Characteristics of the Preliminary Breakdown in Inverted-polarity Intracloud Lightning Flashes
-
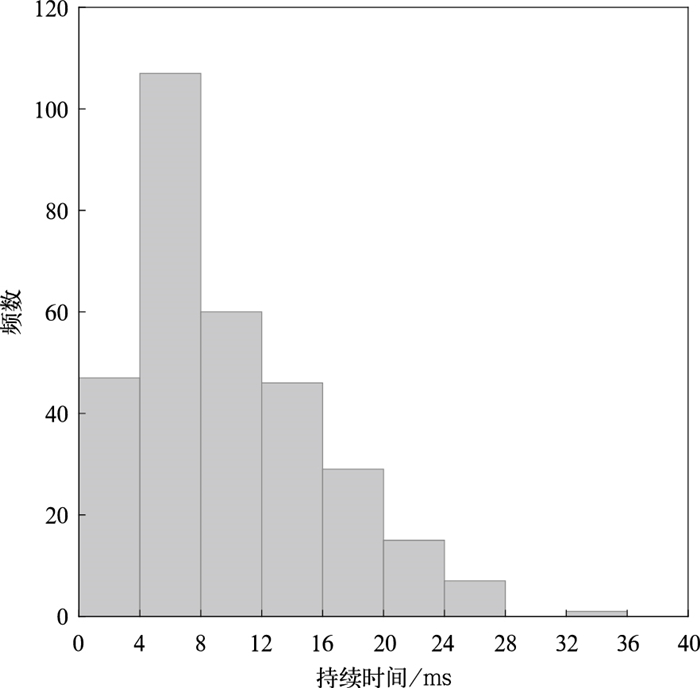
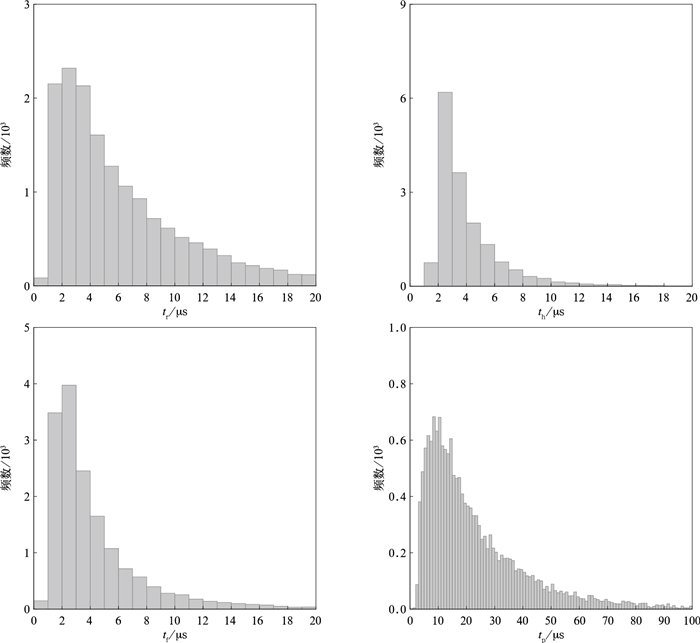
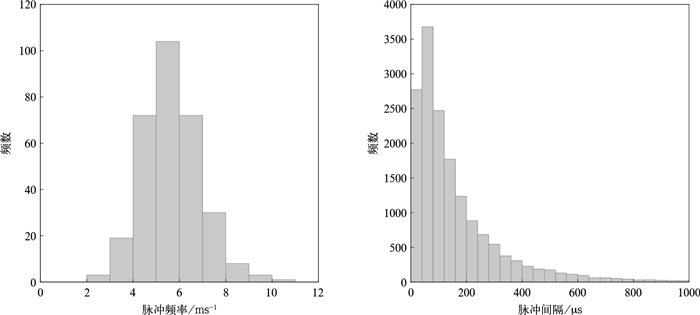
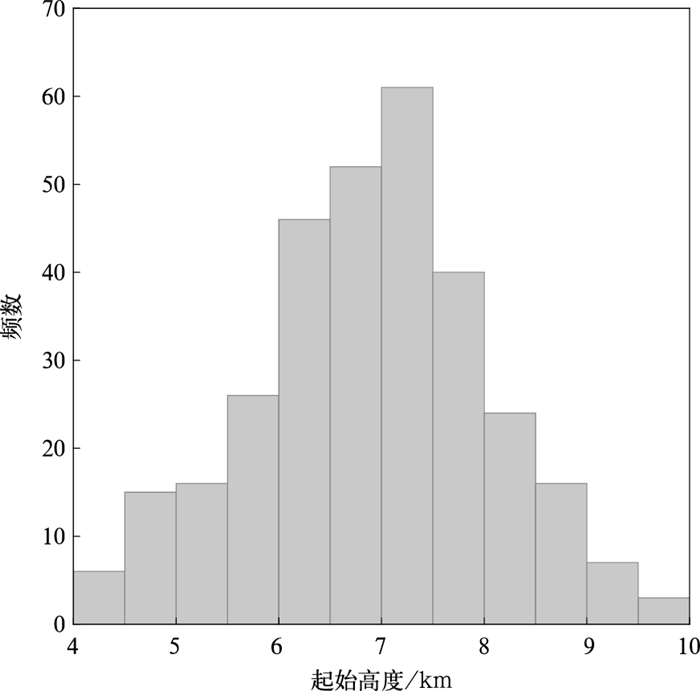
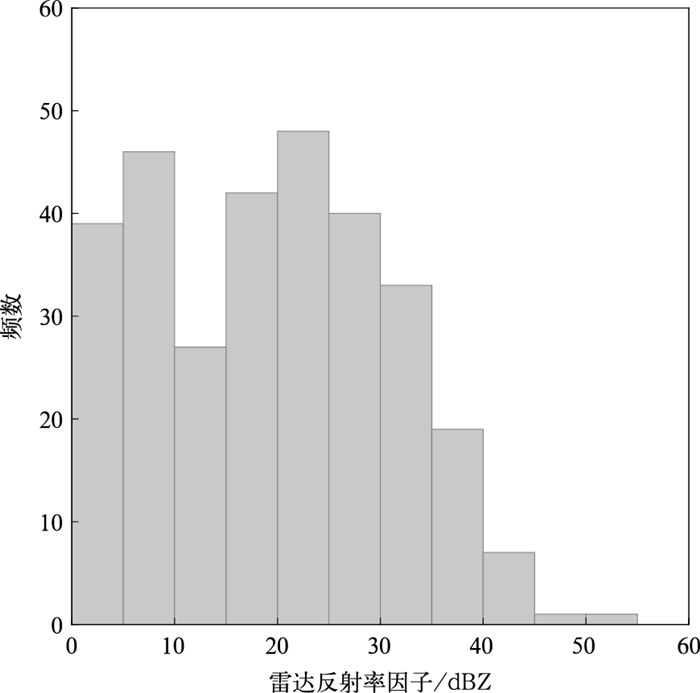
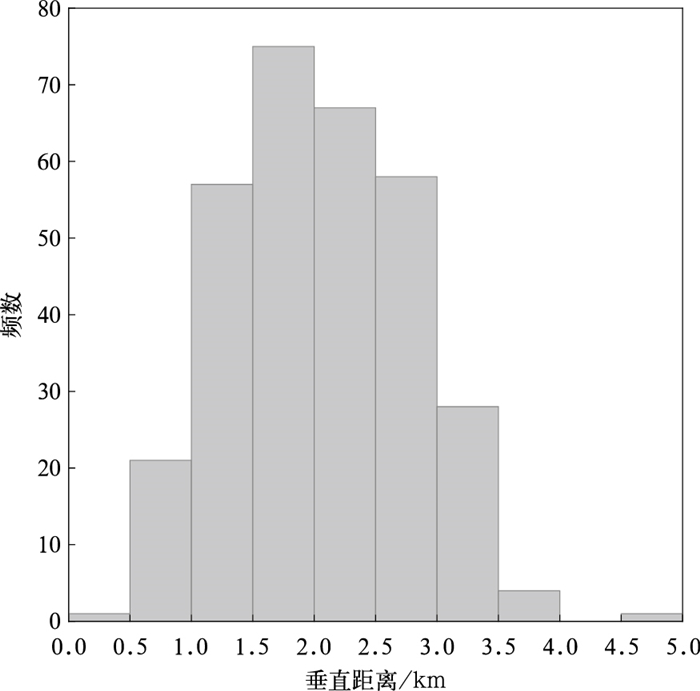
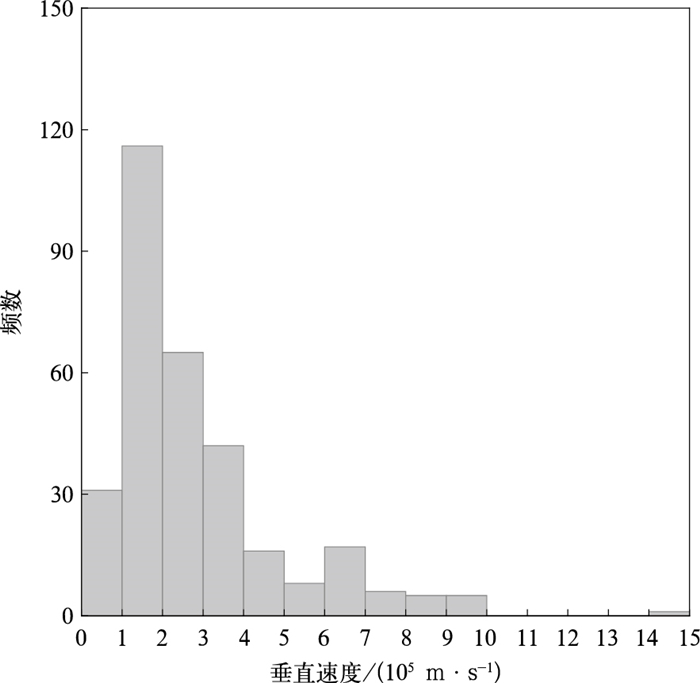
摘要: 基于快天线闪电定位阵列(fast antenna lightning mapping array,FALMA)的观测数据,对2019年8月2日和5日发生于我国宁夏的两次雷暴过程312例反极性云闪的初始击穿(preliminary breakdown,PB)特征进行统计。脉冲参数统计结果显示:PB过程持续时间算术平均值为9.8 ms;脉冲结构由脉冲上升沿、半宽、下降沿和脉冲宽度4个变量表征,算术平均值分别为7.3,4.5,5.6 μs和24.7 μs。脉冲频率和脉冲间隔的算术平均值分别是5.7 ms-1和169.2 μs。通道参数统计结果显示:反极性云闪的起始高度平均值为6.9 km。相比于正极性云闪,反极性云闪PB倾向于在弱雷达回波区域起始,雷达反射率因子算术平均值为19.3 dBZ。垂直发展距离和垂直速度平均值分别是2.0 km和2.8×105 m·s-1。PB参数随起始高度变化的结果表明:PB持续时间、垂直发展距离(垂直速度、脉冲频率)与起始高度呈正(负)相关。Abstract: The intracloud (IC) flashes can be classified into normal and inverted-polarity types according to their initial leader propagation directions. Due to the rare occurrence of inverted-polarity IC flashes with downward preliminary breakdown (PB) processes, the corresponding PB characteristics are much less understood than those in normal IC flashes.Based on the lightning data observed by a low-frequency lightning mapping system FALMA (fast antenna lightning mapping array) deployed in Ningxia, the characteristics of the PB process in 312 inverted-polarity IC flashes are statistically analyzed. The parameters of PB waveforms show that the arithmetical mean (AM) of the PB duration is 9.8 ms. The pulse shape is characterized by rise time, half-peak width, fall time, and pulse width, respectively, with AM values of 7.3 μs, 4.5 μs, 5.6 μs, and 24.7 μs. The pulse rate and pulse interval are 5.7 ms-1 and 169.2 μs.The statistical results for PB channels show that the inverted-polarity IC flashes are usually initiated at the AM altitude about 6.9 km, obviously higher than the initiation altitude of normal-polarity IC flashes. The difference indicates that there could be an inverted dipolar charge structure in the thunderclouds of Ningxia. The superposition of PB locations on the radar reflectivity suggests that these inverted IC flashes tend to be initiated in the region with radar echoes weaker than normal IC flashes (19.3 versus 27.8 dBZ). The vertical length and speed of PB channels are 2.0 km and 2.8×105 m·s-1.Furthermore, PB parameters show significant correlations with the initiation altitude. Specifically, both vertical speed and pulse rate decrease with the initiation altitude, and the correlation coefficients are -0.44 and -0.53, respectively. However, both PB durations and vertical distances show positive correlations with the initiation altitude, with the coefficients of 0.64 and 0.46, respectively.In general, the PB characteristics of inverted IC flashes present both similarities and differences to the PB processes in other flash types. It is believed more lightning observations in the northwest inland of China can facilitate the interpretation of these similarities and differences.
-
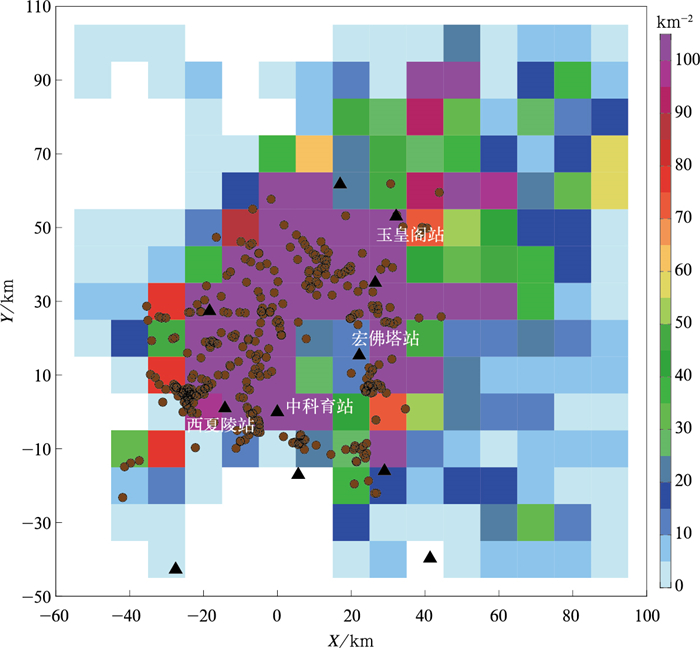
图 1 2019年8月2日和5日宁夏雷暴天气辐射源密度(填色)和反极性云闪始发位置分布
(三角形表示FALMA测站, 圆点表示PB起始位置, 中心位置(0,0)对应位置为38.4°N,106.2°E)
Fig. 1 Distributions of lightning source density(the shaded) and initiation locations of inverted-polarity intracloud flashes of thunderstorms in Ningxia on 2 Aug and 5 Aug in 2019
(triangles and dots denote FALMA sites and lightning initiations, the central position (0, 0) corresponds to 38.4°N, 106.2°E)
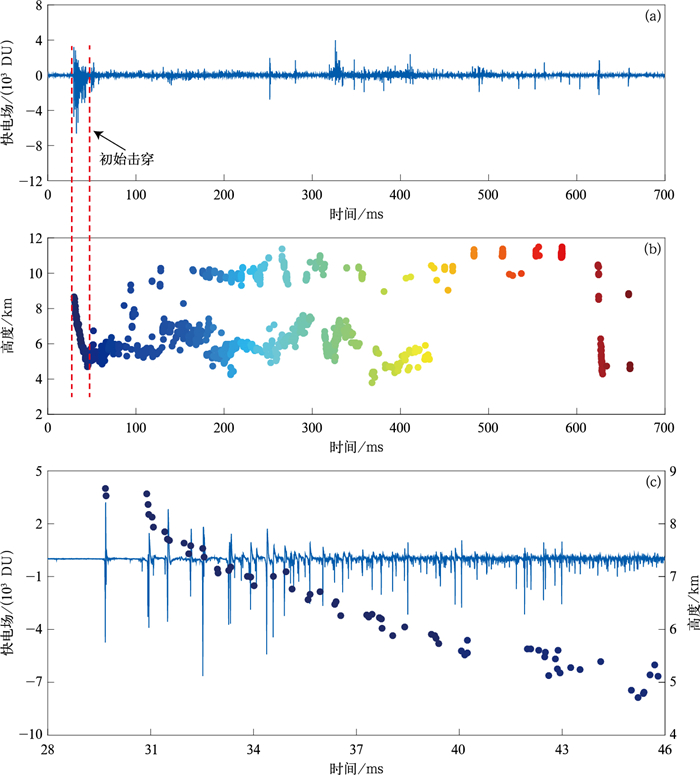
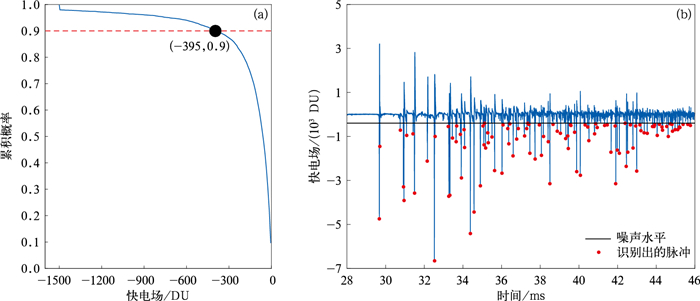
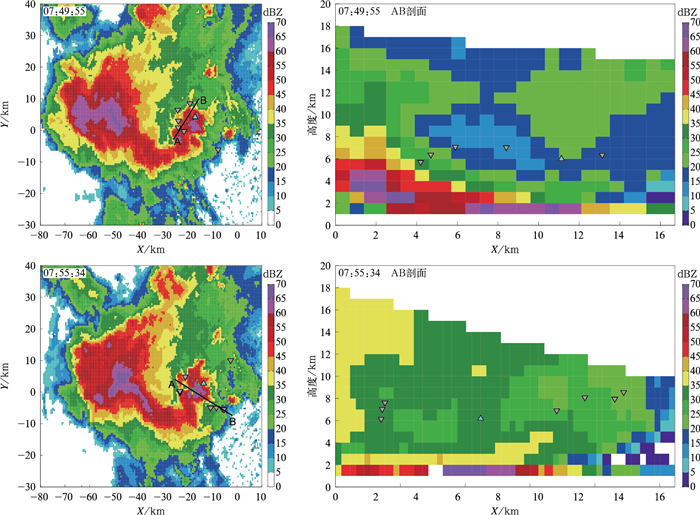
图 2 2019年8月5日16:58:41.8的反极性云闪个例
(a)反极性云闪的电场波形,(b)辐射源定位高度随时间变化,(c)PB过程的电场波形和辐射源定位高度
Fig. 2 A case of an inverted-polarity intracloud flash occurring at 165841.8 UTC 5 Aug 2019
(a)electric field change waveform of inverted-polarity intracloud flash, (b)source located height varying with time, (c)electric field change waveform of PB process and source located height
-
[1] 吕伟涛, 陈绿文, 马颖, 等.广州高建筑物雷电观测与研究10年进展.应用气象学报, 2020, 31(2):129-145. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200201Lü W T, Chen L W, Ma Y, et al. Advances of observation and study on tall-object lightning in Guangzhou over the last decade. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(2): 129-145. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200201 [2] 余骏皓, 谭涌波, 郑天雪, 等. 建筑物群众多上行先导三维模型的建立. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(6): 740-748. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200609Yu J H, Tan Y B, Zheng T X, et al. A three-dimensional model establishment of multiple connecting leaders initiated from tall structures. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(6): 740-748. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200609 [3] 任晓毓, 张义军, 吕伟涛, 等. 雷击建筑物的先导连接过程模拟. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(4): 450-457. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20100408Ren X Y, Zhang Y J, Lü W T, et al. Simulation of lightning leaders and connection process with structures. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2010, 21(4): 450-457. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20100408 [4] 雷艺楠, 谭涌波, 余骏皓, 等. 高矮建筑物多上行先导连接过程的数值模拟. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1): 80-91. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220107Lei Y N, Tan Y B, Yu J H, et al. Numerical simulation on multiple upward leader attachment process of tall and low buildings. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(1): 80-91. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220107 [5] Weidman C D, Krider E P. The radiation field wave forms produced by intracloud lightning discharge processes. J Geophys Res, 1979, 84(C6): 3159-3164. doi: 10.1029/JC084iC06p03159 [6] 张骁, 张阳, 张义军, 等. NBE和IBP始发的闪电初始特征. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29(3): 364-373. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180310Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y J, et al. Initial stage of lightning discharges initiated by NBE and IBP. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(3): 364-373. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180310 [7] 武斌, 张广庶, 文军, 等. 闪电初始预击穿过程辐射脉冲特征及电流模型. 应用气象学报, 2017, 28(5): 555-567. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170504Wu B, Zhang G S, Wen J, et al. The characteristic and current model of radiation impulse in lightning initial preliminary breakdown process. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2017, 28(5): 555-567. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170504 [8] Gomes C, Cooray V, Jayaratne C. Comparison of preliminary breakdown pulses observed in Sweden and in Sri Lanka. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys, 1998, 60(10): 975-979. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(98)00007-8 [9] Baharudin Z A, Ahmad N A, Fernando M, et al. Comparative study on preliminary breakdown pulse trains observed in Johor, Malaysia and Florida, USA. Atmos Res, 2012, 117: 111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.01.012 [10] Makela J S, Porjo N, Makela A, et al. Properties of preliminary breakdown processes in Scandinavian lightning. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys, 2008, 70: 2041-2052. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2008.08.013 [11] 王宇, 郄秀书, 王东方, 等. 正地闪和负地闪预击穿脉冲序列的统计分析与对比. 大气科学, 2014, 38(1): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201401003.htmWang Y, Qie X S, Wang D F, et al. Comparisons of preliminary breakdown pulse trains in positive and negative cloud-to-ground lightning flashes. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2014, 38(1): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201401003.htm [12] Kitagawa N, Brook M. A comparison of intracloud and cloud-to-ground lightning discharges. J Geophys Res, 1960, 65: 1189-1201. doi: 10.1029/JZ065i004p01189 [13] Villanueva Y, Rakov V A, Uman M A, et al. Microsecond-scale electric field pulses in cloud lightning discharges. J Geophys Res Atmos, 1994, 99(D7): 14353-14360. doi: 10.1029/94JD01121 [14] Nag A, Decarlo B A, Rakov V A. Analysis of microsecond- and submicrosecond-scale electric field pulses produced by cloud and ground lightning discharges. Atmos Res, 2009, 91(2): 316-325. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809508002020 [15] Qie X S, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. Characteristics of cloud-to-ground lightning in Chinese inland plateau. J Meteor Soc Japan, 2002, 80(4): 745-754. doi: 10.2151/jmsj.80.745 [16] 王华, 郑栋, 张义军, 等. 北京和广州地区云闪初始击穿电场变化特征. 气象与环境科学, 2016, 39(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNQX201603004.htmWang H, Zheng D, Zhang Y J, et al. Variation characteristics of cloud flashes initial breakdown electric field observed in Beijing and Guangzhou. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 39(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNQX201603004.htm [17] Zhang Y, Zhang Y J, Lu W T, et al. Analysis and comparison of initial breakdown pulses for positive cloud-to-ground flashes observed in Beijing and Guangzhou. Atmos Res, 2013, 129(7): 34-41. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809513000902 [18] 曹冬杰, 郄秀书, 杨静, 等. 闪电初始放电阶段亚微秒电场变化波形特征. 大气科学, 2011, 35(4): 645-656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201104005.htmCao D J, Qie X S, Yang J, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of sub-microsecond electric field change waveforms during the initial stage of lightning discharge. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2011, 35(4): 645-656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201104005.htm [19] Wang Y, Qie X, Wang D, et al. Beijing Lightning Network (BLNET) and the observation on preliminary breakdown processes. Atmos Res, 2015, 171: 121-132. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809515004020 [20] Wu T, Yoshida S, Akiyama Y, et al. Preliminary breakdown of intracloud lightning: Initiation altitude, propagation speed, pulse train characteristics, and step length estimation. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2015(120): 9071-9086. [21] 王东方, 郄秀书, 袁铁, 等. 利用快电场变化脉冲定位进行云闪初始放电过程的研究. 气象学报, 2009, 67(1): 165-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200901018.htmWang D F, Qie X S, Yuan T, et al. An analysis on the initial stage of intracloud lightning with the location technique of fast electric field change pulses. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2009, 67(1): 165-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200901018.htm [22] Yoshida S, Wu T, Ushio T, et al. Initial results of LF sensor network for lightning observation and characteristics of lightning emission in LF band. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2014, 119(21): 12034-12051. [23] Zheng D, Zhang Y, Meng Q. Properties of negative initial leaders and lightning flash size in a cluster of supercells. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2018, 123: 12857-12876. doi: 10.1029/2018JD028824 [24] Zheng D, Shi D D, Zhang Y, et al. Initial leader properties during the preliminary breakdown processes of lightning flashes and their associations with initiation positions. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2019, 124: 8025-8042. [25] 王道洪, 刘欣生, 王才纬. 甘肃中川地区雷暴地闪特征的初步分析. 高原气象, 1990, 9(4): 405-410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX199004007.htmWang D H, Liu X S, Wang C W. A preliminary analysis of the characteristics of ground discharges in thunderstorms near Zhongchuan, Gansu Province. Plateau Meteor, 1990, 9(4): 405-410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX199004007.htm [26] Li Y J, Zhang G S, Wen J, et al. Electrical structure of a Qinghai-Tibet Plateau thunderstorm based on three-dimensional lightning mapping. Atmos Res, 2013, 134: 137-149. [27] 张义军, 徐良韬, 郑栋, 等. 强风暴中反极性电荷结构研究进展. 应用气象学报, 2014, 25(5): 513-526. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20140501Zhang Y J, Xu L T, Zheng D, et al. Review on inverted charge structure of severe storms. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(5): 513-526. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20140501 [28] Li Y, Zhang G, Wang Y, et al. Observation and analysis of electrical structure change and diversity in thunderstorms on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Atmos Res, 2017, 194: 130-141. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809516304495 [29] 刘欣生, 郭昌明, 王伟才, 等. 闪电引起的地面电场变化特征及雷暴云下部的正电荷层. 气象学报, 1987, 45(4): 500-504. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198704015.htmLiu X S, Guo C M, Wang W C. The surface electrostatic field-change produced by lightning flashes and the lower positive charge layer of the thunderstorm. Acta Meteor Sinica, 1987, 45(4): 500-504. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198704015.htm [30] Qie X, Kong X, Zhang G, et al. The possible charge structure of thunderstorm and lightning discharges in northeastern verge of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Atmos Res, 2005, 76(1/2/3/4): 231-246. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809505000591 [31] Qie X, Zhang T, Chen C, et al. The lower positive charge center and its effect on lightning discharges on the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett, 2005, 32: 1-4. [32] 张廷龙, 郄秀书, 袁铁, 等. 中国内陆高原地区典型雷暴过程的地闪特征及电荷结构反演. 大气科学, 2008, 32(5): 1221-1227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200805018.htmZhang T L, Qie X S, Yuan T, et al. The characteristics of cloud-to-ground lightning flashes and charge structure of a typical thunderstorm in Chinese inland plateau. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2008, 32(5): 1221-1227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200805018.htm [33] Qie X, Zhang T, Zhang G, et al. Electrical characteristics of thunderstorms in different plateau regions of China. Atmos Res, 2009, 91(2/3/4): 244-249. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809508001944 [34] Wu T, Wang D, Takagi N. Lightning mapping with an array of fast antennas. Geophys Res Lett, 2018, 45(8): 3698-3705. [35] Gao P L, Wu T, Wang D H. Initial results of long-term continuous observation of lightning discharges by FALMA in Chinese inland plateau region. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(4): 514. [36] Shi D D, Gao P L, Wu T, et al. Pulse parameters and peak currents of return strokes observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese inland areas. Remote Sens, 2022, 14: 1838. [37] 张志孝, 郑栋, 张义军, 等. 闪电初始阶段和尺度判别方法及其特征. 应用气象学报, 2017, 28(4): 414-426. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170403Zhang Z X, Zheng D, Zhang Y J, et al. Identification method and analysis on the lightning flash initiation phase and size. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2017, 28(4): 414-426. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170403 [38] Shi D D, Wang D H, Wu T, et al. Correlation between the first return stroke of negative CG lightning and its preceding discharge processes. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2019, 124(15): 8501-8510. doi: 10.1029/2019JD030593 [39] Zhu Y, Rakov V, Tran M. A study of preliminary breakdown and return stroke processes in high-intensity negative lightning discharges. Atmosphere, 2016, 7(10): 130. [40] 祝宝友, 马明, 陶善昌. 地闪和云闪初始击穿VHF/VLF辐射特征观测和比较. 高原气象, 2003, 22(3): 239-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200303006.htmZhu B Y, Ma M, Tao S C. Measurement and comparison of VHF/VLF radiations of preliminary breakdown of cloud-to-ground and intracloud flashes. Plateau Meteor, 2003, 22(3): 239-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200303006.htm [41] Sharma S R, Fernando M, Gomes C. Signatures of electric field pulses generated by cloud flashes. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys, 2005, 67: 413-422. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364682604002846 [42] Cooray V, Lundquist S. Characteristics of radiation fields from lightning in Sri Lanka in the tropics. J Geophys Res, 1985, 90: 6099-6109. doi: 10.1029/JD090iD04p06099 [43] Ahmad N A, Fernandoa M, Baharudina Z A, et al. The first electric field pulse of cloud and cloud-to-ground lightning discharges. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys, 2010, 72: 143-150. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364682609002934 [44] Shi D D, Wang D H, Wu T, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of preliminary breakdown pulses in intracloud lightning flashes. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2019, 124(23): 12901-12914. doi: 10.1029/2019JD031130 [45] 刘恒毅, 董万胜, 徐良韬, 等. 闪电起始过程时空特征的宽带干涉仪三维观测. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(1): 16-24. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160102Liu H Y, Dong W S, Xu L T, et al. 3D spatial-temporal characteristics of initial breakdown process in lightning observed by broadband interferometer. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(1): 16-24. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160102 [46] Li J, Cai L, Wang J, et al. Electrical field parameters of natural return strokes at different distances. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat, 2022, 64(3): 786-794. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9686607/ -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: