Review of the Influence and Application of SST Anomaly to Flood Season Precipitation in China
-
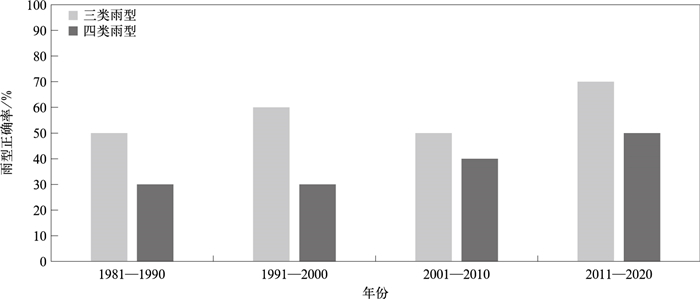
摘要: 以厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(ENSO)循环和其他关键区海温对东亚季风关键系统影响机理的科学认知与应用为线索, 回顾我国汛期降水业务发布预测的技巧。按照三类雨型划分, 1981—2020年每10年的雨型预测正确率分别为50%、60%、50%、70%;按照四类雨型划分, 1981—2020年每10年的雨型预测正确率分别为30%、30%、40%、50%, 即我国汛期旱涝空间分布型的预测准确率明显提高。筛选预测准确率偏低且有显著洪涝发生年用于复盘, 重点分析当年的主要预测依据和预测偏差较大的原因。结果表明:对海温影响东亚夏季风系统机理的有限认知影响很大, 包括ENSO循环不同位相的影响、ENSO影响的不对称性、ENSO空间型的变化、印度洋等海域海温异常的影响均起重要作用, 提出多因子多时间尺度协同作用理论、客观化预测方法、精细化监测预测影响评估一体化系统建设等有助于提高精准化预测能力和精细化服务水平。Abstract: The spatial distribution of precipitation anomalies during flood season and characteristics of drought and flood disasters in China are directly affected by the speed and stagnation of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM). EASM is significantly affected by external forcing such as sea surface temperature, land surface processes, ice and snow cover, and internal dynamic anomalies of atmospheric circulation. The sea surface temperature (SST) anomaly and its evolution have always been important factors for predicting precipitation during the flood season, considering lead time and the strength of precipitation prediction in flood season.Based on the scientific understanding and application of the mechanism of El Niño-southern oscillation (ENSO) cycle and other Ocean SST on the key factors of EASM, the prediction skill of flood season precipitation is reviewed. According to a prediction evaluation spanning over 40 years of historical records, the prediction accuracy for different types of rainfall pattern, the prediction accuracy of rain types in 1981-1990, 1991-2000, 2001-2010, and 2011-2020 is 50%/30%, 60%/30%, 50%/40%, and 70%/50%, respectively. In other words, the prediction of the primary rainfall patterns during the flood season in China is closer to the observation, and the accuracy of predicting spatial distribution patterns of drought and flood has significantly improved. This improvement can be attributed to the in-depth understanding of the impact of SST on EASM activities and enhancements made to dynamic climate models. In the history of flood season prediction, there have been both successful and unsuccessful cases. The years with low prediction accuracy and significant flooding events are as follows: 1983, 1991, 1999, 2003, and 2014. The primary basis for prediction is analyzed, revealing that the limited understanding of the mechanism of SST affecting the EASM had a great impact on the skill of precipitation predictions during the flood season. Among these factors, the influence of different phases of the ENSO cycle, the asymmetry of ENSO's influence, the change in ENSO spatial patterns, and the influence of other local seas, such as the Indian Ocean SST anomaly, all play important roles.The importance of multi-factor and multi-scale synergy theory and application, as well as the technical support of the objectification method for prediction, are emphasized in summarizing causes for low prediction skill cases. Finally, some suggestions for improving future flood season precipitation predictions are put forward, and it is emphasized that the development of a multi-factor and multi-time scale synergistic theory, an objective climate prediction method, and an integrated system for monitoring, predictions and impact assessment will significantly enhance predictions and provide services for flood season precipitation.
-
Key words:
- SST;
- flood season;
- precipitation prediction;
- synergistic effect
-
表 1 汛期三类雨型的预测与实况
Table 1 Prediction and observation of 3 types of rainfall pattern in flood season
年份 实况雨型 预测雨型 年份 实况雨型 预测雨型 1981 1 3 2001 3 2 1982 2 2 2002 3 3 1983 3 1 2003 2 1 1984 2 2 2004 1 1 1985 1 2 2005 2 3 1986 3 1 2006 3 2 1987 3 3 2007 2 3 1988 1 1 2008 2 2 1989 2 2 2009 2 2 1990 2 1 2010 2 2 1991 2 1 2011 3 2 1992 1 1 2012 1 2 1993 3 3 2013 1 1 1994 1 1 2014 3 2 1995 1 1 2015 3 3 1996 3 2 2016 3 3 1997 3 1 2017 3 3 1998 3 3 2018 1 1 1999 3 2 2019 3 3 2000 2 2 2020 3 3 注:1代表华北多,2代表黄河与长江之间多,3代表长江以南多。 表 2 汛期四类雨型的预测与实况
Table 2 Prediction and observation of 4 types of rainfall pattern in flood season
年份 实况雨型 预测雨型 年份 实况雨型 预测雨型 1981 1 1 2001 4 2 1982 2 2 2002 4 2 1983 3 1 2003 2 1 1984 2 2 2004 1 1 1985 1 2 2005 2 3 1986 3 1 2006 4 2 1987 1 3 2007 2 3 1988 2 1 2008 2 2 1989 1 2 2009 2 2 1990 3 1 2010 2 2 1991 1 1 2011 3 2 1992 4 1 2012 1 2 1993 4 3 2013 1 1 1994 1 1 2014 4 2 1995 3 1 2015 3 3 1996 4 2 2016 3 3 1997 3 1 2017 4 4 1998 4 3 2018 1 1 1999 4 2 2019 4 3 2000 2 2 2020 3 4 注:1代表黄河流域及华北多,2代表黄河与长江之间多,3代表长江流域多,4代表江南—华南多。 -
[1] 赵振国.中国夏季旱涝及环境场.北京:气象出版社, 1999.Zhao Z G. Drought, Flood and Environmental Field in Summer in China. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1999. [2] 陈兴芳, 赵振国. 中国汛期降水预测研究及应用. 北京: 气象出版社, 2000.Chen X F, Zhao Z G. Study and Application of Precipitation Forecast in Flood Season in China. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2000. [3] 丁一汇, 李清泉, 李维京, 等. 中国业务动力季节预报的进展. 气象学报, 2004, 62(5): 598-612. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2004.05.007Ding Y H, Li Q Q, Li W J, et al. Advance in seasonal dynamical prediction operation in China. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2004, 62(5): 598-612. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2004.05.007 [4] 李维京, 张培群, 李清泉, 等. 动力气候模式预测系统业务化及其应用. 应用气象学报, 2005, 16(增刊Ⅰ): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2005S1000.htmLi W J, Zhang P Q, Li Q Q, et al. Operation and application of Dynamic Climate Model Prediction System. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2005, 16(Suppl Ⅰ): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2005S1000.htm [5] 吴统文, 宋连春, 刘向文, 等. 国家气候中心短期气候预测模式系统业务化进展. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(5): 533-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.05.003Wu T W, Song L C, Liu X W, et al. Progress in developing the Short-range Operational Climate Prediction System of China National Climate Center. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2013, 24(5): 533-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.05.003 [6] 吴捷, 任宏利, 张帅, 等. BCC二代气候系统模式的季节预测评估和可预报性分析. 大气科学, 2017, 41(6): 1300-1315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201706013.htmWu J, Ren H L, Zhang S, et al. Evaluation and predictability analysis of seasonal prediction by BCC second-generation climate system model. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2017, 41(6): 1300-1315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201706013.htm [7] 王会军, 任宏利, 陈活泼, 等. 中国气候预测研究与业务发展的回顾. 气象学报, 2020, 78(3): 317-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202003001.htmWang H J, Ren H L, Chen H P, et al. Highlights of climate prediction study and operation in China over the past decades. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2020, 78(3): 317-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202003001.htm [8] Wu T W, Yu R C, Lu Y X, et al. BCC-CSM2-HR: A high-resolution version of the Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model. Geosci Model Dev, 2021, 14(5): 2977-3006. doi: 10.5194/gmd-14-2977-2021 [9] 李维京, 陈丽娟. 动力延伸预报产品释用方法的研究. 气象学报, 1999, 57(3): 338-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX200506008.htmLi W J, Chen L J. Research on reexplanation and reanalysis method of dynamical extended range forecast products. Acta Meteor Sinica, 1999, 57(3): 338-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX200506008.htm [10] 陈丽娟, 李维京, 张培群, 等. 降尺度技术在月降水预报中的应用. 应用气象学报, 2003, 14(6): 648-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2003.06.002Chen L J, Li W J, Zhang P Q, et al. Application of a new downscaling model to monthly precipitation forecast. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2003, 14(6): 648-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2003.06.002 [11] 顾伟宗, 陈丽娟, 张培群, 等. 月动力延伸预报最优信息提取和对中国降水的降尺度应用. 气象学报, 2009, 67(2): 280-287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2009.02.011Gu W Z, Chen L J, Zhang P Q, et al. Downscaling precipitation prediction in China based on optimization information extracted from monthly dynamic extended range forecast. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2009, 67(2): 280-287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2009.02.011 [12] Gu W Z, Chen L J, Li W J, et al. Development of a downscaling method in China regional summer precipitation prediction. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2011, 25(3): 303-315. doi: 10.1007/s13351-011-0306-2 [13] Ke Z J, Zhang P Q, Chen L J, et al. An experiment of a statistical downscaling forecast model for summer precipitation over China. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett, 2011, 4(5): 270-275. doi: 10.1080/16742834.2011.11446941 [14] Jia X L, Chen L J, Luo J J. Climate prediction experiment for tropical cyclone genesis frequency using the large-scale circulation forecast by a coupled global circulation model. J Trop Meteor, 2014, 20(2): 103-111. [15] 刘长征, 杜良敏, 柯宗建, 等. 国家气候中心多模式解释应用集成预测. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(6): 677-685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.004Liu C Z, Du L M, Ke Z J, et al. Multi-model downscaling ensemble prediction in National Climate Center. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2013, 24(6): 677-685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.004 [16] Ren H L, Wu Y J, Bao Q, et al. The China multi-model ensemble prediction system and its application to flood-season prediction in 2018. J Meteor Res, 2019, 33(3): 540-552. doi: 10.1007/s13351-019-8154-6 [17] 任宏利, 丑纪范. 动力相似预报的策略和方法研究. 中国科学(地球科学), 2007, 37(8): 1101-1109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200708014.htmRen H L, Chou J F. Research on strategy and method of dynamic similarity prediction. Sci China(Earth Sci), 2007, 37(8): 1101-1109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200708014.htm [18] 任宏利. 动力季节预测中预报误差与物理因子的关系. 应用气象学报, 2008, 19(3): 276-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2008.03.003Ren H L. Relationships between prediction errors and physical predictors in dynamical seasonal prediction. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2008, 19(3): 276-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2008.03.003 [19] 郑志海, 任宏利, 黄建平. 基于季节气候可预报分量的相似误差订正方法和数值实验. 物理学报, 2009, 58(10): 7359-7367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200910115.htmZheng Z H, Ren H L, Huang J P. Analogue correction of errors based on seasonal climatic predictable components and numerical experiments. Acta Phys Sinica, 2009, 58(10): 7359-7367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200910115.htm [20] 封国林, 赵俊虎, 支蓉, 等. 动力-统计客观定量化汛期降水预测研究新进展. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(6): 656-665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.002Feng G L, Zhao J H, Zhi R, et al. Recent progress on the objective and quantifiable forecast of summer precipitation based on dynamical-statistical method. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2013, 24(6): 656-665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.002 [21] 程娅蓓, 任宏利, 谭桂容. 东亚夏季风模式跨季预测的EOF-相似误差订正. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(3): 285-292. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160303Cheng Y B, Ren H L, Tan G R. Empirical orthogonal function-analogue correction of extra-seasonal dynamical prediction of East-Asian summer monsoon. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(3): 285-292. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160303 [22] Liu Y, Fan K, Chen L J, et al. An operational statistical downscaling prediction model of the winter monthly temperature over China based on a multi-model ensemble. Atmos Res, 2021, 249. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105262. [23] 庞轶舒, 张俊, 秦宁生, 等. 长江上游夏季径流量年际增量预测模型及检验. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1): 115-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220110Pang Y S, Zhang J, Qin N S, et al. Forecast model of interannual increment for summer runoff and its verification in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(1): 115-128. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220110 [24] 陈丽娟, 袁媛, 杨明珠, 等. 海温异常对东亚夏季风影响机理的研究进展. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(5): 521-532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.05.002Chen L J, Yuan Y, Yang M Z, et al. A review of physical mechanisms of the global SSTA impact on EASM. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2013, 24(5): 521-532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.05.002 [25] 贾小龙, 陈丽娟, 高辉, 等. 我国短期气候预测技术进展. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(6): 641-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.001Jia X L, Chen L J, Gao H, et al. Advances of the Short-range Climate prediction in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2013, 24(6): 641-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.06.001 [26] Ren H C, Zuo J Q, Li W J. The impact of tropical Atlantic SST variability on the tropical atmosphere during boreal summer. J Climate, 2021, 34: 6705-6723. [27] 李维京. 气候变暖背景下中国南方旱涝变化的机理及预测方法研究. 北京: 气象出版社, 2023.Li W J. Study on the Mechanism and Prediction Methods of Drought and Flood Change in South China under Climate Warming. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2023. [28] 陈金秋, 施晓晖. 青藏高原-孟加拉湾大气热力差异与夏季暴雨. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(2): 244-256. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220210Chen J Q, Shi X H. Possible effects of the difference in atmospheric heating between the Tibetan Plateau and the Bay of Bengal on spatiotemporal evolution of rainstorms. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(2): 244-256. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220210 [29] 符淙斌, 腾星林. 我国夏季的气候异常与埃尔尼诺/南方涛动现象的关系. 大气科学, 1988, 12(增刊Ⅰ): 133-141.Fu C B, Teng X L. Climate anomalies in China associated with E1 Niño/Southern Oscillation. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 1988, 12(Suppl Ⅰ): 133-141. [30] Wang B, Wu R G, Fu X. Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate?. J Climate, 2000, 13(9): 1517-1536. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2 [31] Wu R G, Hu Z Z, Kirtman B P. Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Climate, 2003, 16(22): 3742-3758. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3742:EOERAI>2.0.CO;2 [32] 张人禾, 闵庆烨, 苏京志. 厄尔尼诺对东亚大气环流和中国降水年际变异的影响: 西北太平洋异常反气旋的作用. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(5): 544-553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201705004.htmZhang R H, Min Q Y, Su J Z. Impact of El Niño on atmospheric circulations over East Asia and rainfall in China: Role of the anomalous western North Pacific anticyclone. Sci Sinica(Earth Sci), 2017, 47(5): 544-553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201705004.htm [33] McPhaden M J. Playing hide and seek with El Niño. Nature Clim Change, 2015, 5(9): 791-795. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2775 [34] 任宏利, 郑飞, 罗京佳, 等. 中国热带海-气相互作用与ENSO动力学及预测研究进展. 气象学报, 2020, 78(3): 351-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202003003.htmRen H L, Zheng F, Luo J J, et al. A review of research on tropical air-sea interaction, ENSO dynamics, and ENSO prediction in China. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2020, 78(3): 351-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202003003.htm [35] 薛峰, 段欣妤, 苏同华. El Niño发展年和La Niña年东亚夏季风季节内变化的比较. 气候与环境研究, 2018, 23(3): 321-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201803007.htmXue F, Duan X Y, Su T H. Comparison of intraseasonal variation of the East Asian summer monsoon between El Niño developing years and La Niña years. Clim Environ Res, 2018, 23(3): 321-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201803007.htm [36] Song X M, Zhang R H, Rong X Y. Influence of intraseasonal oscillation on the asymmetric decays of El Niño and La Niña. Adv Atmos Sci, 2019, 36(8): 779-792. doi: 10.1007/s00376-019-9029-6 [37] Zhou X Y, Liu F, Wang B, et al. Different responses of East Asian summer rainfall to El Niño decays. Climate Dyn, 2019, 53(3): 1497-1515. [38] Ashok K, Behera S K, Rao S A, et al. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J Geophys Res Oceans, 2007, 112. DOI: 10.1029/2006JC003798. [39] Feng J, Chen W, Tam C Y, et al. Different impacts of El Niño and El Niño Modoki on China rainfall in the decaying phases. Int J Climatol, 2011, 31(14): 2091-2101. doi: 10.1002/joc.2217 [40] Yuan Y, Yang S. Impacts of different types of El Niño on the East Asian climate: Focus on ENSO cycles. J Climate, 2012, 25(21): 7702-7722. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00576.1 [41] 薛峰, 刘长征. 中等强度ENSO对中国东部夏季降水的影响及其与强ENSO的对比分析. 科学通报, 2007, 52(23): 2798-2805. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074x.2007.23.017Xue F, Liu C Z. Influence of moderate intensity ENSO on summer precipitation in eastern China and its comparative analysis with strong ENSO. Chinese Sci Bull, 2007, 52(23): 2798-2805. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074x.2007.23.017 [42] 翟盘茂, 余荣, 郭艳君, 等. 2015/2016年强厄尔尼诺过程及其对全球和中国气候的主要影响. 气象学报, 2016, 74(3): 309-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201603001.htmZhai P M, Yu R, Guo Y J, et al. The strong El Niño in 2015/2016 and its dominant impacts on global and China's climate. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2016, 74(3): 309-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201603001.htm [43] 刘明竑, 任宏利, 张文君, 等. 超强厄尔尼诺事件对中国东部春夏季极端降水频率的影响. 气象学报, 2018, 76(4): 539-553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201804004.htmLiu M H, Ren H L, Zhang W J, et al. Influence of super El Niño events on the frequency of spring and summer extreme precipitation over Eastern China. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2018, 76(4): 539-553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201804004.htm [44] Ren H L, Lu B, Wan J H, et al. Identification standard for ENSO events and its application to climate monitoring and prediction in China. J Meteor Res, 2018, 32(6): 923-936. doi: 10.1007/s13351-018-8078-6 [45] 孙林海, 赵振国, 许力, 等. 中国东部季风区夏季雨型的划分及其环流成因分析. 应用气象学报, 2005, 16(增刊Ⅰ): 56-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2005S1006.htmSun L H, Zhao Z G, Xu L, et al. Division of summer rain patterns and analysis of circulation causes in monsoon region of East China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2005, 16(Suppl Ⅰ): 56-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYQX2005S1006.htm [46] 李小泉. 1983年全国汛期降水预报会商会概况. 气象, 1983, 9(6): 10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198306002.htmLi X Q. Overview of national flood season precipitation forecast conference in 1983. Meteor Mon, 1983, 9(6): 10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198306002.htm [47] 史久恩, 林学椿, 周琴芳. 厄尼诺现象与我国夏季(6—8月)降水、气温的关系. 气象, 1983, 9(4): 2-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198304000.htmShi J E, Lin X C, Zhou Q F. Relationship between El Niño phenomenon and summer precipitation and temperature in China(June-August). Meteor Mon, 1983, 9(4): 2-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX198304000.htm [48] 中国科学院大气物理研究所. 海气相互作用与旱涝长期预报. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978.Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Air-sea Interaction and Long-term Forecast of Drought and Flood. Beijing: Science Press, 1978. [49] Wyrtki K. El Niño: The dynamic response of the equatorial Pacific Ocean to atmospheric forcing. J Phys Oceanogr, 1975, 5(4): 572-584. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1975)005<0572:ENTDRO>2.0.CO;2 [50] Gill A E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q J R Meteor Soc, 1980, 106(449): 447-462. [51] 王绍武. 1982—1983年的厄·尼诺与南方涛动(ENSO). 气象科技, 1984, 12(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ198403000.htmWang S W. El Niño and southern oscillation(ENSO) in 1982-1983. Meteor Sci Technol, 1984, 12(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXKJ198403000.htm [52] Wagner A J. The climate of summer 1982-A season with increasingly anomalous circulation over the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Mon Wea Rev, 1983, 111(3): 590-601. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1983)111<0590:TCOSSW>2.0.CO;2 [53] 朱益民, 杨修群. 太平洋年代际振荡与中国气候变率的联系. 气象学报, 2003, 61(6): 641-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200306000.htmZhu Y M, Yang X Q. Relationships between Pacific decadal oscillation(PDO) and climate variabilities in China. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2003, 61(6): 641-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB200306000.htm [54] 丁一汇. 1991年江淮流域持续性特大暴雨研究. 北京: 气象出版社, 1993.Ding Y H. Study on the Persistent Torrential Rain in Jianghuai Basin in 1991. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1993. [55] 黄荣辉. 对今夏淮河流域和长江中下游特大洪涝成因的看法及其预报. 中国减灾, 1991(3): 28-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJI199103010.htmHuang R H. Views on the causes of catastrophic floods in Huaihe River Basin and the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River this summer and its forecast. Disaster Reduct China, 1991(3): 28-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJI199103010.htm [56] Huang R H, Yin B Y, Liu A D. Intraseasonal Variability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon and Its Association with the Convective Activities in the Tropical Western Pacific//Climate Variability. Beijing: Chinese Meteorological Press, 1992. [57] 陈文. El Niño和La Niña事件对东亚冬、夏季风循环的影响. 大气科学, 2002, 26(5): 595-610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202002015.htmChen W. Impacts of El Niño and La Niña on the cycle of the East Asian winter and summer monsoon. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2002, 26(5): 595-610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202002015.htm [58] 陆尔, 丁一汇. 1991年江淮持续性特大暴雨的夏季风活动分析. 应用气象学报, 1997, 8(3): 316-324. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/19970345Lu E, Ding Y H. Analysis of summer monsoon activity during the 1991 excessively torrential rain over Changjiang-Huaihe River Valley. J Appl Meteor Sci, 1997, 8(3): 316-324. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/19970345 [59] 毛江玉, 吴国雄. 1991年江淮梅雨与副热带高压的低频振荡. 气象学报, 2005, 63(5): 762-770. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.05.020Mao J Y, Wu G X. Intraseasonal variability in the Yangtze-Huaihe River rainfall and subtropical high during the 1991 Meiyu period. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2005, 63(5): 762-770. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.05.020 [60] 丁一汇, 胡雯, 黄勇, 等. 淮河流域能量和水分循环研究进展. 气象学报, 2020, 78(5): 721-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202005001.htmDing Y H, Hu W, Huang Y, et al. The main scientific achievements of the first China-Japan cooperative GAME/HUBEX experiments: A historical review. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2020, 78(5): 721-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202005001.htm [61] 倪东鸿, 孙照渤, 赵玉春. ENSO循环在夏季的不同位相对东亚夏季风的影响. 南京气象学院学报, 2000, 23(1): 48-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2000.01.008Ni D H, Sun Z B, Zhao Y C. Influence of ENSO cycle at different phases in summer on the East Asian summer monsoon. J Nanjing Inst Meteor, 2000, 23(1): 48-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2000.01.008 [62] Zhang R H, Sumi A, Kimoto M. Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon. J Meteor Soc Japan, 1996, 74(1): 49-62. doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.74.1_49 [63] Hoerling M P, Kumar A, Zhong M. El Niño, La Niña, and the nonlinearity of their teleconnections. J Climate, 1997, 10(8): 1769-1786. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<1769:ENOLNA>2.0.CO;2 [64] 孙颖, 丁一汇. 1999年东亚夏季风异常活动的物理机制研究. 气象学报, 2003, 61(4): 406-420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2003.04.003Sun Y, Ding Y H. A study on physical mechanisms of anomalous activities of East Asian summer monsoon during 1999. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2003, 61(4): 406-420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2003.04.003 [65] Song W L. General circulation and its impact over the Northern Hemisphere in 1999. Meteor Mon, 2000, 26(4): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2000.04.003 [66] 黄荣辉, 刘永, 冯涛. 20世纪90年代末中国东部夏季降水和环流的年代际变化特征及其内动力成因. 科学通报, 2013, 58(8): 617-628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201308003.htmHuang R H, Liu Y, Feng T. Interdecadal variation characteristics and internal dynamic causes of summer precipitation and circulation in eastern China in the late 1990s. Chinese Sci Bull, 2013, 58(8): 617-628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201308003.htm [67] Kao H Y, Yu J Y. Contrasting eastern-Pacific and central-Pacific types of ENSO. J Climate, 2009, 22(3): 615-632. doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2309.1 [68] Kug J S, Jin F F, An S I. Two types of El Niño events: Cold tongue El Niño and warm pool El Niño. J Climate, 2009, 22(6): 1499-1515. doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2624.1 [69] 袁媛, 杨辉, 李崇银. 不同分布型厄尔尼诺事件及对中国次年夏季降水的可能影响. 气象学报, 2012, 70(3): 467-478. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201203010.htmYuan Y, Yang H, Li C Y. Study of El Niño events of different types and their potential impact on the following-summer precipitation in China. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2012, 70(3): 467-478. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201203010.htm [70] Weng H Y, Ashok K, Behera S K, et al. Impacts of recent El Niño Modoki on dry/wet conditions in the Pacific rim during boreal summer. Climate Dyn, 2007, 29(2): 113-129. [71] 黄刚, 严中伟. 东亚夏季风环流异常指数及其年际变化. 科学通报, 1999, 44(4): 421-424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.04.020Huang G, Yan Z W. Anomalous index of East Asian summer monsoon circulation and its interannual variation. Chinese Sci Bull, 1999, 44(4): 421-424. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.04.020 [72] 孙林海, 宋文玲, 龚振淞. 2014年汛期气候预测先兆信号应用及其复杂性初探. 气象, 2015, 41(5): 639-648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201505012.htmSun L H, Song W L, Gong Z S. Preliminary study of precursor and its application in summer climate prediction and its complexity in 2014. Meteor Mon, 2015, 41(5): 639-648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201505012.htm [73] Yuan Y, Yang S, Zhang Z Q. Different evolutions of the Philippine Sea anticyclone between the eastern and central Pacific El Niño: Possible effects of Indian Ocean SST. J Climate, 2012, 25(22): 7867-7883. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00004.1 [74] Xie S P, Kosaka Y, Du Y, et al. Indo-western Pacific Ocean capacitor and coherent climate anomalies in post-ENSO summer: A review. Adv Atmos Sci, 2016, 33(4): 411-432. doi: 10.1007/s00376-015-5192-6 [75] 李维京, 张若楠, 孙丞虎, 等. 中国南方旱涝年际年代际变化及成因研究进展. 应用气象学报, 2016, 27(5): 577-591. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160507Li W J, Zhang R N, Sun C H, et al. Recent research advances on the interannual-interdecadal variations of drought/flood in south China and associated causes. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(5): 577-591. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160507 [76] 李维京. 1998年大气环流异常及其对中国气候的影响. 气象, 1999, 25(4): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX904.005.htmLi W J. General atmospheric circulation anomaly in 1998 and their impact on climate anomaly in China. Meteor Mon, 1999, 25(4): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX904.005.htm [77] 陈丽娟, 顾薇, 龚振淞, 等. 影响2018年汛期气候的先兆信号及预测效果评估. 气象, 2019, 45(4): 553-564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201904010.htmChen L J, Gu W, Gong Z S, et al. Precursory signals of the 2018 summer climate in China and evaluation of real-time prediction. Meteor Mon, 2019, 45(4): 553-564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201904010.htm [78] Chen L J, Gu W, Li W J. Why is the East Asian summer monsoon extremely strong in 2018?-Collaborative effects of SST and snow cover anomalies. J Meteor Res, 2019, 33(4): 593-608. doi: 10.1007/s13351-019-8200-4 [79] 章大全, 袁媛, 韩荣青. 2022年汛期气候预测效果评述及先兆信号分析. 气象, 2023, 49(3): 365-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202303010.htmZhang D Q, Yuan Y, Han R Q. Overview of climate prediction for the summer 2022 in China and its precursors. Meteor Mon, 2023, 49(3): 365-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202303010.htm [80] 章大全, 袁媛, 韩荣青. 2022年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析. 气象, 2023, 49(1): 110-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202301010.htmZhang D Q, Yuan Y, Han R Q. Characteristics and possible causes of the climate anomalies over China in summer 2022. Meteor Mon, 2023, 49(1): 110-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX202301010.htm [81] Okumura Y M, DiNezio P, Deser C. Evolving impacts of multiyear La Niña events on atmospheric circulation and US drought. Geophys Res Lett, 2017, 44(22): 11614-11623. [82] Wang H J. The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970's. Adv Atmos Sci, 2001, 18(3): 376-386. doi: 10.1007/BF02919316 [83] Gao H, Wang Y G, He J H. Weakening significance of ENSO as a predictor of summer precipitation in China. Geophys Res Lett, 2006, 33. DOI: 10.1029/2005GL025511. [84] Ding Y H, Sun Y, Wang Z Y, et al. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part Ⅱ: Possible causes. Int J Climatol, 2009, 29(13): 1926-1944. doi: 10.1002/joc.1759 [85] Sun L Y, Yang X Q, Tao L F, et al. Changing impact of ENSO events on the following summer rainfall in Eastern China since the 1950s. J Climate, 2021, 34(20): 8105-8123. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-21-0018.1 [86] Yuan Y, Gao H, Li W J, et al. The 2016 summer floods in China and associated physical mechanisms: A comparison with 1998. J Meteor Res, 2017, 31(2): 261-277. doi: 10.1007/s13351-017-6192-5 [87] Ding Y H, Liu Y Y, Hu Z Z. The record-breaking Mei-yu in 2020 and associated atmospheric circulation and tropical SST anomalies. Adv Atmos Sci, 2021, 38(12): 1980-1993. doi: 10.1007/s00376-021-0361-2 [88] Zhao J H, Zuo J Q, Zhang H, et al. Extreme precipitation driven by the rapid tropical Atlantic warming and the second developing La Niña over the Yangtze-Huaihe River Basin in August 2021. Climate Dyn, 2023, 61(5): 2581-2598. [89] 陈丽娟, 赵俊虎, 顾薇, 等. 汛期我国主要雨季进程成因及预测应用进展. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(4): 385-400. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190401Chen L J, Zhao J H, Gu W, et al. Advances of research and application on major rainy seasons in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(4): 385-400. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190401 [90] 李维京. 现代气候业务. 北京: 气象出版社, 2012.Li W J. Modern Climate Business. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2012. [91] Johnson S J, Stockdale T N, Ferranti L, et al. SEAS5: The new ECMWF seasonal forecast system. Geosci Model Dev, 2019, 12(3): 1087-1117. doi: 10.5194/gmd-12-1087-2019 [92] Liu Y Y, Hu Z Z, Wu R G, et al. Subseasonal prediction and predictability of summer rainfall over Eastern China in BCC_AGCM2.2. Climate Dyn, 2021, 56(7): 2057-2069. [93] 米前川, 高西宁, 李玥, 等. 深度学习方法在干旱预测中的应用. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1): 104-114. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220109Mi Q C, Gao X N, Li Y, et al. Application of deep learning method to drought prediction. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(1): 104-114. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220109 [94] 谢舜, 孙效功, 张苏平, 等. 基于SVD与机器学习的华南降水预报订正方法. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(3): 293-304. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220304Xie S, Sun X G, Zhang S P, et al. Precipitation forecast correction in South China based on SVD and machine learning. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(3): 293-304. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220304 [95] Jin W X, Luo Y, Wu T W, et al. Deep learning for seasonal precipitation prediction over China. J Meteor Res, 2022, 36(2): 271-281. doi: 10.1007/s13351-022-1174-7 [96] 李莹, 王国复. 气象灾害风险管理系统设计与应用. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(5): 628-640. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220510Li Y, Wang G F. Design and implementation of meteorological disaster risk management system. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(5): 628-640. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220510 -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: