A New MCP Method of Predicting Long-term Wind Speed with Height Error Revision
-
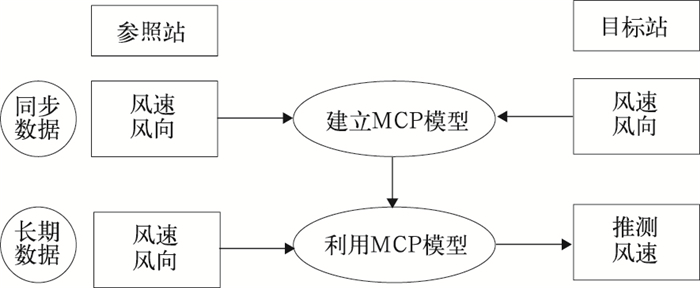
摘要: 测量相关推测法 (measure-correlate-predict,简称MCP方法) 广泛应用于风能评估,它基于风场空间相关原理,利用参照站和目标站同步短期风记录来推测目标站点长期风速和潜在风能大小。但以往任何一种MCP方法都只能推测与参照站在同一海拔高度上目标站的风速,而对于较高或较低处目标站风速的推测会出现较大误差,具有局限性。该文选取内蒙古锡林郭勒草原地区两座风能测风塔2009年5月—2010年4月的6层高度数据,拟合出Weibull双参数分布随高度变化的公式,从而得到高低空风的关系。并通过Weibull双参数分布法,在方差比MCP方法的基础上建立起一种修正的MCP方法,它修正了方差比MCP方法由于海拔高度不同而引起的误差。最后选取了4种检验因子 (相关系数、平均风速、卡方拟合优度、年平均发电量) 对方差比MCP方法和修正的MCP方法分别进行考察,并进行对比分析。结果表明:修正的MCP方法推测结果更接近于实测值,4种检验因子检验结果较方差比MCP方法更优,能够运用到难于测量地区的风能评估。Abstract: In recent years, modern wind turbine generators have grown rapidly and wind power plants have been established, delivering clean and inexhaustible energy. Therefore, the need for effective methods to evaluate wind power. Based on the fact that wind field has some degree of spatial correlation, measure-correlate-predict (MCP) algorithms can use concurrent data from target sites and a nearby reference site to predict the wind resource at target sites for wind power development. During last 15 years, over a dozen of MCP methods have been established, which differ in terms of overall approach, model definition, use of direction sectors, length of data. There are linear regression model, composite of wind speeds at two-site model, vector regression method, composite of standard deviations of two datasets and so on.But MCP algorithms mentioned above can only predict wind speed of target site with the same altitude. If the target site is higher or lower than the reference site too much, the result will be unreliable. So a new MCP method with height error revision is proposed based on data of two wind measurements, including six-layer wind data in one year. The fitted equations of Weibull parameters k and c as the function of height have been derived. By means of fitted equations, the relationship between winds of high and low altitude can be formulated. So, a method for error reduction is presented.At last, a set of performance comparison are carried out. The coefficient of correlation, the mean speed, the wind distribution and the correct annual energy production are selected as metrics at the target site, and a sample wind turbine power curve is analyzed. The mean and standard deviation of those estimates are used to characterize results. Results indicate that the new MCP method with height error revision work much better than previous ones.
-
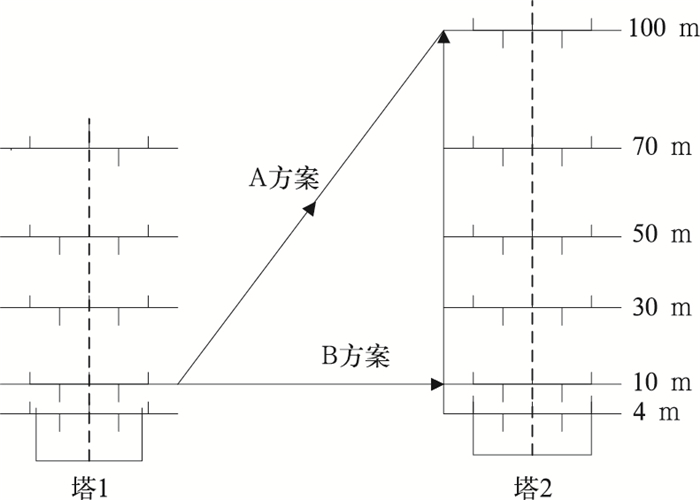
表 1 两座测风塔信息
Table 1 The geographic information of two anemometer towers
塔号 纬度 经度 海拔高度/m 塔高/m 1 44°07.455′N 116°17.812′E 1110 100 2 44°09.825′N 116°20.803′E 1107 70 表 2 2009年5—12月Weibull双参数k,c统计表
Table 2 The estimated value of c and k for wind speed of six layers from May to November in 2009
月份 4 m高度 10 m高度 30 m高度 50 m高度 70 m高度 100 m高度 c k c k c k c k c k c k 5 7.26 2.25 8.24 2.33 9.44 2.55 10.03 2.65 10.30 2.72 10.84 2.77 6 6.69 1.85 7.64 1.94 8.82 2.00 9.43 2.03 9.80 2.08 10.28 2.07 7 5.18 2.15 5.94 2.03 6.87 2.45 7.33 2.49 7.61 2.52 7.95 2.50 8 4.85 2.27 5.58 2.38 6.54 2.43 7.00 2.32 7.21 2.32 7.48 2.29 9 6.11 1.90 6.94 1.99 8.03 2.07 8.55 2.01 8.85 2.15 9.34 2.17 10 5.33 2.06 6.08 2.15 7.18 2.23 7.64 2.26 7.09 2.29 8.35 2.28 11 7.16 2.60 7.86 2.80 9.54 3.00 9.87 3.11 9.90 3.21 10.59 3.17 12 7.28 2.98 7.98 3.20 9.88 3.42 10.12 3.50 9.77 3.53 13.87 1.67 注:5月数据只有21—31日数据。 表 3 α拟合值统计表
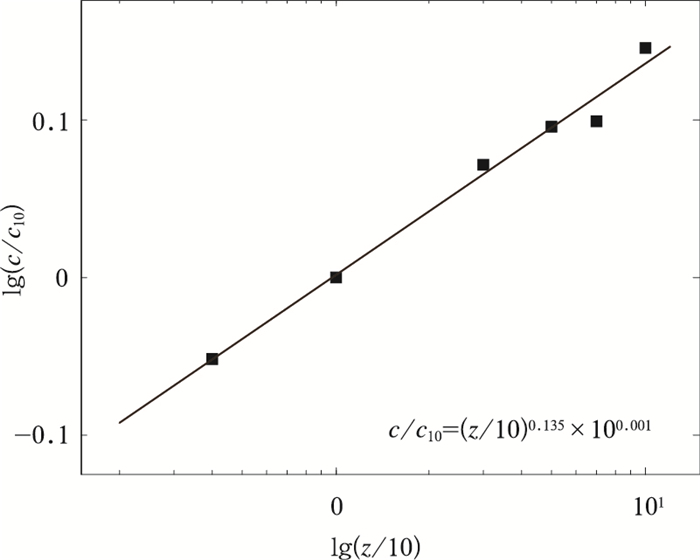
Table 3 The value of α
时间 2009-05 2009-06 2009-07 2009-08 2009-09 2009-10 2009-11 2009-12 α拟合值 0.123 0.133 0.133 0.136 0.130 0.139 0.123 0.163 表 4 两种方案预报结果检验因子统计
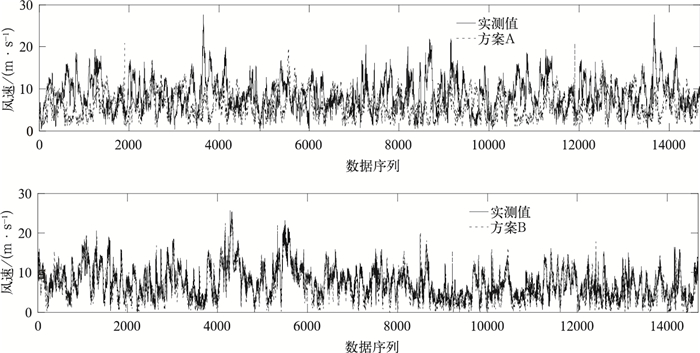
Table 4 Summary of results for Method A and Method B
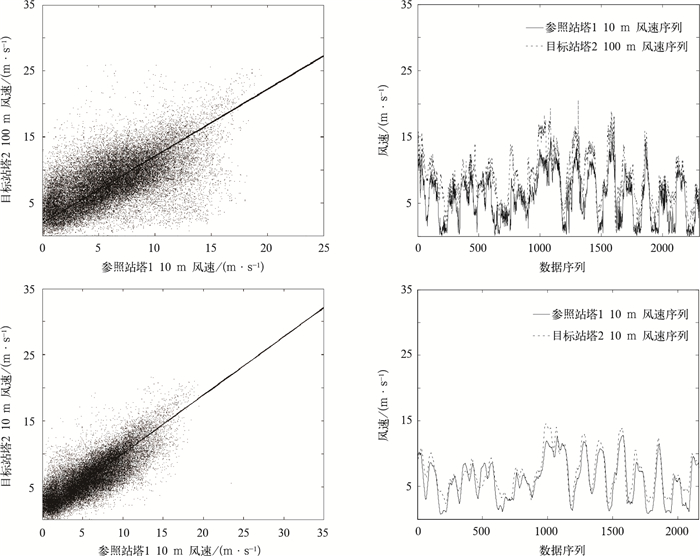
方案 R m1 m2 m3 平均值 标准差 平均值 标准差 平均值 标准差 A 0.5740 0.7652 0.2941 0.2171 0.5493 0.6594 0.4007 B 0.8713 0.9926 0.0077 0.0288 0.0016 1.0013 0.0004 -
[1] Derrick A. Development of the Measure-correlate-predict Strategy for Site Assessment. Proc BWEA, 1992: 259-265. https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/development-measurecorrelatepredict-strategy-site-assesment/ [2] Derrick A. Development of the Measure-correlate-predict Strategy for Site Assessment. Proc EWEC, 1993: 311-315. https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/development-measurecorrelatepredict-strategy-site-assesment/ [3] Nielsen M, Landberg L, Mortensen N, et al. Application of Measure-correlate-predict Approach for Wind Resource Measurement. Proc EWEA, 2001: 12-16. https://www.mysciencework.com/publication/show/f0b240ff6a30b8eedb4a144825f6881a [4] Riedel V, Strack M, Waldl H P. Robust Approximation of Functional Relationships Between Meteorological Data: Alternative Measure-correlate-predict Algorithms. Proc EWEA, 2001:17-18. [5] Draper N R, Smith H. Applied Regression Analysis. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc, 1966. [6] Woods J, Watson S. A new matrix method of predicting long-term wind roses with MCP. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1997, 66(2):85-94. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(97)00009-3 [7] Mortimer A A. A New Correlation Prediction Method for Potential Windfarm Sites. Proc BWEC, 1994: 20-27. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284603935_A_new_correlationprediction_method_for_potential_wind_farm_sites [8] 杨萍, 刘伟东, 仲跻芹, 等.北京地区自动气象站气温观测资料的质量评估.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(6): 706-715. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110608 [9] 牟聿强, 王秀丽, 别朝红, 等.风电场风速随机性及容量系数分析.电力系统保护与控制, 2009, 37(1):65-70. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2009.01.013 [10] Justus G. Nationwide assessment of potential output from wind-powered generators. J Applied Meteor, 1976, 15(7): 673-678. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1976)015<0673:NAOPOF>2.0.CO;2 [11] Dorvlo A. Estimating wind speed distribution. Energy Conversion and Management, 2002, 43(17):2311-2318. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(01)00182-0 [12] Lun I Y F, Lam J C. A study of Weibull parameters using long-term wind observations. Renewable Energy, 2000, 20(2): 145-153. doi: 10.1016/S0960-1481(99)00103-2 [13] Seguro V J, Lambert T W. Modern estimation of the parameters of the Weibull wind speed distribution for wind energy analysis. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2000, 85(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(99)00122-1 [14] Genc A. Estimation of wind power potential using Weibull distribution. Energy Sources, 2005, 27(9):809-822. doi: 10.1080/00908310490450647 [15] 徐宝清, 田德, 王海宽, 等.风速的Weibull分布参数确定方法研究.农业工程学报, 2007, 23(10):31-33. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.10.006 [16] 杨维军, 王斌.二参数Weibull分布函数对近地层风速的拟合及应用.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(1): 119-123. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990148&flag=1 [17] 徐大海, 朱蓉.大气平流扩散的箱格预报模型与污染潜势指数预报.应用气象学报, 2000, 1(4):1-7. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20000101&flag=1 [18] Tony Burton. 风能技术. 武鑫, 谷海涛, 李海东, 等译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. [19] 王国复, 徐枫, 吴增祥.气象元数据标准与信息发布技术研究.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(1):114-121. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050115 [20] 许小峰, 胡欣, 王卫丹, 等.国内大气科学发展状况及优先领域分析.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):657-664. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20060603 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: