Quality Control and Analysis of in Situ Soil Moisture Data in Yunnan
-
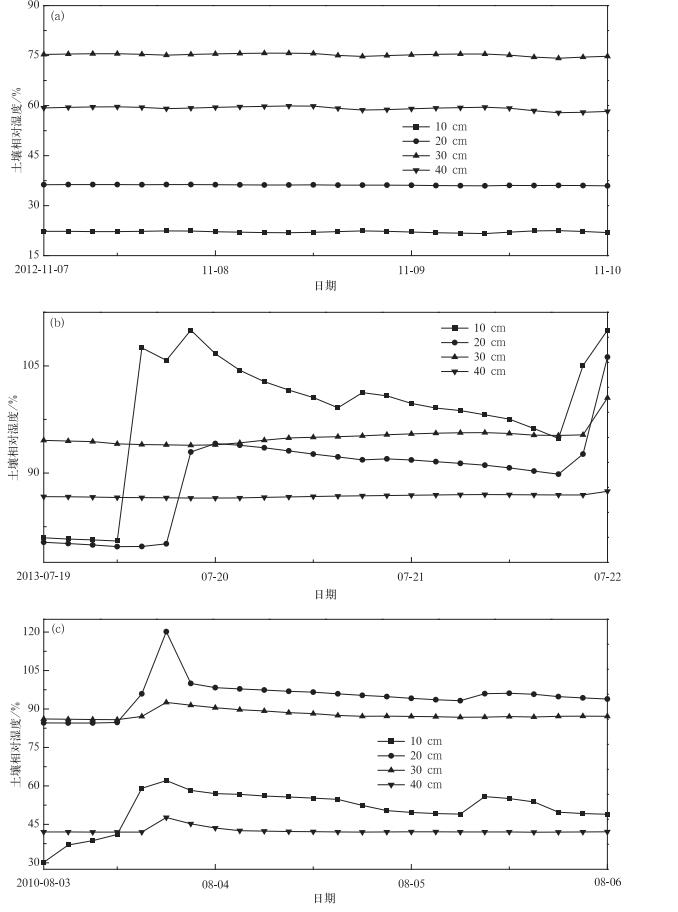
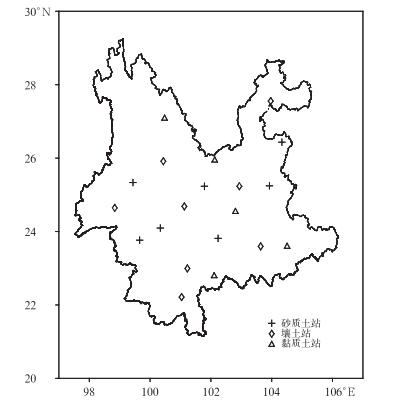
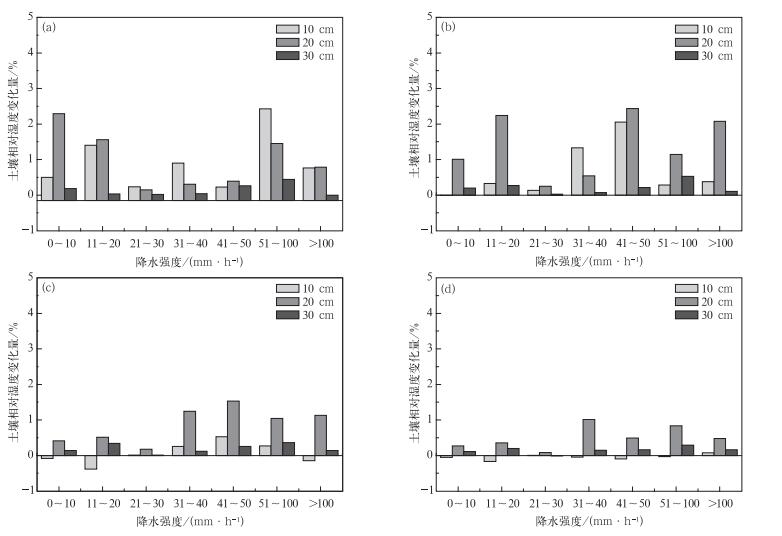
摘要: 土壤湿度是控制陆地和大气间水分和能量交换过程的重要变量,而自动气象站观测是获取地表土壤湿度的主要手段。地表自动气象站观测的准确性能够直接影响其应用效果,因此, 开展自动气象站土壤湿度质量控制分析具有重要意义。基于2010—2014年云南省37个自动气象站土壤湿度数据,采用谱分析方法,以观测值及其Savitzky-Golay二次导数的平均值、均方差、变化率等统计量为判据,筛选剔除了观测数据中的随机噪声、异常峰值和异常平稳值。结果表明:云南省自动气象站观测数据均有缺测,两种异常值中,异常平稳值占绝大部分。与降水时间序列对比发现,不同降水强度下各层土壤湿度变化存在一定差异,砂质土站点对降水的响应最为明显,黏质土站点雨后土壤湿度变化幅度最小。Abstract: Soil moisture is a variable that plays a crucial role in the energy and mass exchange between the atmosphere and land, and it is often used as an environment factor and process parameter in meteorology researches. However, due to the diversity of climatological conditions and differences in measurement setup, the quality of the soil moisture measurement is highly variable, which may have a significant impact on the data accuracy. Therefore, appropriate quality characterization is desired.Based on soil moisture data of 37 stations of Yunnan in 2010-2014, the spectrum-based approaches are used to eliminate 3 kinds of abnormal data. The constant, spike and noisy, caused by saturation of the signal and unresponsive sensors, are screened out by procedures analysis on the time series. The data integrality is shown not good, especially at some stations in the northwest of Yunnan Province, where the instruments are newly set up. After the first instability period, the data quality gradually improves. Among all abnormal values, the proportion of constant is up to 97% in all stations. The distribution of stations containing more spike shows less distinct pattern.Compared to the related meteorological data, different soil types show different responses to the precipitation. Sandy soil shows quicker reaction to the precipitation, and the change of soil moisture is more significant as well. As the rainfall intensity increases, the rise of the moisture increases too. Loam soil shows continuous rise in the few hours after the rainfall, but the variation is rather weaker, and the deeper soil moisture changes relatively smoothly. Clayey soil has a weak relationship with precipitation, and the soil moisture descends more quickly in the deeper layer than other soil type. It's found that the rainfall intensity and the soil moisture rise are not simply positively correlated, the soil moisture rises less after downpour, and these responses need further research.
-
表 1 2010—2014年云南省自动气象站土壤数据缺测值、异常值与有效值所占比例
Table 1 Ratio of missing, abnormal and valid data of automatic meteorological stations in Yunnan during 2010—2014
区站号 缺测值/% 异常值/% 有效值/% 56586 3 23 43 56649 23 6 71 56651 37 23 40 56654 46 14 40 56697 20 34 47 56739 58 11 32 56748 55 5 40 56751 39 17 43 56752 1 74 24 56757 16 7 77 56763 24 15 62 56768 19 19 62 56775 17 26 57 56778 24 44 32 56785 25 29 46 56788 13 24 63 56835 11 24 66 56836 48 5 47 56841 65 8 28 56842 1 36 63 56843 14 12 74 56844 24 18 58 56856 23 22 55 56875 11 29 61 56880 2 27 71 56881 0 44 56 56883 46 6 48 56889 39 20 41 56946 42 11 48 56951 39 25 36 56959 24 25 51 56964 32 5 63 56966 44 14 41 56977 47 3 50 56985 0 66 34 56994 30 26 44 59205 56 16 28 -
[1] 孙丞虎, 李维京, 张祖强, 等.淮河流域土壤湿度异常的时空分布特征及其与气候异常关系的初步研究.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(2):129-138. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050217 [2] 云文丽, 侯琼, 王海梅, 等.不同土壤水分对向日葵光合光响应的影响.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4):476-482. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20140411 [3] Hearn J, Eichler J, Hare C, et al.Effect of soil moisture on chlorine deposition.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 267:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.044 [4] Li Yue, Liu Yinghui, Wang Yalin, et al.Interactive effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil N mineralization in a Stipa krylovii grassland in Inner Mongolia, China.Journal of Arid Land, 2014, 5:571-580. http://manu20.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_ghqkx/EN/abstract/abstract306.shtml [5] Li Xiaolan, Zhang Hongsheng.Soil moisture effects on sand saltation and dust emission observed over the Horqin Sandy Land area in China.J Applied Meteor Sci, 2014, 28(3):444-452. http://d.scholar.cnki.net/detail/SSJD_U/SSJD14071600002597 [6] Chen Lin, Zhang Jiabao, Zhao Bingzi, et al.Carbon mineralization and microbial attributes in straw-amended soils as affected by moisture levels.J Applied Meteor Sci, 2014, 28(2):167-177. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lin_Chen113/publication/260482793_Carbon_Mineralization_and_Microbial_Attributes_in_Straw-Amended_Soils_as_Affected_by_Moisture_Levels/links/56b21dce08aed7ba3fedb908.pdf?inViewer=0&pdfJsDownload=0&origin=publication_detail [7] Yamazaki K.A study of the impact soil moisture and surface albedo changes on global climate using the MRI, GCM-I.J Meteor Soc Japan, 1989, 67:123-145. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.67.1_123 [8] 朱乾根, 兰红平, 沈桐立.土壤湿度和地表反射率变化对中国北方气候影响的数值研究.气象学报, 1996, 54(4):493-500. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1996.051 [9] 李巧萍, 丁一汇, 董文杰.土壤湿度异常对区域短期气候影响的数值模拟试验.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(1):1-11. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20070102 [10] Yin J, Zhan X, Zheng Y, et al.Impact of quality control of satellite soil moisture data on their assimilation into land surface model.Geophys Res Lett, 2014, 41(20):7159-7166. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060659 [11] Yin J, Zhan X, Zheng Y, et al.Enhancing model skill by assimilating SMOPS blended soil moisture product into Noah Land Surface Model.J Hydrometeorology, 2015, 16:917-931. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-14-0070.1 [12] 陈怀亮, 冯定原, 邹春辉, 等.用遥感资料估算深层土壤水分的方法和模型.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(2):105-110. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990262&flag=1 [13] 杨晓峰, 陆其峰, 杨忠东.基于AMSR-E土壤湿度产品的LIS同化试验.应用气象学报, 2013, 24(4):435-445. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20130406 [14] Hubbard K G, Rosenberg N J, Nielsen D C.Automated weather data network for agriculture.Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 1983, 109(3):213-222. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1983)109:3(213) [15] Robock A, Vinnikov K Y, Srinivasan G, et al.The global soil moisture data bank.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2000, 81(6):1281-1299. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(2000)081<1281:TGSMDB>2.3.CO;2 [16] Dorigo W A, Wagner W, Hohensinn R, et al.The International Soil Moisture Network:A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements.Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011, 15(5):1675-1698. http://www.oalib.com/paper/2302340 [17] Albergel C, de Rosnay P, Gruhier C, et al.Evaluation of remotely sensed and modelled soil moisture products using global ground-based in situ observations.Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 118:215-226. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.11.017 [18] Liu Y Y, Dorigo W A, Parinussa R M, et al.Trend-preserving blending of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals.Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 123:280-297. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.03.014 [19] Crow W T, Berg A A, Cosh M H, et al.Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products.Rev Geophysics, 2012, 50(2):3881-3888. http://www.academia.edu/13729156/Upscaling_sparse_ground-based_soil_moisture_observations_for_the_validation_of_coarse-resolution_satellite_soil_moisture_products [20] 陈立春, 戴江平, 吴霭霞, 等.土壤水分自动观测数据分析与订正.安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(29):16299-16303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.29.090 [21] 陈东东, 王明田, 张玉芳, 等.四川省土壤湿度自动站和人工观测数据对比分析.安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(29):18066-18068. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.29.115 [22] 张弢, 王润元, 丁文魁, 等.GStarDZN2型自动站与人工测定土壤湿度对比分析.中国农村小康科技, 2014(4):69-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKKJ201404016.htm [23] 刘瑜, 赵尔旭, 黄玮, 等.2005年初夏云南严重干旱的诊断分析.热带气象学报, 2007, 23(1):35-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200701005.htm [24] 姜丽霞, 李帅, 纪仰慧, 等.1980—2005年松嫩平原土壤湿度对气候变化的响应.应用生态学报, 2009, 20(1):91-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200901016.htm [25] 徐虹, 程晋昕. 基于TVDI的云南省遥感干旱监测//第31届中国气象学会年会S10第四届气象服务发展论坛——提高水文气象防灾减灾水平, 推动气象服务社会化发展, 2014. [26] Dorigo W A, Xaver A, Vreugdenhil M, et al.Global automated quality control of in situ soil moisture data from the International Soil Moisture Network.Vadose Zone Journal, 2013, 12(3):918-924. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274435045_Global_Automated_Quality_Control_of_In_Situ_Soil_Moisture_Data_from_the_International_Soil_Moisture_Network [27] 钟爱华, 黄慧君, 徐安伦."2010.8.27 "大理州大到暴雨过程分析.云南大学学报:自然科学版, 2012(增刊Ⅰ):56-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ2012S1013.htm [28] 黄慧君, 钟爱华, 陈红玉.云南省大理州"2011.7.14 "强降水过程诊断分析.云南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 35(增刊Ⅰ):253-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ2013S1021.htm [29] Albergel C, Dorigo W, Reichle R H, et al.Skill and global trend analysis of soil moisture from reanalyses and microwave remote sensing.J Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(4):1259-1277. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-12-0161.1 [30] 北京农业大学.农业气象.北京:农业出版社, 1981. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: