Hazard Assessment of Peanut Drought and Flood Disasters in Huang-Huai-Hai Region
-
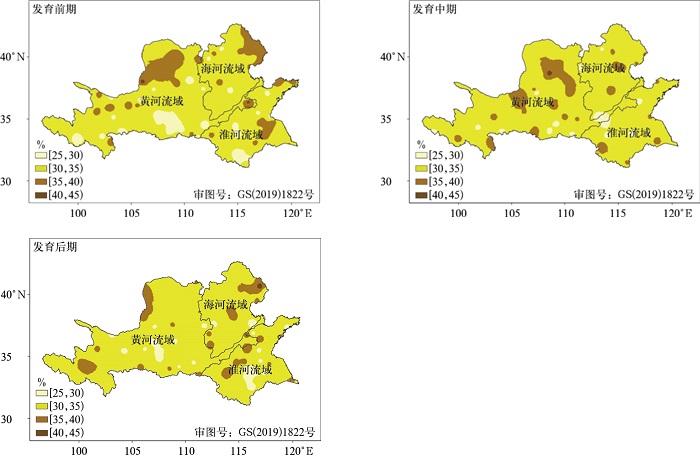
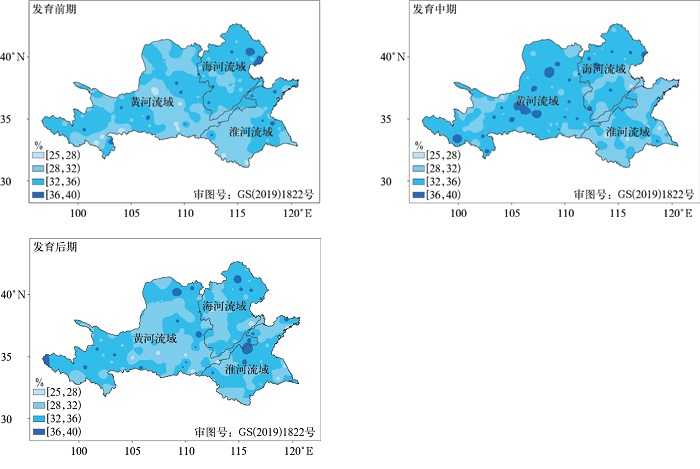
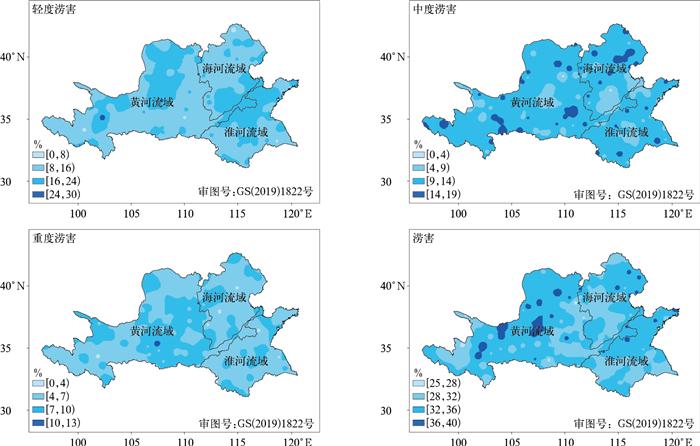
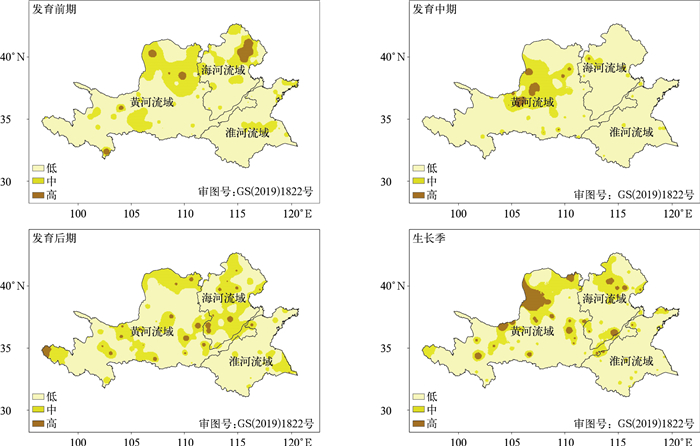
摘要: 利用1960—2019年黄淮海地区186个气象站逐日气象数据,结合春花生发育期数据,采用标准化降水作物需水指数将旱涝灾害分为7个等级,分析春花生旱涝灾害的时空分布特征;并以旱涝灾害发生的强度和频率构建春花生旱涝灾害危险性指数,开展黄淮海地区春花生旱涝灾害危险性评价。结果表明:黄河流域西北部和中部、淮河流域东北部以及海河流域北部是干旱灾害高发区;涝害高发区主要集中在黄河流域的大部分地区、淮河流域北部和南部地区以及海河流域东部,以中度涝害为主。春花生干旱灾害高危险性地区零散分布,主要集中在黄河流域西北部;而涝害中、高危险性地区多分布于黄河流域。Abstract: Peanut is an important kind of food, oil plants and cash crops which promotes the sustainable development in the modern agricultural economy. In recent years, the frequency and intensity of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster in the Huang-Huai-Hai Region has remarkably increased, which poses a huge impact on the production of spring peanut. Therefore, analyzing and making hazard assessment of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster during the growth period of spring peanut has a great significance for preventing drought disaster and waterlogging disaster, minimizing the damage, and taking disaster insurance in this region. Based on the daily meteorological data of 186 meteorological stations from 1960 to 2019 and combined with the growth data of spring peanut, the hazard assessment of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster is divided into 7 grades by using the standardized precipitation requirement index(ISPR), and the spatial and temporary distribution characteristics of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster in Huang-Huai-Hai Region are analyzed. Based on the probability and intensity of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster, hazard index is constructed to evaluate the hazard during the growth period of spring peanut. High incidence of drought disaster is found in the northwestern and central part of the Yellow River Basin, the northeastern part of the Huaihe River Basin and the northern part of the Haihe River Basin. While the areas with high incidence of waterlogging disaster are mainly concentrated in most areas of the Yellow River Basin, the northern, southern part of the Huaihe River Basin and eastern part of the Haihe River Basin, and mainly with moderate waterlogging disaster. The areas with high hazard of drought disaster during the growth period of spring peanut are scattered, mainly concentrated in the northwest of the Yellow River Basin. While the areas with medium and high hazard of waterlogging disaster during the growth period of spring peanut are mainly distributed in the Yellow River Basin. In the northern and central planting areas of the Yellow River Basin, the phenomenon of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster abrupt alternation often occurs. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the hazard of drought disaster and waterlogging disaster abrupt alternation, regulate crop exposure in planting areas, reduce the vulnerability of crop, improve the overall disaster prevention and mitigation capabilities, and promote management level in planting areas. The above research results can provide a reference for the drought disaster and waterlogging disaster prevention and loss reduction during the growth period of spring peanut and the construction of security production guarantee method system in Huang-Huai-Hai Region.
-
表 1 黄淮海地区春花生发育期划分
Table 1 Division of spring peanut growing season in Huang-Huai-Hai Region
发育期 时间 出苗期 4月中旬—4月下旬 幼苗期 5月上旬—5月下旬 花针期 6月上旬—6月下旬 结荚期 7月上旬—8月中旬 饱果期 8月下旬—9月下旬 表 2 春花生作物系数
Table 2 Spring peanut crop coefficient
春花生 开始时间 结束时间 作物系数 发育前期 04-15 05-31 0.50 发育中期 06-01 06-30 1.15 发育后期 07-01 09-30 0.60 表 3 基于标准化降水作物需水指数(ISPR)的旱涝等级划分
Table 3 Drought and flood grade based on standardized precipitation requirement index(ISPR)
灾害等级 ISPR取值范围 重涝 1.5<ISPR≤2.0 中涝 1.0<ISPR≤1.5 轻涝 0.5<ISPR≤1.0 无旱 -0.5<ISPR≤0.5 轻旱 -1.0<ISPR≤-0.5 中旱 -1.5<ISPR≤-1.0 重旱 ISPR≤-1.5 表 4 春花生干旱灾损系数
Table 4 The damage coefficients of drought disaster for spring peanut
发育阶段 干旱等级 轻旱 中旱 重旱 发育前期 0.01 0.03 0.06 发育中期 0.03 0.09 0.18 发育后期 0.06 0.18 0.36 表 5 春花生涝害灾损系数
Table 5 The damage coefficients of waterlogging for spring peanut
发育阶段 涝害等级 轻涝 中涝 重涝 发育前期 0.02 0.06 0.12 发育中期 0.03 0.09 0.18 发育后期 0.05 0.15 0.30 -
[1] 汤松, 禹山林, 廖伯寿, 等. 我国花生产业现状、存在问题及发展对策.花生学报, 2010, 39(3):35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4093.2010.03.008Tang S, Yu S L, Liao B S, et al. Industry status, existing problems and development strategy of peanut in China. Journal of Peanut Science, 2010, 39(3): 35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4093.2010.03.008 [2] 郭洪海, 杨丽萍, 李新华, 等. 黄淮海区域花生生产与品质特征的研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(6): 1233-1238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN201006017.htmGuo H H, Yang L P, Li X H, et al. Characteristics of production and quality of peanut in Huang-Huai-Hai region. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(6): 1233-1238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN201006017.htm [3] 黄荣辉, 杜振彩. 全球变暖背景下中国旱涝气候灾害的演变特征及趋势. 自然杂志, 2010, 32(4): 187-195;184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ201004002.htmHuang R H, Du Z C. Evolution characteristics and trend of droughts and floods in China under the background of global warming. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2010, 32(4): 187-195;184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ201004002.htm [4] 王纯枝, 霍治国, 郭安红, 等. 中国北方冬小麦蚜虫气候风险评估. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(2): 160-174. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210203Wang C Z, Huo Z G, Guo A H, et al. Climatic risk assessment of winter wheat aphids in northern China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(2): 160-174. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210203 [5] 张桂香, 霍治国, 杨建莹, 等. 江淮地区夏玉米涝渍灾害时空分布特征和风险分析. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(3): 747-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201703024.htmZhang G X, Huo Z G, Yang J Y, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristic and risk analysis of summer corn waterlogging disaster in Jianghuai region. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(3): 747-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201703024.htm [6] 杨磊, 韩丽娟, 宋金玲, 等. 基于遥感数据的夏玉米高温热害监测评估. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(6): 749-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX202006010.htmYang L, Han L J, Song J L, et al. Monitoring and evaluation of high temperature and heat damage of summer maize based on remote sensing data. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(6): 749-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX202006010.htm [7] 贾建英, 韩兰英, 万信, 等. 甘肃省冬小麦风险评估及其区划. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(6): 1478-1486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201906017.htmJia J Y, Han L Y, Wan X, et al. Risk assessment and regionalization of winter wheat drought disaster in Gansu Province. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(6): 1478-1486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201906017.htm [8] 王培娟, 唐俊贤, 金志凤, 等. 中国茶树春霜冻害研究进展. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(2): 129-145. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210201Wang P J, Tang J X, Jin Z F, et al. Review on spring frost disaster for tea plant in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(2): 129-145. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210201 [9] 吕佳佳, 王晾晾, 石磊, 等. 寒地水稻关键生育期涝害的过程雨量指标构建. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(5): 1402-1409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201905017.htmLv J J, Wang L L, Shi L, et al. Establishment of process rainfall indices for waterlogging damage in key growth stage of rice in cold region. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(5): 1402-1409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201905017.htm [10] 李燕, 王志伟, 霍治国, 等. 干旱对夏玉米根冠及产量影响试验. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 83-94. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200108Li Y, Wang Z W, Huo Z G, et al. Experiments of water stress on root/shoot growth and yield of summer maize. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 83-94. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200108 [11] 金林雪, 唐红艳, 武荣盛, 等. 内蒙古大豆干旱灾害风险分析与区划. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 106-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKDB202001013.htmJin L X, Tang H Y, Wu R S, et al. Risk analysis and regionalization of soybean drought disasters in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 106-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKDB202001013.htm [12] 杨建莹, 霍治国, 王培娟, 等. 中国北方苹果干旱等级指标构建及危险性评价. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(1): 25-37. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210103Yang J Y, Huo Z G, Wang P J, et al. Evaluation index construction and hazard risk assessment on apple drought in northern China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(1): 25-37. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210103 [13] 郁凌华, 赵艳霞. 黄淮海地区夏玉米生长季内的旱涝灾害分析. 灾害学, 2013, 28(2): 71-75;80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2013.02.015Yu L H, Zhao Y X. Analysis of drought-flood disaster on Huanghuaihai region during summer maize growing season. Journal of Catastrophology, 2013, 28(2): 71-75;80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2013.02.015 [14] 任宗悦, 刘晓静, 刘家福, 等. 近60年东北地区春玉米旱涝趋势演变研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(2): 179-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN202002003.htmRen Z Y, Liu X J, Liu J F, et al. Evolution of drought and flood trend in the growth period of spring maize in northeast China in the past 60 years. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(2): 179-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN202002003.htm [15] 张爱民, 马晓群, 杨太明, 等. 安徽省旱涝灾害及其对农作物产量影响. 应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5): 619-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2007.05.006Zhang A M, Ma X Q, Yang T M, et al. The influence of drought and waterlogging disasters on crop yields in Anhui Province. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2007, 18(5): 619-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2007.05.006 [16] 董奇琦, 艾鑫, 张艳正, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同耐性花生品种生理特性及产量的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020, 51(1): 18-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY202001003.htmDong Q Q, Ai X, Zhang Y Z, et al. Effect of drought stress on physiological characteristics and yield in different tolerant peanut. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020, 51(1): 18-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY202001003.htm [17] 石必显, 林明, 顾元国, 等. 不同干旱胁迫对花生生长发育及产量的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(3): 422-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNX201903005.htmShi B X, Lin M, Gu Y G, et al. Effects of different drought stress on growth and yield of peanut. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(3): 422-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNX201903005.htm [18] 张凤, 王媛媛, 张佳蕾, 等. 不同生育时期淹水对花生生理性状及产量、品质的影响. 花生学报, 2012, 41(2): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4093.2012.02.001Zhang F, Wang Y Y, Zhang J L, et al. Effects of water-logging at different growing periods on physiological characteristics, pod yield and kernel quality of peanut. Journal of Peanut Science, 2012, 41(2): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4093.2012.02.001 [19] Neto A D A, Nogueira R J M C, Melo P A, et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of peanut genotypes to water deficit. J Plant Interact, 2010, 5(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1080/17429140902999243 [20] Junjittakarn J, Girdthai T, Jogloy S, et al. Response of root characteristics and yield in peanut under terminal drought condition. Chil J Agric Res, 2014, 74(3): 249-256. doi: 10.4067/S0718-58392014000300001 [21] 张冠初, 张智猛, 徐扬, 等. 不同基因型花生抗旱耐盐性评价及鉴定指标筛选. 种子, 2020, 39(8): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2020.08.002Zhang G C, Zhang Z M, Xu Y, et al. Evaluation of drought and salt tolerance of peanut with different genotypes and screening of resistance-related identification indexes. Seed, 2020, 39(8): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2020.08.002 [22] 张俊, 汤丰收, 刘娟, 等. 利用隶属函数法对不同花生品种的抗旱性评价. 湖南农业科学, 2014(23): 42-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNK201423015.htmZhang J, Tang F S, Liu J, et al. Evaluations on drought-resistance traits of different peanut varieties by subordinate function values analysis. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2014(23): 42-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNNK201423015.htm [23] 邱柳, 刘登望, 熊路, 等. 花生种质资源耐涝性鉴定的研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 2012(7): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2012.07.002Qiu L, Liu D W, Xiong L, et al. Advances in identification of waterlogging tolerance for peanut germplasm resources. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2012(7): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2012.07.002 [24] 郭洪海, 杨丽萍, 李新华, 等. 黄淮海区域花生生产与品质现状及发展对策. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(14): 123-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201014028.htmGuo H H, Yang L P, Li X H, et al. Situation of production and quality and development countermeasure of peanut in Huang-Huai-Hai region. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(14): 123-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201014028.htm [25] 山仑, 吴普特, 康绍忠, 等. 黄淮海地区农业节水对策及实施半旱地农业可行性研究. 中国工程科学, 2011, 13(4): 37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.04.007Shan L, Wu P T, Kang S Z, et al. Study on agricultural water-saving countermeasures and feasibility of implementing semi-dryland farming in the Huang-Huai-Hai region. Engineering Science China, 2011, 13(4): 37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.04.007 [26] 杨尚. 花生天气指数保险研究与设计. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.Yang S. Research and Design of Peanut Weather Index Insurance. Jinan: Shandong University, 2019. [27] Vicente-Serrano S M, Beguería S, López-Moreno J I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim, 2010, 23(7): 1696-1718. doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1 [28] McKee T B, Doesken N J, Kleist J. The Relationship of Drought Frequency and Duration to Time Scales. The 8th Conference on Applied Climatology. American Meteorological Society, 1993. [29] 王国强. 1961-2015年黄土高原地区玉米生育期干旱演变特征及风险区划. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2017.Wang G Q. Drought Evolution Characteristics and Risk Regionalization of Maize Growth Period in the Loess Plateau during 1961-2015. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2017. [30] 程雪, 孙爽, 张方亮, 等. 我国北方地区苹果干旱时空分布特征. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 63-73. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200106Cheng X, Sun S, Zhang F L, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of apple drought in northern China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 63-73. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200106 [31] 李琪, 李莹莹, 任景全, 等. 吉林省春玉米不同生育期干旱时空特征分析. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(8): 50-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY201808013.htmLi Q, Li Y Y, Ren J Q, et al. Analysis of drought spatial-temporal characteristics of spring maize during different growth periods in Jilin Province. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(8): 50-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY201808013.htm [32] 黄会平, 曹明明, 宋进喜, 等. 黄淮海平原主要农作物全生育期水分盈亏变化特征. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(8): 138-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201508024.htmHuang H P, Cao M M, Song J X, et al. Water budget of main crops during the whole growth period in Huang-Huai-Hai plain. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(8): 138-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201508024.htm [33] 曹永强, 路洁, 李玲慧. 基于SPEI指数的辽宁省多尺度旱涝特征分析. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2021, 19(2): 210-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSX202102003.htmCao Y Q, Lu J, Li L H. Analysis of multi-scale drought and flood characteristic in Liaoning province based on SPEI. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2021, 19(2): 210-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSX202102003.htm [34] Vicente-Serrano S M, Beguería S, López-Moreno J I. Comment on "Characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) during 1900-2008" by Aiguo Dai. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2011, 116: D19112. DOI: 10.1029/2011JD016410. [35] 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等. 中国西北地区干旱气象灾害监测预警与减灾技术研究进展及其展望. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(2): 196-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201502003.htmZhang Q, Yao Y B, Li Y H, et al. Research progress and prospect on the monitoring and early warning and mitigation technology of meteorological drought disaster in Northwest China. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(2): 196-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201502003.htm [36] 宫丽娟, 李秀芬, 田宝星, 等. 黑龙江省大豆不同生育阶段干旱时空特征. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 95-104. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200109Gong L J, Li X F, Tian B X, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought in different growth stages of soybean in Heilongjiang. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 95-104. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200109 [37] 屈振江, 柏秦凤, 梁轶, 等. 气候变化对陕西猕猴桃主要气象灾害风险的影响预估. 果树学报, 2014, 31(5): 873-878. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSKK201405025.htmQu Z J, Bai Q F, Liang Y, et al. Potential impacts of climate change on the main meteorological disaster risk of kiwifruit in Shaanxi province. Journal of Fruit Science, 2014, 31(5): 873-878. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSKK201405025.htm [38] 苗昊翠, 李强, 侯献飞, 等. 不同生育期干旱对花生生长发育及产量的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2021(3): 441-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNX202103007.htmMiao H C, Li Q, Hou X F, et al. Effects of drought on growth and yield of peanut at different growth stages. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021(3): 441-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNX202103007.htm [39] 宋艳玲, 王建林, 田靳峰, 等. 气象干旱指数在东北春玉米干旱监测中的改进. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(1): 25-34. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190103Song Y L, Wang J L, Tian J F, et al. The spring maize drought index in northeast China based on meteorological drought index. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(1): 25-34. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190103 [40] 汪天颖, 霍治国, 杨建莹, 等. 湖南晚稻洪涝过程等级指标构建与演变特征. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(1): 35-48. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190104Wang T Y, Huo Z G, Yang J Y, et al. Process grade indicator construction and evolution characteristics of late rice flood in Hunan. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(1): 35-48. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190104 [41] 高珊, 陈杰, 许朗. 黄淮海地区干旱分区研究. 节水灌溉, 2020(10): 101-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2020.10.021Gao S, Chen J, Xu L. Study on drought zone division in Huang-Huai-Hai area. Water Saving Irrigation, 2020(10): 101-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2020.10.021 [42] 杨志勇, 袁喆, 严登华, 等. 黄淮海流域旱涝时空分布及组合特性. 水科学进展, 2013, 24(5): 617-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201305002.htmYang Z Y, Yuan Z, Yan D H, et al. Study of spatial and temporal distribution and multiple characteristics of drought and flood in Huang-Huai-Hai River basin. Advances in Water Science, 2013, 24(5): 617-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201305002.htm [43] 闵心怡, 王小博, 杨传国, 等. 近500年黄淮海地区洪旱事件时空变化特征. 水资源与水工程学报, 2017, 28(3): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201703013.htmMin X Y, Wang X B, Yang C G, et al. Spatio-temporal changes of floods and droughts at Huang-Huai-Hai region in last 500 years. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2017, 28(3): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201703013.htm [44] 李俊庆. 不同生育时期干旱处理对夏花生生长发育的影响. 花生学报, 2004, 33(3): 33-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PEAN200404008.htmLi J Q. Effects of drought stress on growth and development of summer peanut in different phases. Journal of Peanut Science, 2004, 33(3): 33-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PEAN200404008.htm [45] 赵长星, 程曦, 王月福, 等. 不同生育时期干旱胁迫对花生生长发育和复水后补偿效应的影响. 中国油料作物学报, 2012, 34(6): 627-632. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYW201206009.htmZhao C X, Cheng X, Wang Y F, et al. Effects of drought stress on peanut growth during different growth stages and compensatory effect after water recovery. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2012, 34(6): 627-632. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYW201206009.htm [46] 张智猛, 戴良香, 慈敦伟, 等. 生育后期干旱胁迫与施氮量对花生产量及氮素吸收利用的影响. 中国油料作物学报, 2019, 41(4): 614-621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYW201904017.htmZhang Z M, Dai L X, Ci D W, et al. Drought effects at late growth stage and nitrogen application rate on yield and N utilization of peanut. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2019, 41(4): 614-621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYW201904017.htm [47] 张凤. 淹水对花生生理特性及产量、品质的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012.Zhang F. Effects of Waterlogging on Physiological Characteristics, yield and Quality of Peanut. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2012. [48] 黄茹. 淮河流域旱涝急转事件演变及应对研究. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院, 2015.Huang R. Study on the Evolution and Response of Drought-flood Abrupt Change Events in Huaihe River Basin. Beijing: China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2015. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: