Inter-annual Variability of Winter Asia-Pacific Oscillation and Its Relationship with the East Asian Climate Anomalies
-
摘要: 利用1948—2011年NCEP/NCAR月平均再分析资料和1951—2010年我国160站降水量资料,研究了冬季亚洲—太平洋区域的大气遥相关及其与东亚冬季风和降水的关系。结果表明:冬季在亚洲—西太平洋与中、东太平洋中低纬度对流层上层扰动温度之间存在类似于夏季的亚洲—太平洋涛动 (APO) 现象,即当东亚中低纬度对流层中、上层偏暖时,中东太平洋中低纬度对流层中上层温度偏冷,反之亦然。冬季APO可以反映冬季亚洲—太平洋东西向热力差异强度变化,与夏季相比,冬季APO遥相关在亚洲的中心位置略偏南、偏东,且冬季APO与大气环流关系与夏季也有所不同;当冬季APO指数偏高时,对流层上层东亚大槽位置偏西,而东亚热带地区的高压向北伸展,导致我国南方对流层为深厚的异常反气旋系统所控制,此时南方地区对流层低层盛行异常的偏东北气流,并伴随水汽辐散和异常下沉运动,南方降水偏少;冬季APO指数与ENSO有紧密联系。Abstract: Using 1948-2011 NCEP/NCAR monthly reanalysis data and 1951-2010 precipitation data at 160 meteorological stations of China, the empirical orthogonal function (EOF), correlation analysis and composite analysis methods, the winter (December, January and February) atmospheric teleconnection over the Asian-Pacific and its association with East Asian winter monsoon and precipitation are examined. Results show an Asian-Pacific Oscillation (APO) teleconnection in upper-tropospheric temperature disturbance between the Asian-western Pacific and the central-eastern Pacific region during winter, which is similar to the APO phenomenon during summer. When the mid-upper troposphere temperature in mid-lower latitudes of East Asia is warmer, it is colder in mid-lower latitudes of the central and eastern North Pacific, and vice versa. The APO reflects the variability of the zonal thermal contrast between Asia and North Pacific. Compared to summer, the Asian anomalous center of DJF APO is southward and eastward in position. DJF APO index does not show a significant linear trend. The power spectrum analysis shows that the APO index has the varying periods of 2-6 years. Corresponding to a higher APO index, geopotential height disturbance in mid-upper tropospheres is lower in mid-higher latitudes of East Asia and it is higher in mid-higher latitudes of central and eastern North Pacific. Also, there is a "seesaw" in lower latitudes between the Asian-western Pacific region and the central-eastern Pacific, but with a reversed phase comparing to that in higher latitudes. This anomalous feature in geopotential height in the upper troposphere indicates a westward long-wave trough in East Asia and a northward high pressure in the tropics of East Asia, with a deep anti-cyclonic anomaly over southern China. Wind anomalies of northeasterly prevail over southern China in the lower troposphere, with divergence anomalies of water vapor and downward motion anomalies in southern China. Accordingly, the local precipitation decreases. However, these relationships between DJF APO and atmospheric circulation are different from those during summer. Moreover, the APO index is highly correlated with ENSO as well.
-
图 1 冬季北半球0°~60°N区域200~300 hPa平均T′距平场的EOF模态
(a) EOF1(方框分别代表东亚—西太平洋和中东太平洋区域),(b) EOF2
Fig. 1 EOF modes of anomaly of December-January-February (DJF) 200-300 hPa mean T′ overthe Northern Hemisphere (0°-60°N) (a) EOF1(boxes denote Asian-western Pacific and central-eastern Pacific, respectively), (b) EOF2
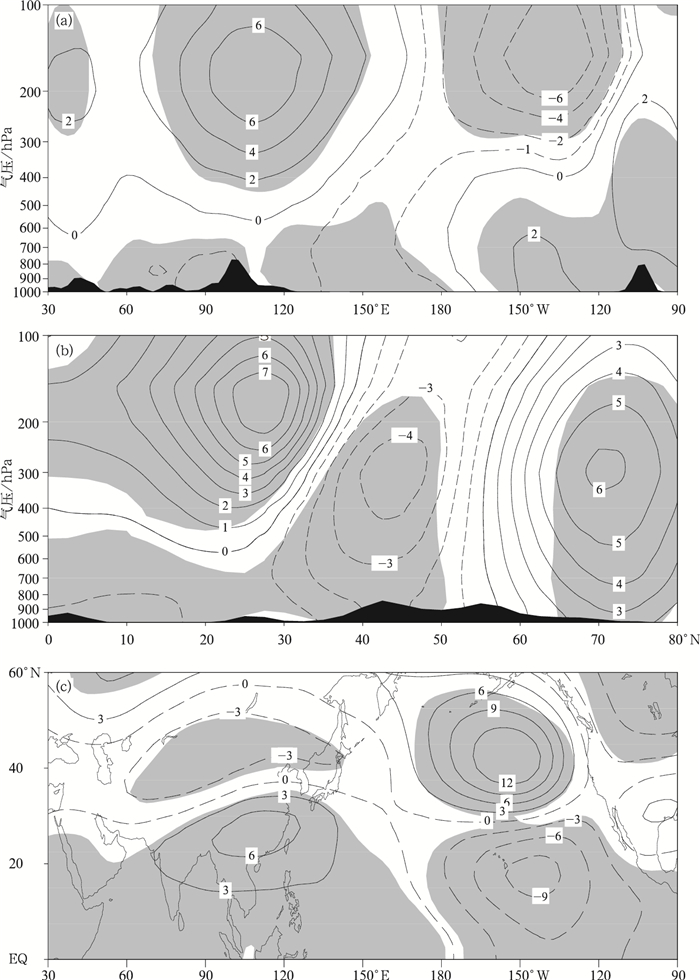
图 3 冬季APO指数回归的同期T′(灰色区域表示达到0.05显著性水平,黑色区域表示地形)
(a) 沿25°N的经度-高度垂直剖面,(b)250 hPa T′水平分布,(c) 表面气温
Fig. 3 Regressed T′ against DJF APO index (the grey denotes passing the test of 0.05 level, the black denotes the topography)
(a) longitude-height cross section along 25°N, (b)T′ at 250 hPa, (c) surface temperature
图 4 冬季APO高指数年和低指数年合成的冬季H′
(单位:dagpm,灰色区域代表达到0.05显著性水平,黑色区域代表地形)(a) 沿25°N的经度-高度剖面,(b) 沿115°E的纬度-高度剖面,(c)200 hPa H′水平分布
Fig. 4 Composite difference of winter mean H′ between high and low DJF APO indices
(the grey denotes passing the test of 0.05 level, the black denotes the topography)(a) longitude-height cross section along 25°N, (b) latitude-height cross section along 115°E, (c)H′ at 200 hPa
图 5 冬季APO高指数年和低指数年合成差值 (灰色区域代表达到0.05显著性水平,黑色区域代表地形)
(a)200 hPa风场,(b)850 hPa风场,(c) 海平面气压 (单位:hPa),(d) 沿107.5°~120°E纬度-垂直环流差值剖面 (水平速度单位:m·s-1,垂直速度单位:10-2 Pa·s-1)
Fig. 5 Composite difference between the high and low DJF APO indices
(the grey denotes passing the test of 0.05 level, the black denotes the topography) (a)200 hPa wind, (b)850 hPa wind, (c) sea level pressure (unit:hPa), (d) latitude-height cross section along 107.5°-120°E (unit for horizontal wind is m·s-1, unit for vetical wind is 10-2 Pa·s-1)
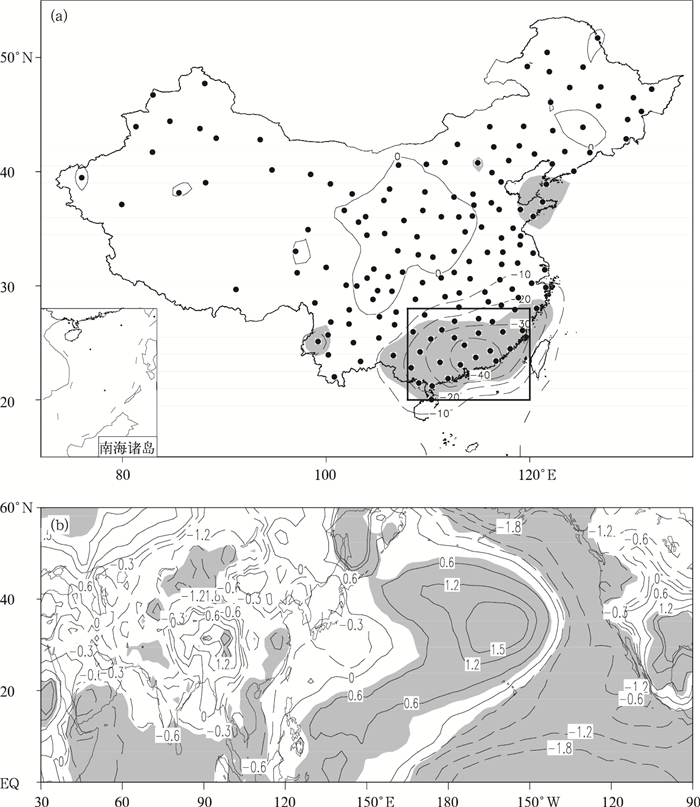
图 6 冬季APO高和低指数年合成的差值 (灰色区域代表达到0.1显著性水平)
(a) 冬季总降水量 (单位:mm,圆圈代表 160站的分布,方框指示着南方地区),(b) 表面气温 (单位:℃)
Fig. 6 Composite difference between the high and low DJF APO indices
(the grey denotes passing the test of 0.1 level) (a) winter total rainfall (unit:mm, dots denote 160 stations in China, the box denotes southern China), (b) surface air temperature (unit:℃)
-
[1] Wallace J M, Gutzler D S.Teleconnections in the geopotential height field during the Northern Hemisphere winter. Mon Wea Rev, 1981, 109:784-812. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1981)109<0784:TITGHF>2.0.CO;2 [2] Nitta T.Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impacts on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J Meteor Soc Japan, 1987, 65:373-390. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.65.3_373 [3] Lau K M.East Asian summer monsoon rainfall variability and climate teleconnection. J Meteor Soc Japan, 1992, 70:211-241. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.70.1B_211 [4] Yang S, Lau K M, Kim K M.Variations of the east Asian jet stream and Asian-Pacific-American winter climate. J Climate, 2002, 15:306-325. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<0306:VOTEAJ>2.0.CO;2 [5] Ding Q H, Wang B.Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer. J Climate, 2005, 18:3484-3505. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254871604_Circumglobal_Teleconnection_in_the_Northern_Hemisphere_Summer [6] Zhang P Q, Yang S, Kousky V E.South Asian high and Asian-Pacific-American climate teleconnection. Adv Atmos Sci, 2005, 22:915-923. doi: 10.1007/BF02918690 [7] Wang B, Wu R G, Fu X H.Pacific-east Asian teleconnection:How does ENSO affect Asian climate? J Climate, 2000, 13:1517-1536. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2 [8] 王振华.西太平洋暖池热含量变化与东亚冬季风关系.海洋通报, 2009, 28(4):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB200904004.htm [9] 陈隽, 孙淑清.东亚冬季风异常与全球大气环流变化I.强弱冬季风影响的对比研究.大气科学, 1999, 23:101-111. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1999.01.12 [10] Zhu Y.An index of East Asian winter monsoon applied to description the Chinese mainland winter temperature changes. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2008, 22(4):522-529. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200805011.htm [11] Wang L, Chen W, Zhou W, et al.Interannual variations of East Asian trough axis at 500 hPa and its association with the East Asian winter monsoon pathway. J Climate, 2009, 22:600-614. doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2295.1 [12] 陈文, 顾雷, 魏科, 等.东亚季风系统的动力过程和准定常行星波活动的研究进展.大气科学, 2008, 32(4):950-966. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200804019.htm [13] 武炳义, 黄荣辉.冬季北大西洋涛动极端异常变化与东亚冬季风.大气科学, 1999, 23(6):641-651. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK199906000.htm [14] Wu B Y, Wang J.Impacts of winter Arctic Oscillation on Siberian high, the East Asian winter monsoon. Adv Atmos Sci, 2002, 19(2):297-320. doi: 10.1007/s00376-002-0024-x [15] Ramage C S.Role of the maritime continent on the atmospheric circulation. Mon Wea Rev, 1968, 96:365-370. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1968)096<0365:ROATMC>2.0.CO;2 [16] Chang C P, Erickson J, Lau K M.Northeasterly cold surges and near-equatorial disturbances over the winter-MONEX area during 1974.Part Ⅱ:Planetary scale aspects. Mon Wea Rev, 1980, 108:293-312. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252229380_Northeasterly_Cold_Surges_and_Near-Equatorial_Disturbances_over_the_Winter_MONEX_Area_During_December_1974_Part_II_Planetary-Scale_Aspects [17] 徐国昌, 李梅芳.青藏高原温度与东亚环流.高原气象, 1985, 4(2):185-189. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX198502010.htm [18] Ding Y H, Krishnamurti T N.Heat budget of the Siberian high and the winter monsoon. Mon Wea Rev, 1987, 115:2428-2449. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<2428:HBOTSH>2.0.CO;2 [19] Zhao P, Chen L X.Interannual variability of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and its relation to circulation. Adv Atmos Sci, 2001, 18(1):106-116. doi: 10.1007/s00376-001-0007-3 [20] 陈海山, 孙照渤.欧亚积雪异常分布对冬季大气环流的影响Ⅰ:观测研究.大气科学, 2003, 27(3):304-316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200303001.htm [21] 赵平, 陈隆勋.青藏高原大气热量源汇在海-地-气相互作用准4年振荡中的作用.科学通报, 2000, 45(15):1666-1671. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.15.018 [22] Zhao P, Zhang X D, Li Y F, et al.Remotely modulated tropical-North Pacific ocean-atmosphere interactions by the South Asian high. Atmos Res, 2009, 94:45-60. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.01.018 [23] Zhao P, Yang S, Jian M Q, et al.Relative controls of Asian-Pacific summer climate by Asian land and tropical-North Pacific sea surface temperature. J Climate, 2011, 24:4165-4188. doi: 10.1175/2011JCLI3915.1 [24] 李崇银.中国东部地区的暖冬与厄尔尼诺.科学通报, 1989, 4:282-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198904011.htm [25] Li Chongyin.Interaction between anomalous winter monsoon in East Asia and El Nio events. Adv Atmos Sci, 1990, 7:36-46. doi: 10.1007/BF02919166 [26] 穆明权, 李崇银.东亚冬季风年际变化的ENSO信息Ⅰ.观测资料分析.大气科学, 1999, 23(3):276-285. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK199903002.htm [27] 布和朝鲁, 纪立人.东亚冬季风活动异常与热带太平洋海温异常.科学通报, 1999, 44(3):252-259. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199903003.htm [28] 梁巧倩, 简茂球, 罗会邦.东亚冬季风与海温在年际尺度上的耦合关系分析.热带海洋学报, 2004, 23(2):19-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY200402003.htm [29] 施能.近40年东亚冬季风强度的多时间尺度变化特征及其与气候的关系.应用气象学报, 1996, 7(2):175-182. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19960227&flag=1 [30] 晏红明, 杞明辉, 肖子牛, 等.冬季亚洲大陆的热力差异对亚洲季风活动的影响.大气科学, 2005, 29(4):549-564. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200504005.htm [31] 武炳义, 苏京志, 张人禾.秋-冬季节北极海冰对冬季西伯利亚高压的影响.科学通报, 2011, 56(27):2335-2343. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201127011.htm [32] 赵平, 张人禾.东亚-北太平洋偶极型气压场及其与东亚季风年际变化的关系.大气科学, 2006, 30(2):307-316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200602012.htm [33] 郭琪蕴.东亚夏季风强度指数及其变化分析.地理学报, 1983, 38(3):207-216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX199602002.htm [34] Jiang X W, Yang S, Li Y Q, et al.Dominant modes and their links to surface climate of the winter tropospheric temperature over the Tibetan Plateau. J Climate, 2013, 26:9043-9060. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00774.1 [35] Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al.The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1996, 77:437-470. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2 [36] Zhao P, Zhu Y N, Zhang R H.An Asia-Pacific teleconnection in summer tropospheric temperature and associated Asian climate variability. Climate Dyn, 2007, 29:293-303. doi: 10.1007/s00382-007-0236-y [37] North G R, Bell T, Cahalan R, et al.Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal function. Mon Wea Rev, 1982, 110:699-706. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<0699:SEITEO>2.0.CO;2 [38] 赵平, 陈军明, 肖栋, 等.夏季亚洲—太平洋涛动与大气环流和季风降水.气象学报, 2008, 66(5):716-729. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2008.066 [39] Jhun J G, Lee E J.A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J Climate, 2004, 15:711-726. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255646209_A_New_East_Asian_Winter_Monsoon_Index_and_Associated_Characteristics_of_the_Winter_Monsoon [40] 郭琪蕴.东亚冬季风的变化与中国气温异常的关系.应用气象学报, 1994, 5(2):218-225. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940238&flag=1 [41] 徐建军, 朱乾根, 周铁汉.近百年东亚冬季风的突变性和周期性.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(1):1-8. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990140&flag=1 [42] 陆琛莉.东亚冬季风经向异常与后期嘉兴梅雨关系.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(2):238-242. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080241 [43] 曾琮, 胡斯团, 梁建茵, 等.东亚冬季风异常与广东前汛期旱涝的初步分析.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(5):645-654. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050511 [44] 王启祎, 丁一汇, 江滢.亚洲季风活动及其与中国大陆降水关系.应用气象学报, 1998, 9(增刊Ⅰ):84-89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX8S1.010.htm [45] 王宁.东亚冬季风指数研究进展.地理科学, 2007, 27(增刊Ⅰ):103-110. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGQX201510004028.htm [46] Wu B, Wang J.Winter Arctic Oscillation, Siberian High and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys Res Lett, 2002, 29(19):1897, doi: 10.1029/2002GL015373. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: