Application of the 2σ Lightning Jump Algorithm Based on DBSCAN Cluster
-
摘要: 针对业务运行中雷达观测存在遮挡和雷达产品延迟,提出利用带噪声基于密度的空间聚类(density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise,DBSCAN)算法对闪电数据的聚类结果替代雷达产品,并分别利用北京三维闪电定位网(Beijing Total Lightning System,BJTLS)和升级后的国家闪电定位网(DDW1)总闪数据,应用2σ闪电跃增算法对北京2022年6月4日和12日两次强对流致灾过程进行临近预警,对比强对流单体识别法和DBSCAN聚类法的预警效果。结果表明:两种算法和两种闪电数据均能有效预警北京地区的灾害性天气,基于BJTLS总闪数据的预警效果较优;对于BJTLS总闪数据,两种方法的预警效果相当,预警命中率、误报率、临近成功指数和平均预警提前时间依次分别为100%,11.9%,88.1%,38.9 min和100%,13.3%,86.7%,42.8 min;仅利用闪电数据并应用2σ闪电跃增算法可对灾害性天气进行临近预警,摆脱对雷达产品的依赖。
-
关键词:
- 闪电定位;
- 闪电跃增;
- DBSCAN聚类算法;
- 灾害性天气;
- 临近预警
Abstract: A DBSCAN (density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise) cluster of lightning data is proposed as the substitute for radar products to solve the problem of beam blockage in radar observation and the delay of radar products in service operations. Two lightning data, BJTLS (Beijing Total Lightning System) and upgraded National Lightning Positioning Network (DDW1), are used and the 2σ lightning jump algorithm is applied to perform severe weather nowcasting on 4 June and 12 June in 2022. The nowcasting effects of the strong convective cell identification method and the DBSCAN clustering method are further compared and analyzed. Based on a determined search radius (R) for neighboring lightning data and a determined minimum number of location results (number of minimum points) in R, the DBSCAN's clustering effect on lightning location data corresponds well with the strong convective radar echo. The ideal parameter combinations for BJTLS, R is 0.05, number of minimum points is 5; and for DDW1 data R is 0.22 and number of minimum points is 3. The results show that both methods and two kinds of data could effectively be used in severe weather nowcast. For BJTLS data, the effects of two methods are equivalent. The probability of detection, false alarm rate, critical success index and lead time of two methods are 100% and 100%, 11.9% and 13.3%, 88.1% and 86.7%, 38.9 min and 42.8 min, respectively. The 2σ lightning jump algorithm can be applied for nowcasting with lightning data, reducing the dependence on radar products. For DDW1 lightning data, compared with the identification method, the start time of the clustering method delays, leading to missing alarms. Since the flash rate of the DDW1 lightning data is low, there will be more missed cases if the flash rate threshold is set to trigger the lightning jump. But without the threshold, there will be more false alarms in operation. Therefore, BJTLS data is more suitable than DDW1 data for applying the 2σ lightning jump algorithm in the service operation. The detection efficiency of BJTLS in Beijing is high and it is necessary to further improve the detection efficiency of DDW1. In conclusion, the DBSCAN clustering method provides a new idea for the service operation of the 2σ lightning jump algorithm. -
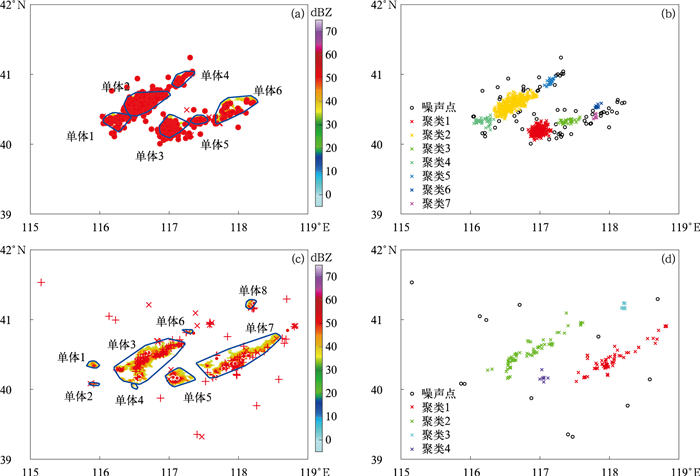
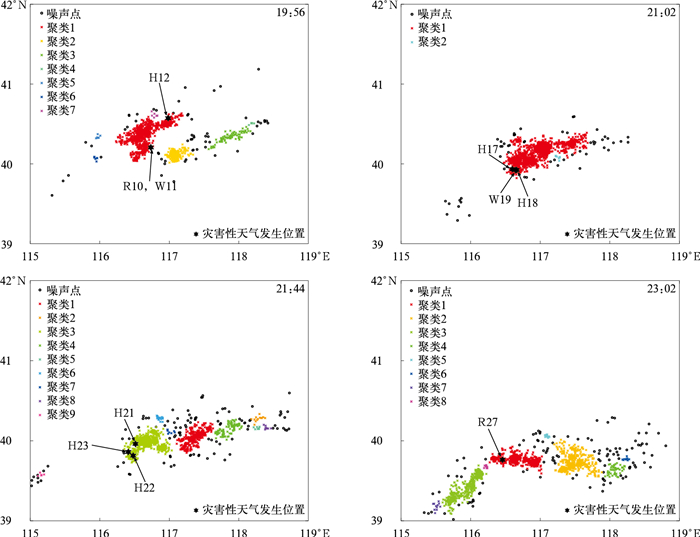
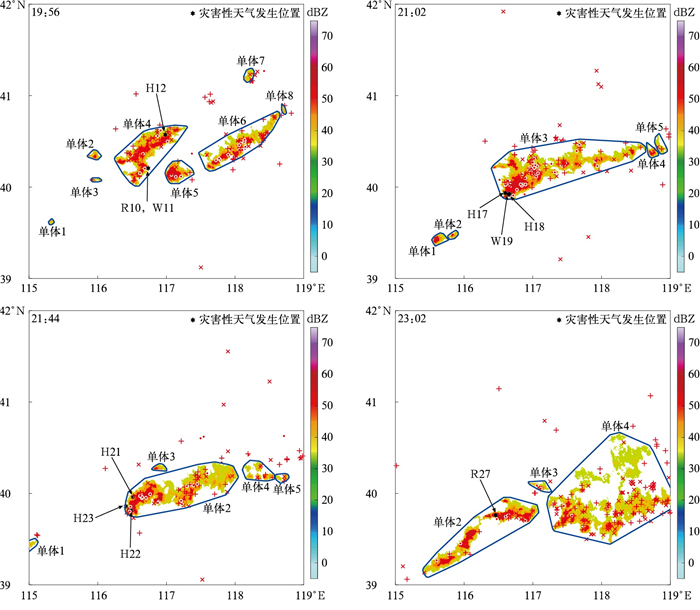
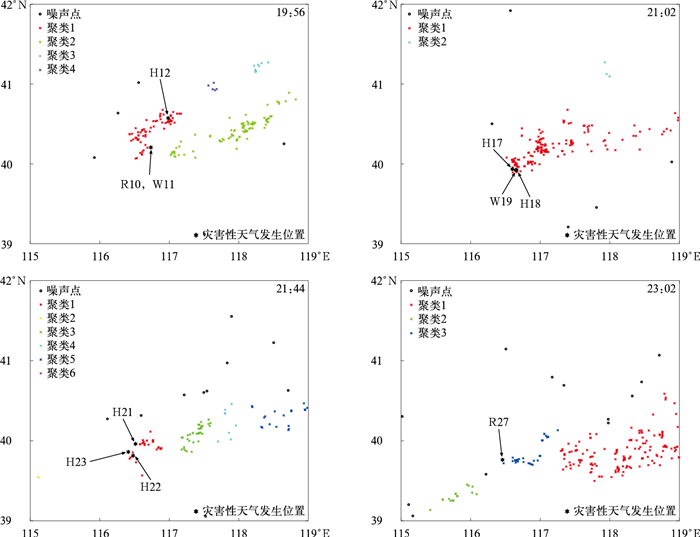
图 2 2022年6月12日强对流单体的识别
(·代表云闪,×表示负地闪, +表示正地闪,蓝色曲线为识别的单体范围,下同)
(a)19:20 BJTLS总闪数据与识别的强对流单体,(b)19:20 BJTLS总闪数据的DBSCAN聚类结果,(c)19:50 DDW1总闪数据与识别的强对流单体,(d)19:50 DDW1总闪数据的DBSCAN聚类结果Fig. 2 Identified strong convective cells on 12 Jun 2022
(· denotes an intracloud(IC) flash, × denotes a negative cloud-to-ground(CG) flash, + denotes a positive CG flash, the blue irregular circle denotes the range of an identified cell, similarly hereinafter)
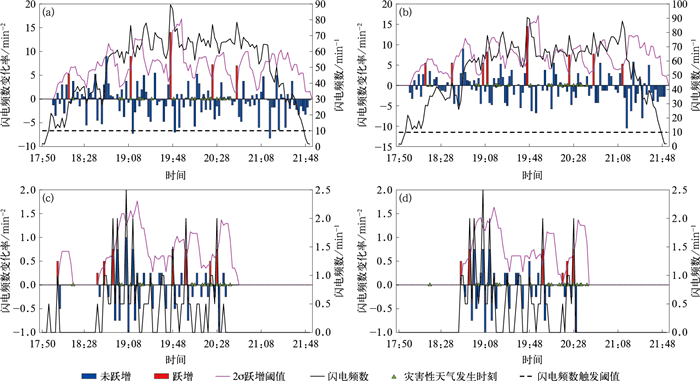
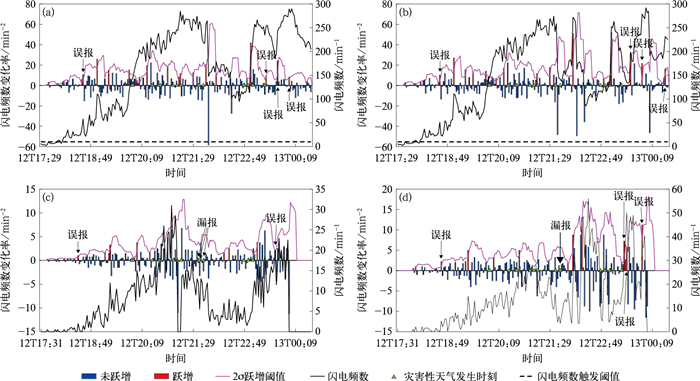
(a)total flashes of BJTLS and the identified strong convective cells at 1920 BT, (b)DBSCAN clustering of total flashes of BJTLS at 1920 BT, (c)total flashes of DDW1 and the identified strong convective cells at 1950 BT, (d)DBSCAN clustering of total flashes of DDW1 at 1950 BT图 5 2022年6月4日超级对流单体的强对流单体识别法和DBSCAN聚类法对BJTLS总闪数据和DDW1总闪数据的2σ闪电跃增预警效果对比
(a)强对流单体识别法和BJTLS总闪数据, (b)DBSCAN聚类法和BJTLS总闪数据, (c)强对流单体识别法和DDW1总闪数据, (d)DBSCAN聚类法和DDW1总闪数据
Fig. 5 Comparison in nowcasting effect of the 2σ lightning jump algorithm between identification method and DBSCAN method using total flash data of BJTLS and DDW1 for the supercell on 4 Jun 2022
(a)identification method and BJTLS data, (b)DBSCAN method and BJTLS data, (c)identification method and DDW1 data, (d)DBSCAN method and DDW1 data
图 10 2022年6月12—13日强对流单体识别法和DBSCAN聚类法对BJTLS总闪数据和DDW1总闪数据的2σ闪电跃增预警效果对比
(a)强对流单体识别法和BJTLS总闪数据, (b)DBSCAN聚类法和BJTLS总闪数据, (c)强对流单体识别法和DDW1总闪数据, (d)DBSCAN聚类法和DDW1总闪数据
Fig. 10 Comparison in nowcasting effect of the 2σ lightning jump algorithm between identification method and DBSCAN method using total flash data of BJTLS and DDW1 for disastrous weather cell on 12-13 Jun 2022
(a)identification method and BJTLS data, (b)DBSCAN method and BJTLS data, (c)identification method and DDW1 data, (d)DBSCAN method and DDW1 data
表 1 2022年6月4日和12日北京地区灾害性天气记录
Table 1 Records of disastrous weather in Beijing on 4 Jun and 12 Jun in 2022
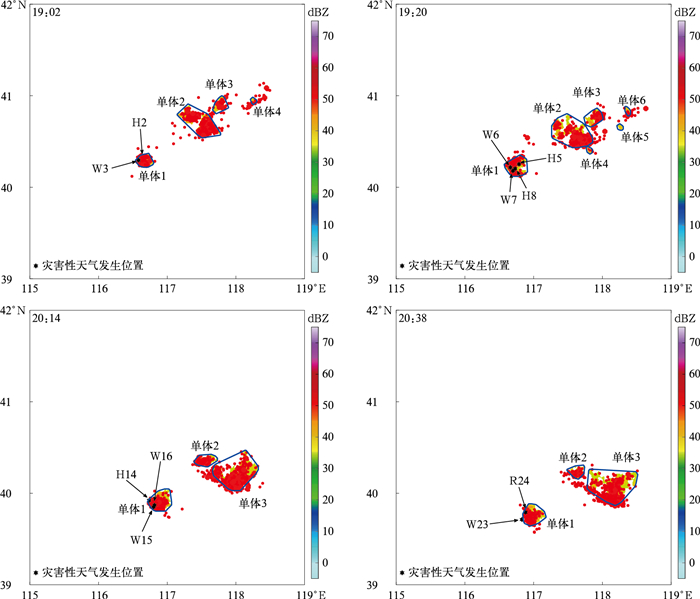
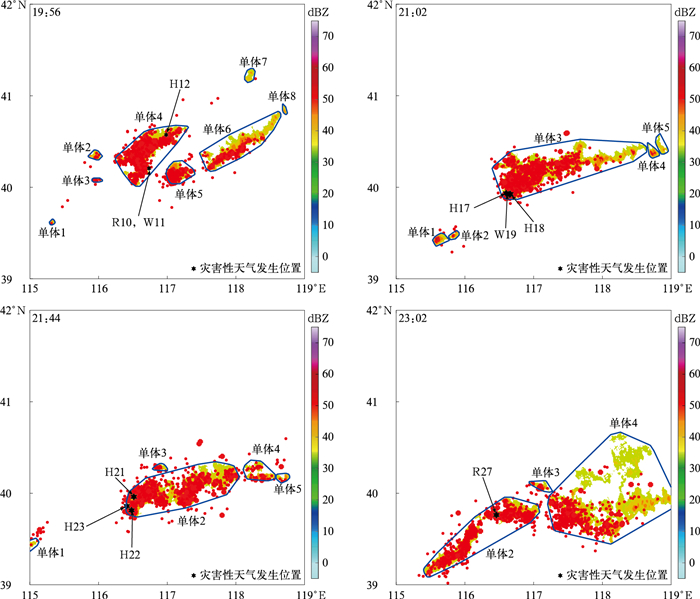
日期 起始时刻 灾害类型 代表符号 发生位置 强度或最大直径 产生单体 4日 18:18 大风 W1 怀柔杏树台 17.2 m·s-1 18:20单体1 19:00 冰雹 H2 怀柔城区 20 mm 19:02单体1 19:02 大风 W3 怀柔桥梓镇 18.1 m·s-1 19:02单体1 19:10 大风 W4 顺义兴农天力 24.2 m·s-1 19:08单体1 19:17 冰雹 H5 顺义木林 10 mm 19:20单体1 19:18 大风 W6 顺义牛栏山 17.4 m·s-1 19:20单体1 19:19 大风 W7 奥林匹克水上公园 24.9 m·s-1 19:20单体1 19:21 冰雹 H8 顺义北小营 10 mm 19:20单体1 19:29 强降水 R9 顺义牛栏山 20 mm·h-1 19:26单体1 19:49 冰雹 H10 顺义杨镇 10 mm 19:50单体1 20:05 大风 W11 通州小邓各庄村 25.2 m·s-1 20:02单体1 20:06 大风 W12 通州北刘各庄村 22.6 m·s-1 20:08单体1 20:08 大风 W13 通州副中心办公楼 14.1 m·s-1 20:08单体1 20:15 冰雹, 大风 H14, W15 通州潞城镇, 中农富通 40 mm, 24.4 m·s-1 20:14单体1 20:17 大风 W16 通州大豆各庄小学 20.2 m·s-1 20:14单体1 20:20 大风 W17 通州西定环卫所 19.7 m·s-1 20:20单体1 20:22 大风 W18 通州马坊村 17.4 m·s-1 20:20单体1 20:23 大风 W19 通州漷县村 18.6 m·s-1 20:20单体1 20:28 大风 W20 通州101农场 29.9 m·s-1 20:26单体1 20:31 大风 W21 通州永乐店二村 20.3 m·s-1 20:32单体1 20:34 大风 W22 通州曹庄村 26.7 m·s-1 20:32单体1 20:35 大风 W23 通州老槐庄 19.3 m·s-1 20:38单体1 20:40 强降水 R24 通州101农场 30 mm·h-1 20:38单体1 12日 19:53 强降水, 大风 R10, W11 顺义北小营 30 mm·h-1, 17.2 m·s-1 19:56单体4 19:55 冰雹 H12 密云不老屯 8 mm 19:56单体4 20:25 冰雹 H13 怀柔北房 8 mm 20:26单体3 20:36 强降水 R14 顺义北小营 50 mm·h-1 20:38单体3 20:38 冰雹 H15, H16 顺义李遂, 龙屯湾 10 mm, 25 mm 20:38单体3 20:58 冰雹 H17 朝阳常营 5 mm 21:02单体3 21:04 冰雹,大风 H18, W19 通州永顺, 通州气象局 30 mm, 17.2 m·s-1 21:02单体3 21:10 强降水 R20 朝阳楼梓庄 20 mm·h-1 21:08单体5 21:37 冰雹 H21 朝阳气象局 8 mm 21:44单体2 21:38 冰雹 H22 北京市观象台 20 mm 21:44单体2 21:45 冰雹 H23 丰台木樨园 30 mm 21:44单体2 22:48 冰雹 H25 朝阳小红门 60 mm 21:50单体6 22:55 冰雹 H26 大兴瀛海 5 mm 21:50单体6 23:02 强降水 R27 大兴瀛海 20 mm·h-1 23:02单体2 23:21 冰雹 H28 大兴气象局 10 mm 23:20单体2 表 2 基于两种数据和两种方法的灾害性天气预警对比
Table 2 Comparison in disastrous weather nowcasting of identification method and DBSCAN method using total flash data of BJTLS and DDW1
统计量 BJTLS DDW1 强对流单体识别法 DBSCAN聚类法 强对流单体识别法 DBSCAN聚类法 预警命中次数 52 52 48 49 预警误报次数 7 8 3 8 预警漏报次数 0 0 4 3 命中率/% 100 100 92.3 94.2 误报率/% 11.9 13.3 5.8 14.0 临界成功指数/% 88.1 86.7 87.3 81.7 预警提前时间/min 38.9 42.8 35.8 28.9 -
[1] 孙明生, 汪细明, 罗阳, 等.北京地区强对流天气展望预报方法研究.应用气象学报, 1996, 7(3):336-343. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/19960349Sun M S, Wang X M, Luo Y, et al. A prospect forecasting method study of severe convective weather in Beijing Area. J Appl Meteor Sci, 1996, 7(3): 336-343. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/19960349 [2] 赵文慧, 姚展予, 贾烁, 等. 1961~2015年中国地区冰雹持续时间的时空分布特征及影响因子研究. 大气科学, 2019, 43(3): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201903006.htmZhao W H, Yao Z Y, Jia S, et al. Characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of hail duration in China during 1961-2015 and its possible influence factors. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2019, 43(3): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201903006.htm [3] 李书严, 马京津, 轩春怡, 等. 195l~2008年北京极端天气事件分析. 气候与环境研究, 2012, 17(2): 244-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201202013.htmLi S Y, Ma J J, Xuan C Y, et al. Analysis of extreme weather events in Beijing during 1951-2008. Climatic Environ Res, 2012, 17(2): 244-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201202013.htm [4] 王迎春, 刘凤辉, 张小玲, 等. 北京地区中尺度非静力数值预报产品释用技术研究. 应用气象学报, 2002, 13(3): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2002.03.006Wang Y C, Liu F H, Zhang X L, et al. Interpretation of the nonhydrostatic mesoscale NWP products in terms of local weather phenomena and air pollution in Beijing Area. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2002, 13(3): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2002.03.006 [5] 陈明轩, 高峰, 孔荣, 等. 自动临近预报系统及其在北京奥运期间的应用. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(4): 395-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.04.002Chen M X, Gao F, Kong R, et al. Introduction of auto nowcasting system for convective storm and its performance in Beijing Olympics meteorological service. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2010, 21(4): 395-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.04.002 [6] 闵晶晶. BJ-RUC系统模式地面气象要素预报效果评估. 应用气象学报, 2014, 25(3): 265-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.03.002Min J J. Evaluation on surface meteorological element forecast by Beijing Rapid Update Cycle System. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(3): 265-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.03.002 [7] 王玉虹, Bica Benedikt. 不同天气背景下京津冀降水临近外推预报. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(3): 270-281. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220302Wang Y H, Benedikt B. Precipitation extrapolation nowcasting in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei under different weather backgrounds. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(3): 270-281. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220302 [8] 全继萍, 李青春, 仲跻芹, 等. "CMA北京模式"中三种不同阵风诊断方案在北京地区大风预报中的评估. 气象学报, 2022, 80(1): 108-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202201008.htmQuan J P, Li Q C, Zhong J Q, et al. Evaluation of three different gust diagnostic schemes in the CMA-BJ for gale forecasting over Beijing. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 108-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202201008.htm [9] Li R M, Sun J Z, Zhang Q H, et al. Model predictability of hail precipitation with a moderate hailstorm case. Part Ⅰ: Impact of improved initial conditions by assimilating high-density observations. Mon Wea Rev, 2022, 150(10): 2675-2696. doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-21-0329.1 [10] Wilson J W, Feng Y, Chen M, et al. Nowcasting challenges during the Beijing Olympics: Successes, failures, and implications for future nowcasting systems. Wea Forecasting, 2010, 25(6): 1691-1714. doi: 10.1175/2010WAF2222417.1 [11] 陶祖钰, 郑永光. "7·21"北京特大暴雨的预报问题. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32(3): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX201303001.htmTao Z Y, Zheng Y G. Forecasting issues of the extreme heavy rain in Beijing on 21 July 2012. Torrential Rain Disaster, 2013, 32(3): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX201303001.htm [12] Williams E R, Boldi B, Matlin A, et al. The behavior of total lightning activity in severe Florida thunderstorms. Atmos Res, 1999, 51: 245-265. doi: 10.1016/S0169-8095(99)00011-3 [13] Schultz C J, Petersen W A, Carey L D. Preliminary development and evaluation of lightning jump algorithms for the real-time detection of severe weather. J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2009, 48: 2543-2563. doi: 10.1175/2009JAMC2237.1 [14] Schultz C J, Petersen W A, Carey L D. Lightning and severe weather: A comparison between total and cloud-to-ground lightning trends. Wea Forecasting, 2011, 26(5): 744-755. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-10-05026.1 [15] Wang Y, Qie X S, Wang D F, et al. Beijing lightning network(BLNET) and the observation on preliminary breakdown processes. Atmos Res, 2016, 171: 121-132. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.12.012 [16] Qie X, Yuan S, Chen Z, et al. Understanding the dynamical-microphysical-electrical processes associated with severe thunderstorms over the Beijing metropolitan region. Sci China Earth Sci, 2021, 64: 10-26. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9656-8 [17] Tian Y, Qie X S, Sun Y, et al. Total lightning signatures of thunderstorms and lightning jumps in hailfall nowcasting in the Beijing Area. Atmos Res, 2019, 230: 104646. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104646 [18] 田野, 姚雯, 尹佳莉, 等. 不同闪电跃增算法在北京地区应用效果对比. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(2): 217-232. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210207Tian Y, Yao W, Yin J L, et al. Comparison of the performance of different lightning jump algorithms in Beijing. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(2): 217-232. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210207 [19] Tian Y, Yao W, Sun Y, et al. A method for improving the performance of the 2σ lightning jump algorithm for nowcasting hail. Atmos Res, 2022, 280: 106404. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106404 [20] 尹晓燕, 胡志群, 郑佳锋, 等. 利用深度学习填补双偏振雷达回波遮挡. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(5): 581-593. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220506Yin X Y, Hu Z Q, Zheng J F, et al. Filling in the dual polarization radar echo occlusion based on deep learning. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(5): 581-593. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220506 [21] Farnell C, Rigo T, Pineda N. Lightning jump as a nowcast predictor: Application to severe weather events in Catalonia. Atmos Res, 2017, 183: 130-141. [22] 周康辉, 郑永光, 蓝渝. 基于闪电数据的雷暴识别、追踪与外推方法. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(2): 173-181. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160205Zhou K H, Zheng Y G, Lan Y. Flash cell identification, tracking and nowcasting with lightning data. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(2): 173-181. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160205 [23] 李庆申, 陈宇涵, 张阳, 等. DDW1闪电定位系统及性能评估. 气象科技, 2020, 48(6): 788-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ202006002.htmLi Q S, Chen Y H, Zhang Y, et al. DDW1 lightning location system and performance evaluation. Meteor Sci Technol, 2020, 48(6): 788-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ202006002.htm [24] 张林, 李峰, 吴蕾, 等. CINRAD/SAD双偏振雷达非降水回波识别技术. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(6): 724-735. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220607Zhang L, Li F, Wu L, et al. Non-precipitation identification technique for CINRAD/SAD dual polarimetric weather radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(6): 724-735. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220607 [25] 徐舒扬, 吴翀, 刘黎平. 双偏振雷达水凝物相态识别算法的参数改进. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(3): 350-360. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200309Xu S Y, Wu C, Liu L P. Parameter improvements of hydrometeor classification algorithm for the dual-polarimetric radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(3): 350-360. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200309 [26] Ester M, Kriegel H P, Sander J, et al. A Density-based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise//Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining(KDD-96). Portland, Oregon: AAAI Press, 1996: 226-231. [27] 侯荣涛, 朱斌, 冯民学, 等. 基于DBSCAN聚类算法的闪电临近预报模型. 计算机应用, 2012, 32(3): 847-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201203071.htmHou R T, Zhu B, Feng M X, et al. Prediction model for lightning nowcasting based on DBSCAN. J Computer Applications, 2012, 32(3): 847-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201203071.htm [28] Edla D R, Jana P K. A prototype-based modified DBSCAN for gene clustering. Procedia Technol, 2012, 6: 485-492. [29] 梁丽, 雷勇, 张帅弛, 等. 基于DBSCAN与网格搜索的雷电定位算法. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(3): 267-278. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190302Liang L, Lei Y, Zhang S C, et al. Lightning location algorithm based on DBSCAN and grid search. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(3): 267-278. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190302 [30] Liang H B, Wang Z. Application of an intelligent early-warning method based on DBSCAN clustering for drilling overflow accident. Cluster Comput, 2019, 22(5): 12599-12608. [31] Ma Z, Jiang R, Qie X, et al. A low frequency 3D lightning mapping network in north China. Atmos Res, 2021, 249: 105314. [32] 金立生, 贺阳, 王欢欢, 等. 基于自适应阈值DBSCAN的路侧点云分割算法. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(7): 987-996. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC202207005.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏



 下载:
下载: