The East Asian Winter Monsoon Background on the Variation of Winter Air Temperature in Northeast China
-
摘要: 利用中国气象局国家气象信息中心1961—2011年我国东北地区72个气象站月平均气温资料及NCEP/NCAR月平均海平面气压、500 hPa高度场及200 hPa与850 hPa风场再分析资料,对东亚冬季风强度与我国东北地区冬季气温序列经去除线性趋势处理后的变化特征进行对比分析。结果表明:去除线性趋势后,东亚冬季风强度与我国东北地区冬季气温序列的相关系数为-0.69,较原始序列更为显著;两者变化的阶段性较为同步,我国东北地区冬季气温于2004年已转入低温阶段,这与东亚冬季风同时转为偏强阶段关系密切;两者均存在20年左右的长周期,同样存在相近的阶段性短周期;我国东北地区冬季气温的增温变化趋势在1986年前后的增暖性气候突变中起重要作用。东亚冬季风强度与我国东北地区冬季气温年代际信号的相关系数达-0.86,较原始序列年代际相关更为显著;两者的年代际变化存在21.5年左右的共同准周期。东亚冬季风强度与我国东北地区冬季气温的年际变化序列存在4年左右的共同准周期。我国东北地区冬季气温的年际和年代际异常存在与东亚冬季风相关联的200 hPa东亚急流、500 hPa东亚大槽、乌拉尔高压、850 hPa风场、地面西伯利亚高压等的异常背景。Abstract: Using monthly mean temperature data from 72 meteorological stations in Northeast China of temperature dataset established by National Meteorological Information Center of CMA and NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data from 1961 to 2011, two sequences of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and winter air temperature in Northeast China are processed, removing the linear trend. The contrastive analysis is made on the variation characteristics between the winter monsoon intensity index and the winter air temperature in Northeast China.The result shows that two sequences change synchronously and the correlation coefficient after removal of linear trend is-0.69, which is greater than that between two original sequences. Under the background of global warming, the increasing trend of winter air temperature in Northeast China makes this relationship become weaker. When Northeast China enters the cold phase in 2004, the East Asian winter monsoon intensity index also enhancs at the same time. The warming trend of winter air temperature plays an important role in the warming climate abrupt change in 1986.Correlation coefficient between the inter-decadal signals of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and the winter air temperature in Northeast China is-0.86, which is also more obvious compared with the original sequences. A quasi-period of about 21.5 years is found for the inter-decadal variation, the winter air temperature in Northeast China is in the low stage, and the East Asian winter monsoon is in strong phase of this period at present. A 4-year quasi-period is found for the inter-annual variability.The inter-annual and inter-decadal anomalies of the winter air temperature in Northeast China are related with the abnormal background of some systems such as the East Asia westerly jet stream at 200 hPa, the East Asia trough and the high in Ural at 500 hPa, wind at 850 hPa, and the Siberian high on the ground associated with the East Asian winter monsoon. During the inter-decadal low temperature stage, the westerly jet moves further south at 200 hPa, the Siberia high and the East Asia trough is stronger at 500 hPa, the Siberia anticyclone is abnormally stronger, and there is the cyclonic circulation anomaly in western continental Europe at 850 hPa and significant northerly wind anomaly in the north region of the Okhotsk Sea. All of these anomalies reflect the inter-decadal stronger characteristic of the East Asian winter monsoon, and vice versa. The possible physical contact between the East Asian winter monsoon intensity and the winter air temperature in Northeast China may be consistent associated with inter-decadal on the inter-annual timescale.
-
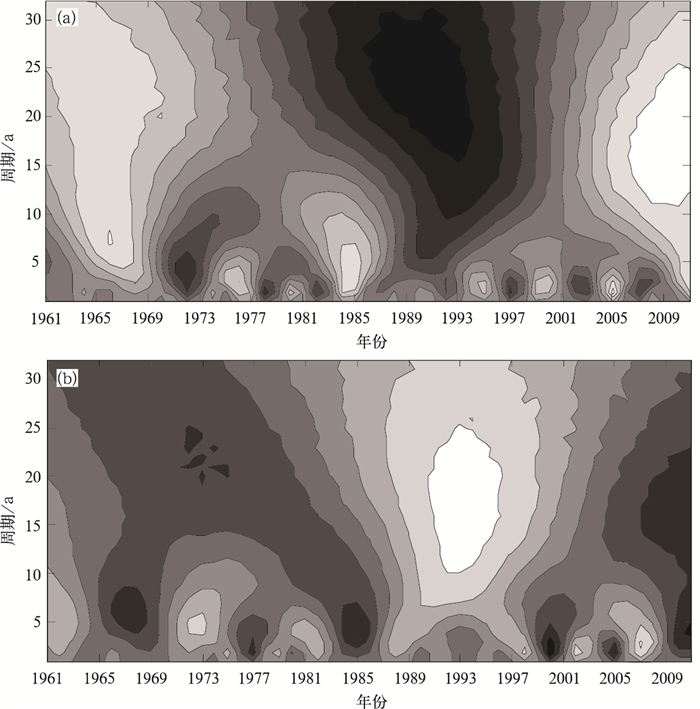
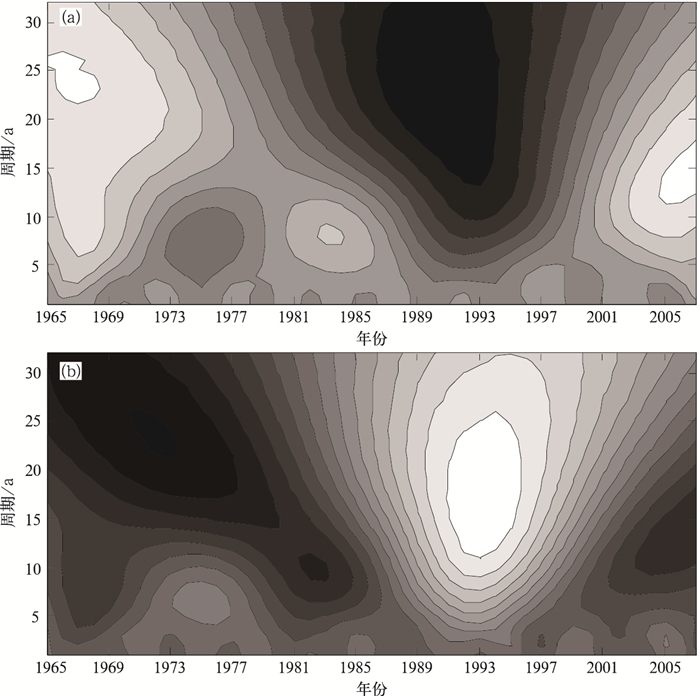
图 1 东北地区冬季气温和东亚冬季风强度指数序列与去除线性趋势后序列 (a) 及去除线性趋势后两者的累积距平曲线 (b)
Fig. 1 Original sequences of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and winter air temperature in Northeast China with the sequences after removal of linear trend (a), and the accumulative anomaly curves (b) of two sequences after removal of linear trend
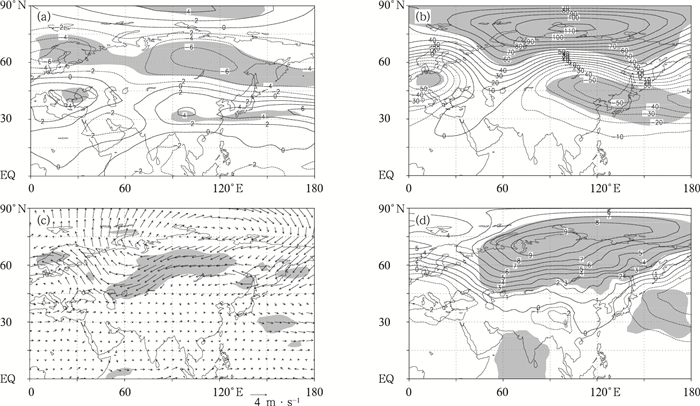
图 5 我国东北地区异常低温阶段和异常高温阶段年代际环流差异 (a) 冬季200 hPa纬向风场的差异 (单位:m·s-1),(b) 冬季500 hPa位势高度场的差异 (单位:gpm),(c) 冬季850 hPa风场的差异,(d) 冬季海平面气压场的差异 (单位:hPa)
(阴影区表示达到0.05显著性水平检验区域)
Fig. 5 Composite difference of winter 200 hPa zonal wind (unit: m·s-1)(a), 500 hPa geopotential height (unit: gpm)(b), 850 hPa wind vector (c) and sea level pressure (unit: hPa)(d) based on the colder stage and the warmer stage of winter air temperature in Northeast China
(the shaded denotes passing the test of 0.05 level)
-
[1] 郭其蕴.东亚冬季风的变化与中国气温异常的关系.应用气象学报, 1994, 5(2):218-224. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940238&flag=1 [2] 施能.近40年东亚冬季风强度的多时间尺度变化特征及其与气候的关系.应用气象学报, 1996, 7(2):175-182. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19960227&flag=1 [3] 施能, 杨永胜.1873—1996年东亚冬夏季风强度指数及其主要特征.南京气象学院学报, 1998, 21(2):208-213. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX802.006.htm [4] 崔晓鹏, 孙照勃.东亚冬季风强度指数及其变化的分析.南京气象学院学报, 1999, 22(3):322-325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX199903004.htm [5] 晏红明, 段玮, 肖子牛.东亚冬季风与中国夏季气候变化.热带气象学报, 2003, 19(4):33-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200304003.htm [6] 刘实.确定东亚冬季风强度指数的一种方法探讨.地理科学, 2007, 27(增刊):10-18. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10269-2010198772.htm [7] 康丽华, 陈文, 魏科.我国冬季气温年代际变化及其与大气环流异常变化的关系.气候与环境研究, 2006, 11(3):88-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200603008.htm [8] 陈少勇, 郭忠祥, 高蓉, 等.我国东部季风区冬季气温的气候变暖特征.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(4):478-485. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.200904013 [9] 陈峪, 任国玉, 王凌, 等.近56年我国暖冬气候事件变化.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(5):539-545. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20090504 [10] 杨萍, 刘伟东, 王启光, 等.近40年我国极端温度变化趋势和季节特征.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1):30-36. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100104&flag=1 [11] 刘实, 闫敏华, 隋波.东北三省冬季气温变化的有关研究进展.气候变化研究进展, 2009, 5(6):357-361. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200906011.htm [12] 陈海山, 孙照渤, 闵锦忠.欧亚大陆冬季积雪异常与东亚冬季风及中国冬季气温的关系.南京气象学院学报, 1999, 22(4):48-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX199904006.htm [13] 周小珊, 李辑, 杨森, 等.沈阳近百年的温度变化特征及其环流形势分析.气象科学, 2004, 24(4):424-431. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200404005.htm [14] 郭冬, 孙照渤.冬季北太平洋涛动异常与东亚冬季风和我国天气气候的关系.南京气象学院学报, 2004, 27(4):461-470. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX200404004.htm [15] 杨素英, 王谦谦, 孙凤华.中国东北南部冬季气温异常及其大气环流特征变化.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(3):334-344. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050308 [16] 秦大河, 陈振林, 罗勇, 等.气候变化科学的最新认知.气候变化研究进展, 2007, 3(2):63-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200702000.htm [17] 丁一汇.季节气候预测的进展和前景.气象科技进展, 2011, 1(3):14-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKZ201103005.htm [18] 张强, 韩永翔, 宋连春.全球气候变化及其影响因素研究进展综述.地球科学进展, 2005, 20(9):990-998. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=ZHXU201702029&dbname=CJFDPREP [19] 解小寒, 杨修群.冬季北极海冰面积异常与中国气温变化之间的年际关系.南京大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 42(6):549-561. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ200606000.htm [20] 赵宗慈, 王绍武, 罗勇, 等.气候变暖中自然和人类强迫的联合估算.科技创新导报, 2009(18):137-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2009.18.104 [21] 李庆祥, 李伟.近半个世纪中国区域历史气温网格数据集的建立.气象学报, 2007, 65(2):293-300. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2007.028 [22] Yamamoto P, Iwashima T, Sanga N K, et al.气候跃变的分析.气象科技, 1987, 15(6):49-53. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/QXKJ198706008.htm [23] 屠其璞, 王俊德, 丁裕国, 等.气象应用概率统计学.北京:气象出版社, 1984:367-369. [24] Wu B Y, Su J Z, Zhang R H.Effects of autumn-winter Arctic sea ice on winter Siberian High.Chinese Sci Bull, 2011, 56:3220-3228, doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4696-4. [25] Jeong J H, Ou T, Linderholm H W, et al.Recent recovery of the Siberian High intensity.J Geophys Res, 2011, 116, D23102, doi: 10.1029/2011JD015904. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: