Impacts of the Regional North Polar Vortex Anomalies on Summer Precipitation of the Tarim River Basin
-
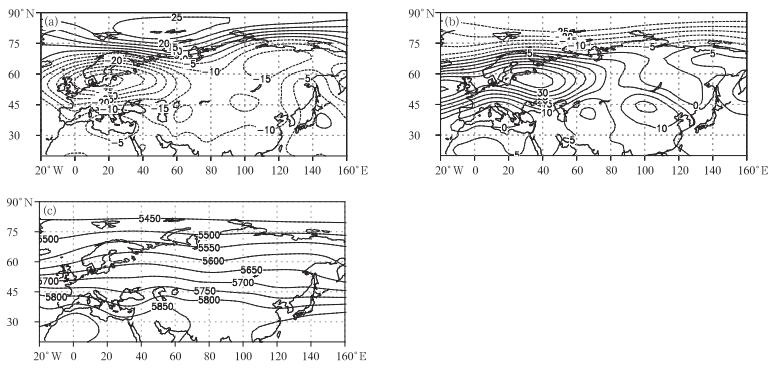
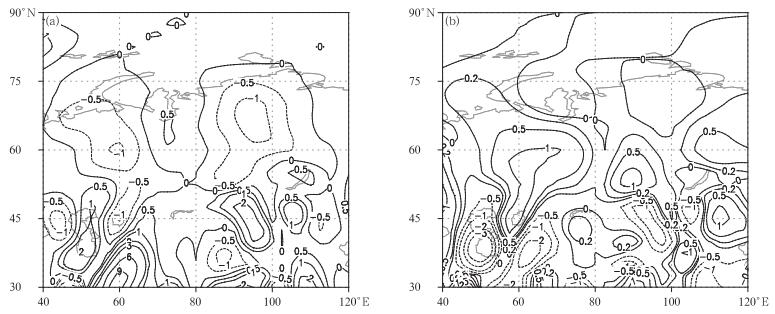
摘要: 采用1961-2015年夏季大西洋-欧洲极涡面积指数和塔里木河流域43个站降水资料,研究该区域极涡面积异常对该流域降水的影响。结果表明:两者年际变化呈显著的反位相关系;在极涡面积异常偏小(大)年,西风急流在西亚和中亚减弱(增强),在东亚则相反;500 hPa欧洲中部和贝加尔湖地区的高压脊偏强(偏弱),东亚低压槽偏弱(偏强),中亚经向环流增强(减弱);700 hPa塔里木河流域天气扰动活跃(不活跃),东风和西南风(西北风)的水汽输送增强,西部和北部等主要降水区水汽辐合(辐散),该流域降水偏多(偏少)。在极涡面积异常偏小年的夏季,塔里木河流域水平风场和垂直运动从高纬度到低纬度的经向变化分布与大西洋-欧洲区相似,大西洋-欧洲极涡区与塔里木河流域之间存在西北-东南的环流异常分布,大西洋-欧洲极涡面积异常可能通过该环流异常分布影响塔里木河流域及周边风场、水汽输送和垂直运动,进而影响到该流域降水。Abstract: With precipitation data of 43 stations in the Tarim River Basin and the polar vortex areas data in the Atlantic-European (polar vortex) in summer of 1961-2015, variation characteristics of the precipitation and the polar vortex, the correlation and impacts of north polar vortex anomaly on precipitation in the Basin are studied. The precipitation in the Basin has been increasing since 1961, while the polar vortex is decreasing, and a significant negative correlation is found. In negative (positive) polar vortex anomaly years, in the upper atmosphere layer, the significantly weaker (stronger) subtropical westerly jet in West Asia and Central Asia, while it is the opposite in East Asia (35°-45°N, 120°-160°E) and the Basin, where the high-middle latitude cold air and mid-low latitude warm wet air that enter the Tarim River Basin increase (decrease) and strengthen (weaken). In the middle layer, negative (positive) polar vortex anomaly may lead to stronger (weaker) Middle European ridge and the Baike Lake ridge, weaker (stronger) East Asia trough, increased (decreased) meridional circulation in the Central Asian, and converging (diverging) stream in this basin. In the low layer, negative (positive) polar vortex anomaly may lead to stronger (weaker) anomaly easterly and southwesterly (northwesterly and northeasterly), stronger (weaker) weather disturbance. More east vapor flux is found entering the Basin comparing to the west vapor flux outflowing away this Basin. Moreover, the southern and eastern vapor flux converging in the southwest borders, and the convergence of vapor flux are strengthened (weakened) in the main precipitation areas of the Basin, which all lead to the increasing (decreasing) of precipitation in the Tarim River Basin.In summer, the polar vortex anomalies in the Atlantic-European have impacts on the meridional wind, zonal wind and the vertical motion from the high latitude to the low latitude by the meridional correlations. In the meridional range of the Tarim River Basin, the meridional variation distributions of the meridional wind, zonal wind and the vertical motion are formed from high latitudes to low latitudes by the zonal correlation, which are similar to those of the Atlantic-European, and anomalies of the wind field and the water vapor transition are also triggered in the Basin and its adjacent areas, impacting the precipitation. Therefore, the north polar vortex anomalies could possibly have significant denotative meaning on the Tarim River Basin precipitation in summer.
-
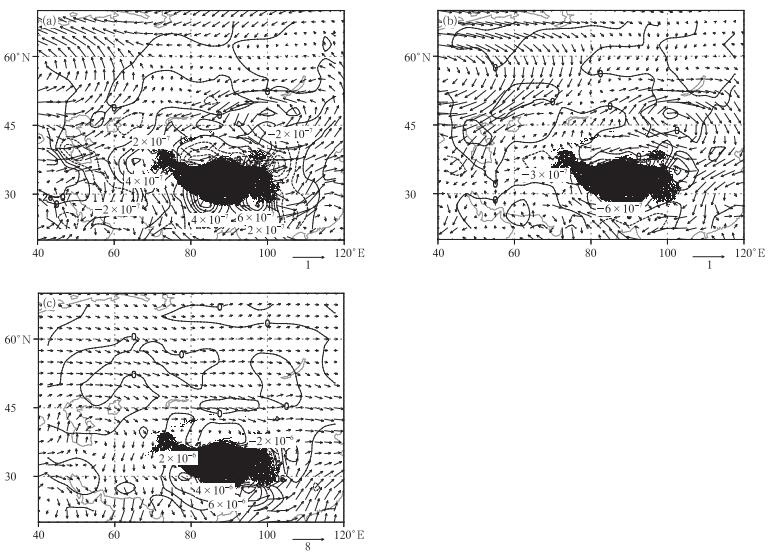
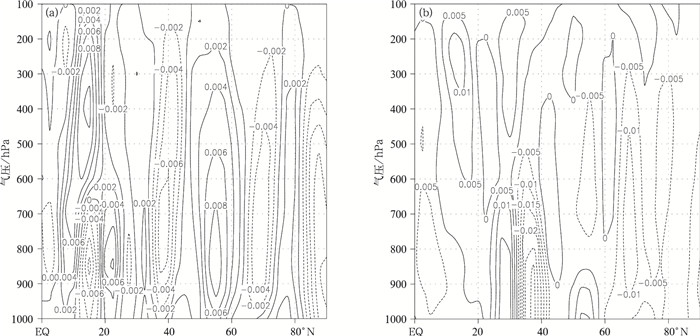
图 7 夏季极涡面积异常偏大年(a)和异常偏小年(b) 700 hPa水汽通量距平场(矢量,单位: g/(hPa·cm·s))与水汽通量散度距平场(等值线为散度, 单位: g/(hPa·cm2·s)及700 hPa水汽通量多年平均场和水汽通量散度多年平均场(c)
Fig. 7 Composites of 700 hPa vapor flux anomaly (vector, unit: g/(hPa·cm·s)), divergence anomaly (contour, unit: g/(hPa·cm2·s)) and mean field according to years of larger area(a) and smaller area(b) with the mean during 1961-2015(c) of north polar vortex in summer
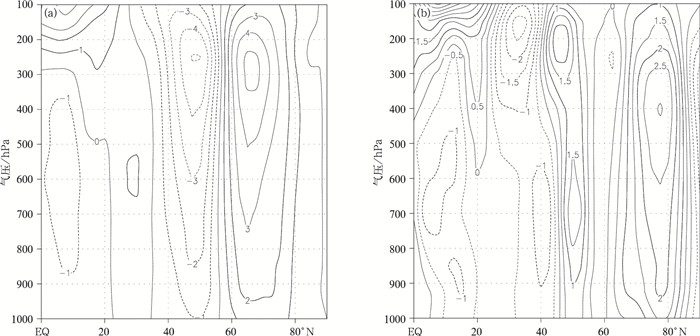
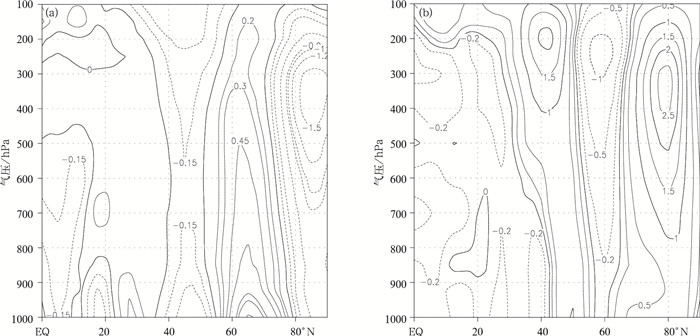
图 8 夏季极涡面积异常偏小年与异常偏大年大西洋—欧洲地区(30°W~60°E)(a)和塔里木河流域(74°~100°E)(b)平均纬向风差异场纬度-高度剖面图(单位:m·s-1)
Fig. 8 Latitude-height cross sections of mean zonal wind difference between years of smaller area and larger area of polar vortex in the Atlantic-Earopean(30°W-60°E)(a) and that in the Tarim River Basin(74°-100°E)(b) in summer(unit: m·s-1)
图 9 夏季大西洋—欧洲地区(30°W~60°E)(a)及塔里木河流域(74°~100°E)(b)极涡面积异常偏小年与异常偏大年平均经向风差异场纬度-高度剖面图(单位:m·s-1)
Fig. 9 Latitude-height cross sections of the mean meridional wind difference between years of smaller area and larger area of polar vortex in the Atlantic-European(30°W-60°E)(a) with that in the Tarim River Basin(74°-100°E)(b) in summer(unit: m·s-1)
图 10 夏季大西洋—欧洲地区(30°W~60°E)(a)及塔里木河流域(74°~100°E)(b)极涡异常偏小年与异常偏大年上升运动的平均差异场纬度-高度剖面图(单位:m·s-1)
Fig. 10 Latitude-pressure cross sections of the mean meridional upward motion difference between years of smaller area and larger area of polar vortex(a) in the Atlantic-European(30°W-60°E)(unit: m·s-1) with that in the Tarim River Basin(74°-100°E)(b) in summer(unit: Pa·s-1)
-
[1] 宋郁东, 樊自立, 雷志栋, 等.中国塔里木河水资源与生态问题研究.乌鲁木齐:新疆人民出版社, 2000:167-173. [2] 施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥.西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨.冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3):219-226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200203000.htm [3] 陈亚宁.全球气候变化对新疆塔里木河流域水资源的可能性影响.中国科学(D辑), 2004, 34(11):1047-1053. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2004.11.007 [4] 马柱国, 黄刚, 甘文强, 等.近代中国北方干湿变化趋势的多时段特征.大气科学, 2005, 29(15):671-681. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200505000.htm [5] 李剑锋, 张强, 陈晓宏, 等.基于标准降水指标的新疆干旱特征演变.应用气象学报, 2012, 23(3):322-330. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120308&flag=1 [6] 栾晨, 宋敏红, 蔡英, 等.西北区西部夏半年强降水分布与变化特征.高原气象, 2012, 31(3):629-637. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201203005.htm [7] 陈春艳, 王建捷, 唐冶, 等.新疆夏季降水日变化特征.应用气象学报, 2017, 28(1):72-85. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170107 [8] 李红军, 江志红, 魏文寿.近40年塔里木河流域旱涝的气候变化.地理科学, 2007, 27(6):801-807. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200706012.htm [9] 王鹏祥, 何金海, 郑有飞, 等.近44年来中国西北干湿特征分析.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(6):769-775. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.200706118 [10] 薛燕, 韩萍, 冯国华.半个世纪以来新疆降水和气温的变化趋势.干旱区研究, 2003, 20(2):127-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ200302009.htm [11] Zhao Yong, Zhang Huqiang.Impacts of SST warming in tropical Indian Ocean on CMIP5 model-projected summer rainfall changes over Central Asia.Clim Dyn, 2015, 2(2):233-248. [12] 杨莲梅, 张庆云.北大西洋涛动对新疆夏季降水异常的影响.大气科学, 2008, 32(5):1187-1196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200805015.htm [13] 戴新刚, 汪萍, 张凯静.近60年新疆降水趋势与波动机制分析.物理学报, 2013, 62(12):29201-29207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB201312075.htm [14] Zhao Y.Impact of the middle and upper troposphere cooling over central Asia on the summer rainfall in the Tarim Basin, China.J Clim, 2014, 7:4721-4732. [15] 张云惠, 杨莲梅, 肖开提·多莱特, 等.1971-2010年中亚低涡活动特征.应用气象学报, 2012, 23(3):312-321. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120307&flag=1 [16] Frauenfeld O W, Davis R E.Northern Hemisphere circumpolar vortex trends and climate change implications.J Geophys Res, 2003, 108(D14):4423-4436. doi: 10.1029/2002JD002958 [17] 时珍玲.九十年代以来江淮流域夏季典型旱涝成因分析.气象, 1996, 22(9):35-38. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.1996.09.009 [18] 姚秀萍, 董敏.东北三江流域夏季旱涝基本特征分析.应用气象学报, 2000, 11(3):297-303. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20000345&flag=1 [19] 张恒德, 金荣花, 张友姝.夏季北极涡与副热带高压的联系及对华北降水的影响.热带气象学报, 2008, 24(4):417-422. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGQX200811004089.htm [20] 谭桂容, 孙照渤, 陈海山.华北夏季早涝的环流特征分析.气象科学, 2003, 23(2):135-143. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=qxkx200302001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [21] 马振锋, 高文良, 刘富明, 等.青藏高原东侧初夏早涝的季风环流分析.高原气象, 2003, 22(增刊Ⅰ):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX2003S1001.htm [22] 黄嘉佑, 刘舸, 赵昕奕.副高、极涡因子对我国夏季降水的影响.大气科学, 2004, 28(4):517-526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200404003.htm [23] 熊光明, 陈权亮, 魏麟晓, 等.平流层极涡偏移对我国冬季降水的影响.应用气象学报, 2012, 23(6):683-690. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20120605 [24] 时兴合, 李凤霞, 扎西才让, 等.1961-2004年青海积雪及雪灾变化.应用气象学报, 2006, 17(3):376-382. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060364&flag=1 [25] 王遵娅, 丁一汇.夏季亚洲极涡的长期变化对东亚环流和水汽收支的影响.地球物理学报, 2009, 52(1):20-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200901005.htm [26] 极涡和气温预报课题协作组.北半球500 hPa极涡特征参量的计算与使用说明.吉林省气象科学研究所报告(2), 1989:1-4. [27] 杨莲梅, 张庆云.新疆夏季降水年际变化与亚洲副热带西风急流.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(2):171-179. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080231 [28] 丁一汇.高等天气学.北京:气象出版社, 1991:19-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJU201513125.htm [29] Richard E M, Cecilia M B, Eric J S.Dynamics of recent climate change in the Arctic.Science, 2002, 297:1497-1502. doi: 10.1126/science.1076522 [30] Ding Q, Wang B.Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer.J Clim, 2005, 18:3483-3505, DOI: 10.1175/JCLI3473.1. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: