Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Probability Classification of Precipitation and Temperature Anomalies over China
-
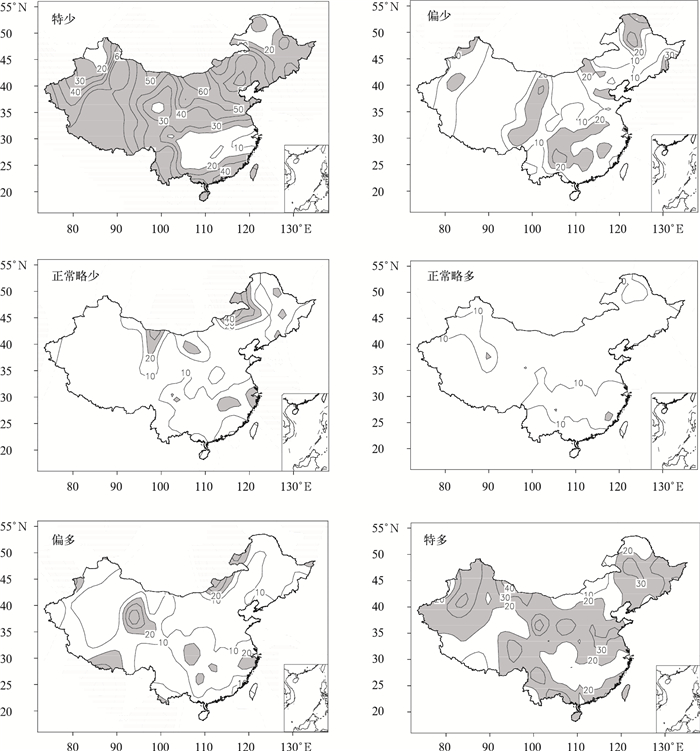
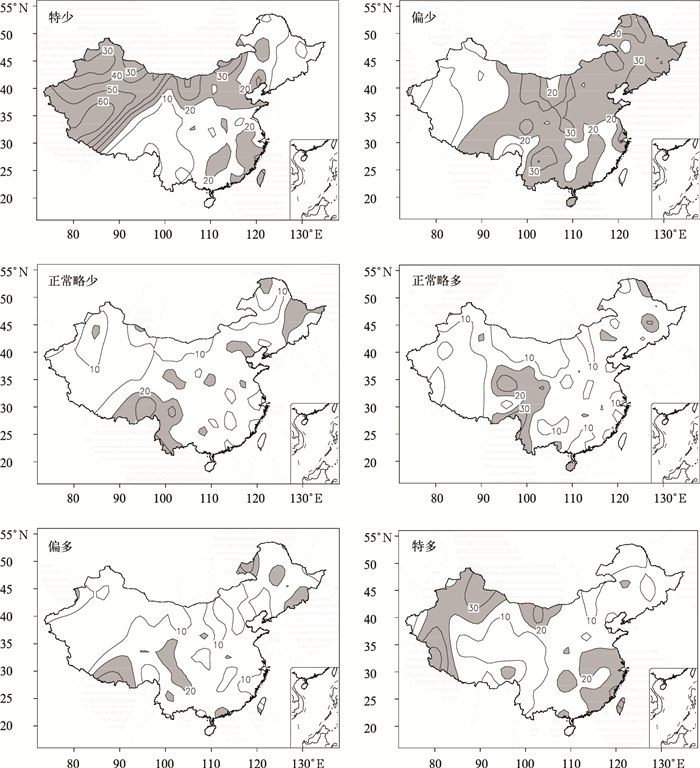
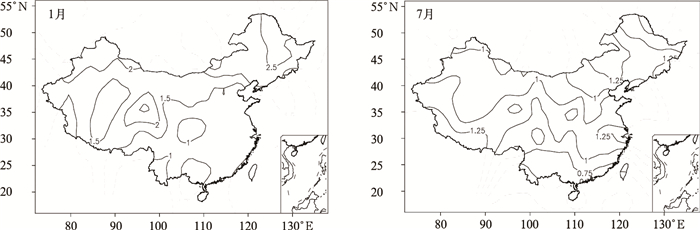
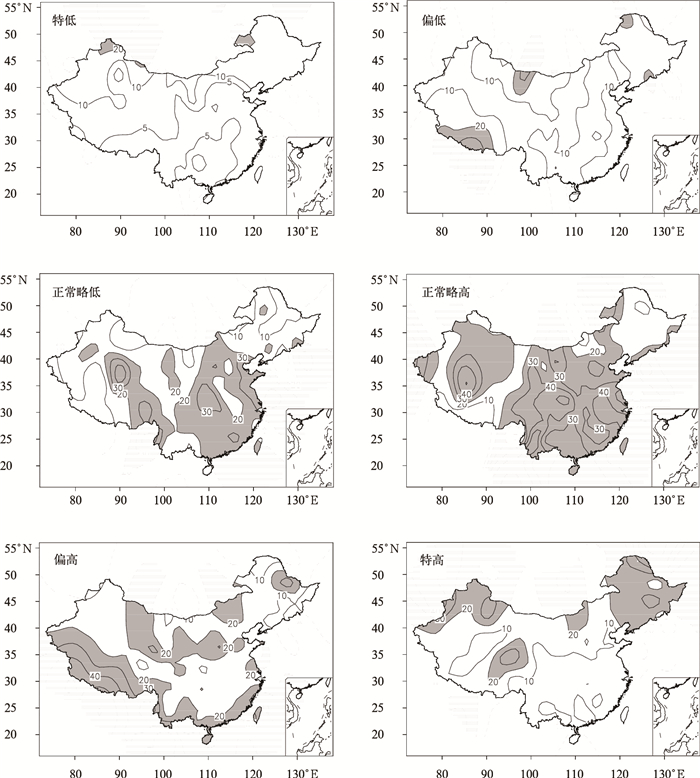
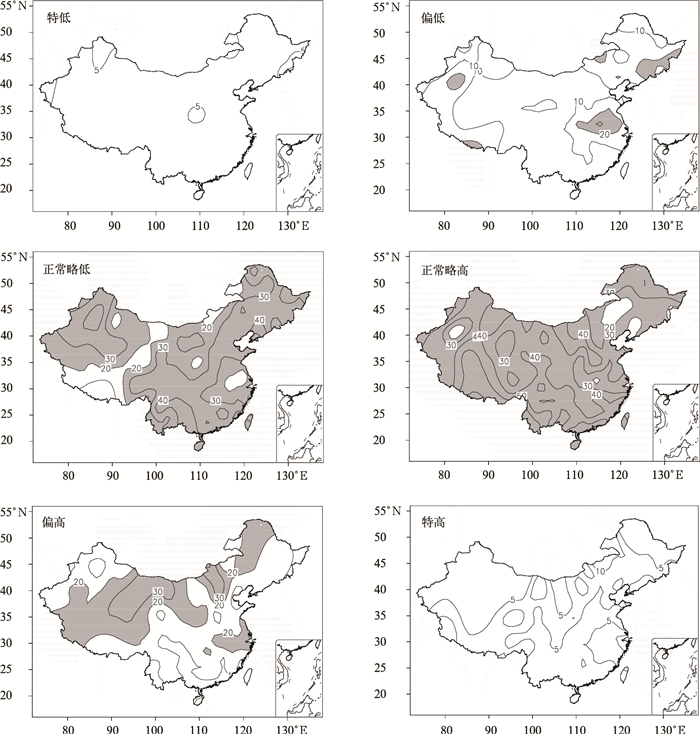
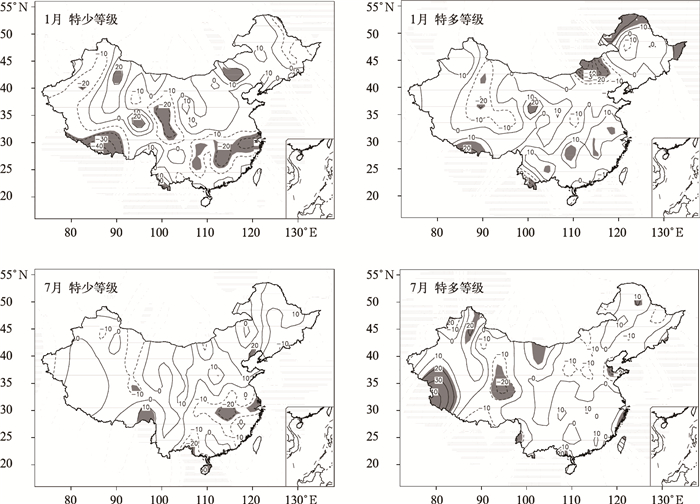
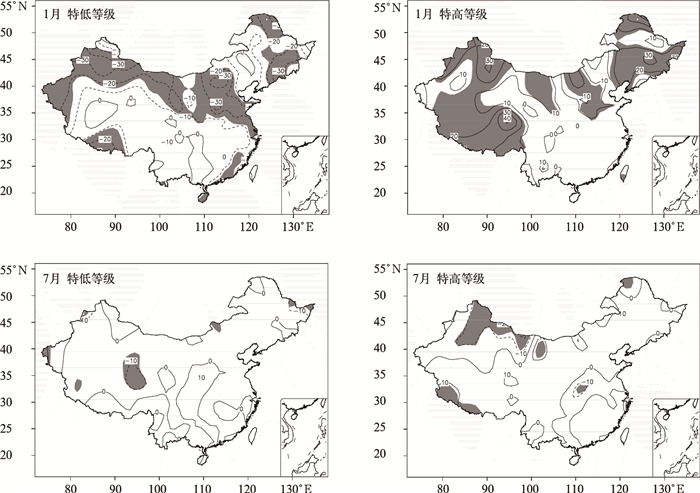
摘要: 采用全国160站1951—2009年月降水和气温资料,分析了短期气候预测业务评分办法中六级要素概率时空分布特征,并以1月、7月为代表获得了不同地区、不同级别降水和气温异常发生频率。结果表明:降水和气温的六级异常分布存在显著空间不均匀性和年代际变化特征,1980—2009年,北方降水在1月出现特少、特多等级和7月出现特少、偏少等级的概率较大,南方降水出现6个等级的概率基本相同;全国气温在1月和7月出现正常略低、正常略高和偏高等级的概率较大。1980—2009年与1951—1979年相比,全国1月降水为特多、偏多等级和7月降水为偏少等级的站数明显增加,全国1月气温为正常略高、偏高和特高等级的站数明显增加,呈明显的年代际变化特征。Abstract: Based on the standard of the probability classification definition and scoring method in short term climate prediction operation, analysis is conducted on six-level probability classification of monthly precipitation and temperature anomalies in January and July. Spatial and temporal distributions are obtained through the monthly precipitation and temperature data at 160 stations in China, which are operationally used by National Climate Center of CMA. The six levels are defined as much more than normal (L1), moderately more than normal (L2), slightly more than normal (L3), slightly less than normal (L4), moderately less than normal (L5), much less than normal (L6).The results indicate that the issued six-level probability classification is suitable for symmetrical distribution cases for positive and negative anomalies but neglecting spatial inhomogeneous distributions and inter-decadal variations of monthly temperature and precipitation. During the period of 1980—2009, the probability of L1 and L6 for precipitation in North China is high in January whereas that of L6 and L5 is elevated in South China in July. The six-level probability for precipitation in January and July is generally similar in South China. The probability of L4, L3, and L2 temperature is high whereas that of L6, L5, and L1 is low for temperature in China in both January and July. Compared to those in the period of 1951—1979, the station numbers of L1 and L2 in January and L5 for precipitation in July have significantly increased but those of L6 precipitation in January and L6 and L4 for precipitation in July have remarkably decreased in the period of 1980—2009. Meanwhile, the station numbers of L4, L5, L6 for temperature in January have substantially decreased but those of L1, L2, L3 for temperature in January increases significantly and the six-level temperature probability in July shows no variability since 1980.The above results could provide an important reference for climate forecasters to fully consider inter-decadal, inter-annual and inter-seasonal variability. The standard of the scoring method for the climate prediction focuses on the accurate rate of classification prediction, and especially emphasizes the abnormal level of precipitation and temperature. Therefore, the scoring method will help promote climate prediction services. The six-level scoring method for precipitation is more reasonable, while for temperature the method needs appropriate improvements.
-
表 1 降水和气温趋势预测六级评分制用语及等级划分标准
Table 1 The terminology of six-level scoring method and the classification standards of each level for precipitation and temperature prediction
预测用语 ΔR/% ΔT/℃ 特少 (特低) ΔR≤-50 ΔT≤-2.0 偏少 (偏低) -50<ΔR≤-20 -2.0<ΔT≤-1.0 正常略少 (正常略低) -20<ΔR<0 -1.0<ΔT<0 正常略多 (正常略高) 0≤ΔR<20 0≤ΔT<1.0 偏多 (偏高) 20≤ΔR<50 1.0≤ΔT<2.0 特多 (特高) 50≤ΔR 2.0≤ΔT 注:ΔR为降水距平百分率; ΔT为气温距平。 表 2 单站降水和气温趋势预测六级评分制评分表
Table 2 The six-level scoring method for precipitation and temperature predictions at one station
实况 预测 特少 (特低) 偏少 (偏低) 正常略少 (正常略低) 正常略多 (正常略高) 偏多 (偏高) 特多 (特高) 特少 (特低) 100 80+10 60 20 0 0 偏少 (偏低) 80+10 100 80 40 20 0 正常略少 (正常略低) 60 80+10 100 60 40 20 正常略多 (正常略高) 20 40 60 100 80+10 60 偏多 (偏高) 0 20 40 80 100 80+10 特多 (特高) 0 0 20 60 80+10 100 -
[1] Kunkel K E, Pielke J R A, Changnon S A. Temporal fluctuations in weather and climate extremes that cause economic and human health impacts: A review. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1999, 80 (6): 1077-1098. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<1077:TFIWAC>2.0.CO;2 [2] Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, et al. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2007. [3] Klein Tank A M G, Konnen G P. Trends in indices of daily temperature and precipitation extremes in Europe, 1946—99. J Climate, 2003, 16: 3665-3680. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3665:TIIODT>2.0.CO;2 [4] 张耀存, 张录军.东北气候和生态过渡区近50年来降水和气温概率分布特征变化.地理科学, 2005, 25(5):561-566. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200505007.htm [5] 孙凤华, 杨素英, 任国玉.东北地区降水日数、强度和持续时间的年代际变化.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5):610-618. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070594&flag=1 [6] Choi G, Collins D, Ren G, et al. Changes in means and extreme events of temperature and precipitation in the Asian-Pacific Network region, 1955—2007. International Journal of Climatology, 2009, Published online in Wiley InterScience, doi: 10.1002/joc.1979. [7] Alexander L V, Zhang X, Peterson T C, et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J Geophys Res, 2006, 111, D05109, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006290. [8] Jiang Y, Luo Y, Zhao Z, et al. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956-2004. Theor Appl Climatol, 2010, 99(3): 421-430. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-BJQX201106001030.htm [9] DeGaetano A T, Allen R J. Trends in twentieth century temperature extremes across the United States. J Climate, 2002, 15: 3188-3205. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<3188:TITCTE>2.0.CO;2 [10] Ren G, Zhou Y, Chu Z, et al. Urbanization effect on observed surface air temperature trend in North China. J Climate, 2008, 21(6): 1333-1348. doi: 10.1175/2007JCLI1348.1 [11] Easterling D R, Horton B, Jones P D, et al. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science, 1997, 277: 364-367. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5324.364 [12] Vose R S, Easterling D R, Gleason B. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe: An update through 2004. Geophys Res Lett, 2005, 32, L23822, doi: 10.1029/2005GL024379. [13] 屠其璞, 邓自旺, 周晓兰.中国近117年年平均气温变化的区域特征研究.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(增刊):34-42. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yyqx9s1.004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [14] 丁一汇, 戴晓苏.中国近百年气温的变化.气象, 1994, 20(12):19-26. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.1994.12.008 [15] 张明庆, 刘桂莲.我国近40年气温变化地域类型的研究.气象, 1999, 25(4):10-14. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.1999.04.002 [16] 唐红玉, 翟盘茂, 王振宇. 1951—2002年中国平均最高、最低气温及日较差变化.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(4):728-735. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504003.htm [17] Zhai P M, Zhang X B, Wan H, et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J Climate, 2005, 18: 1096-1108. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-3318.1 [18] 蔡敏, 丁裕国, 江志红.我国东部极端降水时空分布及其概率特征.高原气象, 2007, 26(2):309-317. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200702012.htm [19] 王小玲, 翟盘茂. 1957—2004年中国不同强度级别降水的变化趋势特征.热带气象学报, 2008, 24(5): 459-466. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200805004.htm [20] 王绍武.近百年气候变化与变率的诊断研究.气象学报, 1994, 52(3):261-273. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1994.035 [21] 黄荣辉, 徐予红, 周连童.我国夏季降水的年代际变化及华北干旱化趋势.高原气象, 1999, 18(4):465-476. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX199904000.htm [22] 钱维宏, 符娇兰, 张玮玮, 等.近40年中国平均气候与极值气候变化的概述.地球科学进展, 2007, 22(7):673-684. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200707006.htm [23] 杨萍, 刘伟东, 王启光, 等.近40年我国极端温度变化趋势和季节特征.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1):29-36. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100104&flag=1 [24] 苏布达, 姜彤, 任国玉, 等.长江流域1960—2004年极端强降水时空变化趋势.气候变化研究进展, 2006, 2(1):9-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200601002.htm [25] 杨金虎, 江志红, 王鹏祥, 等.中国年极端降水事件的时空分布特征.气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(1):75-83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200801009.htm [26] 翟盘茂, 任福民, 张强.中国降水极值变化趋势检测.气象学报, 1999, 57(2):208-216. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1999.019 [27] 翟盘茂, 王志伟, 周旭凯. 全国及主要流域极端气候事件变化//气候变化与中国水资源. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 91-112. [28] 罗阳, 赵伟, 翟景秋.两类天气预报评分问题研究及一种新评分方法.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(2):129-136. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090201&flag=1 [29] 张强, 熊安元, 张金艳, 等.晴雨 (雪) 和气温预报评分方法的初步研究.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(6):692-698. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090606&flag=1 [30] 陈桂英, 赵振国.短期气候预测评估方法和业务初估.应用气象学报, 1998, 9(2):178-185. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980225&flag=1 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: