Circulation Pattern Classification of Persistent Heavy Rainfall in Jianghuai Region Based on the Transfer Learning CNN Model
-
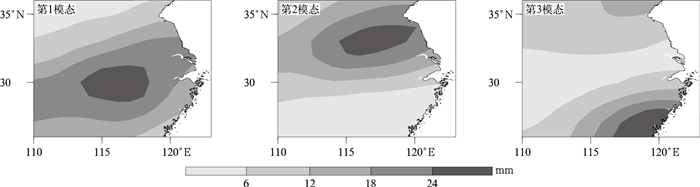
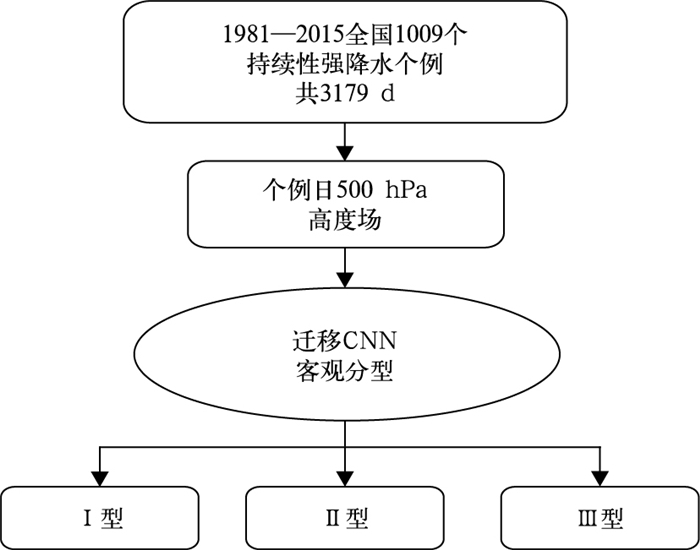
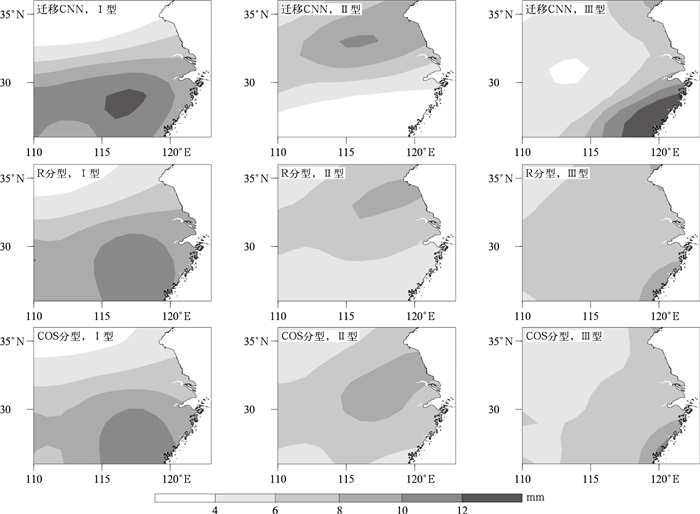
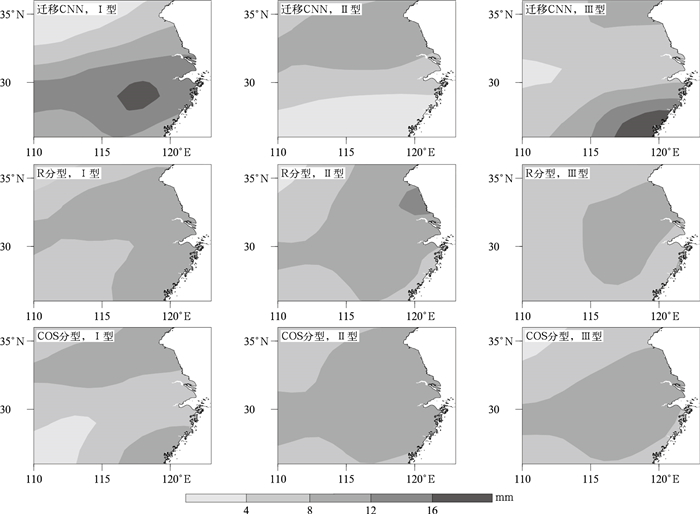
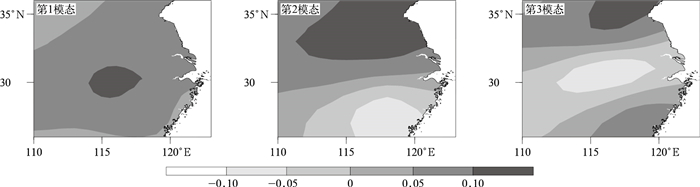
摘要: 利用新建的1981—2018年区域持续性强降水个例集、1981—2018年中国逐日降水量及NCEP/NCAR全球再分析资料,运用江淮地区持续性强降水典型模态个例样本及残差神经网络(CNN),通过迁移学习分步训练建立针对江淮强降水的环流客观分型模型;并运用该模型对1981—2015年全国持续性强降水个例的环流进行客观分型,比较其与相似量(R)分型、余弦相似系数(COS)分型的效果,且对2016—2018年逐日环流进行客观识别与分型。结果表明:迁移CNN在拟合准确率达到100%后,测试集损失函数很快稳定,准确率较高,比R分型、COS分型效果好。在强降水客观分型中,迁移CNN所得各型与典型模态降水之间的相关系数远高于R分型、COS分型,其中不一致型个例分析表明迁移CNN所得各型与典型模态降水间的相关系数明显高于R分型、COS分型。在独立样本分型中,迁移CNN所得各型与典型模态降水的相关系数也均高于R分型、COS分型,且对非持续性强降水环流分型也存在一定的识别能力。Abstract: Newly reconstructed dataset of regional persistent historical heavy rain events in 1981-2018, corresponding daily rainfall data of 2474 observational stations in China, and NCEP/NCAR global reanalysis data of daily geopotential height field are used to study the persistent heavy rain events in Jianghuai Region.Based on 72 persistent heavy rainfall cases, typical rain patterns and circulation fields are refined by empirical orthogonal function(EOF). And the corresponding time coefficient is obtained by projecting rainfall of individual days to the typical rain patterns, and the training and test dataset samples are determined by the time coefficient. Using residual neural network(CNN), a transfer learning CNN classification model of Jianghuai persistent heavy rainfall is established by three transfer learning processes. Compared with the analog quantity(R) and Cosine similarity coefficient(COS) methods, the transfer learning CNN model has the highest classification accuracy on the test dataset.CNN, R and COS methods are used to objectively classify the circulation of all persistent heavy rain cases and to synthesize the distribution of various types of rainfall and circulation during 1981-2015. The statistical analysis shows that the transfer learning CNN model is better at classification. By comparing the correlation coefficients between rain distribution of each type and typical rain patterns, it shows that the transfer learning CNN model performs better than the R and COS methods. The variance between different types of geopotential height fields at 500 hPa obtained by the CNN model is the largest and the CNN model can better distinguish the circulation fields of different types of heavy rainfall.The analysis of samples with inconsistent objective classification of three methods shows that the correlation coefficients of various patterns of rainfall of the transfer learning CNN model are significantly higher than those of R typing and COS typing methods. The spatial distribution of various rainfall patterns of CNN model can clearly show the characteristics of the three typical heavy rain patterns, while the results obtained by R typing and COS typing methods are almost opposite to the typical rain patterns except for type Ⅱ. Considering classification of independent samples in 2016-2018, the correlation coefficients between the rain distribution of each type and typical rain patterns obtained by the transfer learning CNN model are much higher than the R and COS methods. The transfer learning CNN model has certain advantages over R typing and COS typing methods in classification and also has a certain ability to distinguish the non-continuous heavy rainfall circulation pattern.
-
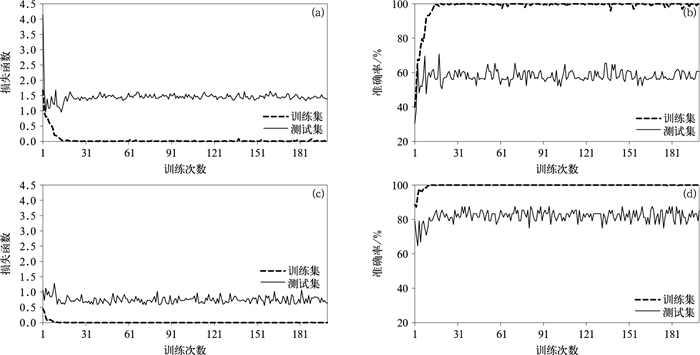
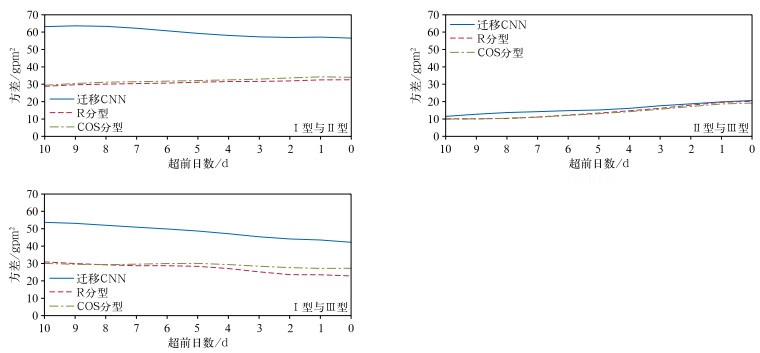
图 3 迁移CNN训练集与测试集的损失函数和准确率
(a)增加训练样本前损失函数, (b)增加训练样本前准确率, (c)增加训练样本后损失函数, (d)增加训练样本后准确率
Fig. 3 The loss and accuracy of training dataset and test dataset of the transfer learning CNN model
(a)the loss before adding training samples, (b)the accuracy before adding training samples, (c)the loss after adding training samples, (d)the accuracy after adding training samples
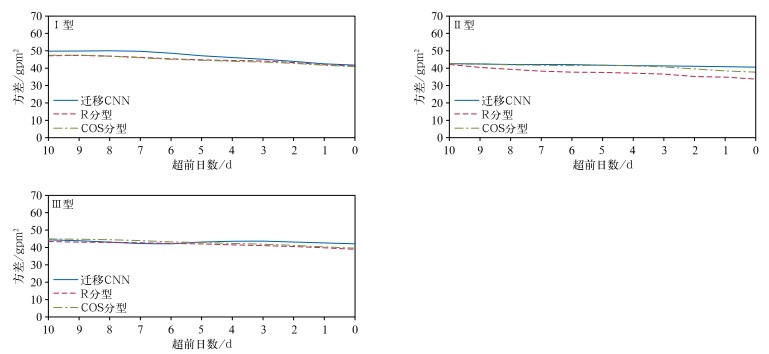
表 1 迁移CNN, R分型和COS分型得到的各型与典型模态强降水之间的相关系数
Table 1 The correlation coefficients between the transfer learning CNN model, R typing, COS typing and heavy rainfall of typical mode patterns
相关类型 分型方法 Ⅰ型 Ⅱ型 Ⅲ型 CNN 0.771 0.986 0.913 平均场相关 R 0.770 0.946 0.702 COS 0.671 0.423 0.791 CNN 0.348 0.224 0.382 个例日相关 R 0.233 0.140 0.129 COS 0.198 0.025 0.146 表 2 个例日样本中迁移CNN,R分型和COS分型得到的各型与典型模态强降水之间的相关系数
Table 2 The correlation coefficients between the transfer learning CNN model, R typing, COS typing and heavy rainfall of typical mode patterns in samples
相关类型 分型方法 Ⅰ型 Ⅱ型 Ⅲ型 CNN 0.877 0.979 0.984 平均场相关 R 0.069 0.513 -0.144 COS -0.559 0.332 -0.077 CNN 0.352 0.238 0.467 个例日相关 R -0.034 0.023 0.060 COS -0.221 -0.010 0.037 表 3 不同部分样本中迁移CNN,R分型和COS分型得到的各型与典型模态强降水之间的相关系数
Table 3 The correlation coefficients between transfer learning CNN model, R typing, COS typing and heavy rainfall of typical mode patterns in samples of different part
相关类型 分型方法 Ⅰ型 Ⅱ型 Ⅲ型 CNN 0.832 0.818 0.541 平均场相关 R 0.592 0.199 0.294 COS 0.485 0.800 -0.224 CNN 0.238 0.090 0.258 个例日相关 R 0.233 0.003 0.132 COS 0.123 0.048 0.058 -
[1] 陈隆勋,李麦村,李维亮,等.夏季的季风环流.大气科学,1979,3(1):78-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK197901008.htmChen L X, Li M C, Li W L, et al. Monsoon circulation in summer. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 1979, 3(1): 78-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK197901008.htm [2] 王同美, 吴国雄, 万日金. 青藏高原的热力和动力作用对亚洲季风区环流的影响. 高原气象, 2008, 27(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200801000.htmWang T M, Wu G X, Wan R J. Influence of the mechanical and thermal forcing of Tibetan Plateau on the circulation of the Asian summer monsoon area. Plateau Meteorology, 2008, 27(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200801000.htm [3] 翟盘茂, 王萃萃, 李威. 极端降水事件变化的观测研究. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 3(3): 144-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200703005.htmZhai P M, Wang C C, Li W. A review on study of change in precipitation extremes. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2007, 3(3): 144-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH200703005.htm [4] 鲍名. 近50年我国持续性暴雨的统计分析及其大尺度环流背景. 大气科学, 2007, 31(5): 779-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200705002.htmBao M. The statistical analysis of the persistent heavy rain in the last 50 years over China and their backgrounds on the large scale circulation. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 31(5): 779-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200705002.htm [5] 刘小宁. 我国暴雨极端事件的气候变化特征. 灾害学, 1999, 14(1): 54-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU199901014.htmLiu X N. Climatic characteristics of extreme rainstorm events in China. Journal of Catastrophology, 1999, 14(1): 54-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU199901014.htm [6] 刘伯奇, 祝从文. 中国夏季降水预测因子潜在技巧分布图及应用. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(5): 570-582. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200505Liu B Q, Zhu C W. Potential skill map of predictors applied to the seasonal forecast of summer rainfall in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(5): 570-582. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200505 [7] 赵平, 周秀骥. 近40年我国东部降水持续时间和雨带移动的年代际变化. 应用气象学报, 2006, 17(5): 548-556. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20060594Zhao P, Zhou X J. Decadal variability of rainfall persistence time and rainbelt shift over eastern China in recent 40 years. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2006, 17(5): 548-556. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20060594 [8] Sun J, Zhao S. The impacts of multi-scale weather systems on freezing rain and snow storms over the southern China. Wea Forecasting, 2010, 25: 388-407. doi: 10.1175/2009WAF2222253.1 [9] Wang W C, Gong W, Wei H. A regional model simulation of the 1991 severe precipitation event over the Yangtze-Huai River valley. Part I: Precipitation and circulation statistics. J Climate, 2000, 13(1): 93-108. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<0093:ARMSOT>2.0.CO;2 [10] 桂海林, 周兵, 金荣花. 2007年淮河流域暴雨期间大气环流特征分析. 气象, 2010, 36(8): 8-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201008004.htmGui H L, Zhou B, Jin R H. Analysis on general circulation characteristics of the heavy rainfall during June-July 2007 in Huaihe valley. Meteor Mon, 2010, 36(8): 8-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201008004.htm [11] 闫之辉, 田华. 1998年6月下旬长江中下游强降水过程成因分析. 应用气象学报, 2002, 13(6): 680-687. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20020689Yan Z H, Tian H. Causality analysis of a heavy rain process over middle and lower reaches of Changjiang River in June 1998. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2002, 13(6): 680-687. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20020689 [12] 陈菊英, 冷春香, 程华琼. 江淮流域强暴雨过程对阻高和副高逐日变化的响应关系. 地球物理学进展, 2006, 21(3): 1012-1022. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200603047.htmChen J Y, Leng C X, Cheng H Q. The ural blocking high anomalous daily variation impact on the heavy rainfall in the Yangtze River Basin and Huai River Basin. Progress in Geophys, 2006, 21(3): 1012-1022. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200603047.htm [13] 马岚, 吴晓京, 江吉喜, 等. 2001年夏季风活动与我国南方暴雨某些特征的分析. 应用气象学报, 2003, 14(4): 445-451. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20030455Ma L, Wu X J, Jiang J X, et al. Analysis of characteristics of summer monsoon and heavy rainfall over south China in 2001. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2003, 14(4): 445-451. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20030455 [14] Chen Y, Zhai P M. Persistent extreme precipitation events in China during 1951-2010. Climate Res, 2013, 57(2): 143-155. doi: 10.3354/cr01171 [15] Samel A N, Liang X Z. Understanding relationship between the 1998 Yangtze River flood and northeast Eurasian blocking. Climate Res, 2003, 23(2): 149-158. http://scholarworks.bgsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1000&context=sees_pub [16] 牛若芸, 张志刚, 金荣花. 2010年我国南方两次持续性强降水的环流特征. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(4): 385-394. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20120401Niu R Y, Zhang Z G, Jin R H. The atmospheric circulation features of two persistent heavy rainfalls over southern China in the summer of 2010. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2012, 23(4): 385-394. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20120401 [17] 陈丽娟, 赵俊虎, 顾薇, 等. 汛期我国主要雨季进程成因及预测应用进展. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(4): 385-400. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190401Chen L J, Zhao J H, Gu W, et al. Advances of research and application on major rain seasons in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(4): 385-400. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190401 [18] 翟盘茂, 李蕾, 周佰铨, 等. 江淮流域持续性极端降水及预报方法研究进展. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(5): 631-640. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160511Zhai P M, Li L, Zhou B Q, et al. Progress on mechanism and prediction methods for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze-Huai River Valley. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(5): 631-640. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160511 [19] 钟元, 李秀莉, 姚嘉玲, 等. 中期天气客观相似预报方法. 气象, 1988, 14(4): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198804002.htmZhong Y, Li X L, Yao J L, et al. An objective analogue method for medium-range weather forecast. Meteor Mon, 1988, 14(4): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198804002.htm [20] 付世军, 竹利, 李晓容. 动力相似法在一次大暴雨过程中的应用. 中低纬山地气象, 2018, 42(3): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZQX201803011.htmFu S J, Zhu L, Li X R. Application of dynamic similarity method in a heavy rainstorm process. Mid-low Latitude Mountain Meteorology, 2018, 42(3): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZQX201803011.htm [21] 吴曼丽, 陆忠艳, 王瀛. 中期延伸天气预报方法研究. 气象与环境学报, 2007, 23(2): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNQX200702001.htmWu M L, Lu Z Y, Wang Y. Study om medium-range extended weather forecast method. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2007, 23(2): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNQX200702001.htm [22] 谭桂容, 范艺媛, 牛若芸. 江淮地区强降水分型及其环流演变. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29(4): 396-409. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180402Tan G R, Fan Y Y, Niu R Y. Pattern classification of heavy rainfall in Jianghuai region and associated circulations. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(4): 396-409. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180402 [23] Zhou B Q, Zhai P M. A new forecast model based on the analog method for persistent extreme precipitation. Wea Forecasting, 2016, 31(4): 1325-1341. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-15-0174.1 [24] Zhang P, Zhang L, Leung H, et al.A Deep-Learning Based Precipitation Forecasting Approach Using Multiple Environmental Factors//IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress), 2017: 193-200. [25] 施丹平. 人工神经网络方法在降水量级中期预报中的应用. 气象, 2001, 27(6): 40-42;46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200106007.htmShi D P. An application of artificial neural network(ANN) to rainfall mid-range forecasting. Meteor Mon, 2001, 27(6): 40-42;46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200106007.htm [26] 孙照渤, 谭桂容, 赵振国. 人工神经网络方法在夏季降水预报中的应用. 南京气象学院学报, 1998, 21(1): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX801.006.htmSun Z B, Tan G R, Zhao Z G. ANN prediction of summer rainfall patterns of east China. Journal of Nanjing Institute Meteorology, 1998, 21(1): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX801.006.htm [27] 谢宝剑. 基于卷积神经网络的图像分类方法研究. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2015.Xie B J.The Research of Image Classification Methods Based on Convolution Neural Network.Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2015. [28] 陈程. 卷积神经网络在气象短临预报的研究与应用. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.Chen C.Application of Convolution Neural Network in Weather Nowcasting.Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018. [29] Ham Y G, Kim J H, Luo J J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 568-572. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1559-7 [30] Liu Y J, Racah E, Prabhat, et al.Application of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Detecting Extreme Weather in Climate Datasets.2016. [31] He K M, Zhang X, Ren S, et al.Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016: 770-778. [32] 牛若芸, 刘凑华, 刘为一, 等. 1981-2015年中国95°E以东区域性暴雨过程时、空分布特征. 气象学报, 2018, 76(2): 182-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201802002.htmNiu R Y, Liu C H, Liu W Y, et al. Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of regional rainstorm processes to the east of 95°E in China during 1981-2015. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2018, 76(2): 182-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201802002.htm [33] 罗阳. 一种新的相似性度量——高分辨率相似系数. 空军气象学院学报, 1996, 17(1): 23-32.Luo Y. A new similarity measure-High-resolution similarity coefficient. Journal of the Air Force Institute of Meteorology, 1996, 17(1): 23-32. [34] 罗阳, 聂新旺, 王广山. 几种相似方法的适用性比较. 气象, 2011, 37(11): 1443-1447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201111018.htmLuo Y, Nie X W, Wang G S. An exploration on the applicability of similarity parameter in similarity forecasting. Meteor Mon, 2011, 37(11): 1443-1447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201111018.htm [35] 段萌, 王功鹏, 牛常勇. 基于卷积神经网络的小样本图像识别方法. 计算机工程与设计, 2018, 39(1): 224-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201801039.htmDuan M, Wang G P, Niu C Y. Method of small sample size image recognition based on convolution neural network. Computer Engineering and Design, 2018, 39(1): 224-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201801039.htm [36] 谭桂容, 段浩, 任宏利. 中高纬度地区500 hPa高度场动力预测统计订正. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(3): 304-311. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20120306Tan G R, Duan H, Ren H L. Statistical correction for dynamical prediction of 500 hPa height field in mid-high latitudes. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2012, 23(3): 304-311. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20120306 [37] 范艺媛. 江淮地区强降水的环流特征及其预报. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2018.Fan Y Y.The Circulation Characteristics and Forecast of Heavy Rainfall in the Jianghuai Region.Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2018. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: