Channel Selection for Hyper Spectral CO2 Measurement at the Near-infrared Band
-
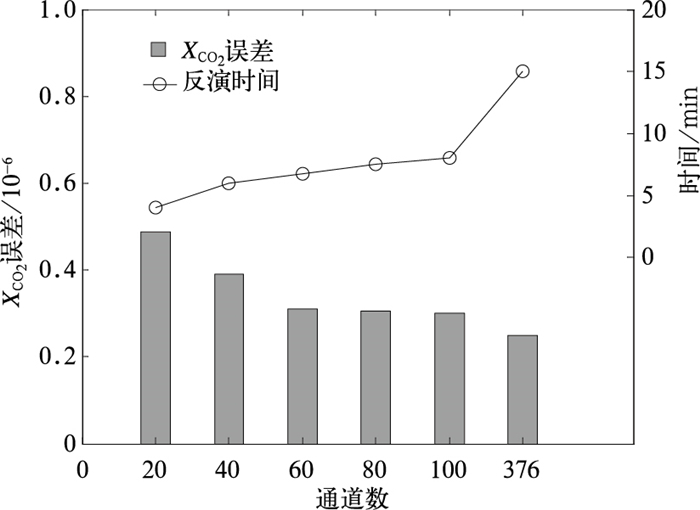
摘要: 近红外波段 (1.6 μm) 遥感可探测大气CO2含量信息,应用于碳循环研究中。宽波段、高分辨率不但对仪器研制是一个挑战,而且巨大的数据量对观测的正演、反演也是一个挑战性课题。该文应用自由度及信息量分析法,对近红外高光谱波段中探测通道进行CO2信息量分析,选择前20~100个高信息量的CO2探测通道,并进行了反演模拟测试。结果表明:前20个高信息量通道占所有通道总信息量的76.4%,仅用所选的前20个通道进行反演,与所有通道参加反演的结果相比,误差增加0.3×10-6;通道数增至60时,信息量增加,通道数再增加,信息量则增加不显著;CO2反演误差存在相似的关系。在高CO2信息量分布上,弱吸收性质的1.6 μm波段和强吸收性质的2.06 μm波段表现出不同特点。Abstract: The remote sensing of CO2 with the near-infrared sunlight can detect the source and sink information of atmospheric CO2 on the earth surface, which can be used in the research of global carbon cycle. The designing hyper spectral CO2 instrument, which will be carried by TanSat to be launched in 2015, measures CO2 column concentration using the near-infrared band. The instrument incorporates three bands with center wavelength of 0.76 μm, 1.6 μm and 2.06 μm. The spatial observing resolution is 1 km and the highest spectral resolution is 0.03 nm with the window width of 40 nm. Broad band and high resolution are a challenge for instrument manufacturing, as well as for observation processing including radiative transfer forward calculating and retrievals. The methods of degree of freedom (DOF) and information content are introduced. The CO2 information content of channels at the near-infrared band is analyzed based on the above methods. The top 20 to 100 high information content channels are selected, which are then used in a retrieval experiment based on full physical retrieval algorithm. Results show that the selected 20 channels provide as much as 74.6% of the total channel information content. There are exactly 10 channels located at P-branch and R-branch of 1.6 micron band respectively, which indicates that two absorption branches are both equally important. The CO2 retrieval error using the selected 20 channels only is 0.3×10-6 larger than retrievals using all the channels at 1.6 μm band. After the convergence of retrieval is achieved, the spectrum residual distribution shows relatively smaller residuals in high information content absorption channels and larger residuals in low information content channels. Therefore, the high information content channels control the retrieval progress.The relationship between information content and channel number is also investigated. First, information content increases with increasing channels amount to 60, but the trend becomes slow after that. The relationship between CO2 retrieval errors and high information channels amount is similar. The weak and strong CO2 absorption bands near 1.6 μm and 2.06 μm have different high information content channel distribution calculated using CO2 DOF and information content method. The high information content channels within 2.06 μm band are located at lines of moderate absorption radiance, and the distribution at two branches of 2.06 micron is asymmetry.It should be noted that the optical depth of aerosol is lower in the retrieval experiment, and cloud (thin cirrus) is also not included. Due to the disturbance of the backscatters of atmospheric aerosol and cirrus to radiation observed by satellite at near-infrared bands, the impact of cloud and aerosol to channel selection needs further investigations.
-
Key words:
- CO2;
- retrieval;
- channel selection;
- information content
-
表 1 1.6 μm波段高CO2信息量通道
Table 1 High information content channels selected at 1.6 μm band
序号 波数 归一化信息量 1 6212.72 1.000 2 6214.58 0.996 3 6238.77 0.994 4 6242.66 0.982 5 6237.37 0.977 6 6243.91 0.976 7 6219.83 0.975 8 6211.03 0.973 9 6241.42 0.966 10 6233.17 0.964 表 2 模拟计算和反演条件
Table 2 The simulation and retrieval conditions
模拟条件 参数 大气参数 美国标准大气 CO2含量 390×10-6 地表反照率 0.15 气溶胶类型 城市型,能见度为23 km 光谱范围 1594~1624 nm 光谱分辨率 0.08 nm 太阳天顶角 60° -
[1] 江志红, 丁裕国.中国近百年气温场变化成因的统计诊断分析.应用气象学报, 1997, 8(2):175-185. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19970224&flag=1 [2] 卞林根, 高志球, 陆龙骅, 等.长江下游农业生态区CO2通量的观测试验.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(6):828-834. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050608 [3] Toon G, Blavier J F, Washenfelder R, et al.Total Column Carbon Observing Network (TCCON).Optical Society of America, 2009. [4] 程红兵, 王木林, 温玉璞, 等.我国瓦里关山、兴隆温室气体CO2, CH4和N2O的背景浓度.应用气象学报, 2003, 14(4):402-409. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030450&flag=1 [5] 温玉璞, 汤洁.瓦里关山大气二氧化碳浓度变化及地表排放影响的研究.应用气象学报, 1997, 8(2):129-136. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19970219&flag=1 [6] 周凌晞, 刘立新, 张晓春, 等.我国温室气体本底浓度网络化观测的初步结果.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(6):641-645. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080601 [7] 温玉璞, 季秉法.用非色散红外气体分析仪进行大气CO2本底浓度的测量.应用气象学报, 1993, 4(4):476-480. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19930480&flag=1 [8] Rayner P J, O'Brien D M.The utility of remotely sensed CO2 concentration data in surface source inversions.Geophys Res Lett, 2001, 28(1):175-178. doi: 10.1029/2000GL011912 [9] Chahine M T, Chen L, Dimotakis P, et al.Satellite remote sounding of mid-tropospheric CO2.Geophys Res Lett, 2008, 35(17):L17807. doi: 10.1029/2008GL035022 [10] Crevoisier C, Chedin A, Matsueda H, et al.First year of upper tropospheric integrated content of CO2 from IASI hyperspectral infrared observations.Atmos Chem Phys, 2009, 9(14):4797-4810. doi: 10.5194/acp-9-4797-2009 [11] Kulawik S S, Jones D, Nassar R, et al.Characterization of Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES) CO2 for carbon cycle science.Atmos Chem Phys, 2010, 10(12):5601-5623. doi: 10.5194/acp-10-5601-2010 [12] Yokota T, Yoshida Y, Eguchi N, et al.Global concentrations of CO2 and CH4 retrieved from GOSAT:First preliminary results.Sola, 2009, 5:160-163. doi: 10.2151/sola.2009-041 [13] Crisp D, Atlas R M, Breon F M, et al.The orbiting carbon observatory (OCO) mission.Advances in Space Research, 2004, 34(4):700-709. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.08.062 [14] Velazco V, Buchwitz M, Bovensmann H, et al.Towards Space Based Verification of CO2 Emissions from Strong Localized Sources:Fossil Fuel Power Plant Emissions as Seen by a CarbonSat Constellation.University of WollongongResearch Online, 2011. [15] Crevoisier C, Chedin A, Scott N A.AIRS channel selection for CO2 and other trace-gas retrievals.Quart J Royal Meteor Soc, 2003, 129(593):2719-2740. doi: 10.1256/qj.02.180 [16] Collard A D.Selection of IASI channels for use in numerical weather prediction.Quart J Royal Meteor Soc, 2007, 133(629):1977-1991. doi: 10.1002/qj.v133:629 [17] Kuai L, Natraj V, Shia R L, et al.Channel selection using information content analysis:A case study of CO2 retrieval from near infrared measurements.Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2010, 111(9):1296-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2010.02.011 [18] Saitoh N, Imasu R, Ota Y, et al.CO2 retrieval algorithm for the thermal infrared spectra of the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite:Potential of retrieving CO2 vertical profile from high-resolution FTS sensor.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2009, 114(D17). [19] Rodgers C D.Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding:Theory and Practice (Series on Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Vol.2).Singapore:World Scientific, 2000. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/24/1/015801/pdf [20] O'Dell C W, Connor B, Bosch H, et al.The ACOS CO2 retrieval algorithm—Part Ⅰ: Description and validation against synthetic observations.Atmos Meas Tech, 2012, 5(1):99-121. doi: 10.5194/amt-5-99-2012 [21] Crisp D, Fisher B M, O'Dell C, et al.The ACOS CO2 retrieval algorithm-Part Ⅱ: Global XCO2 data characterization.Atmos Meas Tech, 2012, 5:687-707. doi: 10.5194/amt-5-687-2012 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: