Retrieval of Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth over Land from AVHRR
-
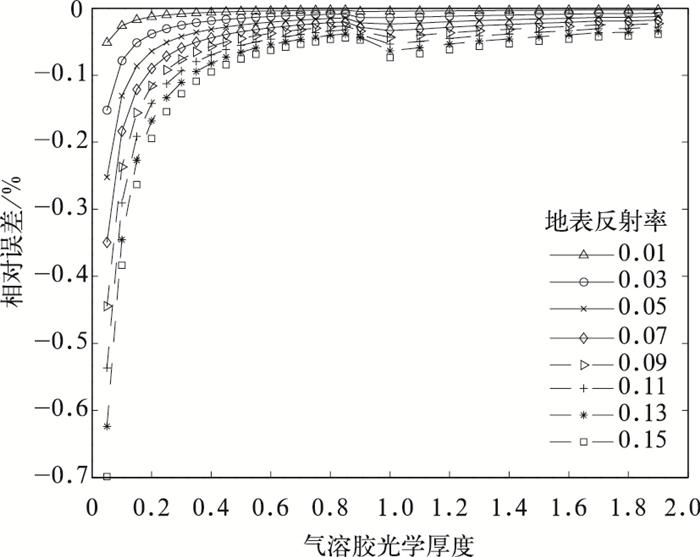
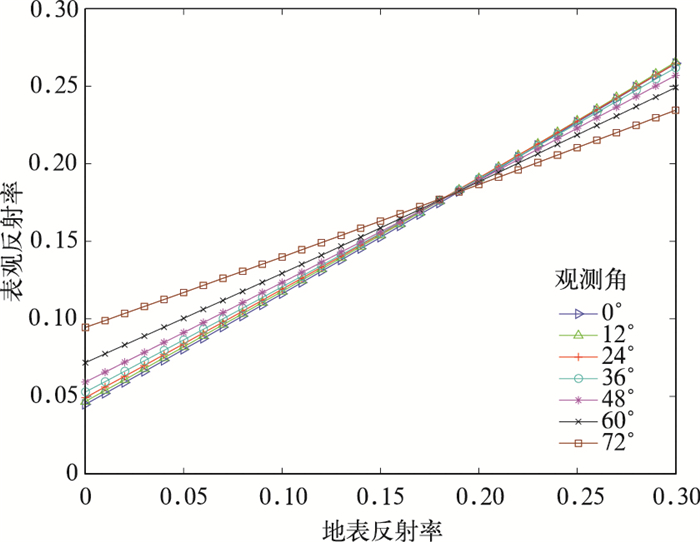
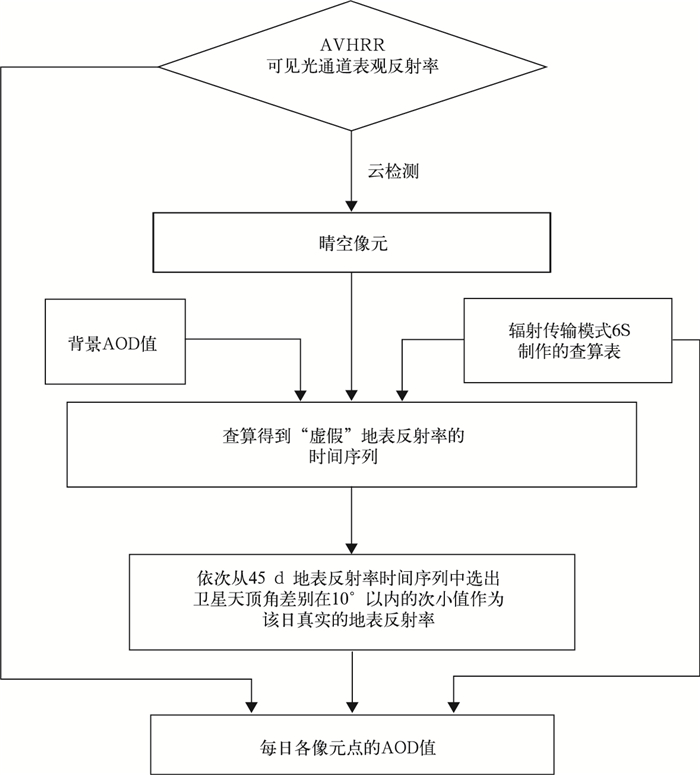
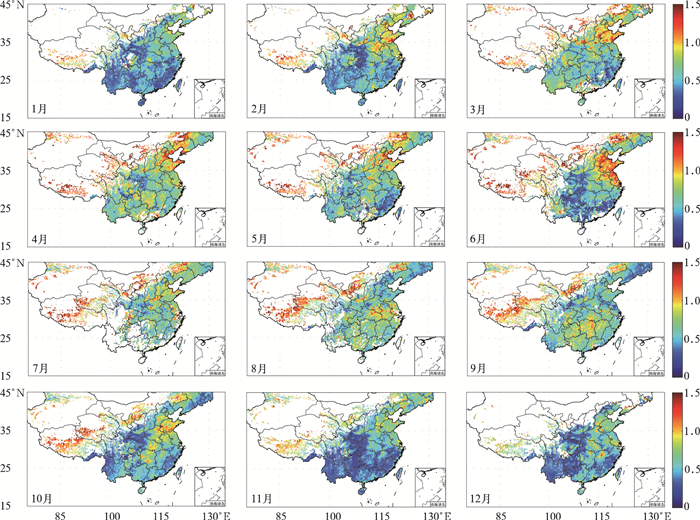
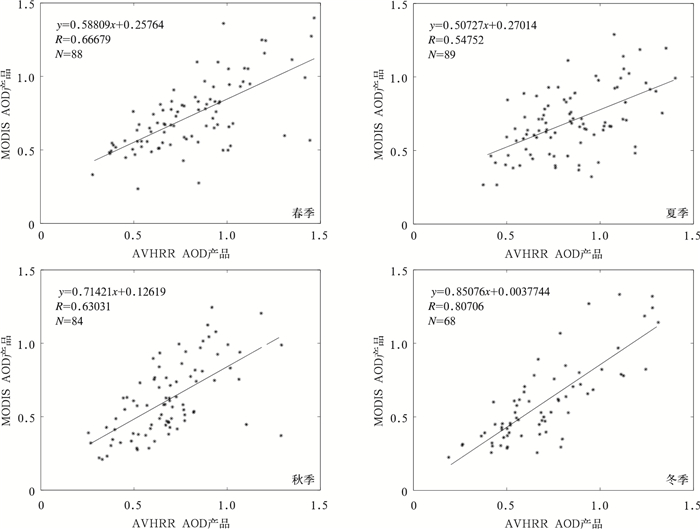
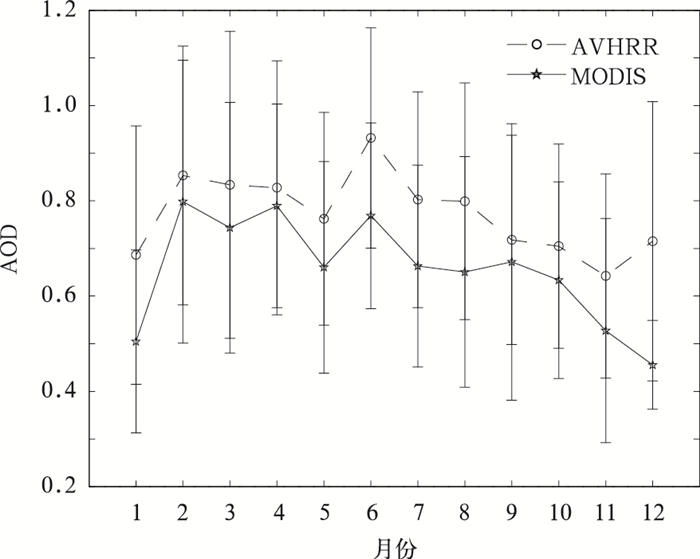
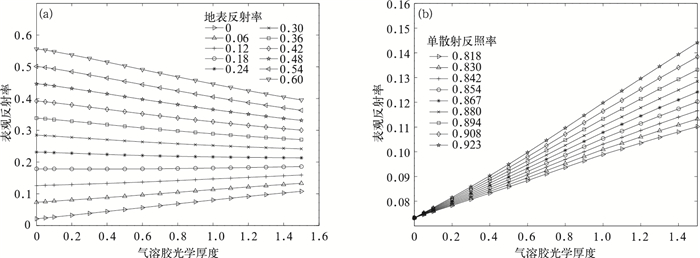
摘要: 开发AVHRR可见光通道反演陆地气溶胶光学厚度 (AOD) 的算法对于研究长时间序列AOD的变化有重要意义。AVHRR由于缺少2.1 μm通道而不能采用MODIS的暗背景算法,该文利用背景合成算法进行陆地AOD反演。背景合成算法是指假设一段时间内地表反射率变化不大且会出现相对清洁大气, 采用最小值合成即可得到地表反射率,再通过辐射传输模式6S制作的查算表查算得到AOD的反演结果。将此算法应用到2009年AVHRR中国部分陆地区域 (15°~45°N,75°~135°E) 得到AOD的时空分布,将反演结果与同期Aqua/MODIS的MOD04 AOD产品进行对比分析表明,华北和华东地区的反演效果较好,西北地区结果较差。以长江三角洲地区为例可知,AVHRR AOD产品与MODIS AOD产品以及AERONET观测的AOD相比相关系数基本在0.6以上,从时间变化规律来看,AVHRR AOD和MODIS AOD产品年变化趋势具有很好的一致性。该文为建立长时间序列AVHRR AOD数据集提供了一个较为可行的方法。Abstract: The moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) onboard NASA EOS Terra and Aqua satellites, advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR) onboard NOAA series provide important aerosol measurements. MODIS provides atmosphere aerosol optical depth (AOD) product since 2000, and AVHRR also provides AOD product since 1981 but only over ocean. Developing AOD retrieval algorithm which can also obtain AOD from AVHRR over land is very important for establishing a long term AOD data record for climate studies. As 2.1 μm band is absent, an algorithm which is different from MODIS is introduced to retrieve AOD over land from AVHRR. With this method, the surface target is assumed to remain radiometrically invariant over a certain time period and some of observations are made under clear-sky background aerosol conditions. When background aerosol conditions are given, surface reflectance can be estimated by extracting the second minimum reflectance during the previous 22 days and the future 22 days. The second darkest reflectance is chosen to reduce cloud shadow contamination. After surface reflectance is selected, AOD is retrieved from a look up table (LUT) generated with the second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum (6S) radiative transfer model. The AOD over part of China (15°—45°N, 75°—135°E) from AVHRR in 2009 is obtained based on this algorithm. The distribution pattern of AOD from this work is consistent with that of MYDO04 from MODIS in North China and East China, but has some difference in Northwest China. The daily regional mean AOD from AVHRR in the Yangtze Delta (28°—36°N, 112°—122°E) agrees well with MODIS AOD with all correlation coefficients larger than 0.5 for four seasons, even up to 0.8 in winter. The correlation coefficients are 0.70 in Beijing, 0.63 in Xianghe and 0.61 in Taihu when AOD from AERONET are used to validate the AVHRR AOD retrievals. To compare temporally varying AERONET data with spatially varying AVHRR, the time match window is limited within 30 minutes and the spatial distance is limited within 0.10. The monthly variation of AOD from AVHRR in the Yangtze River Delta is consistent with that from MODIS, but the former is larger. Error sources about this retrieving algorithm are also discussed, including different satellite zenith angles in the selected period, surface reflectance, aerosol types, background AOD, calibration and sensor noise and so on. According to these results, this algorithm has the potential for deriving long-term AOD climate data record over land from AVHRR although some uncertainties still exist. Quality control and error characterization will be further investigated in the future.
-
Key words:
- AVHRR;
- surface albedo;
- aerosol optical depth;
- MODIS;
- AERONET
-
表 1 AVHRR/3通道范围
Table 1 The band ranges of AVHRR/3
通道 波长/μm 1 0.564~0.704 2 0.696~1.012 3A 1.566~1.665 3B 3.414~4.107 4 10.04~11.60 5 11.28~12.74 -
[1] King M D, Kaufman Y J, T annre D, et al.Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space:Past, present and future.Bull Amer Meter Soc, 1999, 80(11):2229-2259. [2] Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, et al.IPCC Climate Change 2007:The Physics Science Basis.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2007. [3] Chu D A, Kaufman Y J, Zibordi G, et al.Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS).J Geophys Res, 2003, 108 (D21):4661. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234116601_Global_monitoring_of_air_pollution_over_land_from_the_Earth_Observing_System-Terra_Moderate_Resolution_Imaging_Spectroradiometer_MODIS [4] Kaufman Y J, Tanre D, Remer L A, et al.Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer.J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(D14):17051-17067. doi: 10.1029/96JD03988 [5] Kaufman Y J, Tanré D, Gordon H R, et al.Passive remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol and atmospheric correction for the aerosol effect.J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(D14):16815-16830. doi: 10.1029/97JD01496 [6] Ichoku C, Levy R, Kaufman Y J, et al.Analysis of the performance characteristics of the five channel Microtops Ⅱ Sun photometer for measuring aerosol optical thickness and precipitable water vapor.J Geophys Res, 2002, 107(D13):4179. doi: 10.1029/2001JD001302 [7] 刘健, 许健民.利用NOAA卫星AVHRR资料分析云的性质.应用气象学报, 1998, 9(4):449-455. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980466&flag=1 [8] Mishchenko M I, Geogdzhayev I V, Cairns B, et al.Aerosol retrievals over the ocean by use of channels 1 and 2 AVHRR data:Sensitivity analysis and preliminary results.Applied Optics, 1999, 38(36):7325-7341. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.007325 [9] Roger J C, Vermote E F.A method to retrieve the reflectivity signature at 3.75 μm from AVHRR data.Remote Sensing of Environment, 1998, 64(1):103-114. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00173-9 [10] Hauser A, Oesch D, Foppa N, et al.NOAA AVHRR derived aerosol optical depth over land.J Geophys Res, 2005, 110, D08204, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005439. [11] 郑有飞, 关福来, 蔡子颖, 等.我国南方中东部地区地面太阳总辐射变化规律.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(3):312-320. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110307 [12] 杨明, 李维亮, 刘煜, 等.近50年我国西部地区气象要素的变化特征.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(2):198-205. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100209 [13] Vermote E, Tanre D, Deuze J L, et al.6S User Guide Version 2, NASA Godard Space Flight Cent, Greenbelt, MD, 1997. [14] Prados A I, Kondragunta S, Pubu Ciren, et al.GOES aerosol/smoke product (GASP) over North America:Comparisons to AERONET and MODIS observations.J Geophys Res, 2007, D15201, doi: 10.1029/2006JD007968. [15] 高玲, 任通, 李成才, 等.利用静止卫星MTSAT反演大气气溶胶光学厚度.气象学报, 2012, 70(3):598-608. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2012.049 [16] 李成才, 毛节泰, 刘启汉, 等.利用MODIS遥感大气气溶胶以及气溶胶产品的应用.北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 39(增刊):108-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ2003S1014.htm [17] 李成才, 刘启汉.用MODIS遥感资料分析四川盆地气溶胶光学厚度时空分布特征.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(1):1-7. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030101&flag=1 [18] Holben B N, Eck T F, Tanre D, et al.AERONET—A federated instrument network and data achive for aerosol characterization.Rem Sen Envion, 1998, 66:1-16. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00031-5 [19] Holben B N, Tanre D, Smirnov A, et al.An emerging groud-based aerosol climatology:Aerosol optical depth from AERONET.J Geophys Res, 2001, 106(11):12067-12097. https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/new_web/PDF/AERONET_climo.pdf [20] Chu D A, Kaufman Y J, Ichoku C, et al.Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over land.Geophys Res Lett, 2002, 29(12):8007. doi: 10.1029/2001GL013205 [21] 李晓静, 张鹏, 张兴赢, 等.中国区域MODIS陆上气溶胶光学厚度产品检验.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(2):147-156. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20090203 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: