The Soil Moisture Predictive Model Based on the Precipitation in North China
-
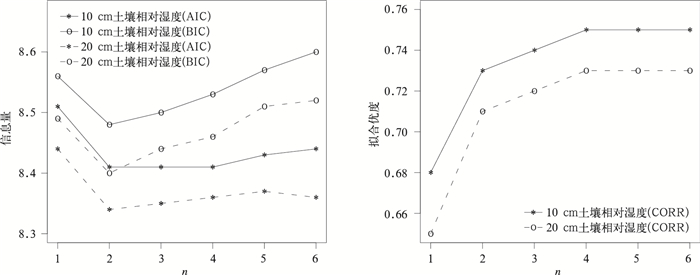
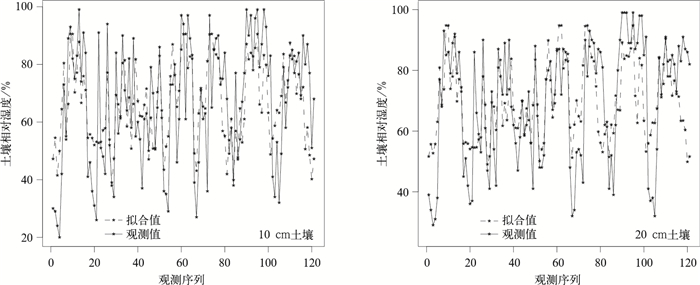
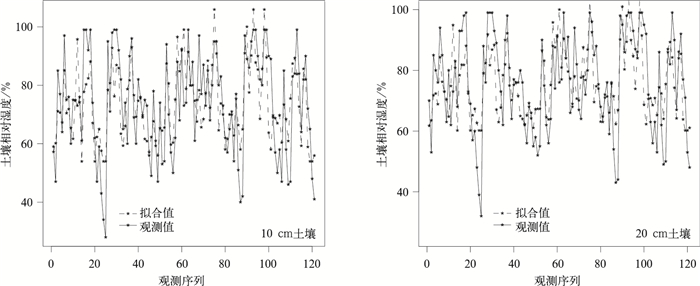
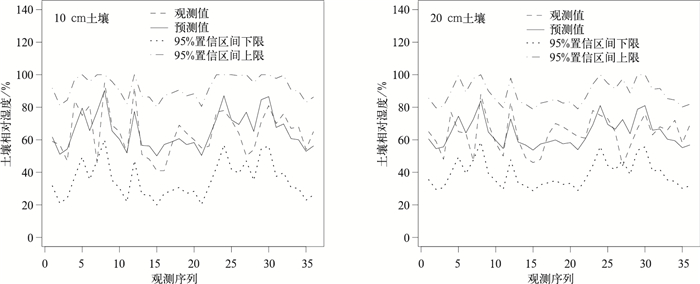
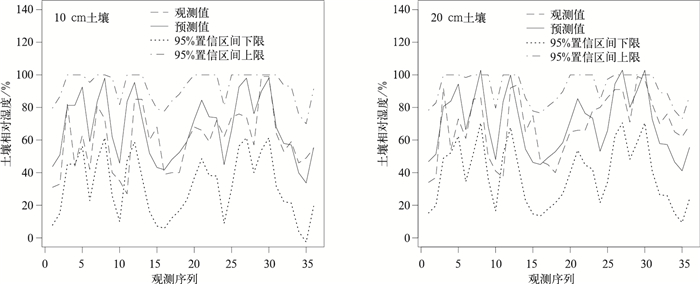
摘要: 基于引入随机变量的机理性模型方法,利用华北地区2000—2008年气象台站观测数据,以大气降水为随机变量,并考虑其延迟效应,利用回归方法建立了预测时效为1旬的土壤相对湿度预测模型。利用预测率和干旱等级预报精度两个评价指标,结合2009年土壤湿度实际观测数据,验证了预测模型预报率均在90%以上,绝大部分站点的干旱等级预报精度均在70%以上,得出该预测模型在华北地区应用的合理性,从而建立了一套客观、动态的土壤湿度预测方法,有利于及时掌握农田旱情程度和分布,主动采取防旱、抗旱应对措施。Abstract: A better soil moisture predictive model for North China can enhance the accuracy of drought forecast, which will have great significance in predicting the extent and distribution of drought, playing an important role in taking positive and active measures for drought in time. It is well acknowledged that one of the key points and difficult points in research on dry farming is the change of soil moisture, which is influenced by various factors, such as rainfall, evaporation, the time of sunshine, the kind and texture of soil and so on. Of all the factors, the amount of rainfall is one of the most important factors, which contributes a lot to the change of the soil moisture, deserves more and more attentions to study their relationships.A random variable's mechanism-rational model is therefore introduced, and the meteorological data in North China during 2000 to 2008 is analyzed, taking the atmosphere precipitation as random variable as well as its delay effect, employing the regression method to set up the soil relative moisture predictive model, which is effective for ten days. 10-cm and 20-cm soil relative moisture predictive models for the 55 stations in the north of China are established, but only the fitting results of 10 stations are given, and their fitness accuracy (the Pearson correlation coefficient) is all above 60%. Meanwhile, the efficiency of this model is verified with soil moisture data of 2009 by means of the two indexes, indicating that all of the forecasting rates are above 90% and most of the drought prediction rates are above 70%, therefore a series of objective, dynamic soil moisture predictive method is established. The fitting graphs and the graphs of 95% confidence interval are also given for the 10 stations, from which the feasibility of this method can be verified. The method provides a new support for the prediction of the soil moisture in the field.The method can extend to every station in the country to set up local unique models. Though this approach is only tentative experiment, it is a success according to the results of fitting and prediction. Moreover, the model involves 10-day rainfall delay effect, whose prediction is effective for 10 days. With the extension of rainfall stations in the country, it is easier to get the daily observations of the rainfall, and it is possible to conduct continuous prediction for the soil moisture with the method, which will have far-reaching influence on the dry farming research.
-
表 1 干旱分布等级标准
Table 1 The rating criteria of drought distribution
土壤相对湿度/% 干旱程度 50~60 轻旱 40~50 中旱 30~40 重旱 <30 特旱 表 2 华北地区10个站点参数拟合结果
Table 2 The results of parameter fitting of ten stations in North China
站名 土壤相对湿度 γ τ α0 α1 β1 β2 相关系数 密云 w1
w20.60
0.7050 32.9
28.90.44
0.561.43
0.52-0.45
-0.210.70
0.70宝坻 w1
w20.60
0.8070 42.8
43.50.27
0.412.51
0.28-0.57
-0.120.62
0.56涿州 w1
w20.80
0.9580 30.3
31.20.34
0.381.39
1.55-0.19
-0.070.67
0.65南阳 w1
w20.35
0.7070 26.0
19.40.37
0.602.08
0.560.22
0.000.74
0.80商丘 w1
w20.55
0.60100 30.7
34.00.25
0.292.36
1.680.55
0.490.65
0.70文登 w1
w20.45
0.60100 26.1
27.00.18
0.286.00
2.611.06
0.630.67
0.71胶州 w1
w20.65
0.8070 33.0
30.50.36
0.451.77
0.740.51
0.250.76
0.78安泽 w1
w20.60
0.70100 20.3
19.70.47
0.552.65
1.290.02
0.030.79
0.77长治 w1
w20.60
0.90100 14.8
21.10.39
0.493.42
0.660.33
0.200.70
0.64万荣 w1
w20.60
0.70100 33.8
34.50.34
0.422.05
0.980.51
0.350.75
0.72表 3 华北地区10个站点土壤相对湿度预测结果
Table 3 The soil moisture forecasting results of 10 stations in North China
站点 w1预测率 w2预测率 w1等级预测率 w2等级预测率 密云 0.98(0.97) 0.95(0.90) 0.80(0.70) 0.81(0.87) 宝坻 0.95(0.90) 0.95(0.93) 0.95(0.73) 0.93(0.93) 涿州 1.00(0.98) 0.98(0.95) 0.90(0.62) 0.95(0.62) 南阳 1.00(1.00) 1.00(1.00) 0.64(0.55) 0.67(0.62) 商丘 0.92(0.90) 0.93(0.89) 0.70(0.60) 0.84(0.56) 文登 1.00(0.98) 1.00(0.95) 0.95(0.48) 0.98(0.55) 胶州 1.00(1.00) 1.00(0.94) 1.00(0.97) 1.00(0.60) 安泽 1.00(0.94) 1.00(0.93) 0.65(0.53) 0.63(0.44) 长治 0.98(0.93) 1.00(0.95) 0.67(0.35) 0.67(0.48) 万荣 0.98(0.93) 1.00(0.95) 0.74(0.38) 0.84(0.23) 注:表 3为华北地区10个站点预测时效分别为1旬和2旬结果比较,其中括号内的数值表示对应站点预测时效为2旬的预测率或者干旱等级预报率。 -
[1] 申双和, 周英.农田土壤水分预测模型应用研究.南京气象学院学报, 1992, 15(4):540-548. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNY200908027.htm [2] 华北平原作物水分胁迫与干旱研究课题组.作物水分胁迫与干旱研究.郑州:河南科学技术出版社, 1990:1-235. [3] 郑剑飞, 范嘉泉.土壤水分系统动态模拟.北京农业大学学报, 1984(4):493-500. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYDX198704020.htm [4] 李保国, 龚元石, 左强, 等.农田土壤水的动态模型及应用.北京:科学出版社, 2000. [5] 申双和, 周英.旱地农田土壤水分动态平衡的模拟.南京气象学院学报, 1994, 17(4):462-469. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX404.010.htm [6] 申双和, 李胜利.一种改进的土壤水分平衡模式.南京气象学院学报, 1998, 24(6):17-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX806.002.htm [7] 龚元石.冬小麦和夏玉米农田土壤分层水分平衡模型.北京农业大学学报, 1995, 21(1):61-67. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYDX199501013.htm [8] 申双和, 周英.农田土壤水分的随机模拟和预测.南京气象学院学报, 1993, 16(3):324-328. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX199303010.htm [9] 左志燕.我国东部春季土壤湿度影响夏季降水.中国气象科学研究院年报, 1997:20-21. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1016723643.htm [10] 刘可群, 刘志雄, 梁益同, 等.基于前期有效降水推算耕作层土壤湿度的方法.中国农业气象, 2009, 30(3):365-369. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNY200903017.htm [11] 陈斌, 丁裕国, 刘晶淼.土壤湿度的一种统计预报模型初步试验.气象科学, 2005, 25(3):232-236. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200503001.htm [12] 李新辉, 宋小宁, 周霞.半干旱区土壤湿度遥感监测方法研究.地理与地理信息科学, 2010, 26(1):90-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201001023.htm [13] Eiko N, Mark A S, Jan K S, et al. Resistance modeling of ammonia exchange over oilseed rape. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 105:405-425. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00206-9 [14] Nemitz E, Sutton M A, Gut A, et al. Sources and sinks of ammonia within an oilseed rape canopy. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 105:385-404. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00205-7 [15] 赵艳霞, 王馥棠, 裘国旺.冬小麦干旱识别和预测模型研究.应用气象学报, 2001, 12(2):234-241. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010231&flag=1 [16] 魏凤英.华北干旱的多时间尺度组合预测模型.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(5):585-592. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030573&flag=1 [17] 刘建栋, 王馥棠, 于强, 等.华北地区农业干旱预测模型及其应用研究.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(5):593-604. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030574&flag=1 [18] 孙家民, 黄朝迎.中国农业气候年景的评估及预测.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(增刊):111-115. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yyqx2005s1014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] 李巧萍, 丁一江, 董文杰.土壤湿度异常对区域短期气候影响的数值模拟试验.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(1):1-11. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070102&flag=1 [20] 周秉荣, 李凤霞, 申双和, 等.从MODIS资料提取土壤湿度信息的主成分分析方法.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(1):114-118. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090115&flag=1 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: