Application of QVP Method to Winter Precipitation Observation Based on Polarimetric Radar
-
摘要: 双偏振雷达是研究降水微物理过程的重要探测设备,为研究我国东部沿海地区冬季降水的微物理特性,选取2019—2020年不同天气背景下(包含相态转换)影响上海的冬季降水过程,基于上海南汇WSR-88D双偏振雷达资料,采用准垂直廓线(QVP)方法反演3次降水过程的反射率因子ZH、差分反射率ZDR和相关系数ρhv的高度-时间廓线。基于QVP,结合探空、再分析资料、地面自动气象站和雨滴谱数据,分析过程时段内融化层高度变化、云中粒子微物理特征,同时借助云雷达观测比对QVP方法的实际效果。结果表明:QVP方法反演的廓线可以体现贝吉龙过程的发生以及融化层高度的变化,并能够有效区分过程时段内的凇附和聚合过程。与此同时,对于非连续性或非均匀性质的降水系统,有针对性地选择方位利用QVP方法进行处理可准确获取重点关注区域降水云系中的微物理过程变化。综上所述,QVP方法反演的高度-时间廓线能够用于降水相态的快速诊断及降水粒子从空中到地面演变的微物理过程分析,为冬季降水相态短时临近预报提供依据。Abstract: Winter precipitation events, especially those involving transitions of precipitation type, continue to pose a formidable forecasting and nowcasting challenge to operational meteorologists. The polarimetric radars provide unique insight into microphysical processes in clouds and precipitation. Using polarimetric radars in conjunction with thermodynamic information is a promising way for better winter precipitation detection. To explore the microphysical characteristic and the internal structure of winter precipitation over eastern coast of China, the data collected by the WSR-88D polarimetric radar at Nanhui, Shanghai are exploited by the quasi-vertical profile (QVP) method. The QVP method involves azimuthal averaging of radar reflectivity factor at horizontal polarization(ZH), differential reflectivity(ZDR) and the copular correlation coefficient (ρhv) at high antenna elevation, presenting QVPs in a height-time format. QVP generation is an efficient way to examine the temporal evolution of microphysical processes governing precipitation production and to display physical links between polarimetric signatures aloft in the ice-phase or mixed-phase parts of the clouds. In 3 different synoptic system governing snow cases affecting Shanghai, the QVPs retrieved from dual-polarization radars at elevations of 19.5ånd 9.9åre demonstrated to successfully monitor the evolution of melting layer and Bergeron process. They also provide opportunities to discriminate between the processes of snow aggregation and riming with the joint analysis of reanalysis data and observations of radio sounding, auto weather station, disdrometer and wind profiler radar. The vertical observation by cloud radar data is used to compare with QVP retrieved profile. Additionally, for discontinuous or multi-scale synoptic precipitation, a selected azimuthal averaging QVP technique is introduced to separate QVPs into before and after the synoptic system for detailed comparisons and monitoring microphysical processes leading to precipitation formation. The method is demonstrated to monitor important microphysical signatures as well as following precipitation development. In conclusion, the procedure for generating quasi-vertical profiles of polarimetric radar variables is very simple and straightforward, and the QVP plots in the height-time format can be produced in real time for operational polarimetric weather radars as a standard product, which is very easy to implement and very promising to use along with traditional weather radar products of PPIs and reconstructed RHIs. The QVP methodology is particularly effective because of its local coverage and high precision as well as its potential for nowcasting.
-
引言
云中粒子的相态变化及微物理过程演变对天气过程的发生发展具有重要作用,传统的飞机探测方式需耗费大量人力物力,连续观测存在困难[1-3]。双偏振雷达的偏振参量能够较经济快捷地探测到云中冰晶的具体形状和结构,进而获悉云中降水相态[4-6]。伴随着双偏振雷达升级工作的逐步开展和顺利完成,国内外学者针对双偏振雷达资料在云物理方面的应用进行了多样性探索。
Brandes等[7]研究双偏振雷达融化层的特点并设计基于ZH,ρhv以及退偏振比Ldr计算融化层高度的算法;Giangrande等[8]结合ZH,ρhv,ZDR和当地气候特征改进融化层高度算法,并利用实况(模式)探空进行检验;曹杨等[9]利用C波段双偏振雷达资料设计零度层亮带识别及融化层厚度估计的算法。Wu等[10]利用双偏振雷达资料分析2016年台风妮妲发展、成熟及衰减阶段对流云微物理过程变化特征。刘黎平等[11]利用Ka,Ku和C波段连续波雷达和激光雷达,并配以微波辐射计、雨滴谱仪等设备,获取高时空分辨率的云和降水宏微观垂直结构特征数据。Williams等[12]比较了冬季暴雪和暖季层状云降水ZDR的差异;杨忠林等[13]利用C波段双偏振雷达和雨滴谱资料进行江淮梅雨期极端对流过程的微物理特征分析。Zawadzki等[14]通过数值模拟发现凇附过程具有ZH增大且融化层“下凹”的特点。Ryzhkov等[15]基于S,C和X波段双偏振雷达资料,利用QVP方法进行MCS、台风和冻雨过程的微物理过程观测;Kaltenboeck等[16]针对一次暖锋影响下的冻雨过程,利用QVP方法反演C波段双线偏振雷达的高度-时间廓线,并结合风廓线雷达资料分析其微物理特征。程周杰等[17]利用3 GHz双偏振雷达RHI探测资料和温度廓线资料,建立Beta型成员函数的模糊逻辑算法识别云粒子相态。梅垚等[18]利用移动式C波段双偏振雷达和多普勒天气雷达观测资料,通过双多普勒天气雷达风场反演、偏振雷达相态识别,揭示两次高原冰雹云发生发展的动力、微物理和热力结构特征。
目前国内工作大多围绕C波段雷达且集中于暖季降水过程的双偏振雷达资料分析,有关华东沿海地区S波段双偏振雷达的分析及冬季降水微物理过程的研究报道较少。鉴于此,本文在前人工作基础上,利用自动气象站、雨滴谱仪、风廓线仪、毫米波雷达及双偏振雷达等多源观测资料,选取回流降水、弱冷空气降水和强冷空气降水共3次包含相态转换的降水过程,基于QVP方法对过程时段内的微物理特性进行分析,以期扩展双偏振雷达资料在华东地区冬季降水中的应用,进一步挖掘双偏振雷达的实际业务应用价值。
1. 资料与方法
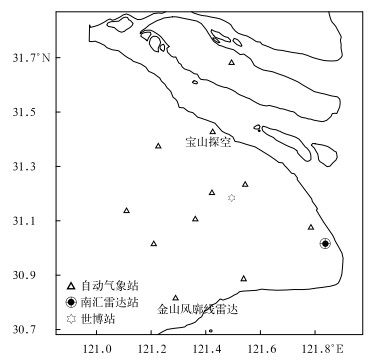
本文选用资料来自上海市辖区内的国家级自动气象站(11个,配备天气现象仪)、探空站(宝山)、雨滴谱仪(世博站)、风廓线雷达(金山站)以及南汇WSR-88D型双偏振雷达,具体观测设备位置分布如图 1所示。所用资料为2019—2020年3次降水过程对应时段。
双偏振雷达的准垂直廓线(quasi-vertical profiles,QVP)方法是一种双偏振资料释用方法,该方法原理清晰并能充分发挥双偏振雷达高时空分辨率的特点。
QVP方法针对指定仰角的所有径向,计算相同距离库数(距离雷达相同距离)所有有效径向雷达参量的平均值。针对某一固定仰角和距离库处的参量平均值计算如下:

(1) 式(1)中,M为取平均值运算,v为对应的雷达参量(如反射率因子ZH、差分反射率ZDR、相关系数ρhv等),i为仰角层数,j为径向方位角,k为距离库数,H为雷达径向距离对应的高度,由式(2)计算得到[19]。

(2) 式(2)中,δ为雷达仰角,R为雷达径向距离,Rm为等效地球半径。为防止高仰角处回波较少导致计算结果代表性较差,引入约束条件:指定仰角和距离处,满足ρhv>0.6且ZH>-10 dBZ的回波点数量超过30个。
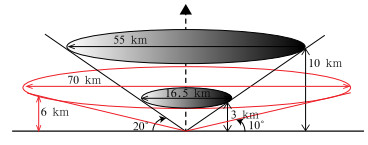
如图 2所示,以19.5°仰角为例,QVP方法在3 km (10 km)高度表征直径为16.5 km(55 km)圆上相关变量的平均值;对9.9°仰角,QVP方法在6 km高度表征直径为70 km圆上相关变量的平均。天气雷达的体扫制式导致相同高度低仰角的取样体积数倍于高仰角,故QVP方法在仰角的选取方面具有“两难”特性。选择较高仰角(10°~ 20°仰角)可以获得局地的精细化降水云系特征,但观测资料较少且不易获得近地面降水粒子微物理特征;选择较低仰角(如6.4°仰角)可以获得范围更广和垂直高度更低的降水微物理特征,但单个取样体积和取样范围的扩大会削弱结果的代表性。综合上海地域范围和精细化观测的客观要求,本文选择19.5°和9.9°仰角利用QVP方法进行反演。
QVP方法计算0°~ 360°方位角内同一径向距离处的参量平均,对层状降水或较大尺度降水系统时相对可靠,但对小尺度或非连续系统(锋面、降水相态存在明显变化)全方位角径向平均会降低结果可靠性。因此有针对性地选择方位角利用QVP方法进行处理,将有效区分降水系统前后的微物理过程变化,本文对个例3的降水相态明显变化时(冷锋过境),采用30°~ 210°方位和210°~ 360°及0°~ 30°方位划分两个“扇形”区域分别进行反演,从而揭示天气系统过境引起(地面)降水相态转变前后云微物理特征变化。
2. 个例应用
本文选择回流降水、弱冷空气降水和强冷空气降水共3种不同天气形势下的降水个例(均包含相态转换过程)。利用QVP方法反演雷达变量的高度-时间廓线,并结合雨滴谱仪、风廓线雷达、自动气象站、实况探空以及NCEP再分析资料讨论降水过程中云微物理变化。俞小鼎[20]、刘晓璐等[21]和何彩芬等[22]指出当对流层大气存在明显干层时,冰雹融化的高度与湿球0℃高度(wet-bulb temperature zero,WBZ)配合较好,故本文采用Bakhshaii等[23]提出的非迭代近似方法计算湿球温度,并以此为基础开展后续分析。
2.1 2019年2月8日降水过程
2019年2月7—8日受500 hPa快速东移短波槽、850 hPa东北风和地面冷高压南下共同影响,华东地区发生一次大范围雨雪天气,水汽为850~925 hPa来自海面的东北—偏东风回流(图略)。受其影响,上海地区2月8日00:30—07:00(北京时,下同)出现3~10 mm降水(雨和雨夹雪)过程(崇明10.5 mm,宝山10.4 mm,浦东7.7 mm),累积降水量自西北向东南呈减少趋势。
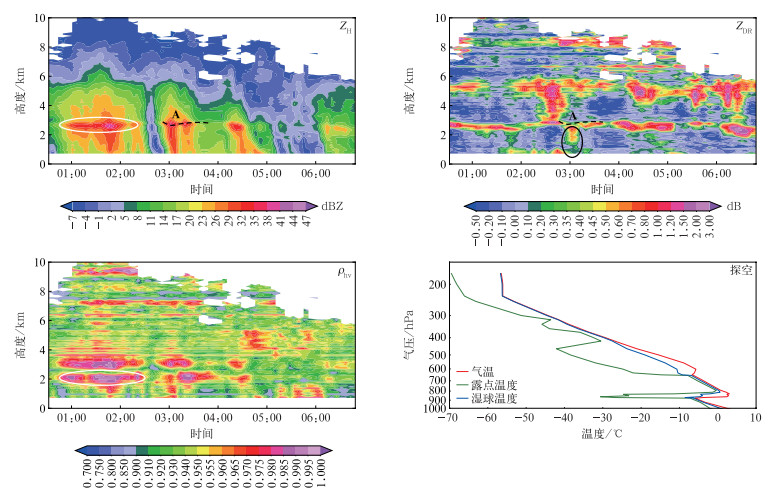
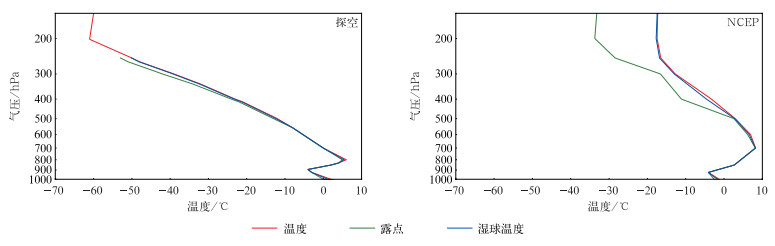
采用19.5°仰角的QVP方法反演的高度-时间分布如图 3所示。5~6 km高度内,ZH自上而下由11~14 dBZ增加至17~20 dBZ,ZDR由低于0.5 dB增加至1.5~2.0 dB,对应的湿球温度为-15~-10℃。顾震潮[24]证明在上述温度下,云内冰面过饱和度增大,贝吉龙过程使冰晶迅速凝结增长,且该温度下易形成枝状的冰晶,枝状冰晶的相碰与勾连促进其聚并增长并形成大雪花。结合QVP方法反演的廓线和探空层结曲线可推断5~6 km高度范围内发生了贝吉龙过程。该层以上的-20℃湿球温度层(500 hPa附近),冰晶通常是柱状,ZDR为较小的正值甚至负值。5 km高度以下,由于雪花下落过程受不同强度垂直气流的影响,可能破碎,也可能保持碰并增长的过程,使得ZDR在-10~-5℃层的差异较大。
01:00—02:00在2.5 km高度附近,ZH显著增长至32~41 dBZ,ZDR增加至0.7~2.0 dB,ρhv低值区(0.91~0.95)呈窄带状分布,明显低于上下层(约0.99)。2月7日20:00探空显示WBZ在800 hPa(2 km高度附近)和950 hPa(0.2 km高度附近)。结合探空WBZ高度和白色线圈内的雷达回波特征,可判定该高度为本次过程的融化层。
02:30—03:00在3~5 km高度,ZH大多低于8 dBZ,ZDR为0.6~2.0 dB,由于该高度内的雪花粒子较少,粒子数密度较低导致ZH较小;雪花多为片状的扁平化结构,表现为ZDR值较大。03:00在A高度ZH比其上方偏大5~10 dBZ,ZDR在4~6 km高度为0.2~1.0 dB,4 km高度以下至A高度迅速减小至0~0.1 dB,同时融化层存在“下凹”特征,上述回波特征表明降水云系中发生凇附过程[13]。进一步分析可知,4 km至A高度为冰相和液态的降水粒子共存状态,冰晶与过冷水滴发生碰撞后发生凇附作用,凇附作用使柱状冰晶在下落过程中的形态更接近球形,从而导致ZDR降低。同时融化层以下黑色线圈内ZDR为0.3~0.8 dB,该高度的ZH为25 dBZ左右,ρhv为0.965~0.98,这是融化层以下粒子的碰并聚合作用所致[16]。由于-4~0℃的过冷水层较厚(约2.5 km),冰晶碎裂后能够形成更多次生冰晶,使冰晶之间的碰并率增高,尺寸增大,降水粒子数浓度和尺寸的增加使得ZH明显增大。-4℃的环境有利于片状冰晶的生成,在近地面WBZ高度附近,冰晶表面较湿,更容易粘连,使其尺寸增大,ZDR增大。
04:00后,2 km高度以下ρhv低值区(0.91~0.94)开始增厚,表明该高度以下存在冰相粒子和液态降水粒子的混合。为进一步得到500 m以下近地面层降水粒子的相态分布,以下对利用QVP方法反演的9.9°仰角雷达参量进行分析(图 4)。
图 4中01:00—05:00在0.5~1 km高度存在一条ρhv低值带,为液态和固态降水粒子混合带。降水粒子由2.5 km高度降落至500 m以下时,可能经过融化-冻结-再融化的物理过程。天气现象仪观测结果显示:01:00—05:00地面降水要素为密度较小的雨夹雪或雪。南汇自动气象站显示地面温度逐渐降低、湿度增大,小时降水量最强时段在03:00 —04:00(1.2 mm),与凇附现象发生时段配合较一致。
05:00—06:00在0.5~1 km高度ZH减小至10 dBZ,ZDR为-0.2~0.1 dB,ρhv为0.965~0.975,表明该高度内多为聚合状冰粒和雪花粒子,自动气象站实况温度大多为0℃,由此可知该时段内上海地区主要为固态降水天气。针对本次过程,提取过程中凇附、聚合等关键时间节点的双偏振雷达参量,并根据Park等[25]和Thompson等[26]关于WSR-88D双线偏振雷达水凝物分类的研究整理得到表 1。
表 1 2019年2月8日关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表Table 1. Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels on 8 Feb 2019仰角 高度 03:00 05:30 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 19.5° 2.5 km 26.5 0.5 0.96 球形小冰晶(凇附) 7.6 0.06 0.92 冰水混合(聚合状冰晶和小水滴) 5.5 km 5.8 0.97 0.94 冰晶 1.4 1.25 0.94 冰晶(枝状) 9.9° 2.5 km 31.7 0.48 0.93 球形小冰晶(凇附) 12.1 -0.13 0.93 冰水混合(聚合状冰晶和小水滴) 5.1 km 10.9 0.56 0.98 冰晶 6.2 0.95 0.97 冰晶(枝状) 2.2 2019年2月9日降水过程
继2019年2月8日后,2月9日凌晨上海地区再次出现一次降水(雨和雨夹雪)过程。该次过程高空形势与8日大致相同,上游地区500 hPa短波槽快速东移,850 hPa低空切变线推至沿江一线,上海地区受地面弱冷空气扩散补充影响。用QVP方法反演的19.5°仰角参量变化分析见图 5。
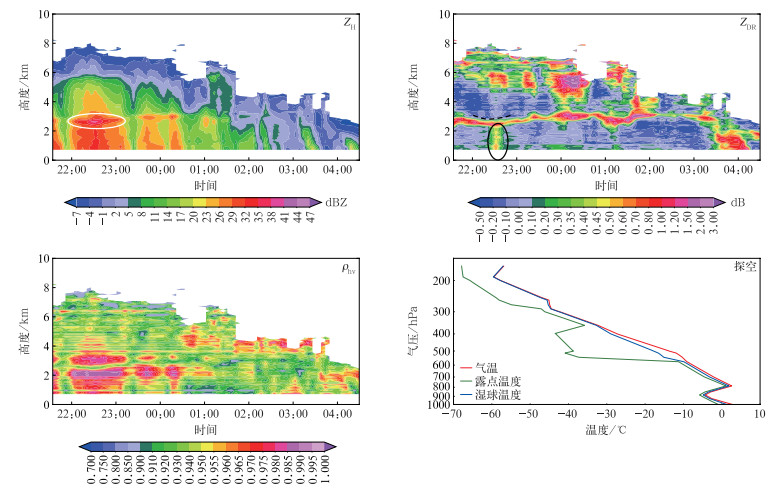
图 5中,2月8日23:45—9日00:45在4~6 km高度ZDR明显偏高,5 km附近达到1.5~3.0 dB,配合8日20:00探空可知该处发生了贝吉龙过程。白色线圈内为融化层,表现为ZH在2.5 km高度存在强度大于40 dBZ的中心,对应ZDR显著高于上下层(0.8~2.0 dB),ρhv为0.95~0.965。2月8日20:00的探空显示,垂直方向上有3个WBZ,位置较高的2个WBZ均位于2.5 km附近,与前述分析的融化层高度吻合。22:30自5 km至黑色虚线高度,ZDR从高到低逐渐减小,ZH逐渐增大,同时融化层存在“下凹”特征,表明该处发生凇附过程。2 km高度以下的黑色线圈内,ZDR再次增大,表明凇附过程完成后融化层高度以下存在降水粒子的聚合作用,通过黏连冰晶或者过冷水,粒子尺度增长,ZDR增大。以下利用QVP方法反演的9.9°仰角雷达参量分析低层变化过程。
图 6中2月8日22:30,ρhv为0.99~1.0,近地面层的融化层(ρhv低值区)高度降低,ZH为25~30 dBZ,ZDR为0.3~0.5 dB,以上回波特征难以诊断粒子具体相态,需引入浦东世博站雨滴谱仪资料进行辅助分析(图略)。结果表明:22:00—23:00粒子直径集中于0.5~1.5 mm,并伴有少量直径大于2 mm的粒子,故可知该时段以小雨滴和少量粒子直径较小的霰粒子为主。22:00—23:00伴随凇附过程发生,冰晶凝结增长的效率变快,上海地区的多个测站天气现象仪于9日00:00开始观测到雨夹雪或间歇性降雪天气。南汇自动气象站观测显示:随降水过程的发生,地面温度逐渐降低,湿度增大,其逐小时降水最强时段在2月8日23:00—9日00:00,小时累积降水量达1.9 mm,可知凇附作用对降水粒子的增长具有促进作用。针对本次过程,结合关键时间节点的双线偏振雷达参量和水凝物分类结果整理得到表 2。
表 2 2019年2月9日关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表Table 2. Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels on 9 Feb 2019仰角 高度 22:30 00:00 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 19.5° 2.5 km 33.6 0.85 0.93 冰水混合 20.0 -0.03 0.975 小水滴 5.5 km 16.8 0.39 0.94 冰晶(柱状) 2.2 16.7 0.91 冰晶(枝状) 9.9° 2.5 km 33.7 0.63 0.93 冰水混合 21.6 0.04 0.92 冰水混合(含小霰粒) 5.1 km 13.0 0.74 0.98 冰晶(柱状) 5.1 1.18 0.97 冰晶(枝状) 2.3 2020年2月15日降水过程
2020年2月15日受寒潮影响,上海地区出现一次由雨转冰粒,再转雨夹雪和小雪的复杂相态降水过程。该过程的主要影响系统是地面冷锋后850 hPa高度上的低空切变线,降水云系移动的引导气流为700 hPa的西南风,地面冷锋向东南方向移动。与2.2节的个例相比,本次过程地面冷高压的中心强度较强,气压梯度更大。从地面加密观测记录到的固态降水开始时间看,本次过程上海地区自西北向东南逐渐由雨转为冰粒或雪,北部的崇明、宝山分别在15日21:40和23:00先后出现冰粒和降雪,其次是西部的青浦、松江,中心城区及闵行在16日00:40—00:50转为雪,东部、南部区县较长时间内表现为冰粒或雨夹雪共存的情况。累积降水(降雪)量较大的站点包括青浦3.0 mm,崇明2.0 mm,嘉定1.0 mm,其余各站雨雪量均小于1 mm。
风廓线雷达观测(图略)显示:2月15日16:00— 16日02:00期间850 hPa切变线(1.5 km高度)逐渐经过该站(风向由偏南风转为西北风),2 km以上仍为西南暖湿急流,其中700 hPa西南风由16 m·s-1逐渐增大至19:00后的24~32 m·s-1,上海地区的地面降水逐渐开始;02:00后700 hPa西南风逐渐转为西西南到偏西风,同时风速减小至16~24 m·s-1,此后降水逐渐停止。以上特征均显示该时段内700 hPa的高空槽正在东移,并与降水的起止有关。
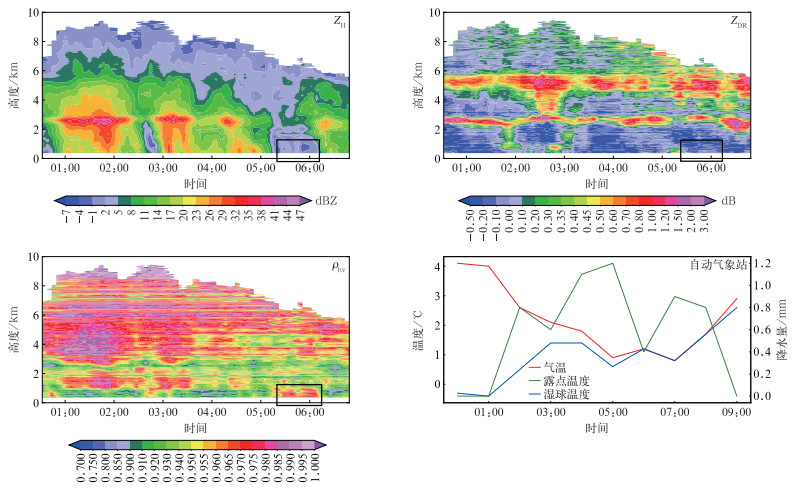
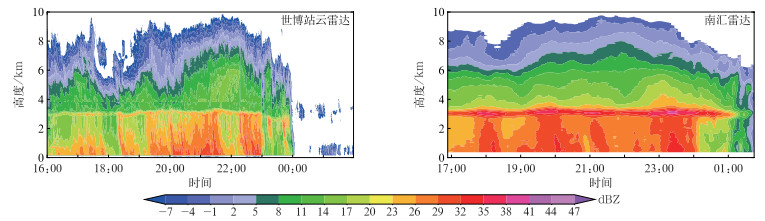
2月16日850 hPa以下风向在02:00转为一致西北风,表明此刻低空切变线已经过境(与风廓线观测结果相符)。由图 7可知,2月15日20:00暖层较深厚(700~850 hPa整层均为暖层),其下至近地面的950 hPa为冻结层。16日02:00探空显示:受冷气团逐渐南压影响,700~850 hPa出现较明显降温,湿球温度位于0℃附近,暖层基本消失,同时地面温度略下降,上述特征表明大气具备由雨转冰粒、再转雨夹雪和小雪的层结条件。针对本次寒潮带来的降水过程,上海市气象局启动了多源资料及人工加密观测,其中世博站毫米波云雷达与南汇雷达利用QVP方法反演的ZH高度-时间廓线对比见图 8。
忽略云雷达的衰减,图 8中QVP方法反演的ZH的时间演变和垂直结构与云雷达较为一致,但由于降水系统先移动到世博站,故QVP方法反演结果存在时间延迟。850 hPa切变线是本次过程的主要影响系统,其两侧冷暖气团的差异导致系统到达前后出现不同降水现象。
沿西南—东北向切变线方向(冷暖气团分界线),划分为系统到达前和到达后的两块区域分别用QVP方法进行反演并讨论。考虑地面锋面的实际尺度,选择9.9°仰角开展工作(图 9)。
由图 9可知,0.5 km和3 km高度存在两条较明显的ρhv低值带,表明存在两个融化层。系统后侧2~3 km高度ρhv低值区的厚度较系统前侧更厚,表明系统后侧的相态转换层更深厚。2月16日00:00—00:30系统后侧两条融化层开始合并,1~3 km高度范围ρhv为0.91~0.955。与之对应,ZDR自6 km高度至3 km高度略有减小,在3 km高度附近较薄的融化层内快速融化,ZDR快速增长至1.5~2 dB。在下落至冻结层的过程中ZDR降为负值,表明多为聚合的冰晶或冰粒(霰),与浦东人工观测到冰粒的时间较为一致(浦东人工加密观测于00:30观测到冰粒)。相比之下,系统前侧两条融化层合并的时间稍滞后,且合并时ZDR较系统后侧偏大(黑色矩形框内),表明该范围内仍以降水粒子为主。
与2.2节个例相比,在强寒潮、大尺度天气系统影响下,本次过程降水云系范围更广且较均一,相关系数廓线上的融化层边界较为清晰,融化层下的冻结层更深厚,温度更低,导致降水粒子冻结较快,降水效率更高。本次过程系统前侧和后侧的双线偏振雷达参量和相关水凝物分类结果整理见表 3。
表 3 2020年2月15日01:30 9.9°仰角关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表Table 3. Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels at 9.9° elevation at 0130 BT 15 Feb 2020c高度 系统后部 系统前部 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 3.0 km 28.0 0.57 0.95 冰水混合 25.4 1.89 0.91 冰水混合(含大水滴) 0.79 km 21.1 -0.14 0.92 小雪花 10.4 -0.21 0.93 冰粒 3. 结论与讨论
研究表明:
1) 基于QVP方法反演的ZH,ZDR和ρhv高度-时间廓线可以充分发挥双偏振雷达高时空分辨率的特性,应挖掘其在云中粒子的微物理过程演变监测中的作用。
2) 通过QVP方法反演的双偏振雷达变量的高度-时间廓线可用于估算融化层高度,结果与WBZ高度较为一致。QVP方法还可用于识别降水粒子的凇附和聚合作用。发生凇附作用时,融化层上方ZH增大和ZDR减小且融化层呈“下凹”状。聚合作用多发生在融化层以下高度,粒子碰并增长导致数密度增大且形态趋于扁平,故ZH和ZDR均增大。凇附作用的发生与降水较大时段吻合,验证了凇附过程对于降水启动和发展的促进作用。
3) 本文讨论3种不同天气背景下的冬季降水天气,其中冷流降水(降雪)和弱冷空气降水(降雪)的融化层较为浅薄,且均能够观测到较明显的凇附和聚合过程。强冷空气降水(降雪)的双融化层较为清楚,但凇附和聚合过程的观测不明显。针对非连续性或非均匀性降水过程,通过划分系统前、后侧区域利用QVP方法分别进行反演,可发现系统后侧中高层的融化层更深厚,液态和固态粒子的混合状态更明显。
本研究仅局限于上海地区,且该地区冬季降水以雨或雨夹雪为主,今后将收集更多高纬度地区的降雪个例,利用QVP方法比较不同地区降水过程的微物理特征差异。此外,在青浦多普勒天气雷达升级双偏振工作完成后,也可利用QVP方法反演青浦雷达高度-时间廓线,与南汇雷达配合使用,比较系统过境前后的不同回波特征。
致谢: 本研究受到上海市气象局强对流科技创新团队资助。 -
表 1 2019年2月8日关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表
Table 1 Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels on 8 Feb 2019
仰角 高度 03:00 05:30 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 19.5° 2.5 km 26.5 0.5 0.96 球形小冰晶(凇附) 7.6 0.06 0.92 冰水混合(聚合状冰晶和小水滴) 5.5 km 5.8 0.97 0.94 冰晶 1.4 1.25 0.94 冰晶(枝状) 9.9° 2.5 km 31.7 0.48 0.93 球形小冰晶(凇附) 12.1 -0.13 0.93 冰水混合(聚合状冰晶和小水滴) 5.1 km 10.9 0.56 0.98 冰晶 6.2 0.95 0.97 冰晶(枝状) 表 2 2019年2月9日关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表
Table 2 Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels on 9 Feb 2019
仰角 高度 22:30 00:00 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 19.5° 2.5 km 33.6 0.85 0.93 冰水混合 20.0 -0.03 0.975 小水滴 5.5 km 16.8 0.39 0.94 冰晶(柱状) 2.2 16.7 0.91 冰晶(枝状) 9.9° 2.5 km 33.7 0.63 0.93 冰水混合 21.6 0.04 0.92 冰水混合(含小霰粒) 5.1 km 13.0 0.74 0.98 冰晶(柱状) 5.1 1.18 0.97 冰晶(枝状) 表 3 2020年2月15日01:30 9.9°仰角关键层降水粒子偏振量和相态时间变化表
Table 3 Polarimetric parameters and hydrometeor classification at key levels at 9.9° elevation at 0130 BT 15 Feb 2020c
高度 系统后部 系统前部 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 ZH/dBZ ZDR/dB ρhv 相态 3.0 km 28.0 0.57 0.95 冰水混合 25.4 1.89 0.91 冰水混合(含大水滴) 0.79 km 21.1 -0.14 0.92 小雪花 10.4 -0.21 0.93 冰粒 -
[1] 傅佩玲, 胡东明, 黄浩, 等.台风山竹(1822)龙卷的双极化相控阵雷达特征.应用气象学报, 2020, 31(6): 706-718. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200606 Fu P L, Hu D M, Huang H, et al.Observation of a tornado event in outside-region of Typhoon Mangkhut by X-band polarimetric phased array radar in 2018.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(6): 706-718. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200606
[2] 胡志群, 刘黎平, 肖艳姣.降水粒子空间取向对双线偏振雷达观测影响模拟研究.应用气象学报, 2008, 19(3): 362-366. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2008.03.013 Hu Z Q, Liu L P, Xiao Y J.A simulation study on faindrop orientation variation to dual linear polarimetric radar observation with different transmitting and receiving model.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2008, 19(3): 362-366. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2008.03.013
[3] 林文, 张深寿, 罗昌荣, 等.不同强度强对流云系S波段双偏振雷达观测分析.气象, 2020, 46(1): 63-72. Lin W, Zhang S S, Luo C R, et al.Observational analysis of different intensity sever convective clouds by S-band dual-polarization radar.Meteor Mon, 2020, 46(1): 63-72.
[4] 蒋银丰, 寇蕾蕾, 陈爱军, 等.双偏振雷达和双频测雨雷达反射率因子对比.应用气象学报, 2020, 31(5): 608-619. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200508 Jiang Y F, Kou L L, Chen A J, et al.Comparison of reflectivity factor of dual polarization radar and dual-frequency precipitation radar.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(5): 608-619. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200508
[5] 徐舒扬, 吴翀, 刘黎平.双偏振雷达水凝物相态识别算法的参数改进.应用气象学报, 2020, 31(3): 350-360. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200309 Xu S Y, Wu C, Liu L P.Parameter improvements of hydrometeor classification algorithm for the dual-polarimetric radar.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(3): 350-360. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200309
[6] 王洪, 孔凡铀, JungYoungsun, 等.面向资料同化的S波段双偏振雷达质量控制.应用气象学报, 2018, 29(5): 546-558. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180504 Wang H, Kong F Y, Jung Y S, et al.Quality control of S-band polarimetric radar measurements for data assimilation.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(5): 546-558. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180504
[7] Brandes E A, Ikeda K.Freezing-level estimation with polarimetric radar.Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2004, 43(11): 1541-1553. DOI: 10.1175/JAM2155.1
[8] Giangrande S E, Krause J M, Ryzhkov A V.Automatic designation of the melting layer with a polarimetric prototype of the WSR-88D radar.J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2008, 47(5): 1354-1364. DOI: 10.1175/2007JAMC1634.1
[9] 曹杨, 陈洪滨, 苏德斌.C波段双线偏振天气雷达零度层亮带识别和订正.应用气象学报, 2018, 29(1): 84-96. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180108 Cao Y, Chen H B, Su D B.Identification and correction of the bright band using a C-band dual polarization weather radar.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(1): 84-96. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180108
[10] Wu D, Zhao K, Kumjian M R, et al.Kinematics and microphysics of convection in the outer rainband of Typhoon Nida (2016) revealed by polarimetric radar.Mon Wea Rev, 2018, 146(7): 2147-2159. DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-17-0320.1
[11] 刘黎平, 郑佳锋, 阮征, 等.2014年青藏高原云和降水多种雷达综合观测试验及云特征初步分析结果.气象学报, 2015, 73(4): 635-647. Liu L P, Zheng J F, Ruan Z, et al.The preliminary analyses of the cloud properties over the Tibetan Plateau from the field experiments in clouds precipitation with the vavious radars.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2015, 73(4): 635-647.
[12] Williams E R, Smalley D J, Donovan M F, et al.Measurements of differential reflectivity in snowstorms and warm season stratiform systems.J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2015, 54(3): 573-595. DOI: 10.1175/JAMC-D-14-0020.1
[13] 杨忠林, 赵坤, 徐坤, 等.江淮梅雨期极端对流微物理特征的双偏振雷达观测研究.气象学报, 2019, 77(1): 58-72. Yang Z L, Zhao K, Xu K, et al. Microphysical characteristics of extreme convective precipitation over the Yangtze-Huaihe river basin during the Meiyu season based on polarimetric radar data.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2019, 77(1): 58-72.
[14] Zawadzki I, Szyrmer W, Bell C, et al.Modeling of the melting layer. Part Ⅲ:The density effect.J Atmos Sci, 2005, 62(10): 3705-3723. DOI: 10.1175/JAS3563.1
[15] Ryzhkov A, Zhang P, Reeves H, et al.Quasi-vertical profiles-A new way to look at polarimetric radar data.J Atmos Oceanic Technol, 2016, 33(3): 551-562. DOI: 10.1175/JTECH-D-15-0020.1
[16] Kaltenboeck R, Ryzhkov A.A freezing rain storm explored with a C-band polarimetric weather radar using the QVP methodology.Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 2017, 26(2): 207-222. DOI: 10.1127/metz/2016/0807
[17] 程周杰, 刘宪勋, 朱亚平.双偏振雷达对一次水凝物相态演变过程的分析.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(5): 594-601. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2009.05.011 Cheng Z J, Liu X X, Zhu Y P.A process of hydrometeor phase change with dual-polarimetric radar.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2009, 20(5): 594-601. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2009.05.011
[18] 梅垚, 胡志群, 黄兴友.青藏高原对流云的偏振雷达观测研究.气象学报, 2018, 76(6): 1014-1028. Mei Y, Hu Z Q, Huang X Y.A study of convective clouds in the Tibetan Plateau based on dual polarimetric radar observations.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2018, 76(6): 1014-1028.
[19] 张培昌, 杜秉玉, 戴铁丕.雷达气象学.北京:气象出版社, 2000: 118-119. Zhang P C, Du B Y, Dai T P.Radar Meteorology.Beijing:China Meteorological Press, 2000: 118-119.
[20] 俞小鼎.关于冰雹的融化层高度.气象, 2014, 40(6): 649-654. Yu X D.A note on the melting level of hail.Meteor Mon, 2014, 40(6): 649-654.
[21] 刘晓璐, 刘建西, 张世林, 等.基于探空资料因子组合分析方法的冰雹预报.应用气象学报, 2014, 25(2): 168-175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.02.006 Liu X L, Liu J X, Zhang S L, et al.Hail forecast based on factor combination analysis method and sounding Data.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(2): 168-175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.02.006
[22] 何彩芬, 黄旋旋, 卢晶晶.基于多普勒天气雷达产品的降雪及冻雨综合分析.应用气象学报, 2009, 20(6): 767-771. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2009.06.016 He C F, Huang X X, Lu J J.Comprehensive analysis on snow and freezing-rain events based on doppler weather radar in Ningbo.J Appl Meteor Sci, 2009, 20(6): 767-771. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2009.06.016
[23] Bakhshaii A, Stull R.Saturated pseudoadiabats-A Noniterative approximation.J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2013, 52(1): 5-15. DOI: 10.1175/JAMC-D-12-062.1
[24] 顾震潮.云雾降水物理基础.北京:科学出版社, 1980: 173-179. Gu Z C.Base of Cloud and Mist Precipitation Physics.Beijing:Science Press, 1980: 173-179.
[25] Park H S, Ryzhkov A V, Zrnić D S, et al.The hydrometeor classification algorithm for the polarimetric WSR-88D:Description and application to an MCS.Wea Forecasting, 2009, 24(3): 730-748. DOI: 10.1175/2008WAF2222205.1
[26] Thompson E J, Rutledge S A, Dolan B, et al.A dual-polarization radar hydrometeor classification algorithm for winter precipitation.J Atmos Oceanic Technol, 2014, 31(7): 1457-1481. DOI: 10.1175/JTECH-D-13-00119.1
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 刘丽景. 基于遥感卫星的极端气象观测数据安全预警系统设计. 计算机测量与控制. 2024(05): 193-200 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蔡杏尧,匡昌武,郑鹏斌,郭佳,李文,李勋. 万宁双偏振天气雷达降水产品参数本地化及评估. 气象与环境科学. 2024(06): 92-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈璇,钟敏,陈赛男,罗昱,熊思章,鲁易,刘瑞雪. 2024年2月初湖北极端冰冻过程的观测和成因分析. 暴雨灾害. 2024(06): 668-679 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨和平,张强,罗兵,陈楠,邓鑫,张志强,孙超,陈京华,赵煜飞,李小汝,郭聪,陈杰,李默予. 气象综合指挥平台建设与应用. 应用气象学报. 2023(01): 117-128 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 周青,李柏,张勇,陶法,胡树贞,李瑞义,杨荣康. 基于北京多源资料的云宏观特征判识. 应用气象学报. 2023(02): 206-219 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 孙钦宏,马洪波,齐彦斌,王秀娟. 2021年夏季长白山麓雨滴谱分布特征. 应用气象学报. 2023(03): 336-347 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 王振超,陈雪娇,刘姝,花家嘉,刘文忠. 微型智能气象站降雨观测对比试验. 应用气象学报. 2023(04): 438-450 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 陈绍婕,郑佳锋,杨吉,车玉章,任涛,黄轩. C-FMCW雷达反演飑线大气垂直速度和雨滴谱. 应用气象学报. 2022(04): 429-441 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 张林,李峰,吴蕾,孙康远. CINRAD/SAD双偏振雷达非降水回波识别技术. 应用气象学报. 2022(06): 724-735 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)

 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: