Development and Verification of a Numerical Forecast Model for Road Meteorological Services
-
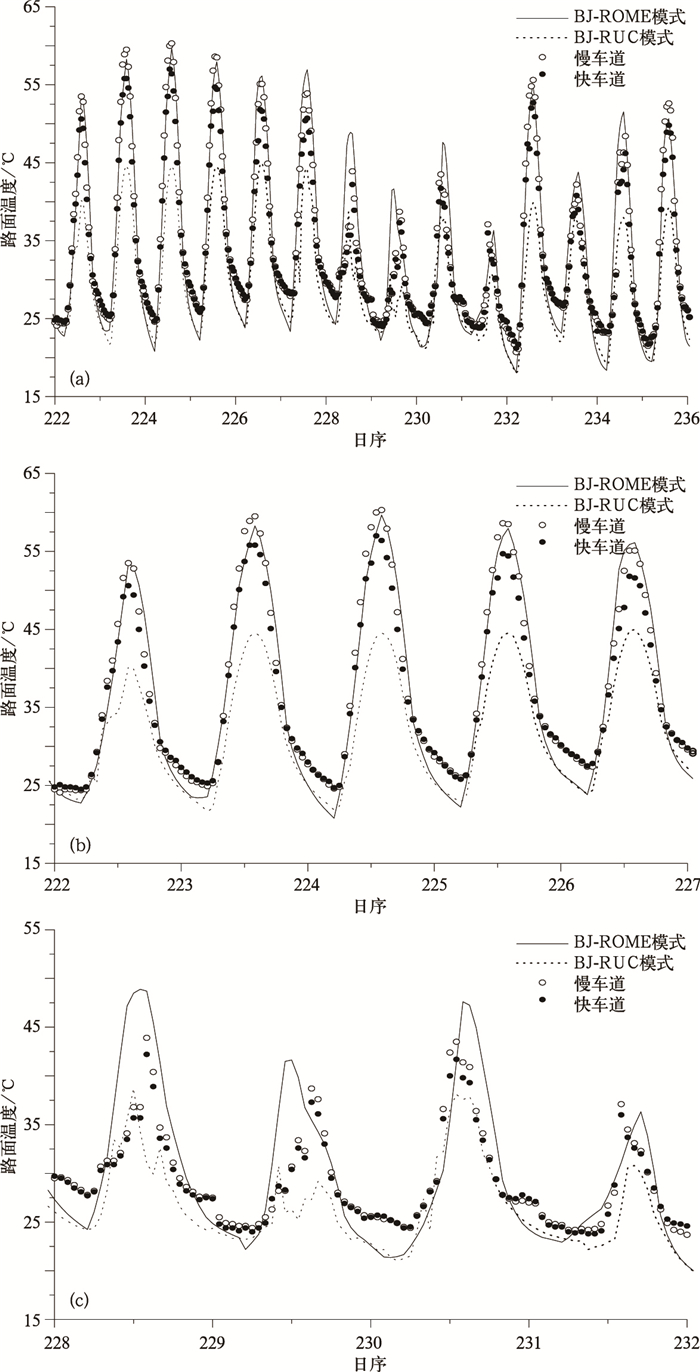
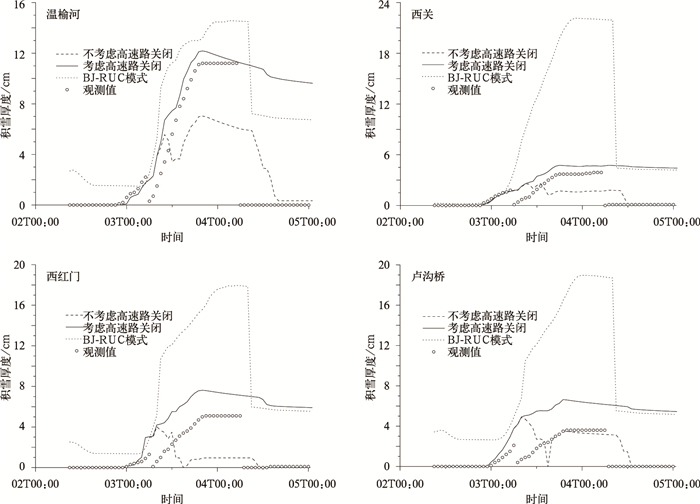
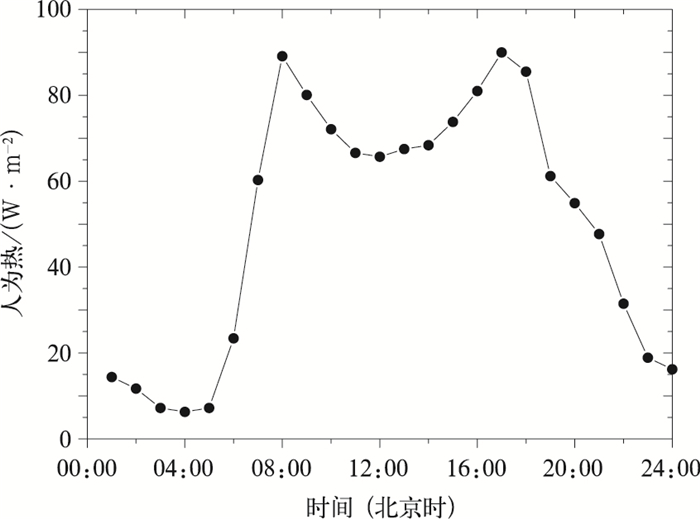
摘要: 该文基于通用陆面模式 (CoLM) 发展了精细化路面参数数值预报模型 (BJ-ROME)。该模型可以预报路面温度、积雪厚度、积冰厚度以及积水厚度。模型不仅考虑了路面的不透水性、相对较低反照率、低热容以及高热导率等特征,还考虑了城市人为热的影响。模型采用北京市气象局快速更新循环预报系统 (BJ-RUC) 产生的气象强迫场驱动,预报时间跨度为24 h,更新时间为3 h。采用北京地区芬兰Vaisala公司路面观测站2009年8月9—24日路面温度及2010年1月3—4日积雪厚度观测结果对模型预报结果进行验证,同时进行了敏感性试验。结果表明:无论是在晴空还是降水的气象条件下,BJ-ROME均能较准确地预报路面温度极值以及日变化。BJ-ROME还可以较准确地模拟积雪厚度的最大值以及随时间变化情况。Abstract: Accurate road meteorology forecast and road traffic information are very important to road transportation security. Road surface temperature is a crucial parameter in traffic weather forecast. Now there are three main kinds of road surface parameters forecast model: Statistical model, GIS-based model and physical model. Physical model is widely used and it mainly considers the road surface energy balance model and the effect of anthropogenic heat. In 2008, based on the rapid update cycling forecast system (BJ-RUC), the road weather information system is developed and run operationally by the Institute of Urban Meteorology. Since 2007, Beijing Meteorological Bureau has established 18 weather stations along the express way using the apparatus manufactured by ROSA Vaisala in Finland, and established 8 visibility observation stations using the digital visibility sensor. These all make the fine traffic weather forecast and operational run possible.A fine numerical model for urban road surface temperature (RST), snow depth and ice depth prediction (BJ-ROME) is developed based on Common Land Model (CoLM). The model is developed according to characteristics of the road surface, and based on the data of express way weather observation and fine land surface data of Beijing. The model is forced by the meteorological data output from BJ-RUC, and the forecast and update time span is 24 hours and 3 hours, respectively. The model is validated using in-situ observation data measured by the ROSA road weather stations of Vaisala Company, Finland. The sensitivity analysis is also implemented.Nine sites are chosen to validate the RST prediction results of BJ-ROME. The validation time is during 9—24 Aug 2009, when the RST is very high in Beijing. Four sites, i.e., Xihongmen, Wenyuhe, Xiguan and Lugouqiao are chosen to validate the snow depth prediction results of BJ-ROME. The validation time is during 2—5 Jan 2010, when a big snowfall happens in Beijing. The validation results indicate that BJ-ROME can successfully simulate the diurnal variation and maximum value of RST both under clear-sky and rainfall conditions. The validation results also indicate that BJ-ROME can successfully simulate the accumulation time and the variation and maximum value of snow depth. The results of sensitivity analysis indicate that road surface evaporation and the anthropogenic heat are very important in road surface temperature forecast. The forecast results of BJ-ROME can be used as an important reference to take measures by traffic administration department and road administration department.In the near future, BJ-ROME will be coupled in double direction with BJ-RUC to improve the forecast. The anthropogenic heat (AH) should be parameterized more precisely, and the variational assimilation algorithm should be used to assimilate the RST observations. The predicting performance of water depth of BJ-ROME should also be validated.
-
表 1 BJ-ROME使用的主要路面参数值
Table 1 Main road surface parameters used in BJ-ROME
路面参数 数值 热容/(J·K-1·m-3) 2.025×106 热导率/(W·K-1·m-1) 2.9 反照率 (无雪覆盖) 0.05 地表粗糙度/m 0.01 密度/(kg·m-3) 2.7×103 表 2 不同时间、模式及气象条件下路面温度预报值与观测值之间的平均误差、均方根误差和相关系数
Table 2 Mean errors, root mean square errors and correlation coefficients between forecasted and observed road temperature at different times, models and weather conditions
模式 平均误差/K 均方根误差/K 相关系数/K BJ-RUC (所有时刻) 6.62 7.82 0.91 BJ-ROME (所有时刻) 2.76 3.57 0.95 BJ-RUC (无降水) 7.89 8.98 0.94 BJ-ROME (无降水) 2.45 2.86 0.98 BJ-RUC (白天无降水) 9.79 11.04 0.87 BJ-ROME (白天无降水) 2.24 2.77 0.96 表 3 4种方案路面温度预报值与观测值之间的偏差、平均误差、均方根误差和相关系数
Table 3 Biases, mean errors, root mean square errors and correlation coefficients between forecasted and observed road temperature of four experiments
方案 偏差/K 平均误差/K 均方根误差/K 相关系数/K 试验1 -1.25 2.76 3.57 0.95 试验2 -4.47 5.59 6.32 0.88 试验3 2.80 5.08 6.02 0.86 试验4 -6.38 7.34 8.51 0.79 -
[1] 张朝林, 张利娜, 程丛兰, 等.高速公路气象预报系统研究现状与未来趋势.热带气象学报, 2007, 23(6): 652-658. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200706018.htm [2] SIRWEC 2010 Conference Volume. 15th International Road Weather Conference, Quebec City, Canada, 2010. [3] Chapman L, Thornes J E, Bradley A V. Statistical modelling of road surface temperature from a geographical parameter database. Meteorol Appl, 2001, 8: 409-419. doi: 10.1017/S1350482701004030 [4] 张德山, 丁德平, 穆启占, 等.北京奥运交通路段精细预报.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(3): 380-384. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20090316 [5] 罗慧, 李良序, 胡胜, 等.公路交通事故与气象条件关系及其气象预警模型.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(3): 350-357. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070357&flag=1 [6] Chapman L, Thornes J E. A geomatics-based road surface temperature prediction model. Sci Total Environ, 2006, 360: 68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.08.025 [7] Crevier L P, Delage Y.METRo: A new model for road-condition forecasting in Canada. J Appl Meteorol, 2001, 40: 2026-2037. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(2001)040<2026:MANMFR>2.0.CO;2 [8] 胡丽琴, 吴蓉璋, 方宗义.大口径闪烁仪及其在地表能量平衡监测中的应用.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(2): 197-205. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030224&flag=1 [9] Chapman L, Thornes J E. The influence of traffic on road surface temperatures: Implications for thermal mapping studies. Meteorol Appl, 2005, 12(4): 371-380. doi: 10.1017/S1350482705001957 [10] 张利娜, 张朝林, 王必正, 等.北京机场高速公路能见度与大气动力和热力因子的诊断及物理分析.气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(3): 260-272. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200803003.htm [11] 张利娜, 张朝林, 王必正, 等.北京高速公路大气能见度演变特征及其物理分析.大气科学, 2008, 32(6): 1229-1240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200806001.htm [12] 田华, 吴昊, 赵琳娜, 等.沪宁高速公路路面温度变化特征及统计模型.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(6): 737-744. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20090612 [13] 刘熙明, 喻迎春, 雷桂莲, 等.应用辐射平衡原理计算夏季水泥路面温度.应用气象学报, 2004, 15(5): 623-628. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040575&flag=1 [14] 范水勇, 郭永润, 陈敏, 等.高分辨率WRF三维变分同化在北京地区降水预报中的应用.高原气象, 2008, 27(6): 1181-1188. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200806001.htm [15] Zhang C L, Zhang L N, Hu H B, et al. The Design and Application of the Fine-resolution Road Weather Information System to Improve Special Meteorological Services over the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area in North China. Proceeding of the 14th International Road Weather Conference (SIRWEC 2008), Prague, Czech, 2008. [16] Zhang C L, Chen F, Miao S G, et al. Impacts of urban expansion and future green planting on summer precipitation in the Beijing metropolitan area. J Geophys Res, 2009, 114, D02116, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010328. [17] Zhang C L, Miao S G, Li Q C, et al. Impacts of fine-resolution land use information of Beijing on a summer severe rainfall simulation. Chinese J Geophys-CH, 2007, 50(5): 1172-1182. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.v50.5 [18] 张朝林, 苗世光, 李青春, 等.北京精细下垫面信息引入对暴雨模拟的影响.地球物理学报, 2007, 50(5): 1373-1382. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200705011.htm [19] Dai Y J, Zeng X B, Dickinson R E, et al. The Common Land Model (CLM). Bull Amer Meter Soc, 2003, 84: 1013-1023. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-84-8-1013 [20] Mitchell V G, Mein R G, McMahon T A. Modelling the urban water cycle. J Environ Modell & Softw, 2001, 16(7): 615-629. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364815201000299 [21] 佟华, 刘辉志, 桑建国, 等.城市人为热对北京热环境的影响.气候与环境研究, 2004, 9(3): 409-421. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200403000.htm [22] Sailor D J, Lu L. A top-down methodology for developing diurnal and seasonal anthropogenic heating profiles for urban areas. Atmos Environ, 2004, 38: 2737-2748. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.01.034 [23] Miao S G, Chen F, Lemone M A, et al. An observational and modeling study of characteristics of urban heat island and boundary layer structures in Beijing. J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2009, 48: 484-501. doi: 10.1175/2008JAMC1909.1 [24] Wang Z W, Zhang C L, Chen S, et al. On Modeling of Atmospheric Visibility Classification Forecast with Nonlinear Support Vector Machine. IEEE Conference Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC'09) and the 6th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD'09), doi: 10.1109/ICNC.2009.418,2009. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: