Identification Method and Analysis on Lightning Flash Initiation Phase and Size
-
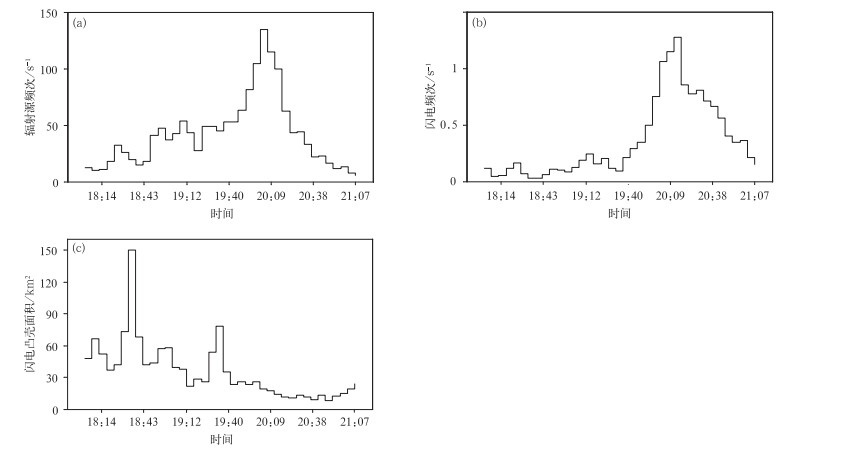
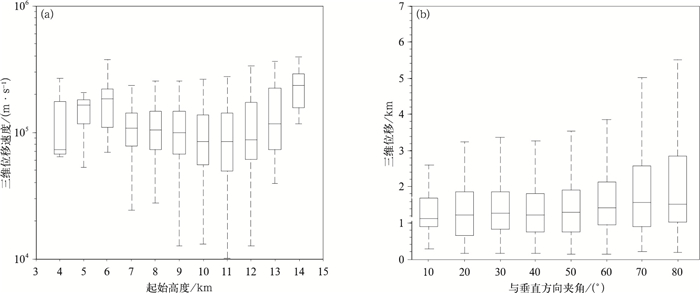
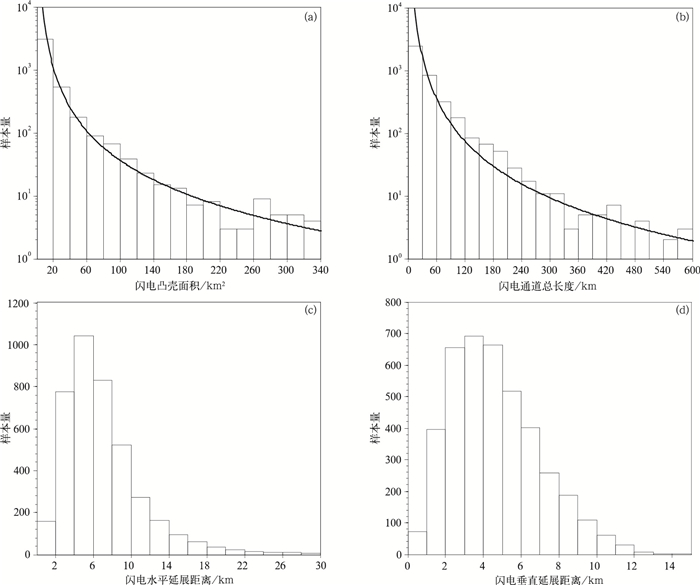
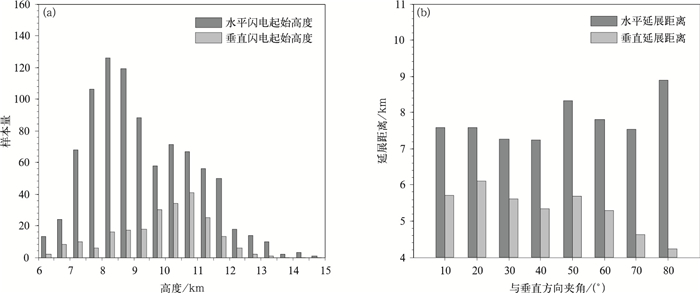
摘要: 基于LMA三维闪电定位数据,对2004年10月5日发生于美国新墨西哥州的一次超级单体过程的闪电初始及其尺度特征进行研究,提出闪电初始阶段自动判别及其特征参量提取方法,并给出参量分布特征。结果显示:闪电初始阶段上行负先导(下行负先导)的持续时间中值为13.5 ms(7.5 ms),三维位移中值为1.4 km(1.0 km),三维平均位移速度中值为9.2×104 m·s-1(1.2×105 m·s-1),上行负先导速度随时间递减,下行反之,二者与垂直方向夹角的中值分别为40°和54°。表征闪电尺度的闪电凸壳面积和闪电总长度的概率密度呈负幂函数分布,在小值方向分布更为集中。闪电水平延展距离中值为6.1 km,垂直延展距离中值为4.3 km,约83%的闪电其水平延展距离大于垂直延展距离;闪电的持续时间中值为271.0 ms。分析发现,以水平延展为主的闪电起始高度分布峰值位于8.5 km,以垂直延展为主的闪电起始高度分布峰值位于11 km。闪电初始阶段位移方向越接近水平,对应闪电垂直延展越小,说明闪电初始段的传播方向对于闪电垂直延展具有重要影响。Abstract: Based on the observation of lightning mapping array, the statistical distribution of characteristic parameters describing the lightning flash initiation and size in a supercell storm occurring in New Mexico, United States on 5 October 2004 is studied. A method automatically identifying the start and end of the negative leaders in initial stage (IS) of lightning is developed. And the flash convex hull, total channel length, horizontal and vertical extent are used to represent the scale characteristics. Distributions and characteristics of flash initiation and size in this storm are shown as follows.Median values of the duration, three-dimensional displacement, vertical displacement and the average displacement velocity for the upward (downward) negative leaders during IS are 13.5 ms (7.5 ms), 1.4 km (1.0 km), 0.9 km (0.5 km), and 9.2×104 m·s-1 (1.2×105 m·s-1), respectively. In addition, the average flash initiation velocity decreases with height from 6 km to 11 km. With time going on, the speed of upward negative leader in initial stage decreases before 24 ms (to ensure the samples is larger than 100), while that of the downward negative leader increases before 12 ms (to ensure the samples is larger than 50). Moreover, negative leaders are dominantly tilted in initial stage, considering that the median angles between the 3-D displacement direction and the vertical direction are 40° for upward leader and 54° for downward leader, respectively.The probability density distribution of flash size described by flash convex hull and total channel length can be well fitted by negative power function, also showing that the distribution and evolution of flash convex hull is consist with that of total channel length. The median of flash duration is 271.0 ms, and the mean of that is 329.1 ms. The flash duration time and size are not significantly correlated. The flash with long duration time is not necessarily large. Moreover, the median of flash horizontal extent is 6.1 km while the vertical extent is 4.3 km, and there are 83% of flashes whose horizontal extent is greater than vertical extent. Flashes with horizontal extent greater than vertical extent are mainly initiated at 8.5 km high, and those with vertical extent greater than horizontal extent are mainly initiated at 11 km high. Greater horizontal displacement of the leader during initial stage accompanies less vertical extent, which indicates that the leader displacement direction at initial stage has an important influence on flash vertical scale.
-
Key words:
- supercell;
- flash initiation;
- flash size
-
图 2 闪电初始阶段自动识别方法示例
(a)闪电起始位置确定,(b)3 ms时间间隔内辐射源的平均高度求解,(c)相邻辐射源高度滑动平均,(d)依据斜率特征判定初始段结束位置
Fig. 2 The diagram of flash initiation identification method
(a)the initial point determined, (b)average heights of sources in every 3 ms temporal span calculated, (c)the curve smoothed by every five adjacent points, (d)the end time of flash initiation determined based on the slope curve
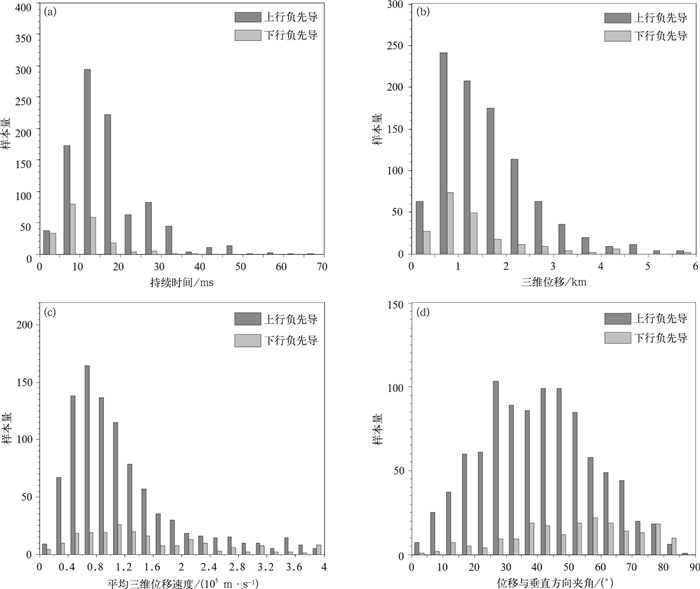
图 5 闪电初始阶段特征参量概率密度分布
(a)持续时间,(b)三维位移,(c)平均三维位移速度,(d)位移方向与垂直方向夹角
Fig. 5 Probability density distribution of characteristic parameters in initiation stage
(a)initiation duration time, (b)3-D displacement, (c)average 3-D displacement velocity, (d)angle between flash initiation displacement and vertical direction
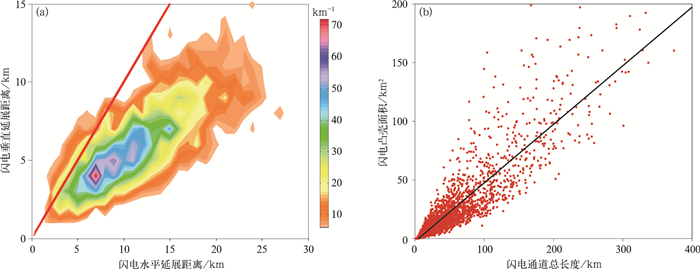
图 9 闪电初始和尺度不同特征参量间关系
(a)闪电水平延展距离与垂直延展距离散点密度分布(只显示每个格点闪电个数大于6的数据,格点大小为1 km×1 km),(b)闪电通道总长度与闪电凸壳面积的散点分布
Fig. 9 Relationship between parameters of flash initiation and size
(a)flash horizontal extent and flash vertical extent(grids where flash number is larger than 6 are displayed, and the statistical grid size is 1 km×1 km), (b)distribution of total channel length and flash convex hull
表 1 闪电初始阶段特征参量的参数统计
Table 1 Statistics of parameters in initiation stage of flashes
统计项目 平均值 中值 标准差 最大值 最小值 上行持续时间/ms 16.2 13.5 9.3 65.1 1.5 下行持续时间/ms 9.9 7.5 5.8 36.0 1.5 上行三维位移/km 1.6 1.4 1.0 5.9 0.1 下行三维位移/km 1.3 1.0 1.0 5.9 0.1 上行垂直位移/km 1.0 0.9 0.7 5.2 0.03 下行垂直位移/km 0.7 0.5 0.6 3.6 0.08 上行三维速度/(105 m·s-1) 1.1 0.9 0.7 4.0 0.10 下行三维速度/(105 m·s-1) 1.5 1.2 0.9 4.0 0.13 上行垂直夹角/(°) 40.3 40.2 17.5 85.5 1.3 下行垂直夹角/(°) 52.0 54.3 19.2 83.1 2.4 表 2 闪电尺度特征参量的参数统计
Table 2 Statistics of parameters describing flash size
统计项目 平均值 中值 标准差 最大值 最小值 凸壳面积/km2 20.3 8.2 39.4 522.8 0.01 通道总长度/km 43.4 22.3 61.4 695.4 0.7 延展的最大水平距离/km 7.1 6.1 4.5 39.3 0.2 延展的最大垂直距离/km 4.6 4.3 2.3 14.0 0.3 持续时间/ms 329.1 271.0 226.7 1798.8 4.2 -
[1] 王艳, 张义军, 马明.卫星观测的我国近海海域闪电分布特征.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(2):157-163. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100204 [2] 王婷波, 郑栋, 张义军, 等.基于大气层结和雷暴演变的闪电和降水关系.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(1):33-41. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20140104 [3] 郑栋, 孟青, 吕伟涛, 等.北京及其周边地区夏季地闪活动时空特征分析.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(5):638-644. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050510 [4] 张阳, 张义军, 孟青, 等.北京地区正地闪时间分布及波形特征.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(4):442-449. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100407 [5] 郑栋, 张义军, 孟青, 等.北京地区雷暴过程闪电与地面降水的相关关系.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(3):287-297. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100304 [6] 张义军, 孟青, 马明, 等.闪电探测技术发展和资料应用.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5):611-620. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20060504 [7] Karunarathne S, Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M, et al.Locating initial breakdown pulses using electric field change network.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2013, 118(13):7129-7141. doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50441 [8] Marshall T, Stolzenburg M, Karunarathne S, et al.Initial breakdown pulses in intracloud lightning flashes and their relation to terrestrial gamma ray flashes.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2013, 118(19):10907-10925. doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50866 [9] Stolzenburg M, Marshall T C, Karunarathne S, et al.Luminosity of initial breakdown in lightning.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2013, 118(7):2918-2937. doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50276 [10] Shao X M, Krehbiel P R.The spatial and temporal development of intracloud lightning.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 1996, 1012(21):26641-26668. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252728635_The_spatial_and_temporal_development_of_intracloud_lightning [11] Behnke S A, Thomas R J, Krehbiel P R, et al.Initial leader velocities during intracloud lightning:Possible evidence for a runaway breakdown effect.J Geophys Res, 2005, 110(10):1187-1203. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229020596_Initial_leader_velocities_during_intracloud_lightning_Possible_evidence_for_a_runaway_breakdown_effect [12] Wu T, Yoshida S, Akiyama Y, et al.Preliminary breakdown of intracloud lightning:Initiation altitude, propagation speed, pulse train characteristics, and step length estimation.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2015, 120(18):9071-9086. doi: 10.1002/2015JD023546 [13] Zheng D, MacGorman D R.Characteristics of flash initiations in a supercell cluster with tornadoes.Atmospheric Research, 2016, 167:249-264. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.08.015 [14] Wu B, Zhang G, Wen J, et al.Correlation analysis between initial preliminary breakdown process, the characteristic of radiation pulse, and the charge structure on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2016, 121(20), 12434-12460. doi: 10.1002/2016JD025281 [15] Bruning E C, MacGorman D R.Theory and observations of controls on lightning flash size spectra.Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 70(12):4012-4029. doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-12-0289.1 [16] Chronis T, Lang T, Koshak W, et al.Diurnal characteristics of lightning flashes detected over the Sao Paulo lightning mapping array.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2015, 120(23):11799-11808. doi: 10.1002/2015JD023960 [17] Koshak W, Peterson H, Biazar A, et al.The NASA Lightning Nitrogen Oxides Model (LNOM):Application to air quality modeling.Atmospheric Research, 2014, 135:363-369. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262989448_The_NASA_Lightning_Nitrogen_Oxides_Model_LNOM_Application_to_air_quality_modeling [18] Zhang R, Zhang G, Li Y, et al.Estimate of NOX production in the lightning channel based on three-dimensional lightning locating system.Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(7):1613-1625. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4812-1 [19] Calhoun K M, MacGorman D R, Ziegler C L, et al.Evolution of lightning activity and storm charge relative to dual-doppler analysis of a high-precipitation supercell storm.Mon Wea Rev, 2013, 141(7):2199-2223. doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-12-00258.1 [20] Thomas R J, Krehbiel P R, Rison W, et al.Accuracy of the Lightning Mapping Array.Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2004, 109(14):1149-1165. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/251679679_Llewelyn_Ralph_Twentyman_6_June_1914-29_April_2010 [21] Krehbiel P R, Thomas R J, Rison W, et al.GPS-based mapping system reveals lightning inside storms.Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2000, 81(3):21-25. doi: 10.1029/00EO00014 [22] MacGorman D R, Rust W D, Schuur T J, et al.TELEX-The Thunderstorm Electrification and Lightning Experiment.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2008, 89(7):997-1013. doi: 10.1175/2007BAMS2352.1 [23] Rison W, Thomas R J, Krehbiel P R, et al.A GPS-based three-dimensional lightning mapping system:Initial observations in Central New Mexico.Geophys Res Lett, 1999, 26(23):3573-3576. doi: 10.1029/1999GL010856 [24] Lund N R, MacGorman D R, Schuur T J, et al.Relationships between lightning location and polarimetric radar signatures in a small mesoscale convective system.Mon Wea Rev, 2009, 137(12):4151-4170. doi: 10.1175/2009MWR2860.1 [25] Coleman L M, Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M, et al.Effects of charge and electrostatic potential on lightning propagation.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2003, 108(9):1601-1612. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259255528_The_Effects_of_Charge_and_Electrostatic_Potential_on_Lightning_Propagation [26] 刘恒毅, 董万胜, 徐良韬, 等.闪电起始过程时空特征的宽带干涉仪三维观测.应用气象学报, 2016, 27(1):16-24. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160102 [27] 李俊, 吕伟涛, 张义军, 等.一次多分叉多接地的空中触发闪电过程.应用气象学报, 2010, 21(1):95-100. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20100113 [28] 张荣, 张广庶, 王彦辉, 等.青藏高原东北部地区闪电特征初步分析.高原气象, 2013, 32(3):673-681. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2013.00083 [29] Lang T J, Pédeboy S, Rison W, et al.WMO world record lightning extremes:Longest reported flash distance and longest reported flash duration.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2016, DOI: 10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0061.1. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: