Prediction Experiment for the South China Sea Summer Monsoon Strength by Physical-statistic Integrated Model
-
摘要: 利用影响南海夏季风年际变化的主要气候现象厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(El Niño-Southern Oscillation,ENSO)和对流层准两年振荡(Tropospheric Biennial Oscillation,TBO)相关的气候因子,提出了以过程判别函数确定物理过程的持续性,建立年际尺度的集成物理统计预测模型,而非年际尺度变率由经验统计模型预测,二者相结合,发展了集成物理-经验统计预测模型。经验模型在拟合时段的回报结果很好,但在独立样本预测时效果明显降低,其中预测评分(PS)降低了23%,距平相关系数(ACC)降低了63%;相比之下,集成物理-经验统计预测模型在独立样本预测时比经验模型有更好的预测结果(PS评分提高了9.5%,ACC提高了75%),且预测结果相对稳定。此外,集成物理-经验统计预测模型对南海夏季风降水的空间分布也有一定预测能力。Abstract: The South China Sea summer monsoon (SCSSM) is a tropical system that plays a key role during the flood season of South China. However, the prediction of the SCSSM strength is difficult by no matter dynamic or statistic methods. Statistic methods are used in practice rather than dynamic model, but empirical-statistic models always have good hindcasting results during the period of building model, while the forecasting skills decrease evidently in practice. Physical-statistic methods have relatively stable predictive skill when the persistence of physical processes is taken into account. Therefore, an integrated technique is introduced based on associated physical processes to establish a predictive model for SCSSM. It is well known that the rainfall of SCSSM has multi-scale climate variability, for example, quasi-biennial and quasi-quadrennial time scale, which are mainly related to TBO (Tropospheric Biennial Oscillation) and ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation), respectively. Based on the corresponding climatic factors, a physical-statistic integrated model is built. Combined with the traditional empirical-statistic method, a new prediction model (namely physical and empirical-statistic integrated model) for SCSSM is developed.First, original data are processed by removing the climatic state (1981-2010) and linear trend, and then anomalous data are filtered on the TBO (12-36 months) and ENSO (36-96 months) time scales since the biennial mode of SCSSM has little connection with the ENSO. Second, regressed results based on climatic factors (e.g., sea surface temperature anomalies in Niño3.4 and the tropical western Pacific, precipitation anomalies over the maritime continent and Australian monsoon region) are assembled according to a discrimination function that is correlation coefficient larger than 0.05 significant level between regressed results and the filtered SCSSM precipitation. Moreover, the rest precipitation with SCSSM inter-annual variations removed is predicted by the traditional empirical-statistic method and results are added to those by the physical-statistic integrated model. Using data throughout 1979-2010, the physical and empirical-statistic integrated model is trained and results of 2011-2016 are predicted for test, compared with that of the empirical-statistic integrated model. It shows that the new model has better prediction skill (9.5% improvements in prediction score and 75% in anomaly correlation coefficient) and relatively stable predicting results. More than that, the new model has some predictive ability for SCSSM rainfall distribution.
-
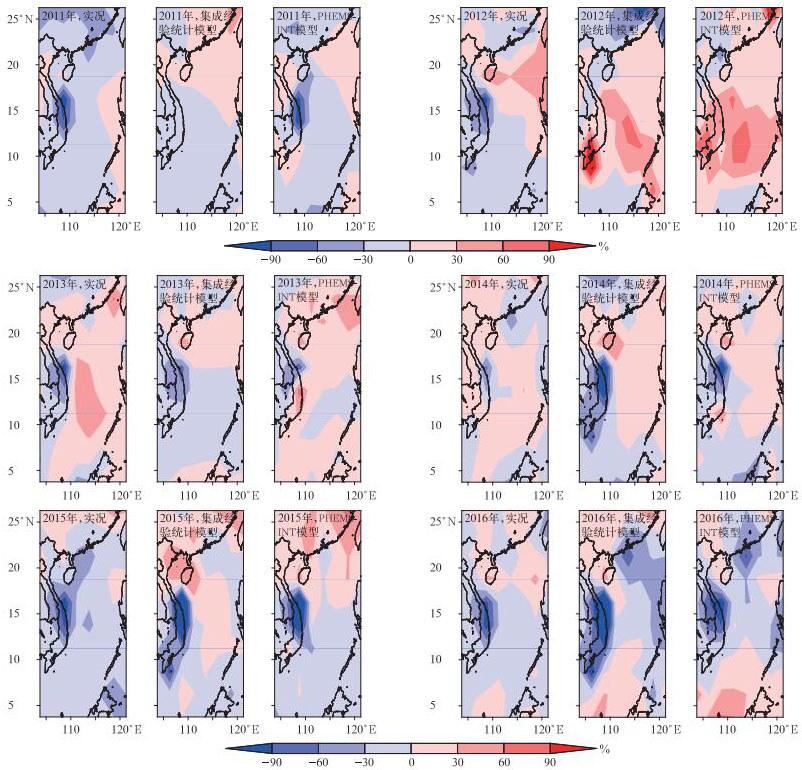
图 3 2012年南海区域夏季降水距平百分率预测结果
(a)集成经验统计模型预测的降水非年际分量,(b)集成物理统计模型预测的降水年际分量
Fig. 3 The predicted summer precipitation anomaly percentage over the South China Sea during 2012
(a)non-interannual component from empirical-statistic integrated model, (b)interannual component from physical-statistic integrated model
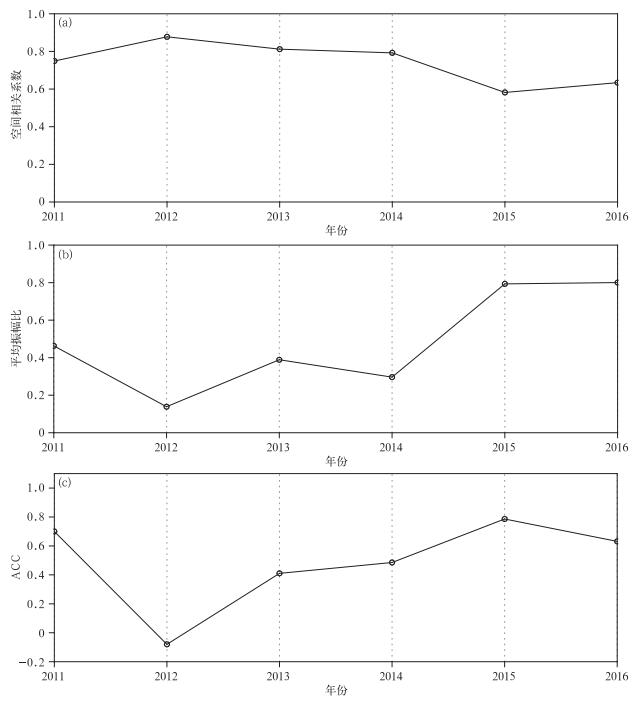
图 4 2011—2016年南海区域夏季降水
(a)年际(12~96月)分量与降水异常的空间相关系数(实线),(b)平均振幅比(年际分量的区域平均方差与总方差之比), (c)PHEMS-INT模型预测结果的ACC检验
Fig. 4 The South China Sea summer precipitation in 2011-2016
(a)area correlation coefficients of summer precipitation anomaly and interannual component(12-96 months), (b)mean amplitude ratios(regional mean ratio of interannual variance to total one), (c)ACC test of predicted precipitation by PHEMS-INT model
表 1 南海夏季风物理统计预测模型的预测因子
Table 1 Predictive factors for the physical-statistic SCSSM predictive model
季节 准两年模态 4~5年模态 海洋大陆 热带西太平洋 澳大利亚季风区 Niño3.4区 西北太平洋 南海季风区 冬季
(12月—次年2月)海温异常 降水异常 海温异常 海温异常 海温异常 春季
(3—5月)海温异常
降水异常海温变率 海温异常 海温异常 表 2 南海夏季风预测模型的预测结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of SCSSM predictive models
检验方法 1982—2010年回报试验 2011—2016年独立样本检验 集成经验统计模型 集成物理-经验统计模型 集成经验统计模型 集成物理-经验统计模型 PS 90.72 79.63 74.27 81.3 ACC 0.75 0.40 0.28 0.49 -
[1] 王绍武, 朱锦红.短期气候预测的评估问题.应用气象学报, 2000, 11(增刊Ⅰ):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2000S1000.htm [2] 李崇银.21世纪的气候变化及其可预报性研究——国际CLIVAR计划及科学大会介绍.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(增刊Ⅰ):158-160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX9S1.019.htm [3] 李崇银, 张利平.南海夏季风活动及其影响.大气科学, 1999, 23(3):257-266. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK199903000.htm [4] 谢炯光, 纪忠萍, 谷德军, 等.南海西南季风异常与广东省汛期重要天气的关系.热带气象学报, 2008, 24(3):209-218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200803003.htm [5] 陈隆勋, 李薇, 赵平, 等.东亚地区夏季风爆发过程.气候与环境研究, 2000, 5(4):345-355. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200004001.htm [6] Sperber K R, Palmer T N.Interannual tropical rainfall variability in general circulation model simulations associated with the Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project.J Climate, 1996, 9:2727-2750. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2727:ITRVIG>2.0.CO;2 [7] Webster P J, Magana V O, Palmer T N, et al.Monsoons:Processes, predictability, and the prospects for forecast.J Geophys Res, 1998, 103:14451-14510. doi: 10.1029/97JC02719 [8] Kang I S, Jin K, Lau K M, et al.Intercomparison of atmospheric GCM simulated anomalies associated with the 1997/98 El Niño.J Climate, 2002, 15(19):2791-2805. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<2791:IOAGSA>2.0.CO;2 [9] Kang I S, Jin K, Wang B, et al.Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs.Climate Dyn, 2002, 19:383-395. doi: 10.1007/s00382-002-0245-9 [10] Waliser D E, Jin K, Kang I S, et al.AGCM simulations of intraseasonal variability associated with the Asian summer monsoon.Climate Dyn, 2003, 21:423-446. doi: 10.1007/s00382-003-0337-1 [11] 黄嘉佑.北京地面气温可预报性及缺测资料恢复的研究.气象学报, 1995, 53(2):211-216. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1995.024 [12] 郭其蕴.季风变率与预测研究.应用气象学报, 1999, 10(增刊Ⅰ):132-141. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX9S1.015.htm [13] 谷德军, 纪忠萍, 李春晖.南海夏季风爆发日期与海温的多尺度关系及最优子集回归预测.海洋学报, 2011, 33(6):55-63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201106007.htm [14] 黄嘉佑, 用典型相关分析作副高的统计动力预报模式可预报性研究, 大气科学, 1995, 19(2):149-155. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK502.002.htm [15] Lau K M, Kim K M, Shen S S P.Potential predictability of seasonal precipitation over the United States from canonical ensemble correlation predictions.Geophys Res Let, 2002, 29(7), DOI: 10.1029/2001GL014263. [16] 吴洪宝, 王盘兴, 林开平.广西夏季降水量潜在可预报性估计.应用气象学报, 2005, 16(4):445-452. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20050404 [17] 乐群, 曹俊武, 林振山, 等.中国月平均温度的气候噪声和潜在可预报性.气象学报, 1999, 57(5):604-612. doi: 10.11676/qxxb1999.058 [18] 林爱兰.多元均生函数模型及其在短期气候预测中的应用.热带气象学报, 2001, 17(3):287-292. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX200103011.htm [19] 李春晖, 林爱兰, 谷德军, 等.基于CFS预报产品的广东省季节降水统计降尺度预测.热带气象学报, 2012, 28(6):797-808. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDQX201206002.htm [20] 段旭, 尤卫红, 李跃清.多时次资料的EOF迭代在云南夏季气候预测中的应用.高原气象, 2001, 20(2):220-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200102017.htm [21] Liu Jianwen, Dong Peiming.Short-range climate prediction experiment of the Southern Oscillation Index based on the singular speetrum Analysis.Adv Atmos Sci, 2001, 18(5):873-881. http://www.oalib.com/paper/1560636 [22] 杨青, 廉毅, 何金海.利用奇异值分解方法预测东北地区夏季气温.气象, 2005, 31(3):31-35. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2005.03.007 [23] 魏凤英.气候统计诊断与预测方法研究进展——纪念中国气象科学研究院成立50周年.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):736-742. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20060611 [24] 何敏, 许力, 宋文玲.南海夏季风爆发日期和强度的短期气候预报方法研究.气象, 2002, 28(10):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2002.10.002 [25] 周文, 温之平, 陈创买.南海西南季风爆发的预报研究.中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 41(3):95-98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ200203024.htm [26] 王澄海, 耿立成.奇异谱分析-最大熵结合最优子集回归方法在中国夏季降水预测中的应用.气象, 2012, 38(1):41-46. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2012.01.004 [27] 熊开国, 封国林, 黄建平, 等.最优多因子动态配置的东北汛期降水相似动力预报试验.气象学报, 2012, 70(2):213-221. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2012.021 [28] 王会军, 张颖, 郎咸梅.论短期气候预测的对象问题.气候与环境研究, 2010, 15(3):225-228. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201003002.htm [29] Xie P, Arkin P A.Global precipitation:A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1997, 78(11):2539-2558. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2539:GPAYMA>2.0.CO;2 [30] Smith T M, Reynolds R W, Peterson T C, et al.Improvements to NOAA's historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880-2006).J Climate, 2008, 21(10):2283-2296. doi: 10.1175/2007JCLI2100.1 [31] Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al.The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1996, 77(3):437-472. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2 [32] Fan Y, van den Dool H.Climate Prediction Center global monthly soil moisture data set at 0.5 degree resolution for 1948 to present.J Geophys Res, 2004, 109, D10102, DOI: 10.1029/2003JD004345. [33] 谷德军, 高晓容, 纪忠萍, 等.广东开汛日期的多尺度物理统计预测模型.高原气象, 2012, 31(3):768-776. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201203020.htm [34] 胡娅敏, 覃志年, 陈丽娟, 等.基于多时间尺度的回归集成预测模型.气象, 2013, 39(9):1182-1189. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2013.09.014 [35] 刘娜, 李双林.基于时间尺度分离的中国东部夏季降水预测.应用气象学报, 2015, 26(3):328-337. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150308 [36] 梁建茵, 吴尚森.南海西南季风多时间尺度变化及其与海温的相互作用.应用气象学报, 2000, 11(1):95-104. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20000115&flag=1 [37] 陈隆勋, 张博, 张瑛.东亚季风研究的进展.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(6):711-724. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20060609 [38] Wang B, Huang F, Wu Z, et al.Multi-scale climate variability of the South China Sea monsoon:A review.Dyn Atmos Oceans, 2009, 47:15-37. doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2008.09.004 [39] Zheng Bin, Lu Feng, Wei Hongcheng.Air-sea interactions associated with tropospheric biennial oscillation in South China Sea summer monsoon and their effects on El Niño-Southern Oscillation.Acta Oceanol Sin, 2013, 32(6):6-12. doi: 10.1007/s13131-013-0319-z [40] Zheng Bin, Gu Dejun, Lin Ailan, et al.Spatial patterns of tropospheric biennial oscillation and its numerical simulation.Adv Atmos Sci, 2008, 25(5):815-823. doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0815-9 [41] Zhang R, Sumi A, Kimoto M.Impact of El Nino on the East Asian Monsoon:A diagnostic study of the '86/87 and '91/92 events.J Meteor Soc Japan, 1996, 74(1):49-62. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.74.1_49 [42] Wang B, Wu R, Fu X.Pacific-East Asia teleconnection:How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Climate, 2000, 13:1517-1536. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2 [43] Zhang R, Li T, Wen M, et al.Role of intraseasonal oscillation in asymmetric impacts of El Niño and La Nia on the rainfall over southern China in boreal winter.Clim Dyn, 2015, 45:559-567. doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2207-4 [44] Guo Z, Zhou T, Wu B.The asymmetric effects of El Niño and La Nia on the East Asian winter monsoon and their simulation by CMIP5 atmospheric models.J Meteorol Res, 2017, 31(1):82-93. doi: 10.1007/s13351-017-6095-5 [45] 魏凤英.我国短期气候预测的物理基础及其预测思路.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(1):1-11. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110101 [46] 李清泉, 孙丞虎, 袁媛, 等.近20年我国气候监测诊断业务技术的主要进展.应用气象学报, 2013, 24(6):666-676. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20130603 [47] 贾小龙, 陈丽娟, 高辉, 等.我国短期气候预测技术进展.应用气象学报, 2013, 24(6):641-655. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20130601 [48] He C, Wang L, Gu D, et al.The fraction of East Asian interannual climate variability explained by SST:An estimation based on 12 CMIP5 models.Atmos Sci Lett, 2017, 18:45-51. doi: 10.1002/asl.722 [49] 陈丽娟, 袁媛, 杨明珠, 等.海温异常对东亚夏季风影响机理的研究进展.应用气象学报, 2013, 24(5):521-532. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20130502 [50] 郭其蕴, 王继琴.青藏高原的积雪及其对东亚季风的影响.高原气象, 1986, 5(2):116-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX198602001.htm [51] Meehl G A.Coupled land-ocean-atmosphere processes and south Asian monsoon variability.Science, 1994, 266(2):263-267. [52] Wu B, Yang K, Zhang R.Eurasian snow cover variability and its association with summer rainfall in China.Adv Atmos Sci, 2009, 26(1):31-44. doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-0031-2 [53] Yim S Y, Jhun J G, Lu R, et al.Two distinct patterns of spring Eurasian snow cover anomaly and their impacts on the East Asian summer monsoon.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D22), DOI: 10.1029/2010JD013996. [54] 许立言, 武炳义.欧亚大陆春季融雪量与东亚夏季风的可能联系.大气科学, 2012, 36(6):1180-1190. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2012.12001 [55] Zhang R, Zhang R, Zuo Z.Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation.J Clim, 2017, 30(9):3421-3437. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0214.1 [56] 李崇银, 龙振夏.西太平洋副高活动与平流层QBO关系的研究.大气科学, 1997, 21(6):670-678. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK706.003.htm [57] Zheng Bin, Gu Dejun, Li Ailan, et al.Dynamical mechanism of the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation impact on the South China Sea summer monsoon.Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(9):1424-1432. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0075-z [58] Meehl G A.A coupled air-sea biennial mechanism in the tropical Indian and Pacific regions:Role of the ocean.J Climate, 1993, 6:31-41. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006<0031:ACASBM>2.0.CO;2 [59] Yang S, Lau K M.Influences of sea surface temperature and ground wetness on Asian summer monsoon.J Climate, 1998, 11:3230-3246. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011<3230:IOSSTA>2.0.CO;2 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: