多作业管理方式在风能资源数值模拟中的应用
Application of Multi job Management Mode to Numerical Simulation for Wind Energy Resource
-
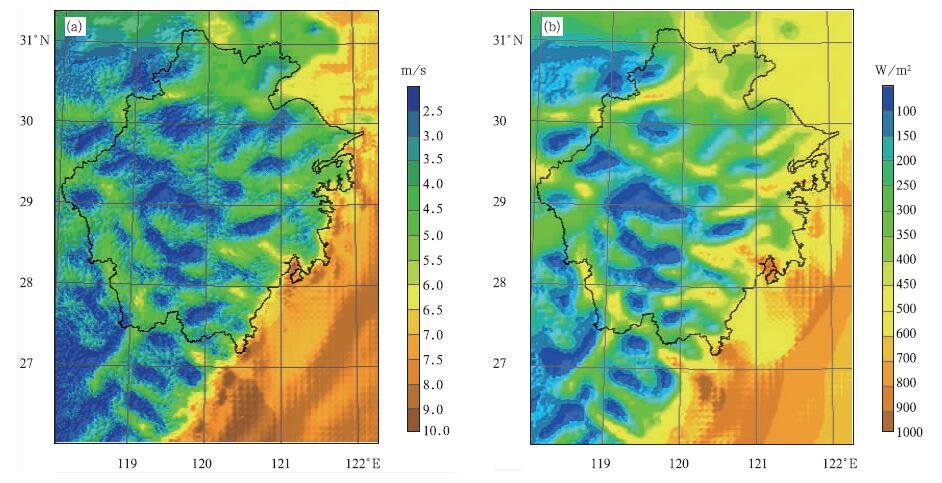
摘要: 通过对MM5和CALMET风能资源数值模拟耦合模式的计算流程分析,基于并行运算思想,设计了MM5和CALMET耦合模式模拟运算的多作业管理方式。在浙江省风能资源高分辨率数值模拟试验中,完成浙江区域1个月时间段的风能资源参数模拟运算,MM5和CALMET耦合模式在实施多作业管理方式前后,CALMET模式的运算时间由原来的1501.2 min缩短为149.5 min,运算时效提高了9倍;整个耦合模式的运算时间由原来的1709.9 min缩短为358.2 min,运算时效提高了4倍。数值模拟试验证实了多作业管理方式可在现有计算资源的基础上,大幅提高数值模式的运算时效,且随着数值模式模拟时间段的加长和模拟区域范围的扩大,多作业管理方式对数值模式运算功效的增强越加明显。
-
关键词:
- 风能资源;
- 数值模拟;
- MM5/CALMET;
- 并行运算
Abstract: Numerical simulation of regional wind energy resource requires high performance computing resource. High spatial/temporal resolution models need more running time due to the limit of computing power. So lots of efforts are devoted to improving calculation efficiency of numerical model. The coupled MM5/CALMET model is proved to be suitable for simulating wind energy resource, and it is also recommended by China Meteorological Administration as a numerical simulation model to estimate provincial wind energy resource. Therefore, interpreting the computational flow of MM5 and CALMET models, a multi job management mode is designed based on parallel calculation principle. The numerical simulation of wind energy resource in Zhejiang Province demonstrates that the multi job management mode can significantly improve calculation efficiency of the coupled MM5/CALMET model. In the numerical simulation experiments of monthly parameters which are related to wind energy resource assessment, the CALMET model without parallel calculation needs 1501.2 minutes, but it only costs 149.5 minutes when implementing the multi job management mode, increasing the calculation efficiency of the coupled MM5/CALMET model by 4 times. The multi job management mode shows the ability to further improve the calculation efficiency of the coupled MM5/CALMET model with its simulation area expanding and simulation period prolonging. -
表 1 MM5/CALMET耦合模式原运算方式与多作业管理方式耗时
Table 1 Time-cost of MM5/CALMET simulation by original calculation mode or multi-job management mode

-
[1] Frank HP, Landberg L. Modeling the wind climate of Ireland. Boundary-Layer MeleoroL, 1997, 85:359-378. doi: 10.1023/A:1000552601288 [2] Keith W A. Computational modeling for wind energy assess-ment. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96: 1571-1590. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2008.02.002 [3] 杨振斌, 薛桁, 王茂新.卫星遥感地理信息与数值模拟应用于风能资源综合评估新尝试.太阳能学报, 2003, 24(4): 536-539. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYLX200304020.htm [4] 邢旭煌, 朱蓉, 翟盘茂.海南省及其近海风能资源的高分辨率数值模拟.热带气象学报, 2009, 25(4):421-426. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200904005.htm [5] 穆海振, 徐家良, 柯晓新.高分辨率数值模式在风能资源评估中的应用初探.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(2):152-158. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060226&flag=1 [6] Dudhia J, James F B. A global version of the PSU-NCAR mesoscale model. Mon Wea Rev, 2002, 130(12): 2989-3007. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2002)130<2989:AGVOTP>2.0.CO;2 [7] Perez S, Jimenez P A, Navarro J. Using the MM5 Model for Wind Prediction in a Complex Terrain Site. European Wind Energy Conference & Exhibition EWEC, Madrid, 2003, 1: 1-7 [8] Pielke R A. A comprehensive meteorological modeling system—RAMS. Meieorol Aimos Phys, 1992, 49: 69-91. http://www.academia.edu/5920131/A_comprehensive_meteorological_modeling_system_RAMS [9] Coppin P A, Ayotte K A, Steggel N. Wind Resource Assessment in Australia—A Planners Guide. CSIRO: Wind Energy Research Unit, 2003: 49-70. [10] Yu W, Benott R, Girard C. Wind Energy Simulation Toolkit (WEST) : A wind mapping system for use by the wind-energy industry. Wind Energy, 2006, 1:15-33. [11] Buness F F, Heimann D, Sausen R. A statistical-dynamical downscaling procedure for global climate simulations. Therr Appl ClimaLol, 1995, 50:117-131. doi: 10.1007/BF00866111 [12] Helmut P F, Ole R, Niels G M. The Numerical Wind Atlas—the KAMM/WAsP Method. Denmark: Ris0 National Laboratory, 2001: 5-26. [13] 龚强, 袁国恩, 张云秋.MM5模式在风能资源普查中的应用试验.资源科学, 2006, 28(1):145-150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY200601023.htm [14] 朱蓉.风能资源数值模拟专项工作方案和实施计划.全国风能资源详查和评价工作研讨会, 北京, 2008:19-21. [15] 王建捷, 胡欣.MM5模式中不同对流参数化方案的比较试验.应用气象学报, 2001, 12(1):41-53. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010105&flag=1 [16] 朱蓉, 徐大海.中尺度数值模拟中的边界层多尺度湍流参数化方案.应用气象学报, 2004, 15(5):543-555. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040567&flag=1 [17] 伯鑫, 丁峰, 徐鹤.大气扩散CALPUFF模型技术综述.环境监测管理与技术, 2009, 21(3):9-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJS200903006.htm [18] Prieto M, Navairro J, Copeland J. A Comparison of Wind Field Simulations through a Coupling of MM5 / CALMET in a Complex Terrain. European Wind Energy Conference, Milan, 2007: 1-8. [19] Yim S H L, Fung J C H, Lau A K H. Mesoscale simulation of year-to-year variation of wind power potential over southern China. Energies, 2009, 2: 340-361. doi: 10.3390/en20200340 [20] YimS H L, FungJ C H, LauAKH. Developing a high res-olution wind map for a complex terrain with a coupled MM5/ CALMET system. J Geophys Rcs, 2007, 112(5) : 106-112. [21] Scire J S, Robe F R, Fernau M F. A User's Guide for the CALMET Meteorological Model (Version 5). Concord, MA: Earth Tech Inc, 2000:1-68. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: