Progress on Mechanism and Prediction Methods for Persistent Extreme Precipitation in the Yangtze-Huai River Valley
-
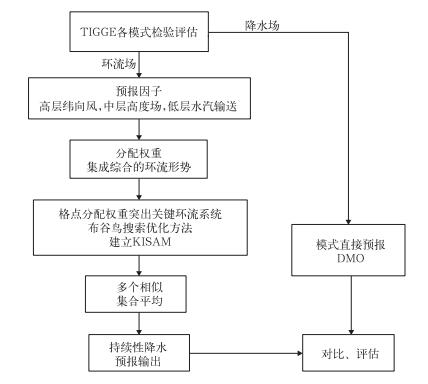
摘要: 持续性极端降水过程会引发严重的洪涝灾害,是我国主要的灾害性天气之一,其形成机理和预报理论与方法研究受到广泛关注。近年来,针对持续性极端降水的形成机理和预报方法研究取得了一系列进展,主要包括:开展了我国区域性持续性极端降水事件的自动识别方法研究,研制建立了江淮流域持续性极端降水的大尺度环流概念模型,并提取了1~2周的前兆信号;从东亚—太平洋遥相关型 (EAP) 角度探究其对持续性极端降水的影响机理,并探讨利用EAP对江淮流域持续性极端降水进行预报的可行性。此外,在上述研究的基础上发展了基于关键影响系统的持续性极端降水的物理统计预报方法。
-
关键词:
- 江淮流域持续性极端降水;
- 东亚—太平洋遥相关型;
- 前期信号;
- 物理统计预报
Abstract: Persistent extreme precipitation (PEP) results in severe floods in China, especially in the Yangtze-Huai River Valley (YHRV), making it one of the main weather disasters in China. There exists an urgent need to enhance understandings on the formation mechanism and developing rules of PEP and extend forecast valid time of the PEP for the scientific decision of government.In recent years, progress has been achieved from related studies on the formation mechanism and forecast method of PEP in the YHRV which has caught wide attention. The method of automatically identifying regional PEP events is established which is named as RePEEI (Regional Persistent Extreme Event Identifier). Conceptual model is established on the large-scale circulation patterns responsible for PEP events, revealing that concurrent anomalies of the key influential systems are important causes for the occurrence and maintenance of PEP, and precursor signals (about 1-2 weeks prior to the onset of PEP) are investigated. Taking East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern (EAP) as a point of penetration, the mechanism of its effects on PEP is explored. Moreover, it indicates that whether the PEP will occur in YHRV is decided by the north-south location of high systems at low latitudes. Schematics for precursor circulation features of typical EAP patterns responsible for persistent extreme precipitation events in the YHRV is established. And corresponding precursor signals are also obtained, the feasibility of predicting PEP on the use of EAP is discussed. Furthermore, based on the key influential systems and precursor signals found above in characteristic large-scale circulation patterns, the physical statistical forecast model for the prediction of PEP is established, which is named as KISAM (Key Influential Systems based Analog Model), with the idea of parameter optimization method and ensemble mean introduced, using different predictors and cosine angular analog method with weight assigned.However, the forecast of PEP is still a challenge, especially when the forecast lead time extends to medium range or even extended range. The performance of numerical models in predicting the occurrence and location of PEP still leaves much to be solved. How to further improve direct outputs of numerical models and combine model outputs with physical statistical methods to improve the forecast of PEP is a research area that needs much more study. -
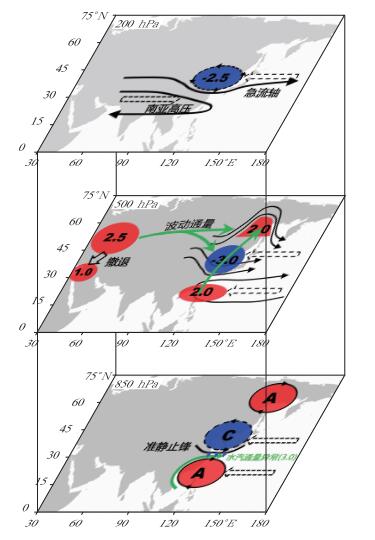
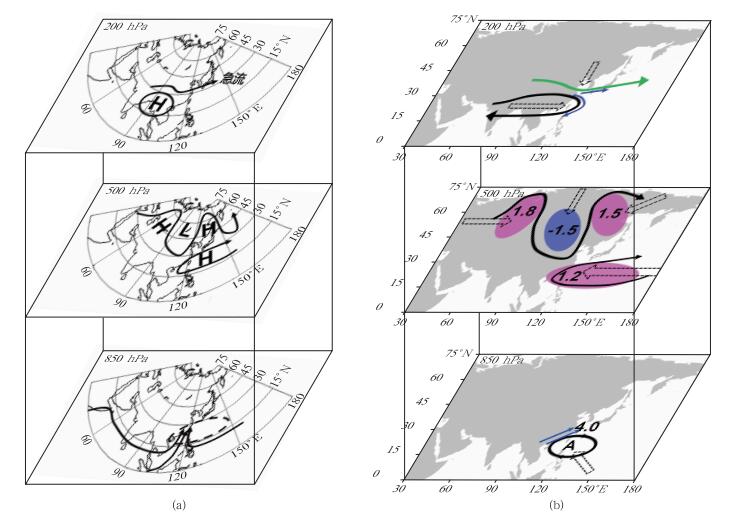
图 1 双阻型持续性暴雨同期和前期环流配置概念模型[20, 23]
(a) 同期三维环流配置概念模型 (H和L分别代表高值 (脊) 和低值 (槽) 的位置;200 hPa, 500 hPa图中粗实线代表位势高度以及急流轴;850 hPa图中粗实线代表水汽输送路径,虚线代表异常反气旋),(b) 前期环流演变特征三维概念模型 (200 hPa图中黑色实线代表 12500 gpm线,绿色实线代表急流轴,空心箭头代表移动方向,蓝色箭头代表风场; 500 hPa图中带箭头实线代表流线,紫色阴影代表正高度距平,蓝色阴影代表负高度距平,数字代表标准差,单位:dagpm; 850 hPa图中A代表异常反气旋中心,蓝色箭头代表风场)
Fig. 1 Schematics for concurrent and precursor circulation features responsible for PEP events of double blocking high type (from reference [20, 23])
(a) concurrent conceptual model schematics (H and L denote locations of high (ridge) and low (trough) systems, respectively; solid lines denote geopotential height contours and locations of the jet axis at 200 hPa and 500 hPa; solid lines with arrowheads denote water-vapour transport paths and dashed line denotes the location of the anomalous anticyclone which contribute most heavily to the anomalous moisture supply at 850 hPa), (b) schematics for precursor circulation features (black solid line with arrowhead denotes geopotential height contour of 12500 gpm, the green line denotes the jet axis, hollow arrows denote moving direction and blue arrows denote direction of the horizontal wind at 200 hPa; black solid lines with arrowhead denote streamlines, purple and blue shadings denote positive anomalies and negative anomalies of geopotential height with the regional average normalized anomaly values (unit:dagpm) at 500 hPa; A denotes the anomalous anticyclone, blue arrows denote anomalous southwesterlies at 850 hPa)
图 2 在江淮流域造成持续性极端降水的典型EAP三维概念模型 (虚箭头刻画各个关键系统的传播轨迹;红色代表正高度场距平,蓝色代表负距平,上面的数字表示标准化高度场距平强度;字母A和C分别代表异常反气旋和气旋)[26]
Fig. 2 Schematics for precursor circulation features of typical EAP patterns responsible for persistent extreme precipitation events in the YHRV (hollow arrows denote propagating routes of these precursors, red and blue shadings denote positive and negative anomalies of geopotential height with regional average normalized anomaly values, respectively; A denotes the anomalous anticyclone, while C denotes the anomalous cyclone)(from refrence [26])
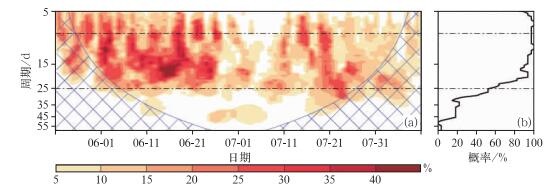
图 3 EAP指数的小波分解[31]
(a) 显著 (达到0.05显著性水平) 的周期成分在某日的累积概率 (阴影),(b) 达到0.05显著性水平的全局能谱的累积概率
Fig. 3 Wavelet analysis of EAP index (from refrence [31])
(a) occurrence frequency (the shaded) of significant oscillations accumulated (0.05 level at least), (b) occurrence frequency of global wavelet spectrums at 0.05 significant level
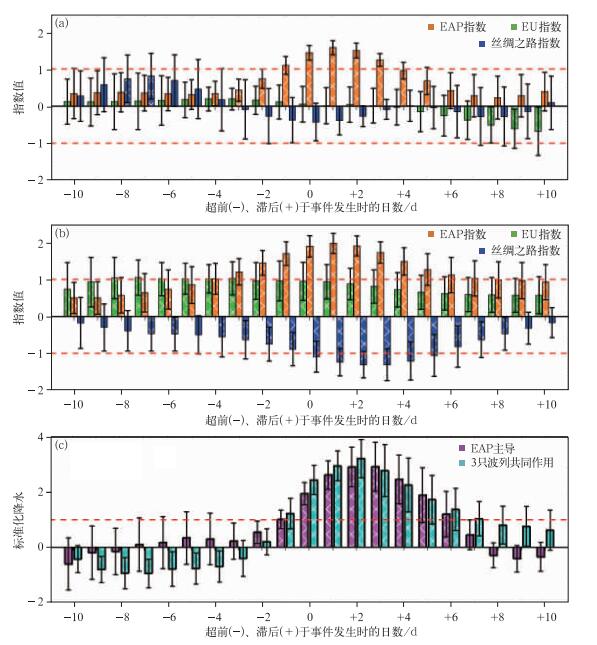
图 5 两种遥相关背景下的持续性极端降水事件中,各遥相关指数合成的时间演变 (横坐标0代表降水开始日数,负数表示降水开始前,正数表征降水开始后)[31]
(a) 只有东亚—太平洋遥相关作用,(b)3支遥相关波列同时存在时,(c) 两种事件中降水的合成
Fig. 5 The composition of the corresponding teleconnection index during PEP events under the effect of two different teleconnection patterns (0 on abscissa indicates the day when precipitation occurred, negative and positive numbers indicate days before and after the occurrence of precipitation, respectively)(from refrence [31])
(a) only East Asia/Pacific teleconnection exists, (b) three kinds of teleconnection exists, (c) the composition of precipitation associated with two teleconnection patterns
表 1 EAP导致的持续强降水事件发生期间降水和EAP的低频性质分布
Table 1 Distribution of low frequency oscillation of precipitation and EAP in each event when PEP occurred
年份 周期 10~30 d 30~60 d 1982 PRE EAP PRE EAP 1983 PRE 1986 PRE EAP 1989 PRE EAP 1991 PRE EAP 1993 PRE 1995 PRE EAP 1996 PRE EAP PRE 1998 PRE EAP PRE EAP 1999 PRE EAP EAP 2000 PRE EAP 2009 PRE EAP EAP -
[1] Lu R Y. Anomalies in the tropics associated with the heavy rainfall in East Asia during the summer of 1998.Adv Atmos Sci, 2000, 17(2):205-220. doi: 10.1007/s00376-000-0004-y [2] 翟盘茂, 倪允琪, 陈阳.我国持续性重大天气异常成因与预报方法研究回顾与未来展望.地球科学进展, 2013, 28(11):1177-1188. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2013.11.1177 [3] 陆尔, 丁一汇.1991年江淮特大暴雨的位涡分析与冷空气活动.应用气象学报, 1994, 5(3):266-274. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940349&flag=1 [4] 陈忠明, 闵文彬, 高文良, 等.一次持续性强暴雨过程的平均特征.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(3):273-280. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060348&flag=1 [5] 陶诗言.中国之暴雨.北京:科学出版社, 1980. [6] 鲍名.近50年我国持续性暴雨的统计分析及其大尺度环流背景.大气科学, 2007, 31(5):779-794. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200705002.htm [7] 钱维宏.气候变化与中国极端气候事件图集.北京:气象出版社, 2011. [8] Tang Y B, Gan J J, Zhao L, et al.On the climatology of persistent heavy rainfall events in China.Adv Atmos Sci, 2006, 23(5):678-692. doi: 10.1007/s00376-006-0678-x [9] Ren F M, Cui D L, Gong Z Q, et al.An objective identification technique for regional extreme events.J Climate, 2012, 25(20):7015-7027. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00489.1 [10] 汪汇洁, 孙建华, 卫捷, 等.近30年我国南方区域持续性暴雨过程的分类研究.气候与环境研究, 2014, 19(6):713-725. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2013.13143 [11] Chen Y, Zhai P M.Persistent extreme precipitation events in China during 1951-2010.Clim Res, 2013, 57(2):143-155. doi: 10.3354/cr01171 [12] Dole R M, Gordon N D.Persistent anomalies of the extratropical northern hemisphere wintertime circulation:Geographical distribution and regional rersistence characteristics.Mon Wea Rev, 1983, 111(8):1567-1586. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1983)111<1567:PAOTEN>2.0.CO;2 [13] Higgins R W, Mo K C.Persistent north Pacific circulation anomalies and the tropical intraseasonal oscillation.J Climate, 1997, 10(2):223-244. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<0223:PNPCAA>2.0.CO;2 [14] Ding Y H, Reiter E R.A relationship between planetary waves and persistent rain-and thunderstorms in China.Archives for Meteorology, Geophysics, and Bioclimatology, Series B, 1982, 31(3):221-252. doi: 10.1007/BF02278295 [15] Lau W K M, Kim K M.The 2010 Pakistan flood and Russian heat wave:Teleconnection of hydrometeorological extremes.Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2012, 13(1):392-403. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-11-016.1 [16] 陶诗言, 张小玲, 张顺利.长江流域梅雨锋暴雨灾害研究.北京:气象出版社, 2004. [17] Liu H B, Zhang D L, Wang B.Daily to submonthly weather and climate characteristics of the summer 1998 extreme rainfall over the Yangtze River Basin.J Geophys Res, 2008, 113, D22101, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010072. [18] 张庆云, 陶诗言.亚洲中高纬度环流对东亚夏季降水的影响.气象学报, 1998, 56(2):199-211. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1998.019 [19] 孙建华, 赵思雄.1998年夏季长江流域梅雨期环流演变的特殊性探讨.气候与环境研究, 2003, 8(3):291-306. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200303003.htm [20] Chen Y, Zhai P M.Two types of typical circulation pattern for persistent extreme precipitation in Central-Eastern China.Q J R Meteorol Soc, 2014, 140(682):1467-1478. doi: 10.1002/qj.2014.140.issue-682 [21] Wei W, Zhang R H, Wen M, et al.Interannual variation of the south Asian high and its relation with Indian and east Asian summer monsoon rainfall.J Climate, 2015, 28(7):2623-2634. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00454.1 [22] Chen Y, Zhai P M.Mechanisms for concurrent low-latitude circulation anomalies responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River Valley.Clim Dyn, 2015:1-18, doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2885-6. [23] Chen Y, Zhai P M.Precursor circulation features for persistent extreme precipitation in Central-Eastern China.Wea Forecasting, 2014, 29(2):226-240. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-13-00065.1 [24] Archambault H M, Bosart L F, Keyser D, et al.Influence of large-scale flow regimes on cool-season precipitation in the Northeastern United States.Mon Wea Rev, 2008, 136(8):2645-2663. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249621804_Influence_of_Large-Scale_Flow_Regimes_on_Cool-Season_Precipitation_in_the_Northeastern_United_States [25] Kucharski F, Kang I S, Straus D, et al.Teleconnections in the atmosphere and oceans.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2010, 91(3):381-383. doi: 10.1175/2009BAMS2834.1 [26] Chen Y, Zhai P M.Synoptic-scale precursors of the East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River Valley.Q J R Meteorol Soc, 2015, 141:1389-1403. doi: 10.1002/qj.2015.141.issue-689 [27] Wheeler M C, Hendon H H.An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index:Development of an index for monitoring and prediction.Mon Wea Rev, 2004, 132(8):1917-1932. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<1917:AARMMI>2.0.CO;2 [28] Mao J Y, Sun Z, Wu G X.20-50-day oscillation of summer Yangtze rainfall in response to intraseasonal variations in the subtropical high over the western north Pacific and south China sea.Clim Dyn, 2010, 34(5):747-761. doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0628-2 [29] Ren X J, Yang X Q, Sun X G.Zonal oscillation of western Pacific subtropical high and subseasonal SST variations during Yangtze persistent heavy rainfall events.J Climate, 2013, 26(22):8929-8946. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00861.1 [30] 齐艳军, 张人禾.1998年夏季长江流域大气季节内振荡的结构演变及其对降水的影响.大气科学, 2016, 40(3):451-462. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201603001.htm [31] 陈阳.大气遥相关影响下的江淮地区持续性极端降水发生机理和预报信号.南京:南京信息工程大学, 2016. [32] Li L, Zhai P M, Chen Y.Low-frequency oscillations of East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern and their impacts on persistent heavy precipitation in the Yangtze-Huai River Valley.J Meteorol Res, 2016, doi: 10.1007/s13351-016-6024-z. [33] Niu R Y, Zhai P M.Synoptic verification of medium-extended-range forecasts of the northwest pacific subtropical high and South Asian high based on multi-center TIGGE data.Acta Meteo Sin, 2013, 27(5):725-741. doi: 10.1007/s13351-013-0513-0 [34] Niu R Y, Zhai P M, Zhou B.Evaluation of forecast performance of Asian summer monsoon low-level winds using the TIGGE Dataset.Wea Forecasting, 2015, 30(2):455-470. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-13-00141.1 [35] Zhou B Q, Niu R Y, Zhai P M.An assessment of the predictability of the east Asian subtropical westerly jet based on TIGGE data.Adv Atmos Sci, 2015, 32(3):401-412. doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-4026-2 [36] Peng X D, Che Y Z, Chang J.A novel approach to improve numerical weather prediction skills by using anomaly integration and historical data.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2013, 118(16):8814-8826. doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50682 [37] Wang H J, Fan K.A new scheme for improving the seasonal prediction of summer precipitation anomalies.Wea Forecasting, 2009, 24(2):548-554. doi: 10.1175/2008WAF2222171.1 [38] Hsu P C, Li T, You L, et al.A spatial-temporal projection model for 10-30 day rainfall forecast in South China.Clim Dyn, 2015, 44(5-6):1227-1244. doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2215-4 [39] 刘琳, 陈静, 程龙, 等.基于集合预报的中国极端强降水预报方法研究.气象学报, 2013, 71(5):853-866. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2013.044 [40] Zhou B Q, Zhai P M.A new forecast model based on the analog method for persistent extreme precipitation.Wea Forecasting, 2016, 31(4):1325-1341. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-15-0174.1 [41] Kosaka Y, Nakamura H.Mechanisms of meridional teleconnection observed between a summer monsoon system and a subtropical anticyclone.Part Ⅰ:The Pacific-Japan pattern.J Climate, 2010, 23:5085-5108. doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3413.1 [42] Kosaka Y, Xie S P, Nakamura H.Dynamics of interannual variability in summer precipitation over east Asia.J Climate, 2011, 24:5435-5453. doi: 10.1175/2011JCLI4099.1 [43] Yuan N M, Fu Z T, Zhang H, et al.Detrended partial-cross-correlation analysis:A new method for analyzing correlations in complex system.Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:8143. doi: 10.1038/srep08143 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: