基于水面实测光谱的太湖蓝藻卫星遥感研究
Satellite Remote Sensing of Cyanophyte Using Observed Spectral Measurements over the Taihu Lake
-
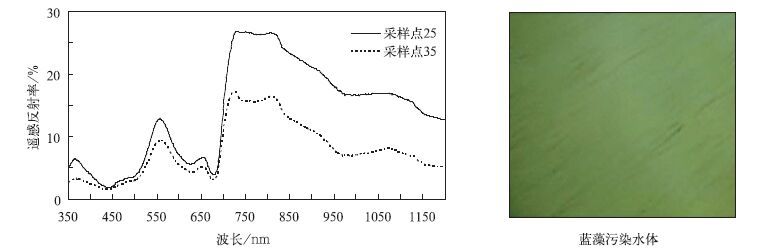
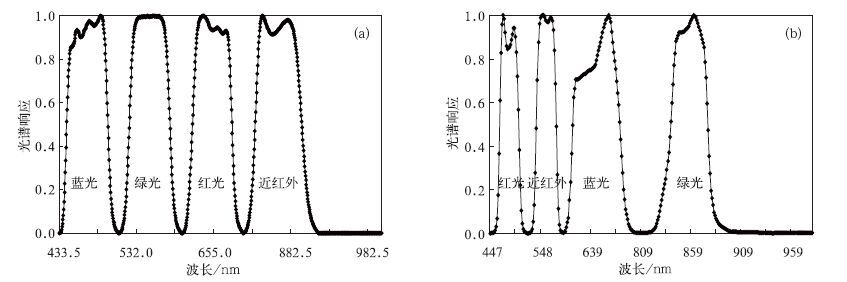
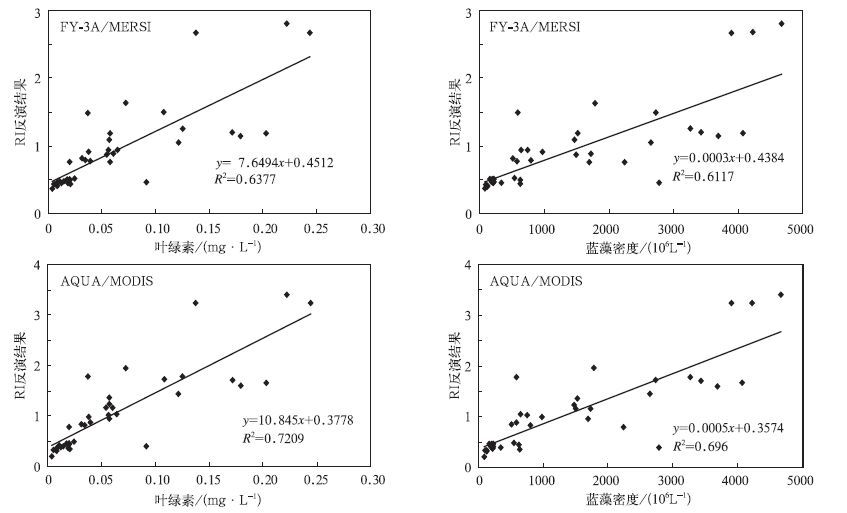
摘要: 水体叶绿素a含量和蓝藻密度是评价水质污染的主要参数,对监测水体蓝藻水华有重要意义。该文利用2008年11月10日和11日太湖水面实测光谱及FY 3A/MERSI,AQUA/MODIS卫星的波段响应函数,计算了卫星波段的水体表面等效反射率。水体实测光谱显示蓝藻污染提高了近红外波段的遥感反射率,在蓝光波段和绿光波段有明显的吸收谷和反射峰。根据这一原理,该文建立了近红外和红光波段的比值指数RI模型,成功反演了太湖水体叶绿素a含量(均方根误差分别为0.0174 mg·L-1和0.0188 mg·L-1)和蓝藻密度(均方根误差分别为247.21×106 L-1和275.64×106 L-1)。这一结果为分析太湖水面光学特性、水质污染状况提供了重要依据。
-
关键词:
- 遥感反射率;
- 蓝藻;
- FY 3A/MERSI;
- AQUA/MODIS
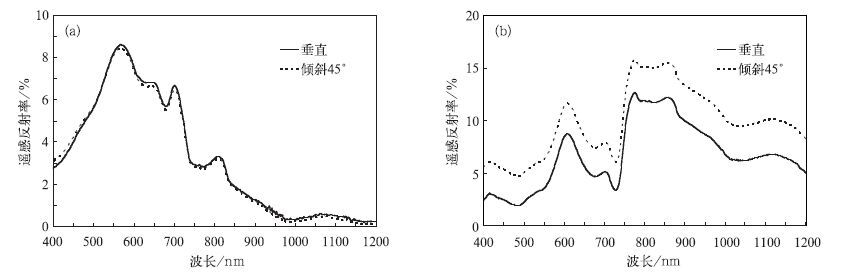
Abstract: The chlorophyll a and cyanobacterial density are important variables for the evaluation of water quality and thus important for red tide monitoring. An evaluation of spectral measurements is implemented for the estimation of chlorophyll a (Chl a) and cyanobacterial density in the Taihu Lake. There are 39 sample points over the Taihu Lake during the experiment from 10 to 12 November in 2008. For each sample point, measurements of spectral reflectance and water quality sampling are conducted. Observation shows that cyanobacterial affect water reflectance greatly, leading to an obvious absorption peak in the red while strong absorption in the blue and near infrared bands. Spectral responses for points with little cyanophyte are similar to that of water reflectance. However, for the cyanobacterial points, spectral responses show the similar trend of vegetation to some extent. Besides, comparison between the reflectance obtained at nadir and at 45° departure indicates that the existence of cyanophytes has great effects on the visible and near infrared regions. This is because the increase of heterogeneity in water will increase the energy that can be acquired by the sensor. To investigate the operational application feasibilities for satellite remote sensing of water quality, equivalent reflectance based on FY 3A/MESRI and AQUA/MODIS band settings is derived using the spectral response functions. Comparison analysis indicates that the equivalent reflectance calculated from FY 3A/MESRI band settings is consistent to that of the AQUA/MODIS. Larger variations are observed for the cyanobacterial water indicating different sensitivity of these bands in water quality evaluation. Furthermore, the Ration Index (RI) model is used for the evaluation of water quality and high determination coefficients (RMS of 0.0174 mg·L-1 and 0.0188 mg·L-1 for Chla; 247.21×106 L-1 and 275.64×106 L-1 for cyanobacterial density) are observed for chlorophyll a and cyanobacterial density. An important meaning lies in the linear regression for all correlations which indicates the sensitivity for high values of water samples. Generally, RI calculated from MODIS bands is more suitable for water quality assessment. A possible explanation is that the much fine spectral resolution of MODIS bands is more sensitive to chlorophyll signals. This result will be helpful for further evaluation of optical characteristics and water quality using FY 3A/MESRI observations.-
Key words:
- water reflectance;
- cyanophytes;
- FY 3A/MESRI;
- AQUA/MODIS
-
表 1 试验选择的水质参数及测量方法
Table 1 The water quality variables and the sampling methods

表 2 典型水体采样点信息
Table 2 Information of typical samples for clean and cyanophytes contaminations water

表 3 基于FY-3A/MERSI和AQUA/MODIS部分波段的等效反射率对比
Table 3 Comparison of equivalent reflectance with FY-3A/ME RSI and AQUA/MODIS standard band setings

-
[1] 马荣华, 孔维娟, 段洪涛, 等.基于MODIS影像估测太湖蓝藻暴发期藻蓝素含量.中国环境科学, 2009, 29(3):254-260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200903009.htm [2] 廖程浩, 刘雪华.MODIS数据水体识别指数的识别效果比较分析.国土资源遥感, 2008, 19(4):22-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200804006.htm [3] 李建国, 孙晓明, 康慧, 等.曹妃甸近海类水体光谱反射率与悬浮泥沙浓度相关性研究.国土资源遥感, 2009, 20(3):54-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200903015.htm [4] 李云亮, 张运.基于TM影像的太湖夏季悬浮物和叶绿a浓度反演.遥感信息, 2008, 6:22-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX200806007.htm [5] 孔维娟, 马荣华, 段洪涛, 等.太湖秋冬季蓝藻水华MODIS卫星遥感监测.遥感信息, 2009, 4:80-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX200904020.htm [6] 祝令亚, 王世新, 周艺, 等.应用MODIS影像估测太湖水体悬浮物浓度.水科学进展, 2007, 18(3):444-450. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ200703021.htm [7] 宋瑜, 宋晓东, 郭照冰, 等.利用MERIS产品数据反演太湖叶绿素a浓度研究.遥感信息, 2009, 4:19-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX200904007.htm [8] 孙德勇, 李云梅, 王桥, 等.基于实测高光谱的太湖水体悬浮物浓度遥感估算研究.红外与毫米波学报, 2009, 28(2):124-128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH200902011.htm [9] 周冠华, 李京, 杨一鹏, 等.基于半分析算法的太湖水质参数多光谱遥感反演.自然灾害学报, 2008, 17(6):142-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH200806031.htm [10] 张春桂, 曾银东, 张星, 等.海洋叶绿素a浓度反演及其在赤潮监测中的应用.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(6):821-831. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200706124&flag=1 [11] 叶晶, 李万彪, 严卫.利用MODIS数据反演多层云光学厚度和有效粒子半径.气象学报, 2009, 67(4):613-622. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200904011.htm [12] 张春桂, 蔡义勇, 张加春.MODIS遥感数据在我国台湾海峡海雾监测中的应用.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(1):8-16. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090102&flag=1 [13] 荀尚培, 翟武全, 范伟.MODIS巢湖水体叶绿素a浓度反演模型.应用气象学报, 2009, 20 (1):95-101. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090112&flag=1 [14] Moses W J, Gitelson A A, Beranikov S, et al. Satellite estimation of Chlorophyll-a concentration using the red and NIR bands of MERIS-the Azov Sea case study. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, doi:10. 1109/LGRS.2009.2026657 [15] Gitelson A A, Dallomo G, Moses W, et al A Simple semianalytical model for remote estimation of Chlorophyll-a in turbid waters : Validation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112: 3582-3593. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.04.015 [16] Dallolmo G, Gitelson A A. Effect of bio-optical parameter variability and uncertainties in reflectance measurements on the remote estimation of Chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters : Modeling results. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(15) 3577-3592. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.003577 [17] Dallolmo G, Gitelson A A, Runaquist C. Towards a unified approach for remote estimation of Chlorophyll-a in both terrestrial vegetation and turbid productive waters. Geophysical Research LeiUr, 2003, 30 (18): 1938, doi: 10. 1029/2003GL018065. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: