Real Time Observing and Forecasting System for Soil Moisture in Anhui Province
-
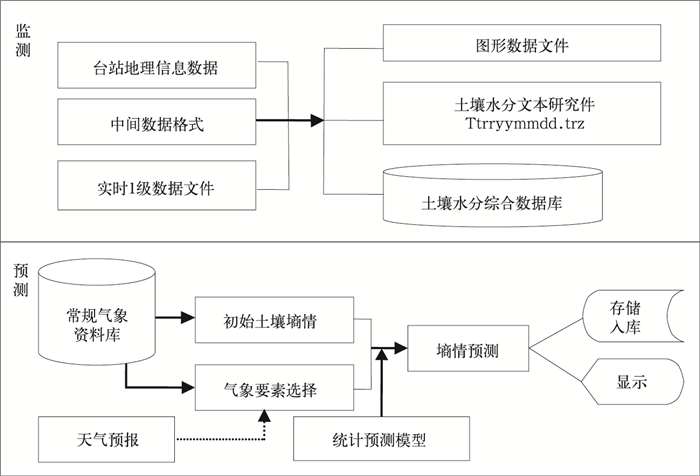
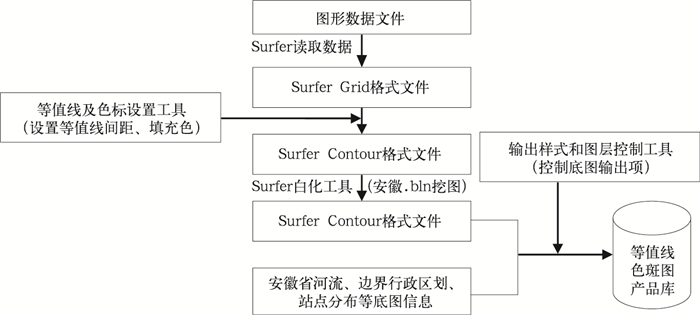
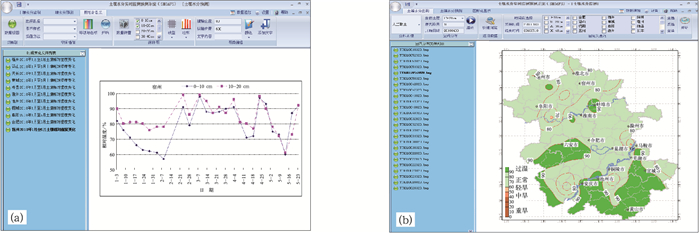
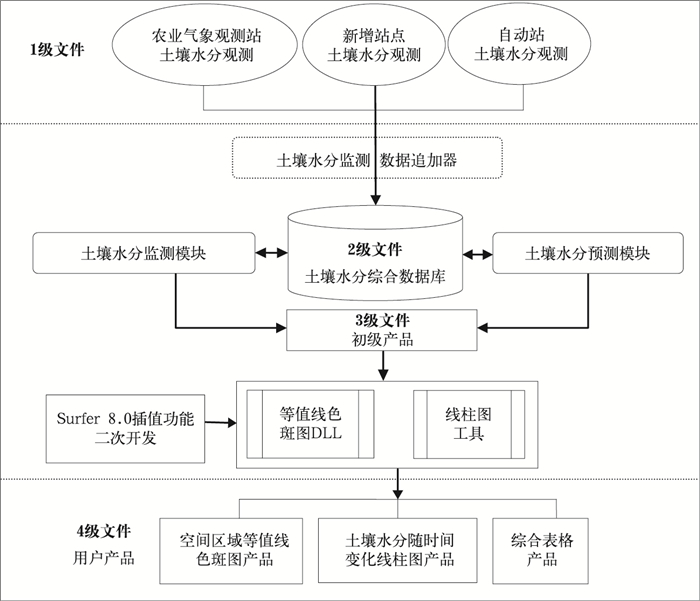
摘要: 基于农业气象业务需求,研发安徽省土壤水分监测预测服务系统,可为防汛抗旱决策服务提供技术支持。该文首先建立人工取土、自动土壤水分观测站等不同渠道土壤水分监测资料的实时传输与处理系统,再利用不同季节资料建立土壤墒情统计预测模型,然后对Surfer 8.0和线柱图控件进行二次开发,实现不同季节和不同土层的土壤墒情监测预测结果表格化、图形化动态显示与输出。该研究建立的土壤旱涝监测预测系统实现了从土壤水分原始监测数据到标准化土壤水分综合数据库、再从监测预测初级产品到动态及图形化显示的服务产品的四级数据文件转化及业务逻辑流程,系统业务实用性和转化力强,该系统已成功应用于安徽省农业旱涝预报预警业务服务。Abstract: In order to meet the needs of flood control and drought relief, the operation of soil moisture observation is launched routinely in meteorological department, by artificial boring stick all the time or by automatic measurer in recent years. However, the use of soil moisture data is always lagging with poor matching service and continuity. Based on the soil water observation network (including the manual and automatic network) and many kinds of approaches for data transmission, Real Time Observing and Forecasting System for Soil Moisture in Anhui Province (SMRTOFS) is developed. SMRTOFS is composed of data observation and transmission subsystem, forecast subsystem, and display subsystem. In data observation and transmission subsystem, the data from manual observers and automatic observation stations is collected in real time and stored in standard soil moisture database, and the data from unexpected transmission approach is also automatically gathered and conserved by defining an intermediate file. In forecast subsystem, predicting models of soil water content for each season are established, and soil moisture forecast is achieved using the latest soil water observation data and the coming 10-day weather information. In the display subsystem, based on the secondary development of Golden Software Surfer 8.0 and line bar chart control, the results of soil water observation and prediction in different seasons and different depths are exported and displayed dynamically, with the patterns of data table, the filled contour in spatial scale, bar chart, and so on. In the system, four-level files from observation to application are constructed including observation raw data, standard database, primary products and user products. The operation flow of soil moisture observation and forecast is reduced to transforming the four-level files. With higher applicability and compatibility, the system is applied triumphantly to the service of agricultural drought and waterlogging operation in Anhui Province. The information could be used to avoid the loss of flood and drought disaster. However, the soil moisture forecasting is based on statistical method, so the model parameters need modification for other regions. Implementing better Soil-Plant-Atmosphere Continuum model can also improve the performance of this system.
-
Key words:
- soil water;
- real time observing;
- forecasting system
-
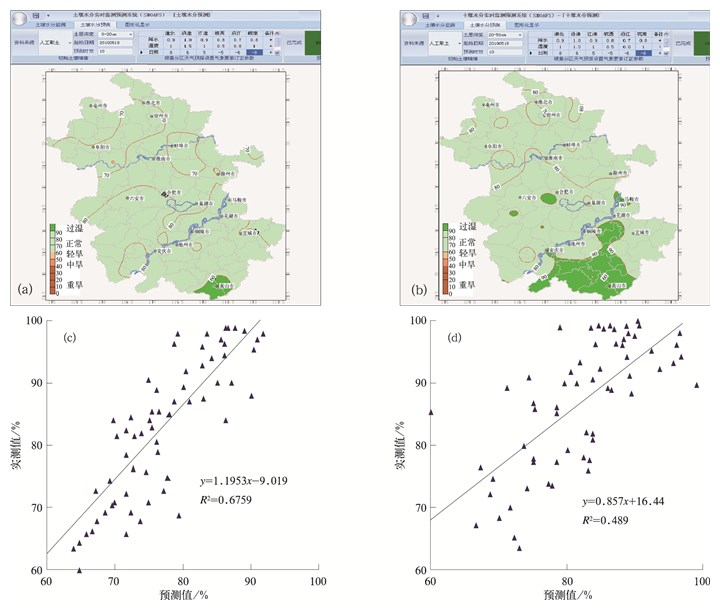
图 5 土壤水分预测实例
(a) 0~20 cm预测,(b)20~50 cm预测,(c)0~20 cm预测值与实测值比较,(d)20~50 cm预测值与实测值比较
Fig. 5 The example of soil water forecasting (a) forecasting in 0—20 cm depth, (b) forecasting in 20—50 cm depth, (c) comparison between predicting value and observing value in 0—20 cm depth, (d) comparison between predicting value and observing value in 20—50 cm depth
表 1 土壤相对湿度θ′的干旱等级
Table 1 Drought index of soil relative humidity
等级 类型 土壤相对湿度/% 1 过湿 θ′>90 2 正常 60<θ′≤90 3 轻旱 50<θ′≤60 4 中旱 40<θ′≤50 5 重旱 θ′≤40 表 2 土壤墒情预测模型参数
Table 2 The parameters of soil water forecasting model
季节 a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 P≤P0 春季 10.70 0.768 -0.034 0.538 -0.024 夏季 32.80 0.657 -0.067 0.540 -0.070 秋季 10.82 0.833 -0.035 0.386 -0.027 冬季 0.72 0.930 -0.016 0.295 -0.015 P>P0 春季 33.28 0.420 -0.020 7.320 -0.137 夏季 44.13 0.280 -0.049 7.580 -0.030 秋季 39.31 0.405 -0.051 7.750 -0.112 冬季 35.08 0.441 -0.021 5.870 -0.010 表 3 土壤水分观测数据表结构
Table 3 Table structure of soil water
列名 中文名称 类型 单位 Rq 日期 character Zhh 站号 character Zhm 站名 character Sjlx* 数据类别 integer Tzlx 台站类型 integer Sgg 灌溉标示 integer S10 0~10 cm single % S20 10~20 cm single % S30 20~30 cm single % S40 30~40 cm single % S50 40~50 cm single % S60 50~60 cm single % S70 60~70 cm single % S80 70~80 cm single % S90 80~90 cm single % S100 90~100 cm single % Sgtc 干土层厚度 integer cm 注:*数据类别有3种:0表示相对湿度,1表示体积含水率,2表示重量含水率。 表 4 类SurferIni属性定义
Table 4 Property of the class of SurferIni
属性 数据类型 备注 Back_layer string 背景图层路径 Grid_txt string 图形数据文件路径 LongLat (1 to 4) single 图像经纬度区间 Level_file string 自定义的色标文件路径 Bln_file string 白化时省边界文件路径 Bmp_width integer 输出图像宽 Bmp_Height integer 输出图像高 Bmp_output string 图像输出路径 BmpWHbili boolean 是否按高/宽比输出 Srf_output string *.srf输出路径 -
[1] 王善型, 宣春生, 王效瑞, 等.安徽省志·气象志.合肥:安徽人民出版社, 1990. [2] 陈家宙, 陈明亮, 何圆球.各具特色的当代土壤水分测量技术.湖北农业科学, 2001(3):25-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNY200103012.htm [3] 冶林茂, 吴志刚, 牛素军, 等. GStar-Ⅰ型电容式土壤水分监测仪设计与应用.气象与环境科学, 2008, 31(3):82-85. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNQX200803018.htm [4] Menziani M, Pugnaghi S, Pilan L, et al. TDR soil moisture measurements at the Lago Maggiore MAP target area: Preliminary results.Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part B: Hydrology, Oceans and Atmosphere, 2001, 26: 431-436. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1909(01)00031-4 [5] 范佳林, 梁秀清.土壤墒情自动化监测及应用.现代农业科技, 2010(7):323; 327. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANHE201007217.htm [6] 国家防汛抗旱总指挥部办公室. 全国旱情监测规划. 2007: 32-35. http://www.docin.com/p-8690746.html. [7] 邵晓梅, 严昌荣, 徐振剑.土壤水分监测与模拟研究进展.地理科学进展, 2004, 23(3): 59-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ200403007.htm [8] 黄妙芬, 康玲玲, 王云璋.气象、水文干旱指数计算访求研究概述.水资源与水工程学报, 2004, 15 (3):15-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ200403004.htm [9] 陈金华, 杨太明, 马晓群, 等.安徽省长江以北地区土壤水分动态模拟初探.中国农业气象, 2007, 28(3): 289-291. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNY200703012.htm [10] 元来福, 王继琴.从农业需水量评价我国的干旱状况.应用气象学报, 1995, 6(3):86-92. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19950355&flag=1 [11] 王晓云, 郭文利, 奚文, 等.利用"3S"技术进行北京地区土壤水分监测应用技术研究.应用气象学报, 2002, 13(4):422-431. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020457&flag=1 [12] 李玉中, 程延年, 安顺清.北方地区干旱规律及抗旱综合技术.北京:中国农业科学技术出版社, 2002. [13] 董振国.作物层温度与土壤水分关系.科学通报, 1986, 31(8):186-190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198608012.htm [14] Caporali E, Entekhabi D, Castelli F. Rainstorm statistics conditional on soil moisture index: Temporal and spatial characteristics. Meccanica, 1996, 31:103-116. doi: 10.1007/BF00444158 [15] Wang J R. An overview of the measurements of soil moisture and modeling of moisture flux in FIFE. J Geophys Res, 1992, 97(D17): 955-959. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4708806_An_overview_of_the_measurements_of_soil_moisture_and_modeling_of_moisture_flux_in_FIFE [16] 郭以明, 郭相平, 樊峻江, 等.蓄水控灌模式对水稻产量和水分生产效率的影响.灌溉排水学报, 2010, 29(3): 61-63;73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS201003015.htm [17] 王传河.小麦不同指标对旱涝反应敏感性差异的比较.中国农业通报, 2003, 19(6):33-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB200306012.htm [18] 张爱民, 马晓群.安徽省旱涝灾害及其对农作物产量影响.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5):619-625. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070595&flag=1 [19] 邵光成, 张展羽, 蔡焕杰, 等.膜下滴灌棉花缺水诊断指标的试验研究.河海大学学报 (自然科学版), 2004, 32(5):546-553. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX200405017.htm [20] 谭宗锟.广西农业气象灾害风险评价及灾害风险区划.广西气象, 1997, 18(1):44-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXQX701.012.htm [21] 李世奎, 霍治国, 王素艳, 等.农业气象灾害风险评估体系及模型研究.自然灾害学报, 2004, 13(1): 77-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH200401013.htm [22] 宋丽莉, 王春霖, 董永春.水稻干旱动态模拟及干旱损失评估.应用气象学报, 2001, 12(2):23-26. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010230&flag=1 [23] Naor A. Relationship between leaf and stem water potential and stomatal conductance in three field-grown woody species. J Hort Sci & Biotechnology, 1998, 73:431-436. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290014488_Relations_between_leaf_and_stem_water_potentials_and_stomatal_conductance_in_three_field-grown_woody_species [24] Nicola M, John D A. Multi-scale assimilation of surface soil moisture data for robust root zone moisture predictions. Advances in Water Resources, 2003, 26(1): 33-44. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00103-3 [25] Nicola B, Maelle A. Operational mapping of soil moisture using synthetic aperture radar data: Application to the Touch Basin (France). Sensors, 2007, 7: 2458-2483. doi: 10.3390/s7102458 [26] 王越, 江志红, 张强, 等.用Palmer湿润指数作西北地区东部冬小麦旱涝评估.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(3):342-349. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080356&flag=1 [27] 刘云辉, 朱渐臣.丹东地区中部春播期土壤水分特征及早涝评价.中国农业气象, 2008, 29(2):174-176. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNY200802016.htm [28] 鞠笑生, 杨贤为, 陈丽娟, 等.我国单站早涝指标确定和区域早涝级别划分的研究.应用气象学报, 1997, 8(1):26-33. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yyqx701.003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [29] 侯琼, 郝文俊.内蒙古地区玉米农田土壤墒情动态预测模式.干旱地区农业研究, 2000, 12(4): 49-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDQ200004010.htm [30] 申惠娟, 严昌荣, 戴亚平.等.农田土壤水分预测模型的研究进展及应用.生态科学, 2003, 22(4):366-370. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STKX200304019.htm [31] 盛绍学, 胡雯, 马晓群, 等.安徽省农业干旱遥感监测指标的确定及应用.安徽气象, 2000(3):16-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNY200104008.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: