Distribution Characteristics of Raindrop Spectrum at Changbai Mountain Foothills in Summer of 2021
-
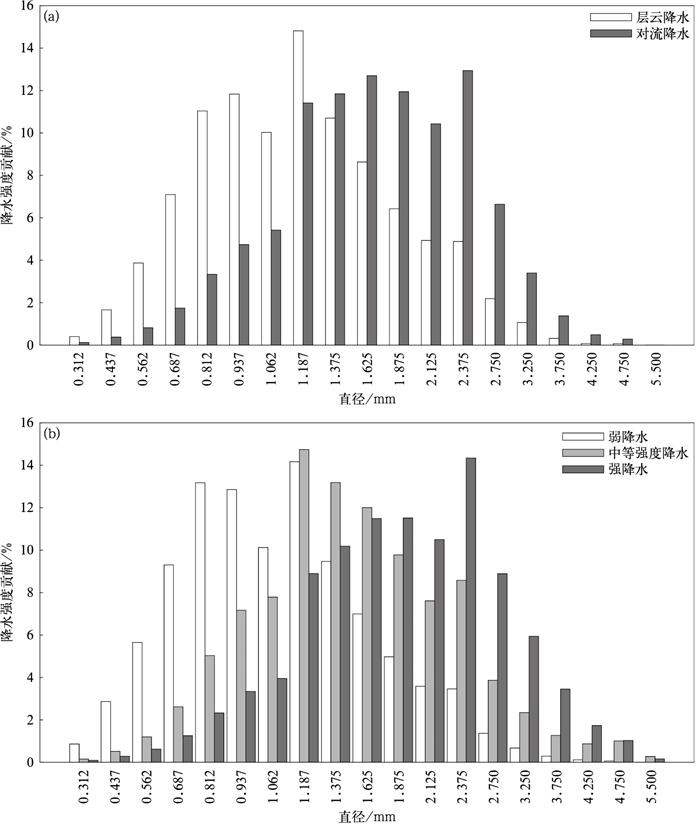
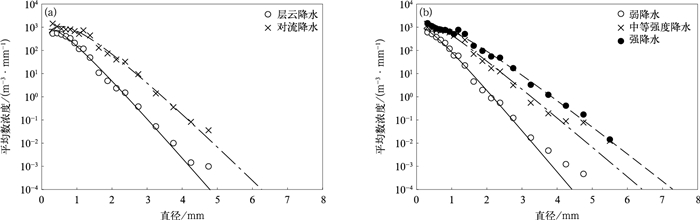
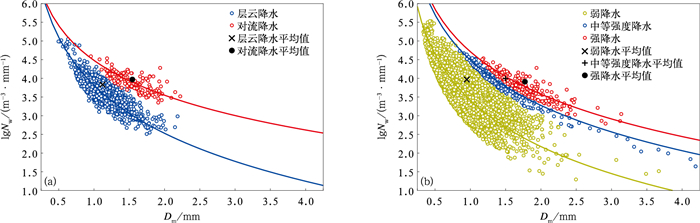
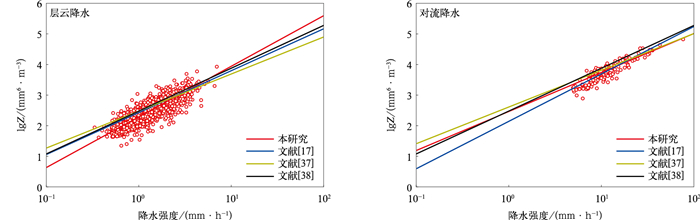
摘要: 利用2021年6—8月吉林靖宇Parsivel2型雨滴谱观测数据,研究长白山麓夏季不同降水类型和不同降水强度条件下雨滴谱特征,并与国内外研究对比。结果表明:长白山麓夏季降水雨滴直径对降水量贡献呈先增大后减小的趋势,贡献较大的直径区间为0.812~2.375 mm,随着降水强度增大,大雨滴(直径D≥2.75 mm)对降水量贡献也增大;对流降水比层云降水的雨滴谱更宽,雨滴数浓度及平均直径也更大;与国外经典对流降水雨滴谱相比,长白山麓对流降水标准截距参数lgNw及质量等效直径Dm特征更接近海洋型降水,与北京延庆及大兴、安徽滁州、江苏浦口相比,长白山麓夏季降水雨滴具有较小的直径和较大的数浓度;长白山麓夏季对流降水和层云降水反射率因子Z与降水强度R拟合关系分别为Z=290.64R1.27和Z=193.36R1.65,经典Z-R关系对该地区降水估测存在低估;形状参数μ、斜率参数Λ存在较好的二项式拟合关系。Abstract: In order to better understand the distribution characteristics of raindrop particle spectrum at Changbai Mountain foothills in summer, the raindrop size distribution with different rainfall types and different rainfall intensities are analyzed based on the observations of Parsivel2 disdrometer at Jingyu, Jilin Province from June to August in 2021. The distribution characteristics of raindrop spectrum are also compared with relevant research results at home and abroad. The results show that the frequency of stratiform cloud rainfall is much higher than that of convective rainfall (88.16% vs 11.84%) in summer at Changbai Mountain foothills, but convective rainfall contributes more to the total rainfall intensity (47.78% vs 52.22%). The contribution of raindrop diameter to rainfall in summer increases first and then decreases, while the diameter of raindrop makes a greater contribution to rainfall ranging from 0.812 mm to 2.375 mm. For large particles (diameter D≥2.75 mm), the contribution of raindrops to rainfall also increase as rainfall intensity increasing. The spectra of convective rainfall has a larger spectrum width, mean number concentration and mean diameter than stratiform precipitation. The Gamma fitting curve underestimates the number concentrations of raindrops larger than 4.25 mm, especially for weak precipitation. Comparing with classical convective raindrop spectra, the normalized intercept parameter lgNw and the mass equivalent diameter parameter Dm of convective rainfall at Changbai Mountain foothills are closer to the oceanic-like cluster. The summer raindrops here have smaller diameter and higher number concentration compared with those of Yanqing and Daxing in North China, and Chuzhou and Pukou in East China. The reflectivity factor Z and rain rate R fitted relationships between convective rainfall and stratiform rainfall at Changbai Mountain foothills are Z=290.64R1.27 and Z=193.36R1.65, respectively. The rainfall of estimation using classical Z-R relationship (Z=300R1.40) is underestimated in this area, especially for heavy rainfall. The shape parameter μ and the slope parameter Λ of Gamma fitting function satisfy binomial relationship, while the parameter Λ increases with the increase of parameter μ. Besides, the shape parameter μ of raindrop spectrum at Changbai Mountain foothills is less than that in North China, East China and South China on the whole, when the slope parameter Λ is equal.
-
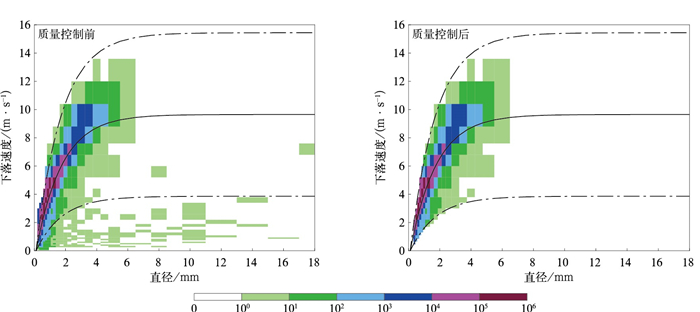
图 1 质量控制前后粒子数量(填色)和雨滴直径与下落速度的关系
(实线表示雨滴直径与下落速度理论关系曲线, 虚线表示雨滴直径与下落速度理论关系的±60%范围)
Fig. 1 Number of particles(the shaded) and relationship of raindrop diameter and falling velocity before and after quality control
(the solid line denotes the theoretical relationship curve between raindrop diameter and the falling speed, dash-dot lines denote the range of ±60% of the theoretical relationship between raindrop diameter and the falling speed)
表 1 夏季降水雨滴谱Gamma函数拟合参数对比
Table 1 Fitting parameters of Gamma function of the raindrop spectrum in summer
-
[1] 梅海霞, 郭文刚, 周林义, 等.雨滴谱谱形参数对梅雨降水模拟能力的影响.气象, 2017, 43(1):34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201701004.htmMei H X, Guo W G, Zhou L Y, et al. Effect of shape parameter of raindrop spectrum on the simulation of Meiyu rainfall. Meteor Mon, 2017, 43(1): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201701004.htm [2] Edward A B, Kyoko I, Zhang G F, et al. A statistical and physical description of hydrometeor distributions in Colorado snowstorms using a video disdrometer. J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2006, 46(5): 634-650. [3] 邵元亭, 刘奇俊, 荆志娟. 祁连山夏季地形云和降水宏微观结构的数值模拟. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(1): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSQX201301004.htmShao Y T, Liu Q J, Jing Z J. Numerical simulation on macrophysics structure of the orographic cloud and precipation insummer of the Qilian Moutain. J Arid Meteor, 2013, 31(1): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSQX201301004.htm [4] Wen L, Zhao K, Wang M Y, et al. Seasonal variations of observed raindrop size distribution in East China. Adv Atmos Sci, 2019, 36(4): 346-362. doi: 10.1007/s00376-018-8107-5 [5] Wang M J, Zhao K, Xue M, et al. Precipitation microphysics characteristics of a Typhoon Matmo(2014) rainband after landfall over eastern China based on polarimetric radar observations. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2016, 121(20): 12415-12433. doi: 10.1002/2016JD025307 [6] 管理, 戴建华, 陶岚, 等. QVP方法在双偏振雷达冬季降水观测中的应用. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(1): 91-101. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210108Guan L, Dai J H, Tao L, et al. Application of QVP method to winter precipitation observation based on polarimetric radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(1): 91-101. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210108 [7] 陈绍婕, 郑佳锋, 杨吉, 等. C-FMCW雷达反演飑线大气垂直速度和雨滴谱. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(4): 429-441. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220404Chen S J, Zheng J F, Yang J, et al. Retrieval of air vertical velocity and droplet size distribution in squall line precipitation using C-FMCW radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(4): 429-441. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220404 [8] 宋灿, 周毓荃, 吴志会, 等. 雨滴谱垂直演变特征的微雨雷达观测研究. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(4): 479-490. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190408Song C, Zhou Y Q, Wu Z H, et al. Vertical profiles of raindrop size distribution observed by micro rain radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(4): 479-490. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190408 [9] 程鹏, 常祎, 刘琴, 等. 祁连山春季一次层状云降水的雨滴谱分布及地形影响特征. 大气科学, 2021, 45(6): 1232-1248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202106006.htmCheng P, Chang Y, Liu Q, et al. A case study of raindrop size distribution and orographic impact characteristics in spring stratiform precipitation over the Qilian Mountains. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2021, 45(6): 1232-1248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202106006.htm [10] 梅海霞, 梁信忠, 曾明剑, 等. 2015—2017年夏季南京雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 117-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200111Mei H X, Liang X Z, Zeng M J, et al. Raindrop size distribution characteristics of Nanjing in summer of 2015-2017. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 117-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200111 [11] 牛生杰, 安夏兰, 桑建人, 等. 不同天气系统宁夏夏季降雨谱分布参量特征的观测研究. 高原气象, 2002, 21(1): 37-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200201006.htmNiu S J, An X L, Sang J R, et al. Observational research on physical feature of summer rain drop size distribution under synoptic systems in Ningxia. Plateau Meteor, 2002, 21(1): 37-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX200201006.htm [12] 王俊, 王文青, 王洪, 等. 山东北部一次夏末雹暴地面降水粒子谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(3): 370-384. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210309Wang J, Wang W Q, Wang H, et al. Hydrometeor particle characteristics during a late summer hailstorm in northern Shandong. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(3): 370-384. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210309 [13] 金祺, 袁野, 纪雷, 等. 安徽滁州夏季一次飑线过程的雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2015, 26(2): 725-734. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150609Jin Q, Yuan Y, Ji L, et al. Characteristic of raindrop size distribution for a squall line at Chuzhou of Anhui during summer. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(2): 725-734. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150609 [14] 朱红芳, 王东勇, 杨祖祥, 等. "海葵"台风(1211号)暴雨雨滴谱特征分析. 暴雨灾害, 2020, 39(2): 167-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX202002008.htmZhu H F, Wang D Y, Yang Z X, et al. Analysis of raindrop spectrum characteristics for a heavy rain event caused by Typhoon Haikui(No. 1211) in Anhui. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2020, 39(2): 167-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX202002008.htm [15] 毛志远, 付丹红, 黄彦彬, 等. 台风贝碧嘉(1816)外围云系结构与降水特征. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(5): 604-616. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220508Mao Z Y, Fu D H, Huang Y B, et al. Peripheral cloud system structure and precipitation characteristics of Typhoon Bebinca(1816). J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(5): 604-616. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220508 [16] 李慧, 苏立娟, 郑旭程, 等. 呼和浩特降雨和降雪过程粒子谱分布特征分析. 气象, 2021, 47(1): 71-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202101007.htmLi H, Su L J, Zheng X C, et al. Analysis on characteristics of particle size distribution during rain and snow processes in Hobhot. Meteor Mon, 2021, 47(1): 71-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202101007.htm [17] 黄泽文, 彭思越, 张浩然, 等. 福建安溪雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(2): 205-217. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220207Huang Z W, Peng S Y, Zhang H R, et al. Characteristic of raindrop size distribution at Anxi of Fujian. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(2): 205-217. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220207 [18] Zwiebel J, Baelen J V, Anquetin S, et al. Impacts of orography and rain intensity on rainfall structure. The case of the HyMeX IOP7a event. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc, 2016, 142(Supple Ⅰ): 310-319. doi: 10.1002/qj.2679 [19] Harikumar R. Orographic effect on tropical rain physics in the Asian monsoon region. Atmos Sci Lett, 2016, 17(10): 556-563. doi: 10.1002/asl.692 [20] 袁野, 朱士超, 李爱华. 黄山雨滴下落过程滴谱变化特征. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(6): 734-740. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160610Yuan Y, Zhu S C, Li A H. Characteristics of raindrop falling process at the Mount Huang. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(6): 734-740. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160610 [21] 李慧, 银燕, 单云鹏, 等. 黄山层状云和对流云降水不同高度的雨滴谱统计特征分析. 大气科学, 2018, 42(2): 268-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201802003.htmLi H, Yin Y, Shan Y P, et al. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution for stratiform and convective precipitation at different altitudes in Mt Huangshan. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2018, 42(2): 268-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201802003.htm [22] 柳臣中, 周筠珺, 谷娟, 等. 成都地区雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2015, 26(1): 112-121. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150112Liu C Z, Zhou Y J, Gu J, et al. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution in Chengdu. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(1): 112-121. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150112 [23] 赵城城, 张乐坚, 梁海河, 等. 北京山区和平原地区夏季雨滴谱特征分析. 气象, 2021, 47(7): 830-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202107006.htmZhao C C, Zhang L J, Liang H H, et al. Microphypical characteristic of the raindrop size distribution between mountain and pain areas over Beijing in summer. Meteor Mon, 2021, 47(7): 830-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202107006.htm [24] Friedrich K, Kalina E A, Masters F J, et al. Drop-size distributionsin thunderstorms measured by optical disdrometers during VORTEX2. Mon Wea Rev, 2013, 141(4): 1182-1203. [25] Jaffrain J, Berne A. Experimental quantification of the sampling uncertainty associated with measurements from PARSIVEL disdrometers. J Hydrometeorol, 2011, 12(3): 352-370. [26] 王俊, 王文青, 王洪, 等. 短时强降水和冰雹云降水个例雨滴谱特征分析. 高原气象, 2021, 40(5): 1071-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX202105010.htmWang J, Wang W Q, Wang H, et al. Characteristics of the raindrop size distribution during a short-time heavy rainfall and a squall line accompanied by hail. Plateau Meteor, 2021, 40(5): 1071-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX202105010.htm [27] 王可法, 张卉慧, 张伟, 等. Parsivel激光雨滴谱仪观测降水中异常数据的判别及处理. 气象科学, 2011, 31(6): 732-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX201106010.htmWang K F, Zhang H H, Zhang W, et al. The detection and elimination of abnormal data for the precipitation observed by Parsivel precipitation particle spectrometer. J Meteor Sci, 2011, 31(6): 732-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX201106010.htm [28] Atlas D, Srivastava R C, Sekhon R S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev Geophys, 1973, 11(1): 1-35. doi: 10.1029/RG011i001p00001 [29] 郑娇恒, 陈宝君. 雨滴谱分布函数的选择: M-P和Gamma分布的对比研究. 气象科学, 2007, 27(1): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200701002.htmZheng J H, Chen B J. Comparative study of exponential and Gamma functional fits to observed raindrop size distribution. J Meteor Sci, 2007, 27(1): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200701002.htm [30] 陈磊, 陈宝君, 杨军, 等. 2009—2010年梅雨锋暴雨雨滴谱特征. 大气科学学报, 2013, 36(4): 481-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX201304011.htmChen L, Chen B J, Yang J, et al. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution of rainstorm on Meiyu front during 2009-2010. Trans Atmos Sci, 2013, 36(4): 481-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX201304011.htm [31] 阮征, 刘褚燚, 马建立, 等. 降水回波谱参数估算雨滴谱参数的算法研究. 高原气象, 2015, 34(4): 1019-1028. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201504013.htmRuan Z, Liu C Y, Ma J L, et al. Research of retrieving Gamma parameters in precipitation cloud from data obtained of vertical radar. Plateau Meteor, 2015, 34(4): 1019-1028. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201504013.htm [32] 李山山, 王晓芳, 万蓉, 等. 青藏高原东坡不同海拔区域的雨滴谱特征. 高原气象, 2020, 39(5): 899-911. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX202005001.htmLi S S, Wang X F, Wan R, et al. The characteristics of raindrop spectrum in different altitude region on the eastern slope of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteor, 2020, 39(4): 899-911. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX202005001.htm [33] Vivekanandan J, Zhang G F, Brandes E. Polarimetric radar estimators based on a constrained gamma drop size distribution model. J Climate Appl Meteor, 2004, 43(2): 217-230. [34] Ulbrich C W, Atlas D. Rainfall microphysics and radar propertise: Analysis methods for drop size spectra. J Climate Appl Meteor, 1998, 37(9): 912-923. [35] Bringi V N, Chandrasekar V, Hubbert J, et al. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J Atmos Sci, 2003, 60(2): 354-365. [36] Chen B J, Yang J, Pu J P. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in Eastern China. J Meteorol Soc Japan, 2013, 91(2): 215-227. [37] 金祺, 袁野, 刘慧娟, 等. 2015. 江淮之间夏季雨滴谱特征分析. 气象学报, 2015, 73(4): 778-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201504013.htmJin Q, Yuan Y, Liu H J, et al. Analysis of microphysical characteristics of the raindrop spectrum over the area between the Yangtze River and the Huaihe River during summer. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2015, 73(4): 778-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201504013.htm [38] Fulton R A, Breidenbach J P, Seo D J, et al. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Wea Forecasting, 1998, 13(2): 377-395. [39] Chu Y H, Su C L. An investigation of the slop-shape relation for gamma raindrop size distribution. J Climate Appl Meteor, 2008, 47(10): 2531-2544. [40] Zhang G F, Vivekanandan J, Brandes E A, et al. The shape slopes relation in observed gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information?. J Atmos Ocean Technol, 2003, 20(8): 1106-1119. [41] Ulbrich C W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J Climate Appl Meteor, 1983, 22(10): 1764-1775. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: