Cloud Microphysical Properties of a Typical Spring Hail Event in Yunnan
-
摘要: 冰雹形成的天气和云微物理机制是人工防雹的基础。采用观测和数值模拟相结合的方法, 研究2023年3月28日云南南部红河州典型冰雹过程的天气和微物理特征。结果表明:此次天气过程与青藏高原南支西风槽波动和南亚副热带高压外围西南暖湿气流输送的协同作用密切相关;地面降雹以小于10 mm的小冰雹粒子为主, 最大冰雹尺度达到20 mm;冰雹云微物理结构显示为暖底云, 暖雨过程活跃;双偏振雷达差分反射率、差分相移率和相关系数显示, 冰雹初始形成区存在接近球形的冰雹和过冷雨滴, 说明冰雹胚胎的形成与过冷雨滴冻结有关;冰雹在下落过程中雷达回波增强, 偏振雷达参数显示冰雹的水平取向显著增加, 形状由球状向盘状转变, 冰雹在下落过程得到进一步增长, 形状也发生变化。这些观测宏微观特征与数值模拟的冰雹形成机制有较好的一致性。Abstract: Synoptic conditions and microphysical formation mechanisms for hail events form the basis for investigating hail suppression technology. There are few relevant studies on hail formation mechanisms in spring in southern China. Most previous theories on hail formation are primarily based on numerical simulations and lack sufficient validation through observations. The atmospheric circulation, stratification, and hail microphysical properties of a typical spring hail event of Honghe in Yunnan on 28 March 2023 are investigated using meteorological and C-band dual-pol radar data. The hail formation mechanisms are compared with those derived from a cloud model with hail-bin microphysics. Results indicate that the synoptic conditions for the hail process are closely associated with the south branch of the westerly winds, which are caused by the blocking effect of the Tibetan Plateau, and the warm moist air carried by the southwesterlies around the western edge of the South Asian tropical high. Due to the relatively weak thermodynamics in spring, small-sized hail below 10 mm is predominant at the surface, with the maximum hail size reaching 20 mm. The microphysical structure of the hail cloud features a warm base and a highly active warm rain process. The dual-polarization radar products of differential reflectivity (ZDR), specific differential phase (KDP) and correlation coefficient indicate that during the initial stage of hail formation, the hail formation region consisted of spherical-shaped hail and supercooled raindrops. It suggests that hail embryos are formed through the freezing process of small-sized supercooled raindrops. As the hail embryos descend, the radar reflectivity increased and the particle shape tended to become discoid, indicating that the hail undergoes a growth process through collision with supercooled cloud water during the descent. The shape also changes from spherical to plate-like. it is because during the initial stage of hail formation, raindrops carry to the upper levels by updrafts are relatively small and had spherical shapes, causing their freezing process to form nearly spherical hail embryos. These spherical hail embryos collide with supercooled cloud water and form discoid hailstones during the falling process, which is consistent with shapes of hailstones collected at the surface. Numerical simulations show that hail embryos are primarily formed through homogeneous freezing of supercooled raindrops, and the growth of these embryos depends on accretion with supercooled cloud water, which is well consistent with products by dual-pol radar.
-
Key words:
- hail;
- spring;
- formation process;
- dual-pol radar;
- modeling
-
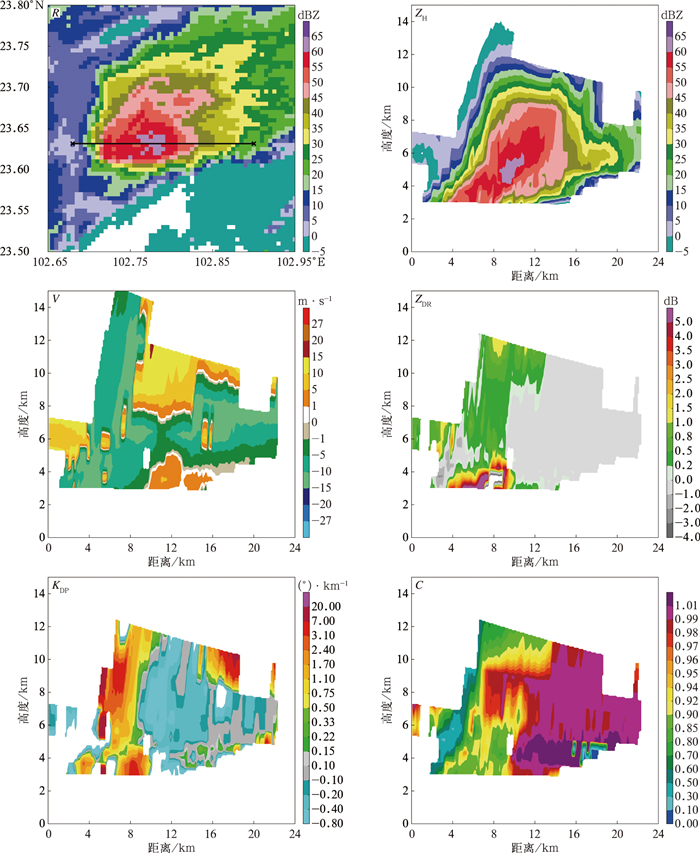
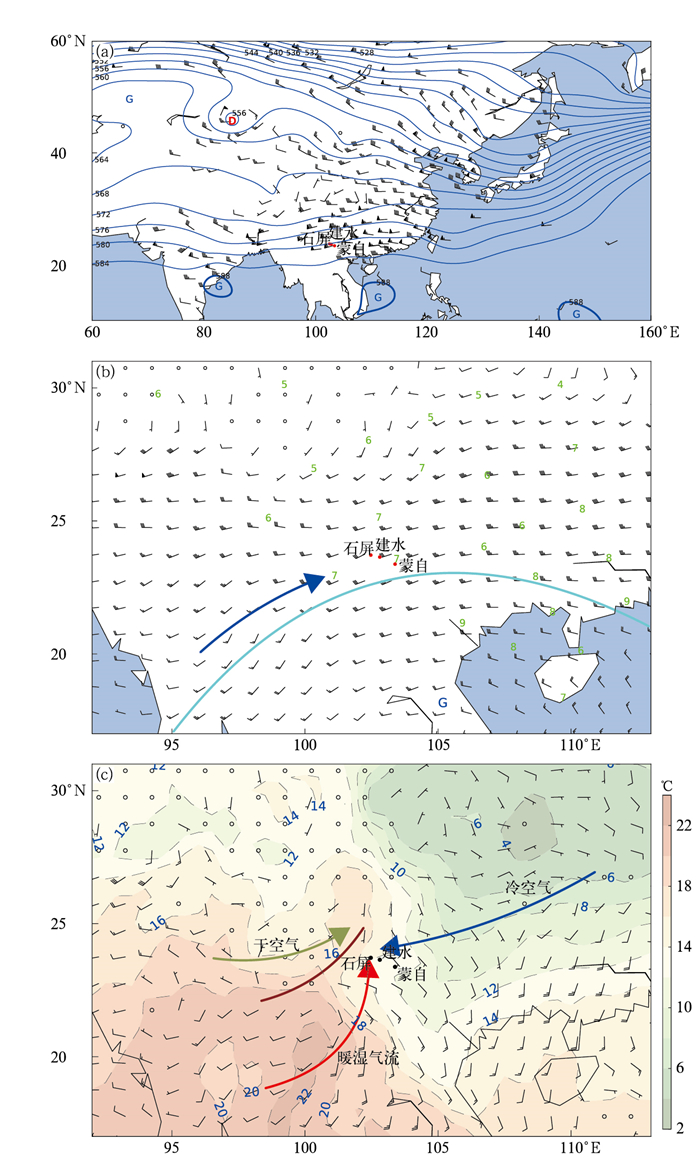
图 1 2023年3月28日08:00天气条件(a)500 hPa位势高度(蓝线,单位:dagpm) 和风场(风羽) 分布,(b)700 hPa层比湿(单位:g·kg-1) 和风场(风羽) 分布(深蓝色箭头表示西南主导风方向,浅蓝色实线为316 dagpm等高线),(c)850 hPa层温度场和风场(风羽) 分布
(不同颜色箭头分别表示为冷暖和干湿气流类型)
Fig. 1 Synoptical condition at 0800 BT 28 Mar 2023 (a)potential height (blue solid lines,unit:dagpm) and wind (barbs) at 500 hPa, (b)specific humidity (unit:g·kg-1) and wind (barbs) (the dark blue arrow denotes the dominant direction of southwesterlies at 700 hPa, the light blue solid line denotes 316 dagpm contour), (c)temperature and wind (barbs) at 850 hPa
(different color arrows denote the cold/warm and dry/wet flow)
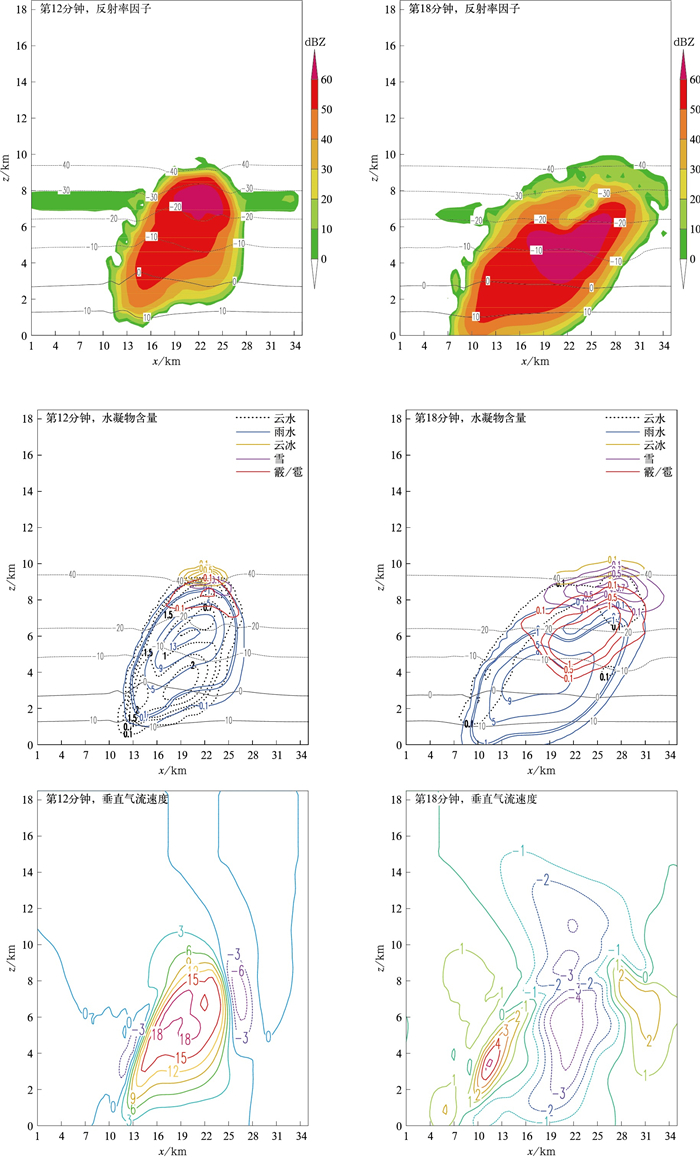
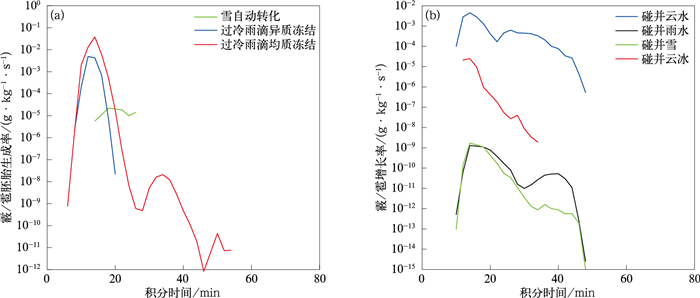
图 7 2023年3月28日云南红河州冰雹云反射率因子、水凝物含量和垂直气流速度模拟结果在积分第12分钟和第18分钟的x-z分布
(填色为反射率因子;水平线为环境温度,单位:℃;水凝物含量单位:g·kg-1;垂直气流速度单位:m·s-1,其中实线为上升气流速度,虚线为下沉气流速度)
Fig. 7 Simulation of radar reflectivity, hydrometeor mixing ratio and vertical velocity in x-z plane at the 12nd minute and the 18th minute for hail cloud of Honghe in Yunnan on 28 Mar 2013
(the shaded denotes reflectivity the horizontal line denotes environmental temperature, unit:℃; unit of hydrometeor mixing ratios:g·kg-1;unit of vertical velocity:m·s-1, the solid line denotes updraft, and the dashed line denotes downdraft)
表 1 观测与模拟的冰雹云比较
Table 1 Comparison of observed and simulated hail cloud
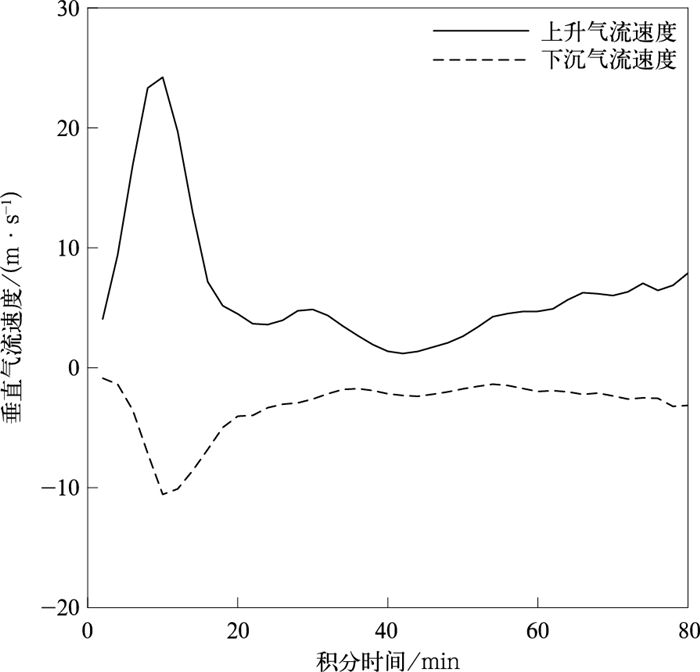
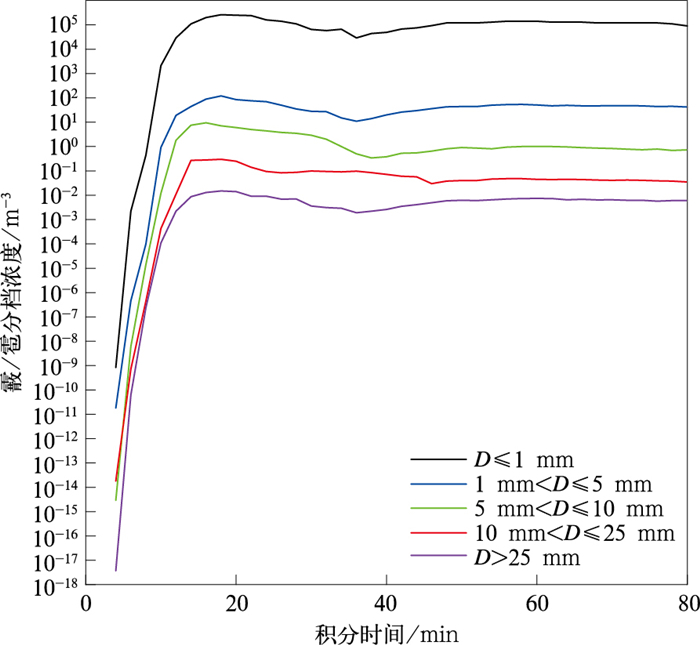
特征量 观测 模拟 云顶高度/km 12 11.5 云顶温度/℃ <-40 <-40 云底温度/℃ >10 >10 生命史/min >30 >30 最大回波强度/dBZ 60 >60 最大上升气流速度/(m·s-1) 24 最大过冷雨水含量/(g·kg-1) 13 地面最大冰雹尺度/mm 20 25 -
[1] Foote G B,Knight C A.Hail:A Review of Hail Science and Hail Suppression.Meteor Monogr,Amer Meteor Soc,1979, 38:277. [2] Barge B L, Isaac G A. The shape of Alberta hailstones. J Rech Atmos, 1973, 1: 11-20. [3] Xu J L. Some hail research in China. Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 1983, 64(2): 124-132. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1983)064<0124:SHRIC>2.0.CO;2 [4] 黄美元, 徐华英, 周玲. 中国人工防雹四十年. 气候与环境研究, 2000, 5(3): 318-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200003012.htmHuang M Y, Xu H Y, Zhou L. 40 years' hail suppression in China. Clim Environ Res, 2000, 5(3): 318-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200003012.htm [5] 黄美元, 沈志来, 洪延超. 半个世纪的云雾、降水和人工影响天气研究进展. 大气科学, 2003, 27(4): 536-551. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2003.04.08Huang M Y, Shen Z L, Hong Y C. Advance of research on cloud and precipitation and weather modification in the latest half century. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2003, 27(4): 536-551. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2003.04.08 [6] 王昂生, 黄美元, 徐乃璋, 等. 冰雹云物理发展过程的一些研究. 气象学报, 1980, 38(1): 64-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198001006.htmWang A S, Huang M Y, Xu N Z, et al. Some research on the development of hail-cloud. Acta Meteor Sinica, 1980, 38(1): 64-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198001006.htm [7] 张杰, 李文莉, 康凤琴, 等. 一次冰雹云演变过程的卫星遥感监测与分析. 高原气象, 2004, 23(6): 758-763. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2004.06.004Zhang J, Li W L, Kang F Q, et al. Analysis and satellite monitor of a developing process of hail cloud. Plateau Meteor, 2004, 23(6): 758-763. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2004.06.004 [8] 廖晓农, 俞小鼎, 于波. 北京盛夏一次罕见的大雹事件分析. 气象, 2008, 34(2): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200802003.htmLiao X N, Yu X D, Yu B. Analysis on infrequent big hail event in Beijing Area. Meteor Mon, 2008, 34(2): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX200802003.htm [9] 张琳娜, 郭锐, 何娜, 等. 北京地区冰雹天气特征. 气象科技, 2013, 41(1): 114-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2013.01.022Zhang L N, Guo R, He N, et al. Characteristic analysis of a hail event in Beijing. Meteor Sci Technol, 2013, 41(1): 114-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2013.01.022 [10] 范皓, 杨永胜, 段英, 等. 太行山东麓一次强对流冰雹云结构的观测分析. 气象学报, 2019, 77(5): 823-834. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201905003.htmFan H, Yang Y S, Duan Y, et al. An observational analysis of the cloud structure of a severe convective hailstorm over the eastern foothill of Taihang Mountain. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2019, 77(5): 823-834. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB201905003.htm [11] 李金辉, 田显, 岳治国. 基于火箭探空资料的冰雹云内部结构个例分析. 大气科学, 2020, 44(4): 748-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202004005.htmLi J H, Tian X, Yue Z G. Case study of hail cloud internal structure based on rocket sounding data. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2020, 44(4): 748-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202004005.htm [12] Xie B G, Zhang Q H, Wang Y Q. Observed characteristics of hail size in four regions in China during 1980-2005. J Climate, 2010, 23(18): 4973-4982. doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3600.1 [13] 王秀玲, 郭丽霞, 高桂芹, 等. 唐山地区冰雹气候特征与雷达回波分析. 气象, 2012, 38(3): 344-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201203013.htmWang X L, Guo L X, Gao G Q, et al. Climatological characteristics and radar echo analysis of hail in Tangshan, Hebei. Meteor Mon, 2012, 38(3): 344-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201203013.htm [14] 赵文慧, 姚展予, 贾烁, 等. 1961—2015年中国地区冰雹持续时间的时空分布特征及影响因子研究. 大气科学, 2019, 43(3): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201903006.htmZhao W H, Yao Z Y, Jia S, et al. Characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of hail duration in China during 1961-2015 and its possible influence factors. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2019, 43(3): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK201903006.htm [15] Ni X, Muehlbauer A, Allen J T, et al. A climatology and extreme value analysis of large hail in China. Mon Wea Rev, 2020, 148(4): 1431-1447. doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-19-0276.1 [16] Tang J, Guo X L, Chang Y, et al. Temporospatial distribution and trends of thunderstorm, hail, gale and heavy precipitation events over the Tibetan Plateau and associated mechanisms. J Climate, 2021, 34(24): 1-74. [17] 许焕斌, 王思微. 二维冰雹云数值模式. 气象学报, 1988, 46(2): 227-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198802013.htmXu H B, Wang S W. Two-dimension hail cloud model. Acta Meteor Sinica, 1988, 46(2): 227-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB198802013.htm [18] 孔凡铀, 黄美元, 徐华英. 对流云中冰相过程的三维数值模拟Ⅰ: 模式建立及冷云参数化. 大气科学, 1990, 14(4): 441-453. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1990.04.07Kong F Y, Huang M Y, Xu H Y. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of ice phase microphysics in cumulus clouds, part Ⅰ: Model establishment and ice phase parameterization. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 1990, 14(4): 441-453. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1990.04.07 [19] 洪延超. 冰雹形成机制和催化防雹机制研究. 气象学报, 1999, 57(1): 30-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB901.002.htmHong Y C. Study on mechanism of hail formation and hail suppression with seeding. Acta Meteor Sinica, 1999, 57(1): 30-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB901.002.htm [20] 林文实, 范绍佳, 王雪梅, 等. 山地上冰雹云的数值试验研究. 高原气象, 2000, 19(1): 59-65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2000.01.008Lin W S, Fan S J, Wang X M, et al. Numerical simulation of the hail cloud over mountainous terrain. Plateau Meteor, 2000, 19(1): 59-65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2000.01.008 [21] 许焕斌, 段英. 冰雹形成机制的研究并论人工雹胚与自然雹胚的"利益竞争" 防雹假说. 大气科学, 2001, 25(2): 277-288. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2001.02.14Xu H B, Duan Y. The mechanism of hailstone's formation and the hail-suppression hypothesis: "Beneficial competition". Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2001, 25(2): 277-288. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2001.02.14 [22] 郭学良, 黄美元, 洪延超, 等. 三维冰雹分档强对流云数值模式研究Ⅰ. 模式建立及冰雹的循环增长机制. 大气科学, 2001, 25(5): 707-720. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2001.05.13Guo X L, Huang M Y, Hong Y C, et al. A study of three-dimensional hail-category hailstorm model, part Ⅰ: Model description and the mechanism of hail recirculation growth. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2001, 25(5): 707-720. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2001.05.13 [23] Guo X L, Huang M Y. Hail formation and growth in a 3D cloud model with hail-bin microphysics. Atmos Res, 2002, 63(1/2): 59-99. [24] 刘术艳, 肖辉, 杜秉玉, 等. 北京一次强单体雹暴的三维数值模拟. 大气科学, 2004, 28(3): 455-470. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2004.03.12Liu S Y, Xiao H, Du B Y, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of a strong convective storm in Beijing. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2004, 28(3): 455-470. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2004.03.12 [25] 李兴宇, 洪延超. 三维冰雹云数值催化模式改进与个例模拟研究. 气象学报, 2005, 63(6): 874-888. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.06.005Li X Y, Hong Y C. The improvement of 3D hail cloud model and case simulation. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2005, 63(6): 874-888. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.06.005 [26] 胡朝霞, 郭学良, 李宏宇, 等. 慕尼黑一次混合型雹暴的数值模拟与成雹机制. 大气科学, 2007, 31(5): 973-986. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.05.20Hu Z X, Guo X L, Li H Y, et al. Numerical simulation of a hybrid-type hailstorm in Munich and the mechanism of hail formation. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2007, 31(5): 973-986. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.05.20 [27] 陈宝君, 郑凯琳, 郭学良. 超级单体风暴中大冰雹增长机制的模拟研究. 气候与环境研究, 2012, 17(6): 767-778. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201206015.htmChen B J, Zheng K L, Guo X L. Numerical investigation on the growth of large hail in a simulated supercell thunderstorm. Clim Environ Res, 2012, 17(6): 767-778. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH201206015.htm [28] Yin L, Ping F, Mao J H. Impact of cloud microphysical processes on the simulation of a hailstorm in East China. Atmos Res, 2019, 219: 36-56. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.12.014 [29] Guo X L, Fu D H, Li X Y, et al. Advances in cloud physics and weather modification in China. Adv Atmos Sci, 2015, 32(2): 230-249. doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-0006-9 [30] 刁秀广, 李芳, 万夫敬. 两次强冰雹超级单体风暴双偏振特征对比. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(4): 414-428. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220403Diao X G, Li F, Wan F J. Comparative analysis on dual polarization features of two severe hail supercells. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(4): 414-428. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220403 [31] 郑皎, 韩迁立, 徐艳, 等. 一次人工防雹作业的双偏振雷达特征分析. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2022, 16(6): 124-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJQX202206016.htmZheng J, Han Q L, Xu Y, et al. Characteristics of dual-polarization radar in an artificial anti-hail operation. Desert Oasis Meteor, 2022, 16(6): 124-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJQX202206016.htm [32] 刘春文, 郭学良, 段玮, 等. 云南一次典型降雹过程的冰雹微物理形成机理数值模拟研究. 大气科学, 2021, 45(5): 965-980. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202105003.htmLiu C W, Guo X L, Duan W, et al. Numerical simulation on the microphysical formation mechanism of a typical hailstorm process in Yunnan, Southwestern China. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2021, 45(5): 965-980. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK202105003.htm [33] 郭欣, 郭学良, 陈宝君, 等. 一次大冰雹形成机制的数值模拟. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(6): 651-664. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190602Guo X, Guo X L, Chen B J, et al. Numerical simulation on the formation of large-size hailstones. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(6): 651-664. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190602 [34] Guo X, Guo X L, Fu D H, et al. Storm splitting process and the associated mechanisms for a long-lived hailstorm. Atmos Res, 2023, 281. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106472. [35] 吴举秀, 胡志群, 夏凡, 等. 基于贝叶斯方法的冰雹大小识别研究. 气象学报, 2023, 81(5): 801-814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202305009.htmWu J X, Hu Z Q, Xia F, et al. Hail size discrimination based on the Bayesian method. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 801-814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202305009.htm [36] 袁凯, 李武阶, 庞晶. 基于决策树算法的鄂东地区冰雹识别技术. 应用气象学报, 2023, 34(2): 234-245. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20230209Yuan K, Li W J, Pang J. Hail identification technology in Eastern Hubei based on decision tree algorithm. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2023, 34(2): 234-245. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20230209 [37] 姚展予, 屠琦, 安琳, 等. 冰雹形成过程及人工防雹研究综述. 气象学报, 2022, 80(6): 835-863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202206001.htmYao Z Y, Tu Q, An L, et al. A summary of hail formation process and artificial hail suppression research. Acta Meteor Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 835-863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXB202206001.htm [38] Browning K A, Ludlam F H, Macklin W C. The density and structure of hailstones. Q J R Meteor Soc, 1963, 89(379): 75-84. doi: 10.1002/qj.49708937905 [39] Miller L J, Tuttle J D, Knight C A. Airflow and hail growth in a severe northern high Plains supercell. J Atmos Sci, 1988, 45(4): 736-762. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1988)045<0736:AAHGIA>2.0.CO;2 [40] Tessendorf S A, Miller L J, Wiens K C, et al. The 29 June 2000 supercell observed during STEPS. Part Ⅰ: Kinematics and microphysics. J Atmos Sci, 2005, 62(12): 4127-4150. doi: 10.1175/JAS3585.1 [41] Sulakevelize G K, Binilashvei N S, Lapcheva V F. Formation of Precipitation and Modification of Hail Processes. Press of Hydrometeorology, 1967. [42] Cotton W, Anthes R. Storm and Cloud Dynamics. The International Geophysics Series, 1992. [43] Knight C A, Knight N C, Dye J E, et al. The mechanism of precipitation formation in northeastern Colorado cumulus Ⅰ. Observations of the precipitation itself. J Atmos Sci, 1974, 31(8): 2142-2147. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1974)031<2142:TMOPFI>2.0.CO;2 [44] 周玲, 陈宝君, 李子华, 等. 冰雹云中累积区与冰雹的形成的数值模拟研究. 大气科学, 2001, 25(4): 536-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200104009.htmZhou L, Chen B J, Li Z H, et al. A numerical simulation of hailstorm accumulation zone and hail formation. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2001, 25(4): 536-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXK200104009.htm [45] 陈宝君, 肖辉. 过冷雨水低含量条件下冰雹形成和增长机制及其催化效果的数值模拟. 大气科学, 2007, 31(2): 273-290. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.02.09Chen B J, Xiao H. Numerical simulation of hail formation and growth in a storm with low supercooled rain water content and the effect of AgI seeding on hail suppression. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2007, 31(2): 273-290. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.02.09 [46] 洪延超, 肖辉, 李宏宇, 等. 冰雹云中微物理过程研究. 大气科学, 2002, 26(3): 421-432. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2002.03.13Hong Y C, Xiao H, Li H Y, et al. Studies on microphysical processes in hail cloud. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 2002, 26(3): 421-432. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2002.03.13 [47] 刘晓璐, 刘建西, 张世林, 等. 基于探空资料因子组合分析方法的冰雹预报. 应用气象学报, 2014, 25(2): 168-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.02.006Liu X L, Liu J X, Zhang S L, et al. Hail forecast based on factor combination analysis method and sounding data. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(2): 168-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.02.006 [48] 蓝渝, 郑永光, 毛冬艳, 等. 华北区域冰雹天气分型及云系特征. 应用气象学报, 2014, 25(5): 538-549. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20140503Lan Y, Zheng Y G, Mao D Y, et al. Classification and satellite nephogram features of hail weather in North China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(5): 538-549. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20140503 [49] 闵晶晶, 刘还珠, 曹晓钟, 等. 天津"6.25"大冰雹过程的中尺度特征及成因. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22(5): 525-536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2011.05.002Min J J, Liu H Z, Cao X Z, et al. The mesoscale characteristics and causes of a severe hail event in Tianjin. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2011, 22(5): 525-536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2011.05.002 [50] 李英, 段旭. 湿位涡在云南冰雹天气分析中的应用. 应用气象学报, 2000, 11(2): 242-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2000.02.015Li Y, Duan X. Diagnostic analysis of moist potential vorticity for hail in southern Yunnan. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2000, 11(2): 242-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2000.02.015 [51] 刘黎平, 徐宝祥, 王致君, 等. 用C波段双线偏振雷达研究冰雹云. 大气科学, 1992, 16(3): 370-376. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1992.03.14Liu L P, Xu B X, Wang Z J, et al. Study of hail with C-band dual linear polarization radar. Chinese J Atmos Sci, 1992, 16(3): 370-376. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1992.03.14 [52] 苏德斌, 马建立, 张蔷, 等. X波段双线偏振雷达冰雹识别初步研究. 气象, 2011, 37(10): 1228-1232. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.10.005Su D B, Ma J L, Zhang Q, et al. Preliminary research on method of hail detection with X band dual linear polarization radar. Meteor Mon, 2011, 37(10): 1228-1232. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.10.005 [53] 朱君鉴, 刁秀广, 黄秀韶. 一次冰雹风暴的CINRAD/SA产品分析. 应用气象学报, 2004, 15(5): 579-589. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2004.05.008Zhu J J, Diao X G, Huang X S. Study of CINRAD/SA products for a hail storm. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2004, 15(5): 579-589. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2004.05.008 [54] 胡胜, 罗聪, 张羽, 等. 广东大冰雹风暴单体的多普勒天气雷达特征. 应用气象学报, 2015, 26(1): 57-65. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150106Hu S, Luo C, Zhang Y, et al. Doppler radar features of severe hailstorms in Guangdong Province. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(1): 57-65. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150106 [55] 陈秋萍, 陈齐川, 冯晋勤, 等. 2015. "2012.4.11"两个强降雹超级单体特征分析. 气象, 2015, 41(1): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201501003.htmChen Q P, Chen Q C, Feng J Q, et al. Analysis of two severe hail supercell storms on 11 April 2012. Meteor Mon, 2015, 41(1): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201501003.htm [56] 王瑾, 刘黎平. WSR-88D冰雹探测算法在贵州地区的评估检验. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22(1): 96-106. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20110110Wang J, Liu L P. The evaluation of WSR-88D hail detection algorithm over Guizhou Region. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2011, 22(1): 96-106. http://qikan.camscma.cn/article/id/20110110 [57] 张秉祥, 李国翠, 刘黎平, 等. 基于模糊逻辑的冰雹天气雷达识别算法. 应用气象学报, 2014, 25(4): 415-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.04.004Zhang B X, Li G C, Liu L P, et al. Identification method of hail weather based on fuzzy-logical principle. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2014, 25(4): 415-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2014.04.004 [58] 张曦, 黄兴友, 刘新安, 等. 北京大兴国际机场相控阵雷达强对流天气监测. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(2): 192-204. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220206Zhang X, Huang X Y, Liu X A, et al. The hazardous convective storm monitoring of phased-array antenna radar at Daxing International Airport of Beijing. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(2): 192-204. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220206 [59] 李哲, 吴翀, 刘黎平, 等. 双偏振相控阵雷达误差评估与相态识别方法. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(1): 16-28. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220102Li Z, Wu C, Liu L P, et al. Error evaluation and hydrometeor classification method of dual polarization phased array radar. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(1): 16-28. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220102 [60] 王一童, 王秀明, 俞小鼎. 产生致灾大风的超级单体回波特征. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(2): 180-191. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220205Wang Y T, Wang X M, Yu X D. Radar characteristics of straight-line damaging wind producing supercell storms. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2022, 33(2): 180-191. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20220205 [61] 石宝灵, 王红艳, 刘黎平. 云南多普勒天气雷达网探测冰雹的覆盖能力. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29(3): 270-281. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180302Shi B L, Wang H Y, Liu L P. Coverage capacity of hail detection for Yunnan Doppler weather radar network. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(3): 270-281. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180302 [62] 蒋瑛, 朱克云, 张杰. 贵州地区冰雹云微物理过程及发展机制数值模拟研究. 气象, 2016, 42(8): 920-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201608002.htmJiang Y, Zhu K Y, Zhang J. Microphysical process of hail cloud in Guizhou and numerical simulation research on its dynamic developing mechanism. Meteor Mon, 2016, 42(8): 920-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXXX201608002.htm [63] Kang F Q, Zhang Q, Lu S H. Validation and development of a new hailstone formation theory: Numerical simulations of a strong hailstorm occurring over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112(D2). DOI: 10.1029/e2005jd006227. [64] Tang J, Guo X L, Chang Y, et al. Long-term variations of clouds and precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau and its subregions, and the associated mechanisms. Int J Climatol, 2022, 42(16): 9003-9022. -


 设为首页
设为首页 加入收藏
加入收藏


 下载:
下载: