High-performance Computing System Performance Evaluation Method and Its Application
-
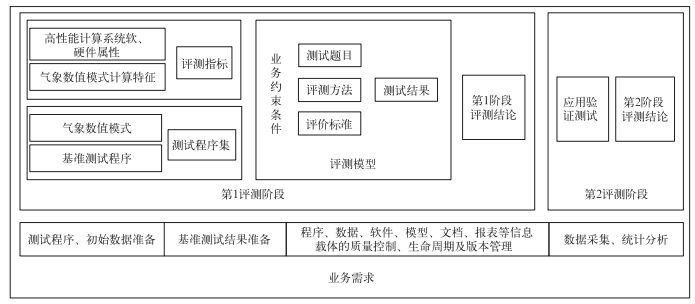
摘要: 为满足国家级气象数值模式业务系统对高性能计算资源不断增长的需求,提供规模更大、性能更优的高性能计算支撑平台,在高性能计算系统引进工作中开展了基于气象数值模式应用的高性能计算系统性能评测技术研究。该文将行业标准与实际业务应用相结合,设计了高性能计算系统性能评测方案,建立了中国气象局气象行业高性能计算系统性能评测模型。共选取10个测试程序,分别对单节点性能、网络性能和加速比等8个指标进行了测试和量化评分,并对主要测试结果中具有代表性的气象要素场进行了物理意义合理性检查。评测结果表明:评测方案设计合理,评测模型研究取得较好效果,保障了高性能计算系统引进工作顺利完成。Abstract: Meteorological numerical simulation has a high requirement on hardware structure, software realization and system performance of high performance computing system. It's one of the main applications of high performance computing (HPC). With the development of HPC, the scale of the high performance computers is expanded rapidly. The peak performance of computers increases in a continuous and rapid way. But the sustained performance achieved by the real applications does not increase in the same scale as the peak performance does. As the computer architectures and program structures are becoming much more complex, more and more factors may affect the performance of programs.Combined with the real meteorological numerical model, the technical research work of effective performance evaluation to high performance computing system has more and more important guiding significance of each stage in system's procurement, installation and performance optimization.In order to promote the ability of dealing with climate change science and technology support, China Meteorological Administration starts a new generation of national meteorological high performance computing power construction. The high performance computing system performance evaluation technology research during this period is carried out.The computing features of meteorological numerical models and its demand for high performance computing systems are analyzed in detail. Combined with the existing high performance computing system architectures and the attributes of software and hardware, the performance evaluation scheme of high performance computing system is proposed. Adopting the actual measurement, benchmark test and evaluation model methods, the comprehensive performance test of high performance computing system is carried out. The test is divided into two stages. In system selection stage, the evaluation model method and benchmark test method are used. In the system installation and debugging stage, the actual measurement method is used. The research results are applied to the practical work, conducting reasonable inspection, performance and function analysis and contrasting to the test results of mainstream high performance computing systems. Through quantitative marking, the high performance computing systems are evaluated reasonably and objectively. The practice result shows that the evaluation scheme design is reasonable and evaluation model research has achieved good results, ensuring the new generation of high performance computing system bidding work successfully completed.With the rising requirements of meteorological numerical model and the development of high performance computing environment, the test program set, evaluation method and evaluation model will be optimized and improved continuously. And on this basis, scalable high performance computing system performance evaluation model for heterogeneous system will be built.
-
表 1 测试程序清单
Table 1 The list of test programs
序号 测试程序 1 GRAPES-GLOBAL模式 (并行) 2 GRAPES-MESO模式 (并行) 3 GRAPES-4DVAR四维变分模式 (并行) 4 BCC_CSM气候系统模式 (并行) 5 BCC_AGCM大气模式 (并行) 6 GRAPES-SVD全球集合预报奇异向量分析系统 (串行) 7 WRF模式 (并行) 8 IOzone Benchmark 9 Stream Benchmark 10 PMaC_HPC_Benchmarks -
[1] 洪文董.高性能计算机的发展与气象的应用.计算机工程与应用, 2004, 40(5):32-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG200405010.htm [2] Nudd G R, Kerbyson D J, Papaefstathiou E, et al.PACE-A toolset for the performance prediction of parallel and distributed systems.Journal of High Performance Applications, 2000, 14(3): 228-251. doi: 10.1177/109434200001400306 [3] Snavely A, Wolter N, Carrington L.Modeling Application Perfo-rmance by Convolving Machine Signatures with Application Profiles.IEEE 4th Annual Workshop on Workload Characterization, Austin, 2001. [4] 宗翔, 王彬.国家级气象高性能计算机管理与应用网络平台设计.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5):629-634. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20060506 [5] 王彬, 宗翔, 田浩.国家气象计算网格的设计与建立.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(5):632-640. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100514 [6] 王斌, 周天军, 俞永强, 等.地球系统模式发展展望.气象学报, 2008, 66(6):857-869. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2008.078 [7] Yang Junli, Shen Xueshun.The construction of SCM in GR-APES and its applications in two field experiment simulations.Adv Atmos Sci, 2011, 28(3):534-550. doi: 10.1007/s00376-010-0062-8 [8] 伍湘君, 金之雁, 黄丽萍, 等.GRAPES模式软件框架与实现.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(4):539-546. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050415 [9] 薛纪善, 陈德辉, 沈学顺, 等.数值预报系统GRAPES的科学设计与应用.北京:科学出版社, 2008. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [10] 胡江林, 沈学顺, 张红亮, 等.GRAPES模式动力框架的长期积分特征.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(3):276-284. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070349&flag=1 [11] Wu Tongwen, Yu Rucong, Fang Zhang, et al.The Beijing Climate Center atmospheric general circulation model:Description and its performance for the present-day climate.Clim Dyn, 2010, 34:123-147, doi10.1007/s00382-008-0487-2. doi: 10.1007/s00382-008-0487-2 [12] 颉卫华, 吴统文.全球大气环流模式BCC_AGCM2.0.1对1998年夏季江淮流域强降水过程的回报试验研究.大气科学, 2010, 34(5):962-978. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201005010.htm [13] Dong Min, Wu Tongwen, Wang Zaizhi, et al.A simulation st-udy on the extreme temperature events of the 20th century by using the BCC_AGCM.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2012, 26(4):489-506, doi: 10.1007/s13351-012-0408-5. [14] 魏敏, 罗勇, 王兰宁, 等.海气耦合模式的优化方法研究.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(3):408-412. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050316 [15] Wu Tongwen, Li Weiping, Ji Jinjun, et al.Global carbon bud-gets simulated by the Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model for the last century.J Geophys Res, 2013, 118(10):4326-4347, doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50320. [16] Zhang Li, Wu Tongwen, Xin Xiaoge, et al.Projections of Annual mean air temperature and precipitation over the Globe and in China during the 21st century by the BCC Climate System Model BCC_CSM1.0.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2012, 26(3):362-375. [17] 辛晓歌, 吴统文, 张洁.BCC气候系统模式开展的CMIP5试验介绍.气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(5):378-382. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH201205012.htm [18] Xin Xiaoge, Wu Tongwen, Li Jianglong, et al.How well does BCC_CSM1.1 reproduce the 20th century climate change over China? Oceanic Sci Lett, 2013, 6:1-6. doi: 10.1080/16742834.2013.11447085 [19] Wei Min, Wang Lanning.The Implementation of Coupling Algorithm for MOM4 and BCC_CSM Model.International Conference on Information Science and Engineering, 2010. [20] 都志辉.高性能计算并行编程技术——MPI并行程序设计.北京:清华大学出版社, 2001. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [21] 赵立成.气象信息系统.北京:气象出版社, 2011. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm [22] Lei Hu, Ian Gorton.Performance Evaluation for Parallel Systems:A Surve.Technical Report UNSW-CSE-TR-9707, University of NSW, Sydney, Australia, 1997. [23] Brewer E A, Dellarocas C N, Colbrook A, et al.PROTEUS: A High Performance Parallel-architecture Simulator.Technical Report MIT/LCS/TR-516, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1991. [24] Hoisie A, Lubeck O, Wasserman H.Performance and scalab-ility analysis of teraflop-scale parallel architectures using multidimensional wave front applications.International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, 2000, 14(4):30-346. [25] [2012-09-25].http://www.netlib.org/linpack/. [26] 洪文董, 田浩.TFLOPS级HPC性能测试方案设计.计算机工程与应用, 2004, 40(34):57-67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2004.34.019 [27] [2006-10-28].http://www.iozone.org/. [28] [2013-01-17].http://www.cs.virginia.edu/stream/. [29] [2012-10-20].http://www.sdsc.edu/PMaC. [30] 王彬, 宗翔, 魏敏, 等.一个精细粒度实时计算资源管理系统.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(4):507-512. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080416 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载:
