Seasonal Distribution Characteristics of Raindrop Spectrum in Taiyuan
-
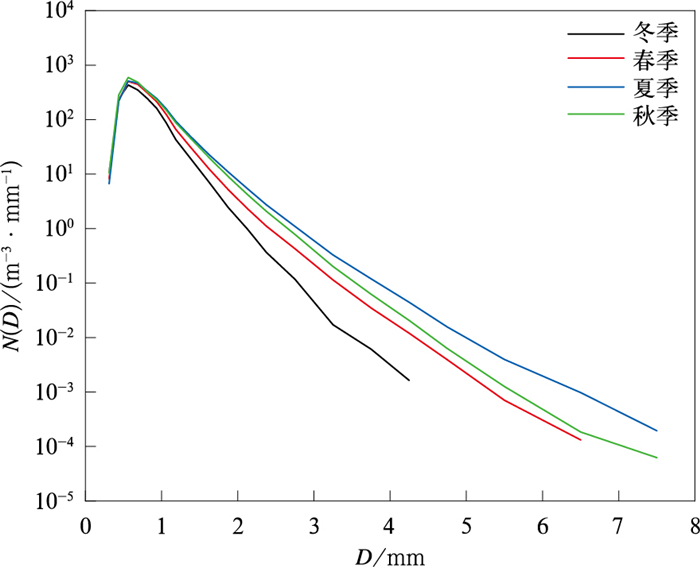
摘要: 利用2017年12月—2022年11月太原雨滴谱数据,研究太原地区不同雨强和不同降水类型雨滴谱季节分布特征。结果表明:太原地区四季谱分布均呈单峰结构且均以雨滴直径D<1 mm的小雨滴为主,但对雨强R贡献最大的是D为1~2 mm的雨滴。各季节R<1 mm·h-1的降雨均占比最大,但夏季超过50%雨量来自R≥5 mm·h-1雨滴的贡献;R<2 mm·h-1时,冬季大雨滴浓度更高,而小雨滴浓度相对较低;R≥5 mm·h-1时,夏季雨滴浓度更高。四季均以层状云降水为主,标准化截距参数lgNw和质量加权直径Dm差异较小;对流云降水多发生在夏季且更接近海洋性对流,春、秋季既非大陆性也非海洋性对流。采用最小二乘法得到形状因子与斜率参数的μ-λ、降水动能以及反射率因子与雨强的Z-R关系曲线,其中μ-λ季节变化小,但地域性差异显著;幂函数和二项式函数分别对于降水动能参数关系Et-R和Ed-Dm拟合效果更优;Z-R关系系数与指数成反比,对于层状云降水,春、秋季经典关系均高估降雨,冬、夏季存在经典关系由高估转为低估的情况;对于对流云降水,夏、秋季经典关系略高估降雨。Abstract: The raindrop size distribution (RSD) and parameter characteristics of different climate regions, rain types, topographies or weather systems have been extensively studied focusing on summer precipitation. However, even microphysical characteristics of precipitation in the same region can show significant seasonal differences. Seasonal distribution characteristics of RSD with different rain rates and rainfall types in Taiyuan are investigated and compared with conclusions from other regions based on observations of precipitation phenomenometer from December 2017 to November 2022. It can provide references for localized application of the parameterization of rainfall microphysics in numerical weather and climate prediction models, the rainfall kinetic energy flux estimation and the radar quantitative precipitation estimation. In addition, satellite measurements, ground observations, and reanalysis data are applied to explain the possible mechanism of seasonal differences in RSD. The RSD presents a unimodal structure with a peak of 0.562 mm and the decrease trend of concentration is more obvious in winter. Small raindrops with diameter less than 1.0 mm contribute more than 80% of the total number concentration, while the rain rate (R) is contributed primarily from mid-size raindrops with diameter of 1-2 mm during all seasons. The rainfall with R < 1 mm·h-1 are most frequent in different seasons, but the rainfall with R ≥ 5 mm·h-1 is predominant in summer. For the RSD of different rain rate, the highest (lowest) concentration of large (small) raindrops in winter is observed from the first two rain rate classes, while the concentration is higher in summer when the rain rate exceeds 5 mm·h-1. Rainfall at Taiyuan is dominated by stratiform rain throughout the year, lgNw or Dm has minor seasonal differences, and the distribution of lgNw and Dm is more similar to Nanjing. The convective rain occurs most often during summer and is close to the maritime-like cluster, the convective rain during spring and autumn is neither continental nor maritime, and there is no convective rain in winter. The stratiform rain has a wider spectrum width and higher concentration compared with the convective rain. μ-λ, Et-R, Ed-Dm, and Z-R relationships are derived by the least square method for different seasons. μ-λ relationships change little with seasons, but vary significantly compared with Florida in America. The power function and the binomial function has better fitting performance for Et-R and Ed-Dm, respectively. There is an inverse relationship between the coefficient and the exponent of the Z-R relationships. For stratiform rain, the classical relationship overestimates rainfall in spring and autumn, while the classical relationship turns from overestimated to underestimated as the rain rate increases. For convective rain, the classical relationship overestimates rainfall slightly in summer and autumn.
-
图 2 四季微物理参数箱线图
(圆圈和虚线分别为平均值和中值,箱体底线和顶线分别表示第25和第75百分位数,垂直实线的底线和顶线分别表示第5和第95百分位数,下同)
Fig. 2 Box plots for microphysical parameters in four seasons
(the circle and the dashed line of each box denote the average value and median value, bottom and top edges of the box denote the 25th and 75th percentiles, bottom and top of solid vertical lines denote the 5th and 95th percentiles, similarily hereinafter)
图 6 lgNw-Dm分布
(黑色表示冬季,红色表示春季,蓝色表示夏季,绿色表示秋季;误差棒表示四季层状云和对流云降水的lgNw与Dm的标准差,虚线为层状云和对流云降水分界线,两个黑色矩形框对应文献[3]研究的大陆性和海洋性对流范围)
Fig. 6 Distribution of lgNw-Dm
(the black for winter, the red for spring, the blue for summer, the green for autumn; error bars denote standard deviations of lgNw and Dm, the dashed line denotes the separation of stratiform rain and convective rain, two black rectangles denote maritime and continental types of convection from Reference [3])
表 1 四季不同雨强下的平均微物理参数
Table 1 Averaged microphysical parameters for different rain rate classes in four seasons
季节 雨强分档/(mm·h-1) 样本量 R/(mm·h-1) NT/m-3 Z/(mm6·m-3) W/(g·m-3) Dm/mm lgNw/(m-3·mm-1) μ λ/mm-1 冬季 0<R<1 1023 0.442 144.50 120.07 0.037 1.002 3.446 9.81 15.52 1≤R<2 163 1.323 304.01 541.17 0.099 1.194 3.611 2.91 6.13 春季 0<R<1 10310 0.422 169.36 93.52 0.038 0.940 3.561 13.77 21.47 1≤R<2 3149 1.402 321.22 477.76 0.107 1.154 3.716 6.87 10.31 2≤R<5 2376 2.994 440.07 1596.31 0.201 1.352 3.718 4.87 7.35 5≤R<10 452 6.636 556.70 5384.95 0.387 1.626 3.685 3.74 5.27 10≤R<20 49 12.930 521.23 18667.33 0.627 2.106 3.456 3.68 3.89 R≥20 10 34.894 466.51 98166.33 1.357 2.846 3.237 5.32 3.47 夏季 0<R<1 19052 0.410 141.79 105.13 0.034 1.018 3.390 15.62 22.68 1≤R<2 6058 1.427 332.88 504.61 0.106 1.188 3.681 9.67 13.52 2≤R<5 5452 3.103 476.39 1469.11 0.209 1.331 3.767 6.99 9.49 5≤R<10 1591 6.812 612.67 4583.83 0.405 1.551 3.795 5.74 6.92 10≤R<20 680 13.788 723.87 13666.96 0.731 1.806 3.786 5.20 5.43 R≥20 422 34.786 1044.34 62804.02 1.579 2.262 3.692 3.42 3.47 秋季 0<R<1 14000 0.411 190.42 89.57 0.038 0.926 3.597 14.98 23.90 1≤R<2 5593 1.464 331.53 500.80 0.111 1.167 3.707 6.48 9.85 2≤R<5 5228 3.081 423.67 1593.01 0.203 1.364 3.695 4.52 6.76 5≤R<10 1489 6.753 529.69 5501.84 0.385 1.649 3.655 3.72 5.05 10≤R<20 318 12.954 637.32 14019.31 0.664 1.893 3.646 3.74 4.32 R≥20 58 31.770 916.56 68359.38 1.381 2.421 3.547 2.82 2.98 表 2 四季不同降水类型的平均微物理参数
Table 2 Averaged microphysical parameters for different rain types in four seasons
降水类型 季节 NT/m-3 R/(mm·h-1) W/(g·m-3) Z/(mm6·m-3) Dm/mm lgNw/(m-3·mm-1) μ λ/mm-1 层状云降水 冬季 221.63 0.804 0.064 259.93 1.056 3.544 7.30 12.00 春季 283.39 1.265 0.094 528.90 1.064 3.701 9.12 14.45 夏季 287.47 1.366 0.098 533.67 1.123 3.616 10.41 15.28 秋季 309.62 1.548 0.110 726.34 1.113 3.699 8.53 13.73 对流云降水 春季 675.07 8.773 0.492 9679.98 1.747 3.671 2.29 4.04 夏季 892.78 20.731 1.029 24640.75 1.800 3.876 4.58 5.14 秋季 659.03 12.540 0.647 12771.84 1.787 3.701 3.42 4.35 -
[1] Morrison H, Lier-Walqui M, Fridlind A M, et al. Confronting the challenge of modeling cloud and precipitation microphysics. J Adv Model Earth Sy, 2020, 12(8). DOI: 10.1029/2019MS001689. [2] 陈绍婕, 郑佳锋, 杨吉, 等. C-FMCW雷达反演飑线大气垂直速度和雨滴谱. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(4): 429-441. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220404Chen S J, Zheng J F, Yang J, et al. Retrieval of air vertical velocity and droplet size distribution in squall line precipitation using C-FMCW radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(4): 429-441. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220404 [3] Bringi V N, Chandrasekar V, Hubbert J, et al. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J Atmos Sci, 2003, 60(2): 354-365. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(2003)060<0354:RSDIDC>2.0.CO;2 [4] Suh S H, Kim H J, Lee D I, et al. Geographical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the southern parts of south Korea. J Appl Meteor Climatol, 2021, 60(2): 157-169. doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-20-0102.1 [5] 陈磊, 陈宝君, 杨军, 等. 2009-2010年梅雨锋暴雨雨滴谱特征. 大气科学学报, 2013, 36(4): 481-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2013.04.011Chen L, Chen B J, Yang J, et al. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution of rainstorm on Meiyu front during 2009-2010. Trans Atmos Sci, 2013, 36(4): 481-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2013.04.011 [6] 袁野, 朱士超, 李爱华. 黄山雨滴下落过程滴谱变化特征. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(6): 734-740. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160610Yuan Y, Zhu S C, Li A H. Characteristics of raindrop falling process at the Mount Huang. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(6): 734-740. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160610 [7] 赵城城, 张乐坚, 梁海河, 等. 北京山区和平原地区夏季雨滴谱特征分析. 气象, 2021, 47(7): 830-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202107006.htmZhao C C, Zhang L J, Liang H H, et al. Microphypical characteristic of the raindrop size distribution between mountain and pain areas over Beijing in summer. Meteor Mon, 2021, 47(7): 830-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202107006.htm [8] Zeng Y, Yang L M, Zhou Y S, et al. Characteristics of orographic raindrop size distribution in the Tianshan Mountains, China. Atmos Res, 2022, 278. DOI: 10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2022.106332. [9] Li R, Wang G L, Zhou R R, et al. Seasonal variation in microphysical characteristics of precipitation at the entrance of water vapor channel in Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon. Remote Sens, 2022, 14(13): 3149-3170. doi: 10.3390/rs14133149 [10] 黄泽文, 彭思越, 张浩然, 等. 福建安溪雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(2): 205-217. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220207Huang Z W, Peng S Y, Zhang H R, et al. Characteristic of raindrop size distribution at Anxi Fujian. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(2): 205-217. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220207 [11] Luo L, Guo J, Chen H N, et al. Microphysical characteristics of rainfall observed by a 2DVD disdrometer during different seasons in Beijing, China. Remote Sens, 2021, 13(12). DOI: 10.3390/RS13122303. [12] Wen L, Zhao K, Wang M Y, et al. Seasonal variations of observed raindrop size distribution in East China. Adv Atmos Sci, 2019, 36(4): 346-362. doi: 10.1007/s00376-018-8107-5 [13] 孙钦宏, 马洪波, 齐彦斌, 等. 2021年夏季长白山麓雨滴谱分布特征. 应用气象学报, 2023, 34(3): 336-347. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20230307Sun Q H, Ma H B, Qi Y B, et al. Distribution characteristics of raindrop spectrum at Changbai Mountain foothills in summer of 2021. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2023, 34(3): 336-347. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20230307 [14] Atlas D, Srivastava R C, Sekhon R S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev Geophys, 1973, 11(1): 1-35. doi: 10.1029/RG011i001p00001 [15] 陈子健, 胡向峰, 陈宝君, 等. 河北省中南部暴雨雨滴谱特征. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(4): 586-596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSQX201904008.htmChen Z J, Hu X F, Chen B J, et al. Raindrop size distribution of rainstom in central-southern Hebei Province. J Arid Meteor, 2019, 37(4): 586-596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSQX201904008.htm [16] 李欣, 张璐. 北上台风强降水形成机制及微物理特征. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1): 29-42. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220103Li X, Zhang L. Formation mechanism and microphysics characteristics of heavy rainfall caused by northward-moving typhoons. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(1): 29-42. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220103 [17] 金祺, 袁野, 纪雷, 等. 安徽滁州夏季一次飑线过程的雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2015, 26(6): 725-734. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150609Jin Q, Yuan Y, Ji L, et al. Characteristic of raindrop size distribution for a squall line at Chuzhou of Anhui during summer. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(6): 725-734. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150609 [18] 王俊, 王文青, 王洪, 等. 山东北部一次夏末雹暴地面降水粒子谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2021, 32(3): 370-384. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210309Wang J, Wang W Q, Wang H, et al. Hydrometeor particle characteristics during a late summer hailstorm in northern Shandong. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(3): 370-384. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210309 [19] Chen B J, Yang J, Pu J P. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J Meteor Soc Japan Ser Ⅱ, 2013, 91(2): 215-227. [20] Ulbrich C W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J Climate Appl Meteor, 1983, 22(10): 1764-1775. [21] 郑娇恒, 陈宝君. 雨滴谱分布函数的选择: M-P和Gamma分布的对比研究. 气象科学, 2007, 27(1): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200701002.htmZheng J H, Chen B J. Comparative study of exponential and Gamma functional fits to observed raindrop size distribution. J Meteor Sci, 2007, 27(1): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX200701002.htm [22] 濮江平, 张伟, 姜爱军, 等. 利用激光降水粒子谱仪研究雨滴谱分布特性. 气象科学, 2010, 30(5): 701-707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX201005017.htmPu J P, Zhang W, Jiang A J, et al. Characteristics of Gamma raindrop size distribution based on the precipitation particle spectrometer. J Meteor Sci, 2010, 30(5): 701-707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKX201005017.htm [23] Kinnell P I A. Rainfall intensity-kinetic energy relationships for soil loss prediction 1. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 1981, 45(1): 153-155. [24] Seela B K, Janapati J, Lin P L, et al. A comparison study of summer season raindrop size distribution between Palau and Taiwan, two islands in Western Pacific. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2017, 122(21): 11787-11805. [25] Zeng Q W, Zhang Y, Lei H C, et al. Microphysical characteristics of precipitation during pre-monsoon, monsoon, and post-monsoon periods over the South China Sea. Adv Atmos Sci, 2019, 36(10): 1103-1120. [26] Zeng Y, Yang L M, Tong Z P, et al. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution duringrainy seasons in Northwest China. Adv Meteorol, 2021. DOI: 10.1155/2021/6667786. [27] Chen B J, Hu Z Q, Liu L P, et al. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-Ⅲ. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2017, 122(20): 11092-11106. [28] 林文, 林长城, 李白良, 等. 登陆台风麦德姆不同部位降水强度及谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(2): 239-248. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160212Lin W, Lin C C, Li B L, et al. Rainfall intensity and raindrop spectrum for different parts in landing Typhoon Matmo. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(2): 239-248. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160212 [29] 梅海霞, 梁信忠, 曾明剑, 等. 2015-2017年夏季南京雨滴谱特征. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31(1): 117-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200111Mei H X, Liang X Z, Zeng M J, et al. Raindrop size distribution characteristics of Nanjing in summer of 2015-2017. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 117-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200111 [30] Zhang G F, Vivekanandan J, Brandes E A, et al. The shape-slope relation in observed Gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information?. J Atmos Ocean Technol, 2003, 20(8): 1106-1119. [31] Seela B K, Janapati J, Lin P L, et al. Raindrop size distribution characteristics of the western Pacific tropical cyclones measured in the Palau islands. Remote Sens, 2022, 14(3). DOI: 10.3390/rs14030470. [32] Janapati J, Seela B K, Lin P L, et al. Microphysical features of typhoon and non-typhoon rainfall observed in Taiwan, an island in the Northwestern Pacific. Hydro Earth Syst Sci, 2021, 25: 4025-4040. [33] 汪学渊, 阮征, 李效东, 等. 雨滴谱仪与风廓线雷达反射率对比试验. 气象, 2016, 42(1): 107-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201601013.htmWang X Y, Ruan Z, Li X D, et al. Comparison of the reflectivities of wind profile radar and raindrop disdrometer. Meteor Mon, 2016, 42(1): 107-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201601013.htm -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载:









