Interdecadal Variation of Haze Days over China with Atmospheric Causes in Recent 50 Years
-
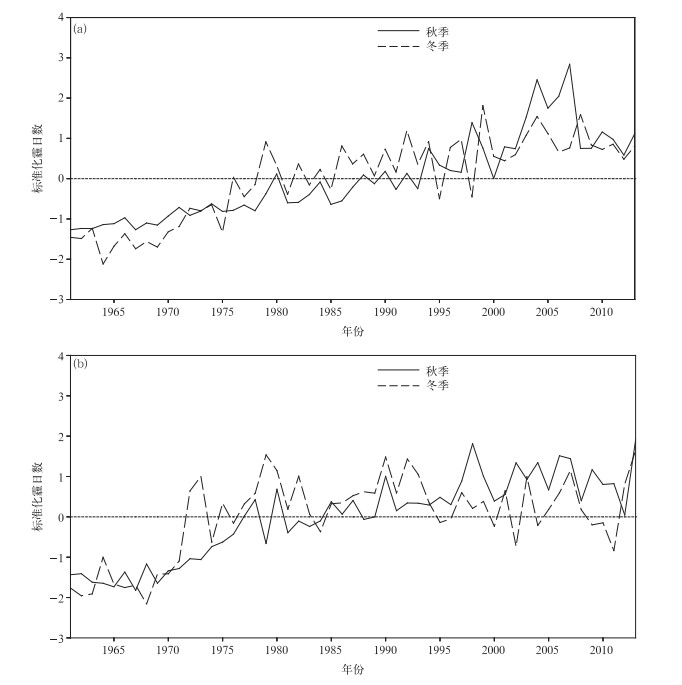
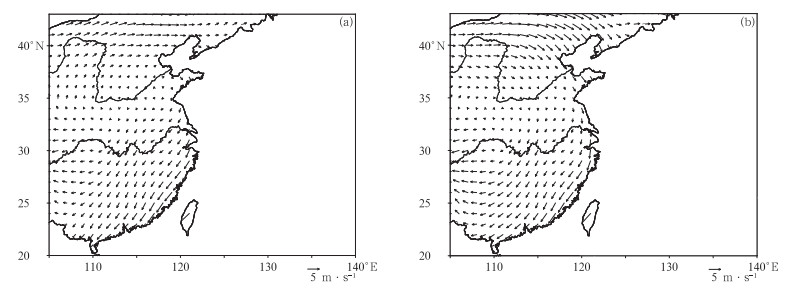
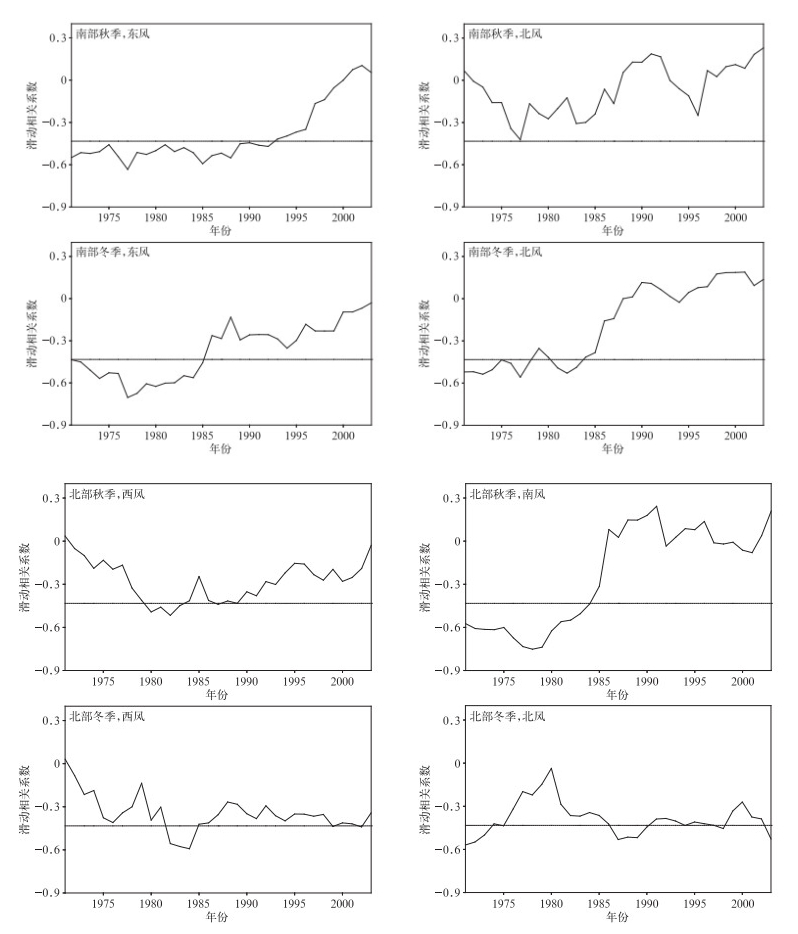
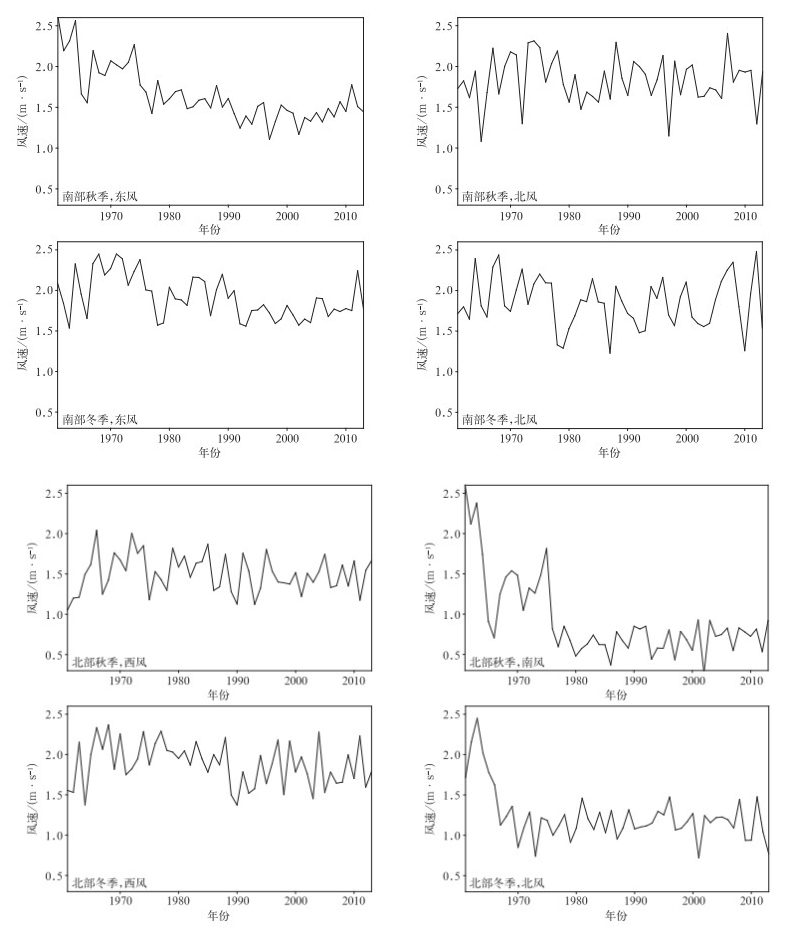
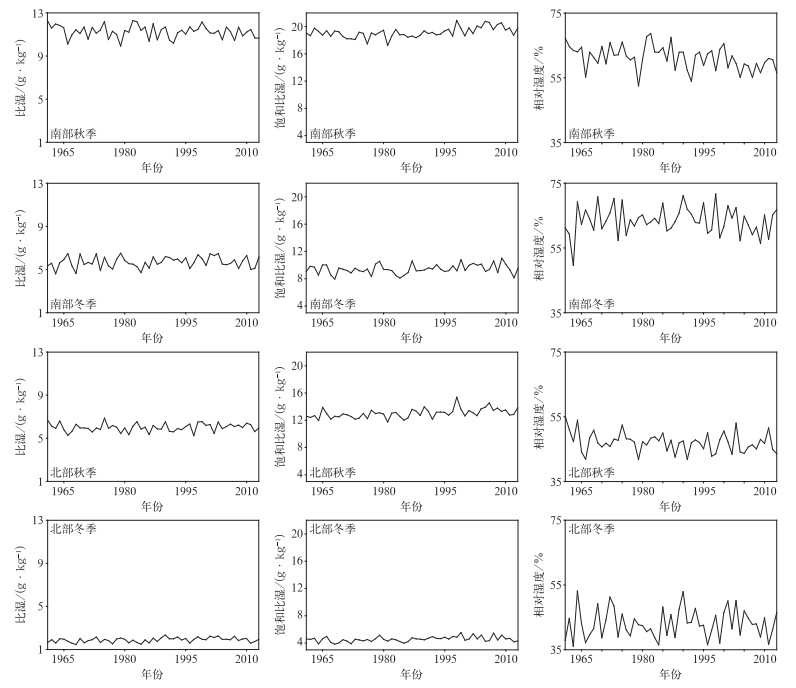
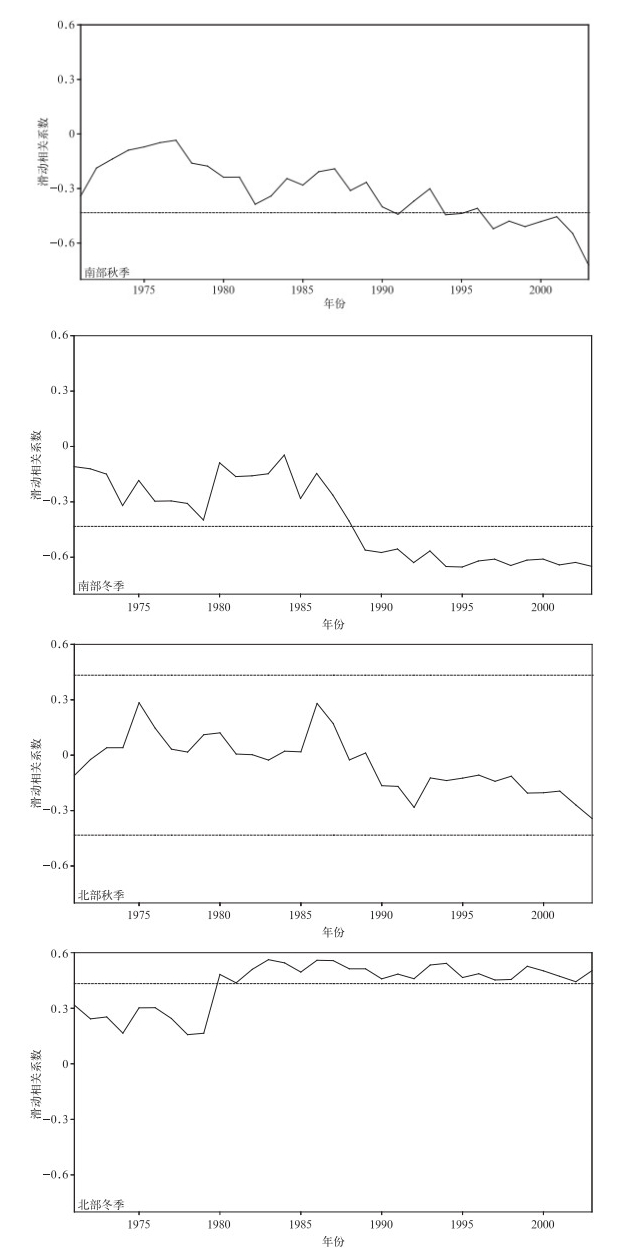
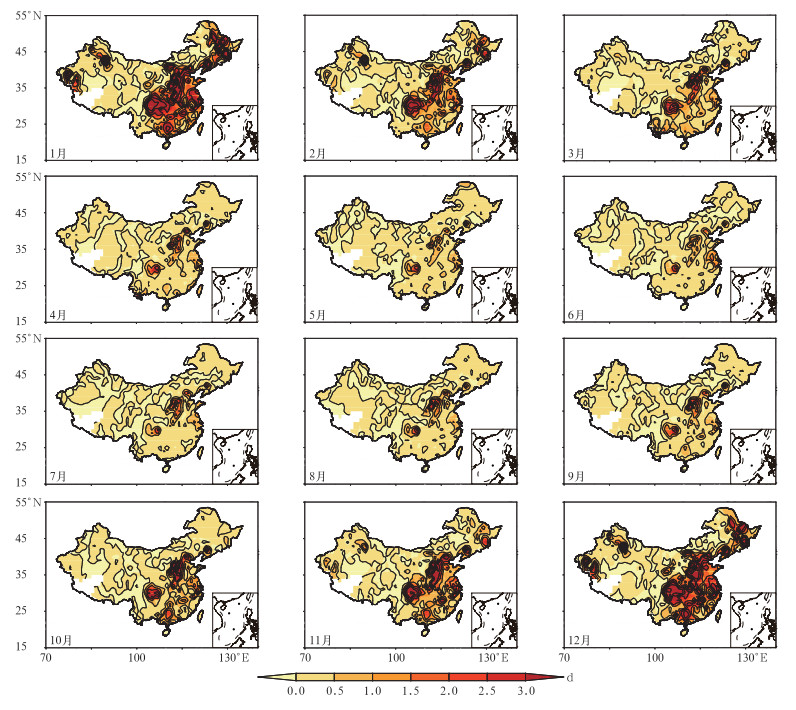
摘要: 根据1961-2013年全国745个国家基准站的长期观测资料,分析中国霾日数年代际变化特征及可能的气象成因。结果表明:近50年来,中国霾天气主要集中在东部从华南到华北的大部分地区,霾日数呈增加趋势。秋冬两季是霾天气发生最频繁、变化最明显的两个季节。中国东部淮河以南地区秋冬两季霾日数在2000年前呈增加趋势,其后增加趋势变得较为平缓,20世纪90年代前霾日数与近地面风速呈显著负相关关系,90年代后则与大气相对湿度呈显著负相关关系,随着90年代前近地面风速减小和90年代后大气相对湿度降低,该区域霾日数表现出明显的增加趋势。中国东部从淮河到华北大部分地区秋冬两季霾日数1980年后增加趋势变得不明显,这可能与该区域近地面风速和大气相对湿度的变化趋势较为平缓有关。Abstract: Characteristics of interdecadal variations of haze days over China and plausible meteorological causes during 1961 to 2013 are analyzed, using observations from 745 meteorological stations in China. Results show that most haze weather occurs over the east part of China from South China to North China where haze days exhibit an increasing trend especially in economically developed areas, such as North China, the Huanghuai and Jianghuai Plains. Haze days are fewer in large parts of Northeastern China and Western China, and haze days show decreasing tendency in these regions. Generally, haze days are more frequent in autumn and winter than those in spring and summer. Also, autumn and winter are seasons that variation of haze days is most significant. Haze days occur more frequently in January and December than other months. The first mode of EOF reflects a monotonically increasing trend in the east part of China. The second mode shows that the region from South China to the Huaihe River and the region from the Huaihe River to North China present opposite variation tendency of phase. Focusing on regions from South China to the Huaihe River and from the Huaihe River to North China, haze days show an increasing trend year by year over the region from South China to the Huaihe River in autumn and winter before 2000, and then the trend is smoother. In the region from the Huaihe River to North China, however, haze days change gently in recent 30 years in autumn and winter. The variation of haze days relate to surface wind speed and relative humidity. Haze days show a significant negative relationship with surface wind speed before 1990s. Haze days may be influenced by variations of east wind in the region from South China to the Huaihe River in autumn, while northeast wind in the winter. For region from the Huaihe River to North China, haze days is concerned with south wind in autumn, while haze days have nothing to do with wind in winter. The relativity between haze days and surface wind speed weakens, but haze days have significant relationship with relative humidity after 1990s. Haze days experience an increasing tendency because of the reduced surface wind before 1990s and the decrease of relative humidity after 1990s over the region from South China to the Huaihe River in autumn and winter. In comparison, haze days show moderate variations in the region from the Huaihe River to North China, which are probably related to the moderate variability in surface speed and relative humidity in autumn and winter.
-
Key words:
- haze days;
- relative humidity;
- surface wind
-
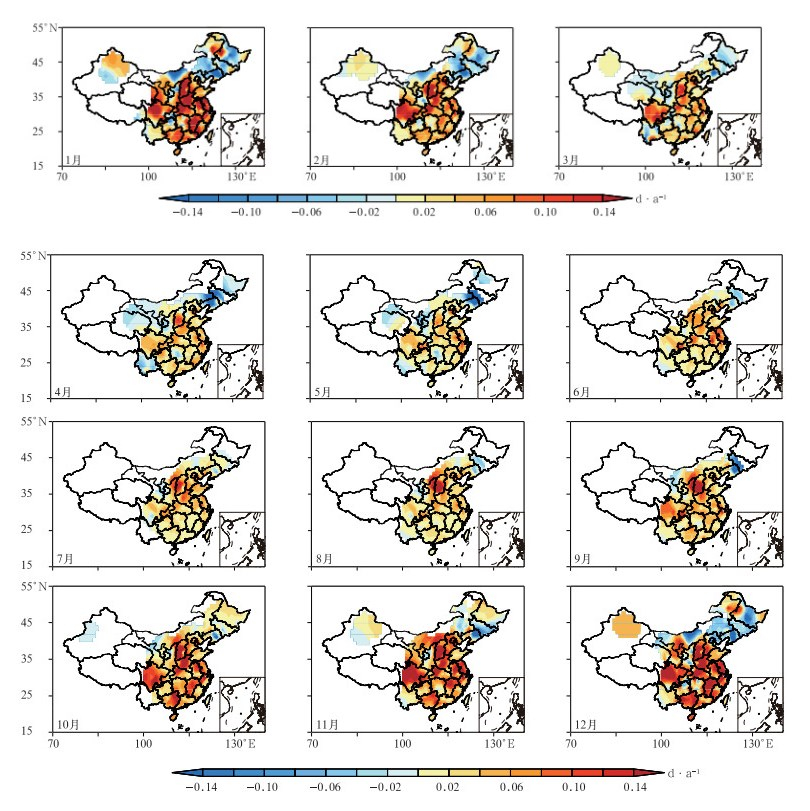
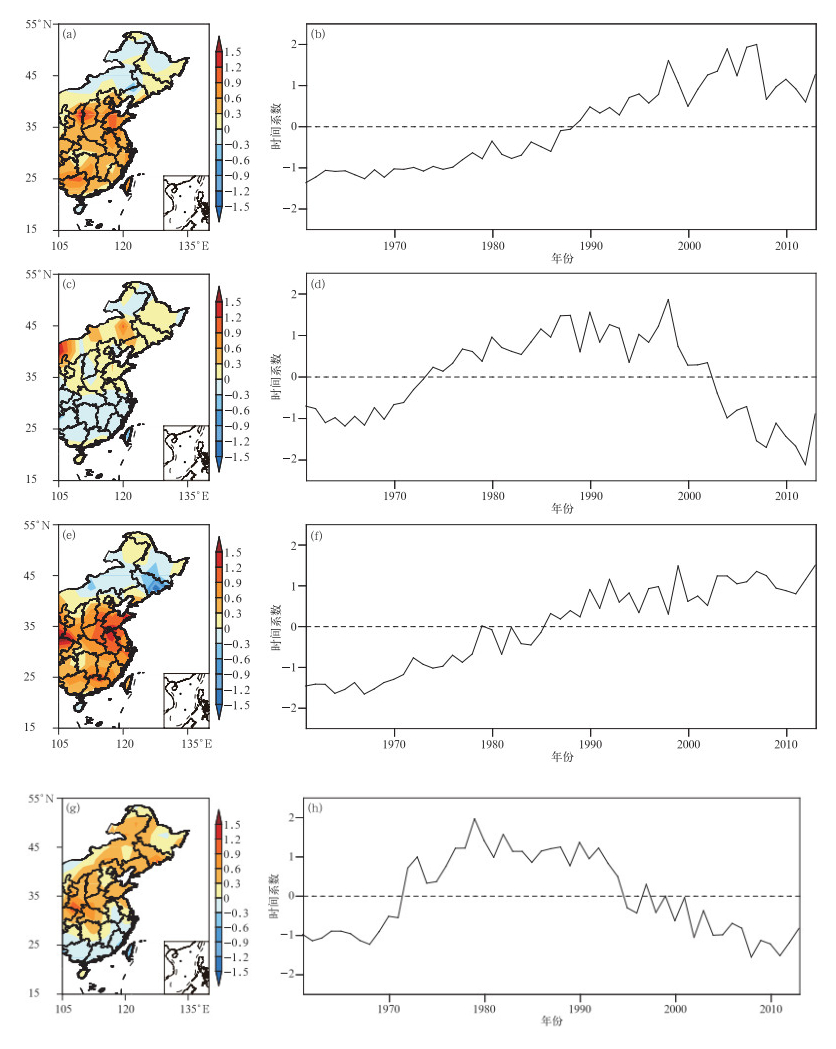
图 3 1961—2013年中国年霾日数秋冬两季EOF分析
(a) 秋季第1模态空间分布,(b) 秋季第1模态对应的时间系数,(c) 秋季第2模态空间分布,(d) 秋季第2模态对应的时间系数,(e) 冬季第1模态空间分布,(f) 冬季第1模态对应的时间系数,(g) 冬季第2模态空间分布,(h) 冬季第2模态对应的时间系数
Fig. 3 The EOF analysis of haze days in autumn and winter during 1961-2013
(a) the spatial distribution of the first characteristic vector in autumn, (b) the temporal variation of the first characteristic vector in autumn, (c) the spatial distribution of the second characteristic vector in autumn, (d) the temporal variation of the second characteristic vector in autumn, (e) the spatial distribution of the first characteristic vector in winter, (f) the temporal variation of the first characteristic vector in winter, (g) the spatial distribution of the second characteristic vector in winter, (h) the temporal variation of the second characteristic vector in winter
-
[1] 张小曳, 孙俊英, 王亚强, 等.我国雾-霾成因及其治理的思考.科学通报, 2013, 58(13):1178-1187. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201313003.htm [2] 中国气象局.地面气象观测规范.北京:气象出版社, 2003. [3] 徐晓斌.我国霾和光化学污染观测研究进展.应用气象学报, 2016, 27(5):604-619. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160509 [4] Ma J, Xu X, Zhao C, et al.A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China:Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions.Adv Atmos Sci, 2012, 29(5):1006-1025. doi: 10.1007/s00376-012-1188-7 [5] 廖国莲, 曾鹏, 郑凤琴, 等.1960-2009年广西霾日时空变化特征.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(6):732-739. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110611 [6] 黄健, 吴兑, 黄敏辉, 等.1954-2004年珠江三角洲大气能见度变化趋势.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(1):61-70. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080111 [7] 吴兑, 吴晓京, 李菲, 等.1951-2005年中国大陆霾的时空变化.气象学报, 2010, 68(5):680-688. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2010.066 [8] 高歌.1961-2005年中国霾日气候特征及变化分析.地理学报, 2008, 63(7):761-768. doi: 10.11821/xb200807010 [9] 宋连春, 高荣, 李莹, 等.1961-2012年中国冬半年霾日数的变化特征及气候成因分析.气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(5):313-318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH201305001.htm [10] Zhang X Y, Wang Y Q, Niu T, et al.Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China:Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(2):779-799. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-779-2012 [11] 尹志聪, 王会军, 郭文利.华北黄淮地区冬季雾和霾的时空气候变化特征.地球科学, 2015, 45(5):649-655. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201505009.htm [12] 尹志聪, 王会军, 袁东敏.华北黄淮冬季霾年代际增多与东亚冬季风的减弱.科学通报, 2015, 60(15):1395-1400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201515008.htm [13] 张雅斌, 林琳, 吴其重, 等."13·12"西安重污染气象条件及影响因素.应用气象学报, 2016, 27(1):35-46. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160104 [14] 颜鹏, 刘桂清, 周秀骥, 等.上甸子秋冬季雾霾期间气溶胶光学特性.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(3):257-265. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100301 [15] Song Y F, Liu Y J, Ding Y H.A study of surface humidity change in China during the recent 50 years.Acta Meteor Sin, 2012, 26:541-553. doi: 10.1007/s13351-012-0501-9 [16] 丁一汇, 柳艳菊.近50年我国雾与霾的长期变化特征及其与大气湿度的关系.中国科学 (地球科学), 2014, 44(1):37-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201401005.htm [17] Li Q, Zhang R H, Wang Y.Interannual variation of the wintertime fog-haze days across central and eastern China and its relation with east Asian winter monsoon.Int J Clim, 2016, 36(1):346-354. doi: 10.1002/joc.4350 [18] Lin C G, Yang K, Huang J P, el at.Impacts of wind stilling on solar radiation variability in China.Nature Scientific Reports, 2015, 5, 15135, DOI: 10.1038/srep15135. [19] Xiao D, Li Y, Fan S J, et al.Plausible influence of Atlantic Ocean SST anomalies on winter haze in China.Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2015, 122(1):249-257. [20] Zhao S, Li J P, Sun C.Decadal variability in the occurrence of wintertime haze in central eastern China tied to the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 27424, DOI: 10.1038/srep27424. [21] Feng J, Liao H, Li J P.The impact of monthly variation of Pacific-North America (PNA) teleconnection pattern on wintertime surface-layer aerosol concentrations in the United States.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16:4927-4943. doi: 10.5194/acp-16-4927-2016 [22] 靳军莉, 严鹏, 马志强, 等.北京及周边地区2013年1-3月PM2.5变化特征.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(6):690-700. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20140605 [23] 司鹏, 高润祥.天津雾和霾自动观测与人工观测的对比评估.应用气象学报, 2015, 26(2):240-246. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150212 [24] 吴兑, 廖国莲, 邓雪娇.珠江三角洲霾天气的近地层输送条件研究.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(1):1-9. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080101 [25] 史军, 崔林丽, 贺千山, 等.华东雾和霾日数的变化特征及成因分析.地理学报, 2010, 65(5):533-541. doi: 10.11821/xb201005003 [26] 张利, 吴涧, 张武.1955-2000年中国能见度变化趋势分析.兰州大学学报 (自然科学版), 2011, 47(6):46-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201106011.htm [27] 吴兑.再论相对湿度对区别都市霾与雾 (轻雾) 的意义.广东气象, 2006(1):9-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDCX200601002.htm [28] Schichtel B A, Husar R B, Falker S R, et al.Hzae trends over the United Sates 1980-1995.Atmos Environ, 2001, 35:5205-5210. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00317-X [29] Doyle M, Dorling S.Visibility trends in the UK 1950-1997.Atmos Environ, 2001, 36:3161-3172. [30] 吴兑, 吴晓京, 朱小祥.雾与霾.北京:气象出版社, 2009. [31] 赵普生, 徐晓峰, 孟伟, 等.京津冀区域霾天气特征.中国环境科学, 2012, 32(1):31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201201004.htm [32] 胡亚旦, 周自江.中国霾天气的气候特征分析.气象, 2009, 35(7):73-78. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2009.07.011 [33] 孙彧, 马振锋, 牛涛.最近40年中国雾日数和霾日数的气候变化特征.气候与环境研究, 2013, 18(3):397-406. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2013.12170 [34] 张人禾, 李强, 张若楠.2013年1月中国东部持续性强雾霾天气产生的气象条件分析.中国科学 (地球科学), 2014, 44(1):27-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201401004.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: