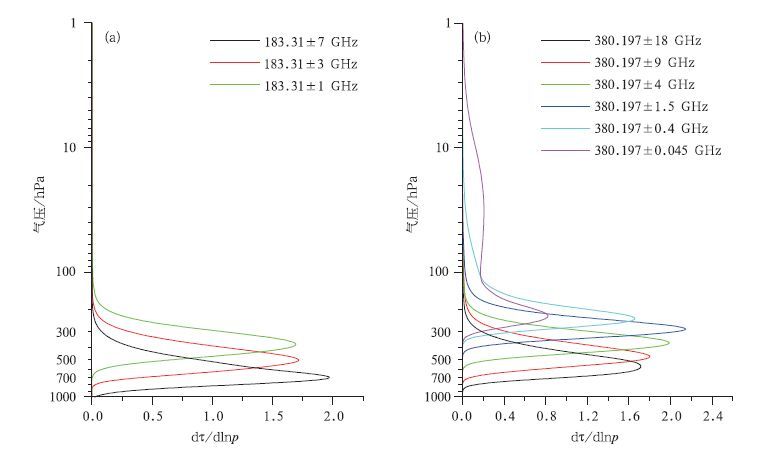
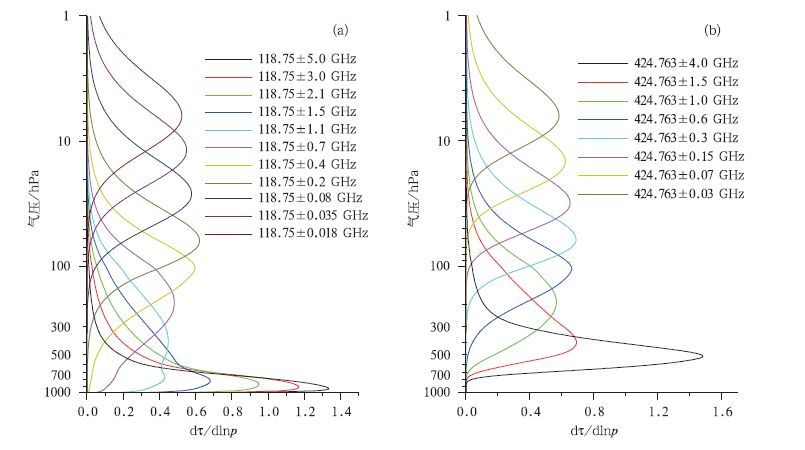
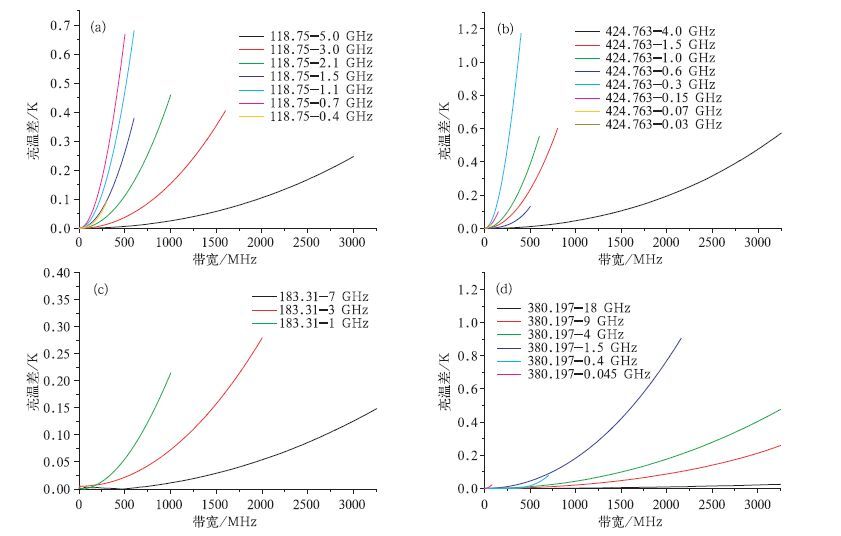
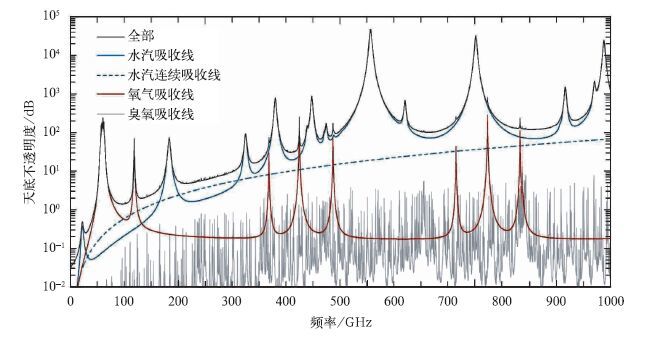
摘要: 利用热带大气温湿廓线计算了热带地区毫米/亚毫米波段微波大气透过率权重函数。对权重函数峰值高度的分析结果显示:对流层低层的大气温度可以选择118 GHz通道的远翼频率来探测,而对高层大气温度进行探测时,选择425 GHz通道的远翼频率较为合适;在大气湿度探测方面,183 GHz通道组合适合探测对流层中层大气的湿度,高层大气湿度探测应该首先考虑380 GHz通道组合来实现。根据大气温度探测通道和大气湿度探测通道的权重函数分布,鉴于国内现有遥感仪器的制造水平,建议选择118 GHz 3个通道与425 GHz 8个通道共11个大气温度探测通道和183 GHz 3个通道与380 GHz 5个通道共8个大气湿度探测通道作为未来静止轨道微波探测的候选通道。Abstract: The weather systems generated over tropical oceans are difficult to be detected by conventional observation, so the satellite remote sensing becomes the most effective way to monitor them. Geostationary Meteorological Satellites can observe the earth with high temporal resolution and is desirable for severe weather monitoring. But the spatial resolution for microwave instrument on board GEO could be poor because the satellites are in their high altitude orbits. To improve the spatial resolution, millimeter/submillimeter wave sounders are considered. Passive microwave sounding from geosynchronous orbit is first studied in the mid 1970s. During the early 1990s, it's suggested that the use of submillimeter wavelength water vapor and oxygen bands can significantly reduce the antenna size and costs, while retaining good spatial resolution. Based on this notion, a practical submillimeter wave geosynchronous microwave (GEM) sounder and imager is developed by the Geosynchronous Microwave Sounder Working Group (GMSWG). During the mid 1990s aperture synthesis is proposed to geostationary microwave imaging and sounding. The Geo STAR (Geostationary Synthetic Thinned Aperture Radiometer) and GAS (Geostationary Atmospheric Sounder) concept are put forward by America and Europe respectively based on this technique. In order to explore the potential applicability of millimeter/submillimeter sounders in tropical observation, weight functions for O2 and H2O absorption bands are calculated based on the atmosphere profiles of tropical region. The peak distribution of weight functions show that the far wings of 118 GHz can be chosen to measure the atmospheric temperature in lower troposphere, and for the temperature of the upper level, the far wings of 425 GHz are more suitable. In terms of humidity observation, the 183 GHz and 380 GHz channel combinations can be used for the middle and upper levels. Based on the analyses above, considering industry capability as well, eleven temperature channel combination including three channels around 118 GHz and eight channels around 425 GHz, eight humidity channel combination including three channels around 183 GHz and five channels around 380 GHz are recommended as the microwave observation channels for the geostationary orbit in the future. Furthermore, the differences of brightness temperature in different bandwidth range of O2 and H2O absorption bands are calculated using the temperature and water vapor profiles. Through this bandwidth selection test, retrieval results of temperature and humidity are statistically analyzed.It shows that in the temperature detection channel, 5.3 GHz or less and 4 GHz or less can be set as the bandwidth range for 118 GHz and 425 GHz respectively. As for the humidity detection channel, 183 GHz with a range of bandwidth 8.5 GHz or less and 380 GHz with a range of bandwidth 15 GHz avoiding 360.498 GHz is recommended, which is the oxygen absorption channel.
-
表 1 大气温度和大气湿度探测的通道设置表
Table 1 Channels selected for detecting temperature and humidity

-
[1] 张晓虎.卫星监测台风信息处理系统.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(4) 505-508. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030464&flag=1 [2] 方宗义, 覃丹宇.暴雨云团的卫星监测和研究进展.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5) :583-593. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200605100&flag=1 [3] 刘喆, 韩志刚, 赵增亮, 等.利用ATOVS反演产品分析"云娜"台风.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(4): 473477. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060481&flag=1 [4] 陈洪滨.利用髙频微波被动遥感探测大气.遥感技术与应用, 1999, 14(2):49-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGJS902.008.htm [5] Gasiewski A J, Barret J W, Bonanni PG, et al. Aircraft-based radiometric imaging of tropospheric temperature and precipitation using the 118. 75 GHz oxygen resonance. J Appl Meteor, 1997, 29:620-632. [6] Evans K F, Walter S J, Heymsfield A J, et al. Modeling of sub-millimeter passive remote sensing of cirrus cloud. J Appl Meleorol, 1998, 37: 184-205. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1998)037<0184:MOSPRS>2.0.CO;2 [7] Evans K F, Evans A H, Marshall B T, et al. The prospect for remote sensing of cirrus clouds with a sub-millimeter-wave spectrometer. J Appl Meteor, 1999, 38:514-525. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1999)038<0514:TPFRSO>2.0.CO;2 [8] Bizzarri B, Albin JG, David H S, et al Requirements and Perspectives for MW/Sub-mmsounding from Geostationary Satellite. EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, 2002:97-105. [9] Catherine P, Juan R P, William B R. Comparisons of the millimeter and submillimeter bands for atmospheric temperature and water vapor soundings for clear and cloudy skies. J Appl Meieorol, 2006, 45:1622-1633. [10] Buenos Aires. Finial Report. The Sixth Consultative Meetings on High-Level Policy on Satellite Matters, 2006. [11] Tsou J J, Smith W L, Rosenkranz P W, et al. Precipitation Study Using Millimeter-wave Temperature Sounding Channels. Specialist Meeting on Microwave Remote Sensing, 2001. [12] Klein M, Gasiewski AJ. The sensitivity of millimeter and submillimeter frequencies to atmospheric temperature and water vapor variations. J Geophys Res, 2000, 13: 17481-17511. [13] Pinoi S, Baordo F, Medaglia C M, et al. On the potential of sub-mm passive MW observations from geostationary satellites to retrieve heavy precipitation over the Mediterranean Area. Advances in Geosciences, 2006, 7 : 387-394. doi: 10.5194/adgeo-7-387-2006 [14] Meteorological Institute, University of Munich (MIM), LER-MA, et al. Simulation Study of Precipitating Clouds from Geostationary Orbits with Passive Microwaves Final Report 2005. [15] Weng F. A multi-layer discrete-ordinate method for vector radiative transfer in a vertically-inhomogeneous, emitting and scattering atmosphere—Theory.J Quant Radiat Transfer, 1992, 47:19-34 doi: 10.1016/0022-4073(92)90076-G [16] 刘长盛, 刘文保.大气辐射学 (第一版).南京:南京大学出版社, 1990. [17] 漆成莉, 刘辉, 马刚, 等.中国区域典型大气廓线样本库的一种选择方法.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1):70-75. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100109&flag=1 [18] Roger Saunders, Pascal Brunel.RTTOV-7-Technical Report. NWPSAF-MO-TR-009, 2002.http://www.metoffice.com/research/interproj/nwpsaf/rtm/. [19] Roger Saunders, Pascal Brunel.RTTOV-7-Users Guide.NW-PSAF-MO-TR-009, 2002.http://www.metoffice.com/re-search/interproj/nwpsaf/rtm/. [20] Roger Saunders, Pascal Brunel.RTTOV-7-Science and Validation Report.NWPSAF-MO-TR-009, 2002.http://www.metoffice.com/research/interproj/nwpsaf/rtm/. [21] 张培昌, 王振会.大气微波遥感基础 (第一版).北京:气象出版社, 1995. [22] 吴雪宝, 漆成莉, 刘辉. 风云三号卫星地面应用系统工程研发项目技术报告. 北京: 国家卫星气象中心, 2007. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: