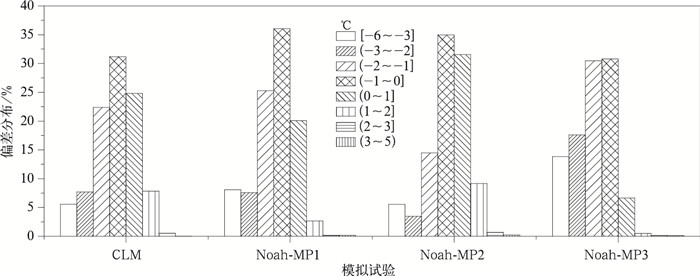
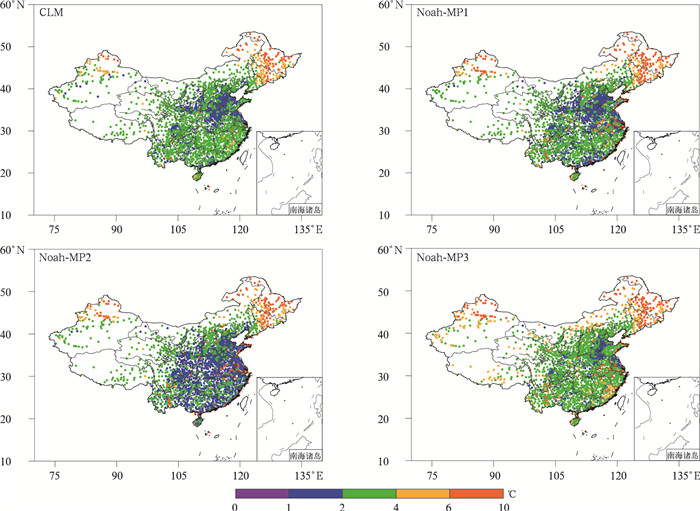
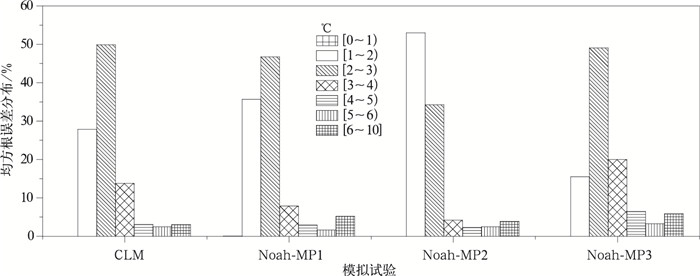
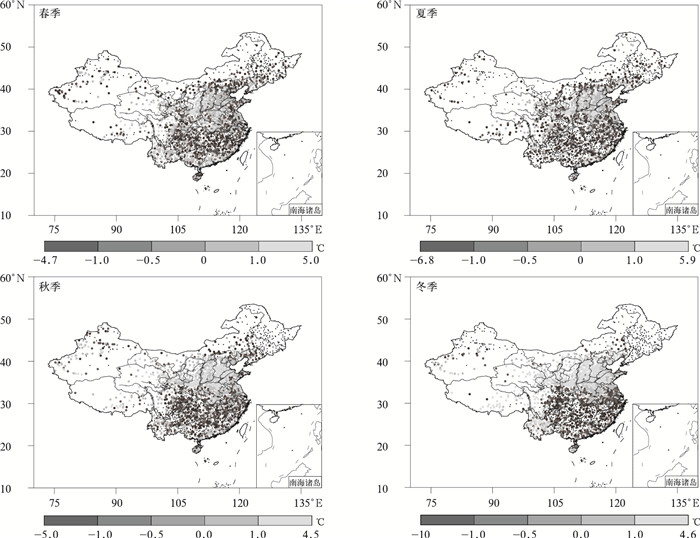
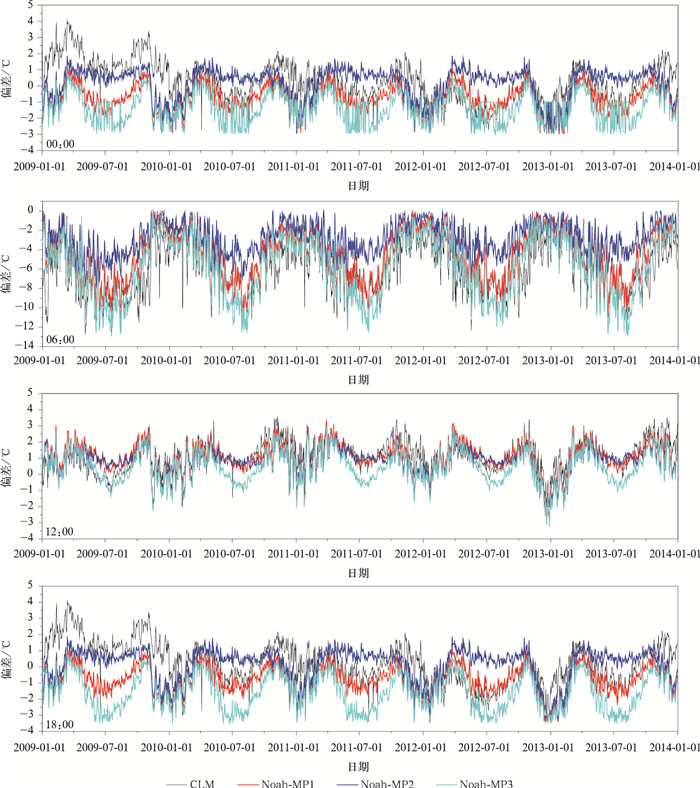
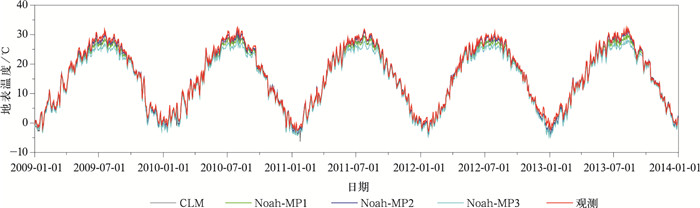
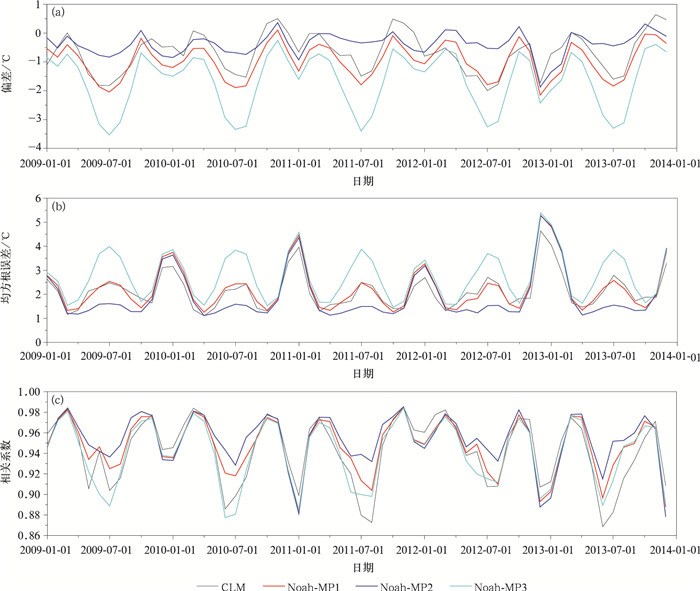
|
[1]
|
张仁华.对于定量热红外遥感的一些思考.国土资源遥感, 1999, 10(1):1-6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.1999.01.01
|
|
[2]
|
甘甫平, 陈伟涛, 张绪教, 等.热红外遥感反演陆地表面温度研究进展.国土资源遥感, 2006, 17(1):6-11. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2006.01.02
|
|
[3]
|
杨晓月. 基于MODISLAI的陆面模式地表温度模拟研究. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10300-1012369209.htm
|
|
[4]
|
李晓萌, 孙永华, 孟丹, 等.近10年北京极端高温天气条件下的地表温度变化及其对城市化的响应.生态学报, 2013, 33(20):6694-6703. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201320029
|
|
[5]
|
张宏群, 杨元建, 荀尚培, 等.安徽省植被和地表温度季节变化及空间分布特征.应用气象学报, 2011, 22(2):232-240. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20110212
|
|
[6]
|
王圆圆, 闵文彬.西藏林芝地区混合像元MODIS地表温度产品验证.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(6):722-730. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20140608
|
|
[7]
|
孙菽芬.陆面过程的物理、生化机理和参数化模型.北京:气象出版社, 2005.
|
|
[8]
|
孙菽芬, 金继明.陆面过程模式研究中的几个问题.应用气象学报, 1997, 8(增刊Ⅰ):50-57. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yyqx7s1.007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
|
|
[9]
|
史学丽.陆面过程模式研究简评.应用气象学报, 2001, 12(1):102-112. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jams/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010114&flag=1
|
|
[10]
|
辛羽飞, 卞林根, 张雪红.CoLM模式在西北干旱区和青藏高原区的适用性研究.高原气象, 2006, 25(4):567-574. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx200604002
|
|
[11]
|
刘少锋, 林朝晖.通用陆面模式CLM在东亚不同典型下垫面的验证试验.气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(3):684-699. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhyhjyj200503034
|
|
[12]
|
陈莹莹, 施建成, 杜今阳, 等.基于GLDAS的中国区地表能量平衡数值试验.水科学进展, 2009, 20(1):25-31. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/skxjz200901004
|
|
[13]
|
孟现勇, 王浩, 刘志辉, 等.基于CLDAS强迫CLM3.5模式的新疆区域土壤温度陆面过程模拟及验证.生态学报, 2017, 37(3):979-995. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201703028
|
|
[14]
|
刘小宁, 任芝花, 王颖, 等.自动观测与人工观测地面温度的差异及其分析.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(5):554-563. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080506
|
|
[15]
|
Entin J K.Evaluation of global soil wetness project soil moisture simulations.J Meteor Soc Japan, 2009, 77(1):183-198. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10014597430
|
|
[16]
|
Guo Z, Dirmeyer P A, Hu Z, et al.Evaluation of the second global soil wetness project soil moisture simulations:2.Sensitivity to external meteorological forcing.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2006, 111(D22S03):5307-5314.
|
|
[17]
|
Li M X, Ma Z G.Comparisons of simulations of soil moisture variations in the Yellow River basin driven by various atmospheric forcing data sets.大气科学进展, 2010, 27(6):1289-1302. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqjz201006007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
|
|
[18]
|
Wang Aihui, Zeng Xubin.Sensitivities of terrestrial water cycle simulations to the variations of precipitation and air temperature in China.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2011, 116(D2):2166-2181. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010AGUFM.H51A0852W
|
|
[19]
|
师春香, 谢正辉, 钱辉, 等.基于卫星遥感资料的中国区域土壤湿度EnKF数据同化.中国科学(地球科学), 2011(3):375-385. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdxk201103009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
|
|
[20]
|
梁晓, 郑小谷, 戴永久, 等.EnKF中误差协方差优化方法及在资料同化中应用.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4):397-405. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20140402
|
|
[21]
|
韩帅, 师春香, 姜立鹏, 等.CLDAS土壤湿度模拟结果及评估.应用气象学报, 2017, 28(3):369-378. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170310
|
|
[22]
|
Xie Y, Koch S, Mcginley J, et al.A Space-time multiscale analysis system:A Sequential variational analysis approach.Mon Wea Rev, 2011, 139(4):1224-1240. doi: 10.1175/2010MWR3338.1
|
|
[23]
|
潘旸, 沈艳, 宇婧婧, 等.基于最优插值方法分析的中国区域地面观测与卫星反演逐时降水融合试验.气象学报, 2012, 70(6):1381-1389. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2012.116
|
|
[24]
|
徐宾, 师春香, 姜立鹏, 等.东亚多卫星集成降水业务系统.气象科技, 2015, 43(6):1007-1014. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qxkj201506001
|
|
[25]
|
Rybicki G B.Radiative transfer.Journal of Astrophysics & Astronomy, 1996, 17(3-4):95-112. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201001009
|
|
[26]
|
Stamnes K, Tsay S C, Nakajima T.Computation of eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the discrete ordinate and matrix operator methods in radiative transfer.Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 1988, 39(5):415-419. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022407388901070
|
|
[27]
|
Hoffman.Community Land Model Version 3.0(CLM3.0) Developer's Guide.J Climate, 2004.
|
|
[28]
|
张正秋, 孙菽芬.陆面网格尺度变换时植被类型处理方法的探讨.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(2):129-136. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20080225
|
|
[29]
|
Yang Z L, Niu G Y.The versatile integrator of surface and atmosphere processes-Part 1.Model description.Global & Planetary Change, 2003, 38(1):175-189. https://arizona.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/the-versatile-integrator-of-surface-and-atmosphere-processes-part
|
|
[30]
|
Yang Zongliang, Niu Guoyue, Mitchell Kenneth E, et al.The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP):2.Evaluation over global river basins.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres (1984-2012), 2011, 116(D12):D12110. doi: 10.1029/2010JD015140
|
|
[31]
|
Niu G Y, Yang Z L.Effects of vegetation canopy processes on snow surface energy and mass balances.J Geophys Res, 2004, 109(D23):D23111. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2004JGRD..10923111N
|
|
[32]
|
王颖, 刘小宁, 鞠晓慧.自动观测与人工观测差异的初步分析.应用气象学报, 2007, 18(6):849-855. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.200706128
|
|
[33]
|
中国气象局.地面气象观测规范.北京:气象出版社, 2005.
|
|
[34]
|
杨士弘.城市生态环境学.北京:科学出版社, 2006.
|


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: