Comparative Analysis on the Applicability of Drought Indexes in the Huaihe River Basin
-
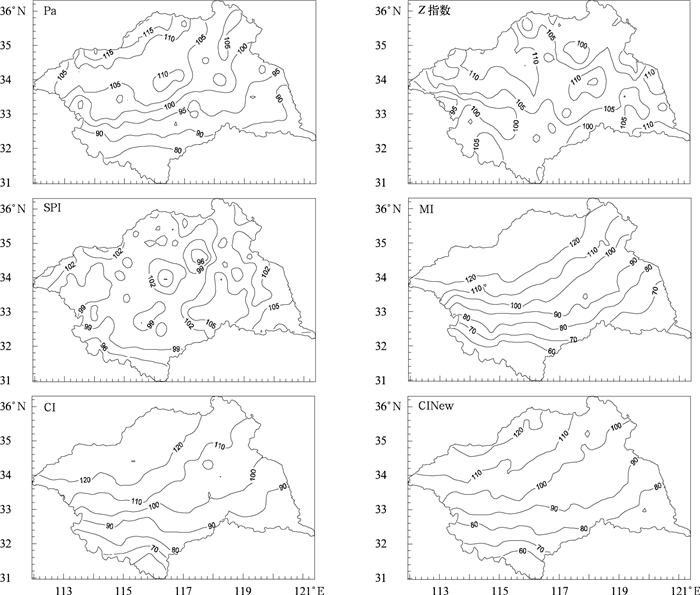
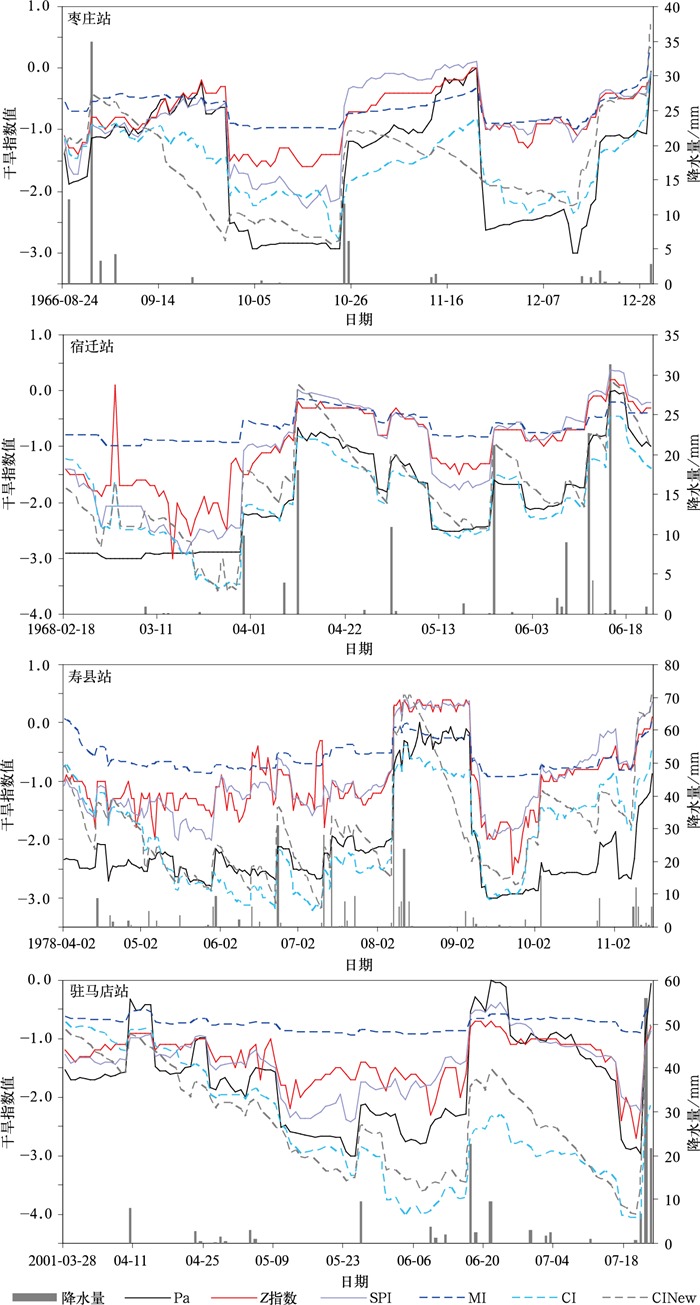
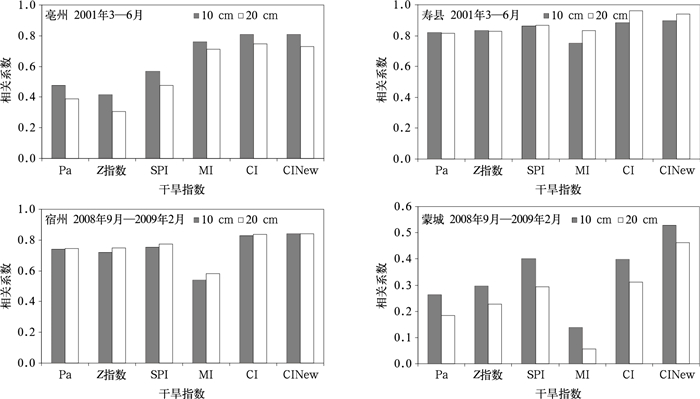
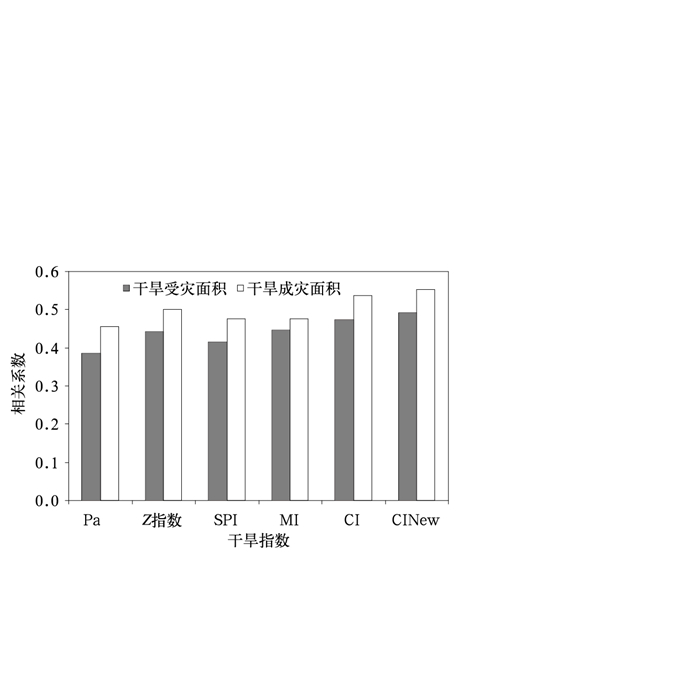
摘要: 利用淮河流域河南、安徽、山东、江苏4省170个站1961—2010年逐日气温、降水以及土壤墒情和干旱灾情资料,从干旱年际变化、季节演变、空间分布、典型干旱过程诊断、不合理跳跃点以及与土壤墒情、干旱灾情相关性等方面,对比分析降水距平百分率 (Pa)、Z指数、标准化降水指数 (SPI)、相对湿润度指数 (MI)、综合气象干旱指数 (CI) 和改进的CI (CINew) 在淮河流域的适用性。结果表明:各干旱指数对淮河流域的典型旱年均有较好的诊断能力;在干旱季节演变及空间分布的诊断方面,Pa,MI,CI和CINew与实际较为吻合,而Z指数和SPI诊断效果较差;在典型干旱过程诊断以及不合理跳跃次数方面,CI和CINew更能刻画出干旱发生发展机制,而Pa,Z指数,SPI,MI效果较差;与土壤墒情和历史干旱灾情相关性方面,CI和CINew比Pa,Z指数,SPI,MI具有更好的相关性。即对于淮河流域的干旱监测诊断,CI和CINew要优于Pa,Z指数,SPI及MI,具有更好的适用性。Abstract: Based on daily temperature and precipitation data of 170 meteorological stations from 1961 to 2010, as well as the soil moisture data and historical drought disaster information in the Huaihe River Basin, the applicability of drought indexes is analyzed. The indexes include the precipitation anomaly percentage (Pa), the Z index (Z), the standardized precipitation index (SPI), the relative moisture index (MI), the compound drought index (CI), the improved CI (CINew) and so on. They are examined from the aspects of inter-annual variation, seasonal evolution, spatial distribution, diagnostic analysis of typical drought processes, unreasonable jumps, the relativity analysis of the soil moisture and drought disaster information. The following results can be reached: All of these drought indexes can be used to diagnose the typical drought years in the Huaihe River Basin effectively, including the year of 1966, 1968, 1976, 1978, 1986, 1988, 1997, 1999, 2001 and so on. When analyzing the seasonal evolution and spatial distribution, both Z index and SPI are not effective, while the diagnosis results of indexes such as Pa, MI, CI and CINew are relatively in consistency and accordant with the fact. As to the diagnoses of typical drought processes and unreasonable jumps, CI and CINew are more effective in describing the mechanism. Analysis on drought relevance to soil moisture and historical drought disaster information shows that CI and CINew have more stable relativity and higher correlation coefficients than Pa, Z index, SPI and MI.In conclusion, as to the monitoring and diagnosis of the drought in the Huaihe River Basin, the applicability of CI and CINew indexes are superior to indexes of Pa, Z index, SPI and MI. The drought is a very complex scientific problem, which is related with many factors such as underlying surface, crop, soil type, rainfall, evaporation and so on. The drought index can have better applicability only when it is built based on reasonable consideration of the occurrence and development mechanism of drought and various influencing factors.
-
Key words:
- drought index;
- drought process;
- applicability;
- the Huaihe River Basin
-
表 1 各干旱指数对应的干旱等级划分标准
Table 1 The division standard of drought grades corresponding to the drought indexes
干旱指数 干旱等级 无旱 轻旱 中旱 重旱 特旱 Pa/% (-40,+∞) (-60,-40] (-80,-60] (-95,-80] [-100,-95] Z指数 (-0.5,+∞) (-1.0,-0.5] (-1.5,-1.0] (-2.0,-1.5] (-∞,-2.0] SPI (-0.5,+∞) (-1.0,-0.5] (-1.5,-1.0] (-2.0,-1.5] (-∞,-2.0] MI (-0.4,+∞) (-0.65,-0.4] (-0.8,-0.65] (-0.95,-0.8] (-1.0,-0.95] CI (-0.6,+∞) (-1.2,-0.6] (-1.8,-1.2] (-2.4,-1.8] (-∞,-2.4] CINew (-0.6,+∞) (-1.2,-0.6] (-1.8,-1.2] (-2.4,-1.8] (-∞,-2.4] 表 2 代表站及典型干旱过程
Table 2 The representative stations and typical drought processes
代表站 干旱时段 枣庄站 1966年8—12月 宿迁站 1968年2—6月 寿县站 1978年4—11月 驻马店站 2001年3—7月 -
[1] 叶笃正, 黄荣辉.长江黄河流域旱涝规律和成因研究.济南:山东科学技术出版社, 1996. [2] 邹旭恺, 张强.近半个世纪我国干旱变化的初步研究.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(6):679-687. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080607 [3] 江剑民.我国大陆干旱指数及其年际变化.大气科学, 1991, 15(1):43-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK199101004.htm [4] 吴洪宝.我国东南部夏季干旱指数研究.应用气象学报, 2000, 11(2):137-144. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20000222&flag=1 [5] 张强, 邹旭恺, 肖风劲, 等. 气象干旱等级. GB/T20481—2006, 中华人民共和国国家标准. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006: 1-17. [6] 邹旭恺, 任国玉, 张强.基于综合气象干旱指数的中国干旱变化趋势研究.气候与环境研究, 2010, 15(4):371-378. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201004006.htm [7] 江远安, 赵逸舟, 陈颖, 等.干旱指数CI的确定及其在新疆的应用.沙漠与绿洲气象, 2010, 4(2):18-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJQX201002006.htm [8] 赵海燕, 高歌, 张培群, 等.综合气象干旱指数修正及在西南地区的适用性.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(6):698-705. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110607 [9] 杨丽慧, 高建芸, 苏汝波, 等.改进的综合气象干旱指数在福建省的适用性分析.中国农业气象, 2012, 33(4):603-608. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNY201204019.htm [10] 王劲松, 黄玉霞, 冯建英, 等.径流量Z指数与Palmer指数对河西干旱的监测.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(4):471-477. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.200904012 [11] 李剑锋, 张强, 陈晓宏, 等.基于标准降水指标的新疆干旱特征演变.应用气象学报, 2012, 23(3):322-330. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120308&flag=1 [12] 冯建设, 王建源, 王新堂, 等.相对湿润度指数在农业干旱监测业务中的应用.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(6):766-772. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110616 [13] 侯威, 张存杰, 高歌.基于气候系统内在层次性的气象干旱指数研究.气象, 2012, 38(6):701-711. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2012.06.008 [14] 张强, 鞠笑生, 李淑华.三种干旱指标的比较和新指标的确定.气象科技, 1998, 27(2):48-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ802.008.htm [15] 于敏, 王春丽.不同卫星遥感干旱指数在黑龙江的对比应用.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(2):221-231. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110211 [16] 杨世刚, 杨德保, 赵桂香, 等.三种干旱指数在山西省干旱分析中的比较.高原气象, 2011, 30(5):1406-1414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201105029.htm [17] 吴永祥, 姚惠明, 王高旭, 等.淮河流域极端旱涝特征分析.水利水运工程学报, 2011(4):149-153. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSY201104028.htm [18] 温克刚, 庞天荷.中国气象灾害大典河南卷.北京:气象出版社, 2007:7-82. [19] 温克刚, 翟武全.中国气象灾害大典安徽卷.北京:气象出版社, 2007:10-73. [20] 温克刚, 王建国, 孙典卿.中国气象灾害大典山东卷.北京:气象出版社, 2007:9-119. [21] 温克刚, 卞光辉.中国气象灾害大典江苏卷.北京:气象出版社, 2007:124-159. [22] 安徽省水利厅.安徽水旱灾害.北京:中国水利水电出版社, 1998:182-184. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: