Ground Clutter Detection Algorithm for Array Weather Radar at Changsha Airport
-
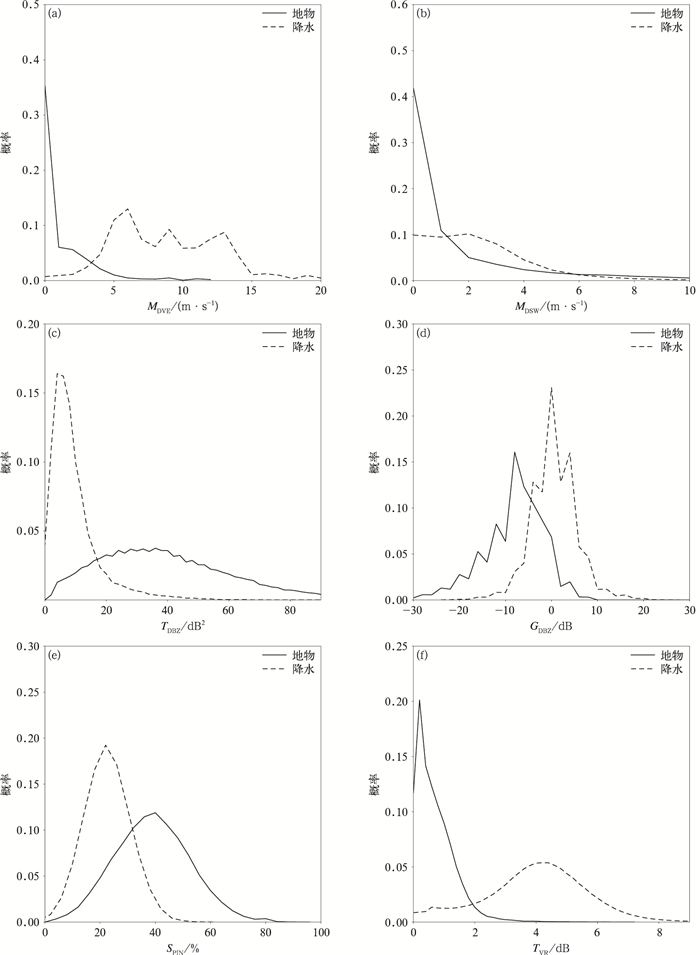
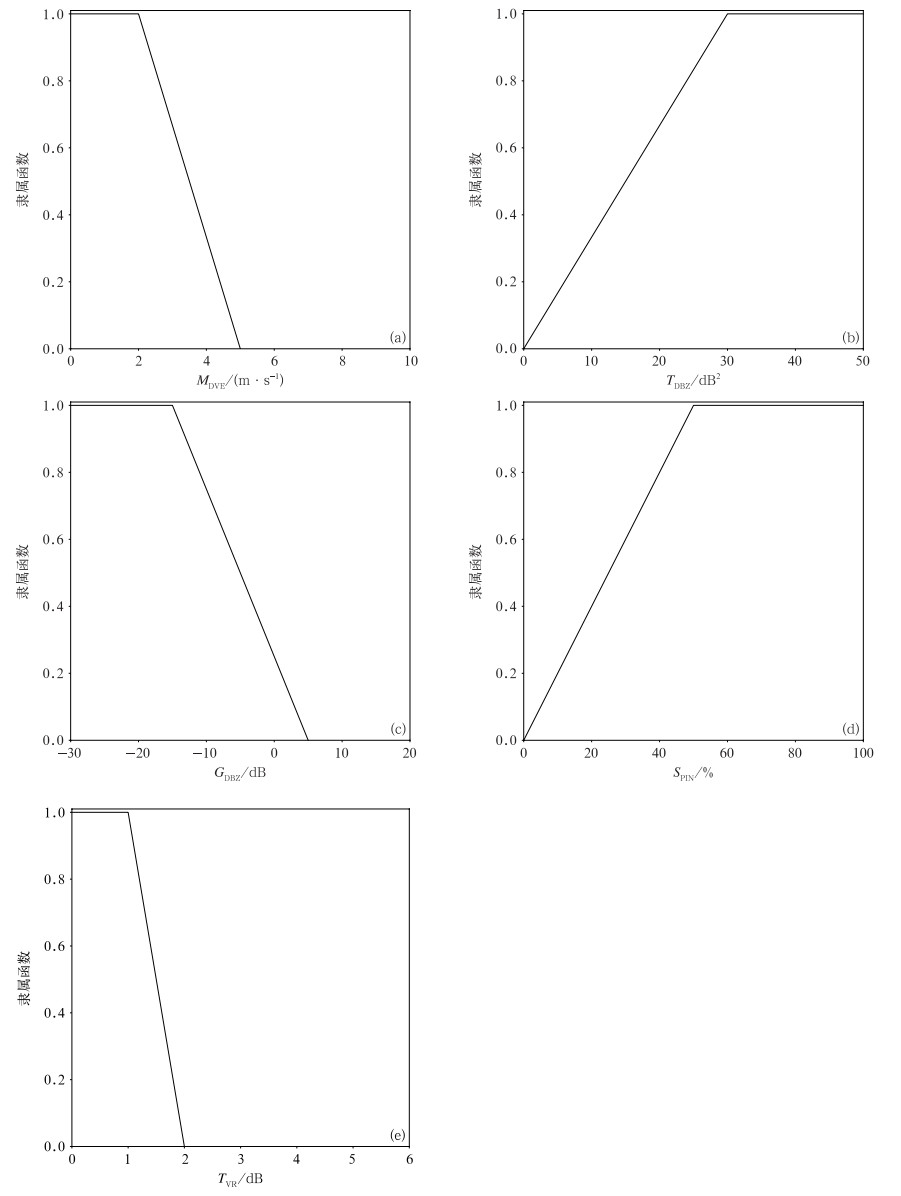
摘要: 地物杂波是影响雷达产品准确性的重要因素。该文提出了一种改进的基于模糊逻辑的阵列天气雷达地物识别算法。在Kessinger模糊逻辑基础上,加入回波强度时间变化量(time variability of reflectivity factor,TVR)参数,利用收集到的雷达数据统计出各输入参数的概率分布,确定隶属函数;分析TVR参数对地物识别算法的贡献,并在不同天气情况下进行识别算法有效性验证。试验结果表明:加入TVR参数,长沙机场阵列天气雷达地物识别准确率最大可提高4%,降水识别误判率最多可降低2%。该文提出的地物杂波识别算法,无降水时,地物识别准确率达96%;有降水时,地物识别准确率达92%;降水回波误判为地物杂波的误判率约为10%,能较好地区分降水回波和地物杂波。
-
关键词:
- 地物杂波;
- 模糊逻辑;
- 回波强度时间变化量(TVR);
- 阵列天气雷达
Abstract:In order to obtain more detailed small-scale weather system data, Meteorological Observation Center of China Meteorological Administration (CMA) designed and developed X-band array weather radar (AWR), cooperating with relevant manufacturers. In March of 2018, the first prototypeis deployed at Changsha Airport for field experiments. Combing advantages of networked radars and a distributed phased array technology, the AWR has a highly coordinated scanning mode and high spatial and temporal resolutions to acquire fine echo intensity and wind field data. Compared with conventional parabolic antenna weather radars, a phased array antenna has wider beams and stronger side lobes, so that more ground clutter will appear in radar echoes. If the ground clutter cannot be effectively detected and removed, the accuracy of radar products will be affected seriously.Data collected by the X-band AWR at Changsha Airport are used to study the ground clutter detection algorithm for the AWR. According to the research progress all over the world, characteristic parameters of reflectivity factors, radial velocity and velocity spectrum width are extracted. In addition, time variability of reflectivity factor (TVR), a new parameter, is added due to the high temporal and spatial resolution of the AWR. Based on analyzing statistical characteristics of each feature parameter, membership functions are determined. The contribution of TVR to the clutter detection algorithm and the performance of the algorithm on different weather conditions are analyzed. Results show that the accuracy of ground clutter detection for Changsha Airport AWR can be maximally increased by 4% by adding TVR, and the error rate of detecting the precipitation echo as clutter echo can be decreased by 2%. The accuracy of the proposed ground clutter detection algorithm reaches 96% in the detection of ground clutter when no precipitation processes happen. In the precipitation weather, the accuracy is 92%, and the error rate of detecting the precipitation echo as clutter echo is about 10%. The algorithm can basically detect and remove the ground clutter echoes from precipitation echoes.
-
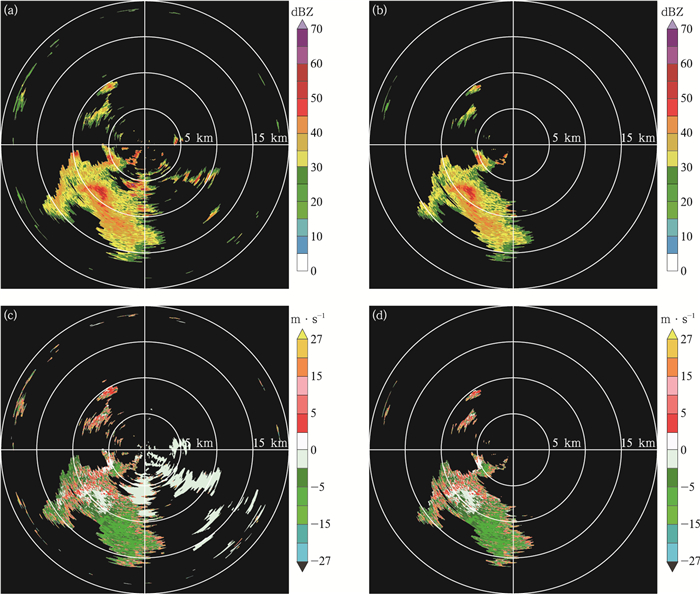
图 5 2019年6月21日15:17子阵1在1.4°仰角的回波强度和径向速度(相邻距离圈间距为5 km) (a)识别前的回波强度,(b)识别后的回波强度,(c)识别前的径向速度,(d)识别后的径向速度
Fig. 5 The echo intensity and radial velocity of subarray 1 at 1.4°elevation angle at 1517 BT 21 Jun 2019 (the distance between adjacent range rings is 5 km) (a)echo intensity before ground clutter detection, (b)echo intensity after ground clutter detection, (c)radial velocity before ground clutter detection, (d)radial velocity after ground clutter detection
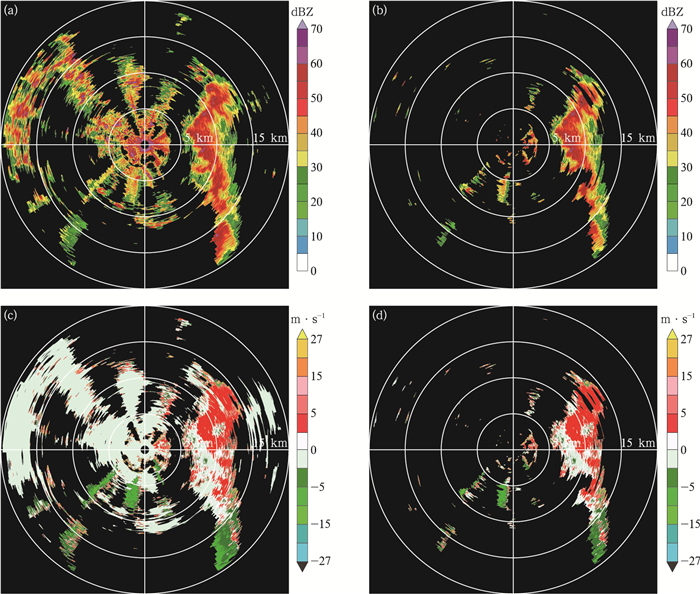
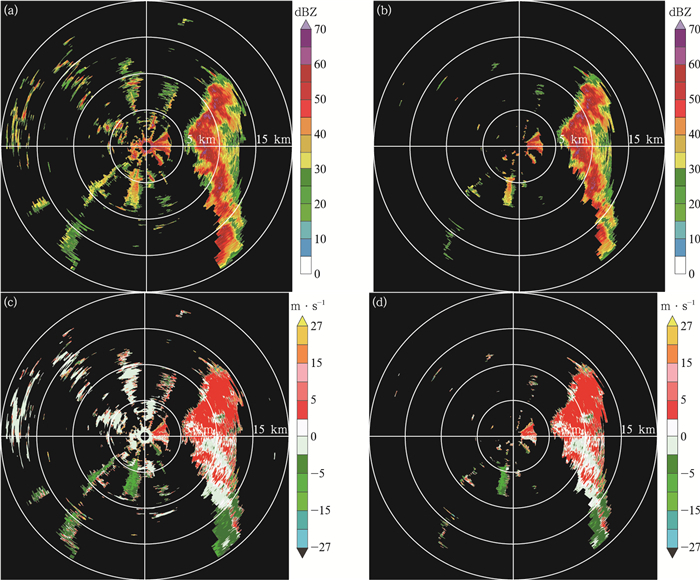
图 6 2019年7月21日13:57子阵2在1.4°仰角的回波强度和径向速度(相邻距离圈间距为5 km) (a)识别前的回波强度,(b)识别后的回波强度,(c)识别前的径向速度,(d)识别后的径向速度
Fig. 6 The echo intensity and radial velocity of subarray 2 at 1.4°elevation angle at 1357 BT 21 Jul 2019 (the distance between adjacent range rings is 5 km) (a)echo intensity before ground clutter detection, (b)echo intensity after ground clutter detection, (c)radial velocity before ground clutter detection, (d)radial velocity after ground clutter detection
图 7 2019年7月21日13:57子阵2在2.8°仰角的回波强度和径向速度(相邻距离圈间距为5 km) (a)识别前的回波强度,(b)识别后的回波强度,(c)识别前的径向速度,(d)识别后的径向速度
Fig. 7 The echo intensity and radial velocity of subarray 2 at 2.8° elevation angle at 1357 BT 21 Jul 2019 (the distance between adjacent range rings is 5 km) (a)echo intensity before ground clutter detection, (b)echo intensity after ground clutter detection, (c)radial velocity before ground clutter detection, (d)radial velocity after ground clutter detection
表 1 地物识别准确率和降水识别误判率
Table 1 Accuracy of ground clutter detection and error rate of precipitation detection
阈值 地物识别准确率/% 降水识别误判率/% 采用TVR 未采用TVR 采用TVR 未采用TVR 0.40 96 93 12 14 0.45 91 87 10 11 0.50 80 80 7 8 0.55 75 72 4 4 0.60 64 63 3 3 表 2 无降水情况下地物识别算法效果
Table 2 Accuracy of ground clutter detection algorithm under no precipitation condition
子阵 地物识别准确率/% 1 96 2 93 3 94 表 3 混合性降水算法识别效果
Table 3 Accuracy of ground clutter detection and error rate of precipitation detection under mixed prcipitation condition
子阵 地物识别准确率/% 降水识别误判率/% 1 94 9 2 92 10 3 91 10 表 4 对流性降水算法识别效果
Table 4 Accuracy of ground clutter detection and error rate of precipitation detection under convective precipitation condition
子阵 地物识别准确率/% 降水识别误判率/% 1 92 10 2 91 12 3 94 10 -
[1] Smith P.Siting Considerations for Weather Radars//Preprints, 15th Conference on Radar Meteorology.Champaign-Urbana, IL, American Meteorological Society, 1972: 99-100. [2] Mann D, Evans J E, Merritt M W.Clutter Suppression for Low Altitude Wind Shear Detection by Doppler Weather Radars//Preprints, 23rd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Snowmass, CO, American Meteorological Society, 1986: R9-R13. [3] Michelson D B, Andersson T.Identification and Suppression of Anomalous Propagation Echoes in Two-dimensional Radar Images//Preprints, 27th International Conference on Radar Meteorology, Vail, CO, American Meteorological Society, 1995: 665-658. [4] Torres S, Zrnic D.Ground clutter canceling with a regression filter.J Atmos Ocean Tech, 1999, 16(10):1364-1372. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wQ0z/bjrMeCV3n6F1KbR4lb3tZ8RkExHthP2NiSYQYk= [5] Passarelli R E.Autocorrelation Techniques for Ground Clutter Rejection//Preprints, 20th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Boston, MA, American Meteorological Society, 1981: 308-313. [6] Schmid W, Hogl D, Joss J.Test of Clutter Suppression Techniques in the Swiss Alps//Preprints, 25th InternationalConference on Radar Meteorology, Paris, France, American Meteorological Society, 1991: 875-878. [7] Siggia A D, Passarelli R E.Gaussian Model Adaptive Processing (GMAP) for Improved Ground Clutter Cancellation and Moment Calculation//Preprints, 3rd European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Visby, Gotland, Sweden, ERAD, 2004: 67-73. [8] Li Y, Zhang G, Doviak R J, et al.A new approach to detect ground clutter mixed with weather signals.IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4):2373-2387. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1f84041aa2495aa71f72efc07c158ee0 [9] Steiner M, SmithJ.Use of three-dimensional reflectivity structure for automated detection and removal of nonprecipitating echoes in radar data.J Atmos Ocean Tech, 2002, 19(5):673-686. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=21ba06b231021e0736bfd5e95a5ed986 [10] Zhang J, Wang S, Clarke B.WSR-88D Reflectivity Quality Control Using Horizontal and Vertical Reflectivity Structure//Preprints, 11th Conferenceon Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology, Hyannis, MA, American Meteorological Society, 2004: 5. [11] Lakshmanan V, Hondl K, Stumpf G, et al. Quality Control of Weather Radar Data Using Texture Features and a Neural Network//Preprints, 31st Conference on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, Washington. American Meteorological Society, 2003: 522-525. [12] Lakshmanan V, Fritz A, Smith T, et al.Anautomated technique to quality control radar reflectivity data.J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2007, 46(3):288-305. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.383.6893 [13] Kessinger C, Ellis S, Vanandel J, et al.The AP Clutter Mitigation Scheme for the WSR-88D//Preprints, 31st Conference on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, Washington.American Meteorological Society, 2003: 526. [14] Ferrer M B, Torres D S, Alexandri C C, et al.A fuzzy logic technique for identifying nonprecipitatingechoes in radar scans.J Atmos Ocean Tech, 2006, 23(9):1157-1180. doi: 10.1175/JTECH1914.1 [15] Cho Y H, Lee G W, Kim K E, et al.Identification and removal ofground echoes and anomalous propagation using the characteristics of radar echoes.J Atmos Ocean Tech, 2006, 23(9):1206-1222. doi: 10.1175/JTECH1913.1 [16] 刘黎平, 吴林林, 杨引明.基于模糊逻辑的分步式超折射地物回波识别方法的建立和效果分析.气象学报, 2007, 65(2):252-260. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qxxb200702011 [17] 江源, 刘黎平, 庄薇.多普勒天气雷达地物回波特征及其识别方法改进.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(2):203-213. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20090210 [18] 李丰, 刘黎平, 王红艳, 等.S波段多普勒天气雷达非降水气象回波识别.应用气象学报, 2012, 23(2):147-158. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20120203 [19] 李丰, 刘黎平, 王红艳, 等.C波段多普勒天气雷达地物识别方法.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(2):158-167. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20140205 [20] Ruiz J J, Miyoshi T, Satoh S, et al.Aquality control algorithm for the Osaka phased array weather radar.SOLA, 2015, 11:48-52. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/sola/11/0/11_2015-011/_article/-char/ja/ [21] 刘黎平, 吴翀, 汪旭东, 等.X波段一维扫描有源相控阵天气雷达测试定标方法.应用气象学报, 2015, 26(2):129-140. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150201 [22] 吴翀, 刘黎平, 汪旭东, 等.相控阵雷达扫描方式对回波强度测量的影响.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4):406-414. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20140403 [23] 杨金红, 高玉春, 程明虎, 等.相控阵天气雷达波束特性.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(1):119-123. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20090116 [24] 马舒庆, 陈洪滨, 王国荣, 等.阵列天气雷达设计与初步实现.应用气象学报, 2019, 30(1):3-14. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190101 [25] 程周杰, 刘宪勋, 朱亚平.双偏振雷达对一次水凝物相态演变过程的分析.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(5):594-601. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20090511 [26] 赵瑞金, 刘黎平, 张进.硬件故障导致雷达回波错误数据质量控制方法.应用气象学报, 2015, 26(5):578-589. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150507 [27] 张秉祥, 李国翠, 刘黎平, 等.基于模糊逻辑的冰雹天气雷达识别算法.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4):415-426. http://qikan.camscma.cn/jamsweb/article/id/20140404 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: