| [1] |
Duan Hailai, Qian Huaisui.Responses of the electric power consumption to climate change in Guangzhou City. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2009, 20(1): 80-87. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2009.01.010
|
| [2] |
Guo Jianping.Research progress on agricultural meteorological disaster monitoring and forecasting. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2016, 27(5): 620-630. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20160510
|
| [3] |
Wang Chunzhi, Huo Zhiguo, Zhang Lei, et al.Construction of forecasting model of meteorological suitability for wheat aphids in the Northern China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(3): 280-289. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200303
|
| [4] |
Zhou Yu, Liu Zhiping, Zhang Guoping.Probability forecasting model of geological disaster along the Yingxia Railway induced by precipitation with its application. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(6): 743-749. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150611
|
| [5] |
Hou Yingyu, Zhang Lei, Wu Menxin, et al.Advances of modern agrometeorological service and technology in China. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(6): 641-656. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180601
|
| [6] |
Gao Taichang, Liu Lei, Zhao Shijun, et al.The actuality and progress of whole sky cloud sounding techniques. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2010, 21(1): 101-109. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2010.01.014
|
| [7] |
Zhai Panmao, Liu Jing.Extreme weather/climate events and disaster prevention and mitigation under global warming background.Engineering Sciences, 2012, 14(9): 55-63.
|
| [8] |
穆穆, 陈博宇, 周菲凡, 等.气象预报的方法与不确定性.气象, 2011, 37(1): 1-13.
Mu Mu, Chen Boyu, Zhou Feifan, et al.Methods and uncertainties of meteorological forecast.Meteorological Monthly, 2011, 37(1): 1-13.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
Cleveland A.The physical basis of long-range weather forecasts.Mon Wea Rev, 1901, 29(12): 551.
|
| [11] |
Bjerknes V.Das Problem der Wettervorhersage betrachtet vomStandpunkt der Mechanik und Physik.Meteorol Z, 1904, 21: 1-7.
|
| [12] |
Richardson L F.Weather Prediction by Numerical Process.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 1922.
|
| [13] |
Charney J G, Fjoertoft R, Von Neumann J.Numerical integration of the barotropic vorticity equation.Tellus, 1950, 2: 237-254.
|
| [14] |
Lynch P.The origins of computer weather prediction and climate modeling. J Comput Phys, 2008, 227: 3431-3444. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.02.034
|
| [15] |
Li Zechun, Chen Dehui.The development and application of the operational ensemble prediction system at National Meteorological Center. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2002, 13(1): 1-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2002.01.001
|
| [16] |
Shen Xueshun, Su Yong, Hu Jianglin, et al.Development and operation transformation of GRAPES global middle-range forecast system. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2017, 28(1): 1-10. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20170101
|
| [17] |
He Yanan, Gao Song, Xue Feng, et al.Design and implementation of intelligent grid forecasting platform based on MICAPS4. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(1): 13-24. DOI: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180102
|
| [18] |
Li Zechun, Bi Baogui, Jin Ronghua, et al.The development and application of the modern weather forecast in China for the recent 10 years. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2014, 72(6): 1069-1078. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4965.2014.06.007
|
| [19] |
Bauer P, Thorpe A, Brunet G.The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature, 2015, 525(7567): 47-55. DOI: 10.1038/nature14956
|
| [20] |
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A.Deep Learning.Cambridge:MIT Press, 2016.
|
| [21] |
Jain A K.Data clustering: 50 years beyond k-means.Pattern Recognition Letters, 2009, 31(8): 651-666.
|
| [22] |
Yang J, Zhang D, Frangi A F, et al.Two-dimensional PCA:A new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattem Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(1): 131-137. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1261097
|
| [23] |
周志华.机器学习.北京:清华大学出版社, 2016.
Zhou Zhihua.Machine Learning.Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2016.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
Graves A.Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks.Studies in Computational Intelligence, 2012, 385: 1-131.
|
| [26] |
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al.Generative Adversarial Nets//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 2672-2680.
|
| [27] |
Qin Z, Yu F, Liu C, et al.How convolutional neural networks see the world-A survey of convolutional neural network visualization methods. Mathematical Foundations of Computing, 2018, 1(2): 149-180. DOI: 10.3934/mfc.2018008
|
| [28] |
Pearl J, Mackenzie D.The Book of Why.London:Allen Lane, 2019.
|
| [29] |
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, et al.How Transferable are Features in Deep Neural Networks?//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 3320-3328.
|
| [30] |
Akhtar N M A.Threat of adversarial attacks on deep learning in computer vision:A Survey. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 14410-14430. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2807385
|
| [31] |
Feurer M, Klein A, Eggensperger K, et al.Efficient and robust automated machine learning.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016, 28: 2944-2952.
|
| [32] |
Jin H, Song Q, Hu X.Auto-Keras: An Efficient Neural Architecture Search System//Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 2019: 1946-1956.
|
| [33] |
Francois-Lavet V, Henderson P, Islam R, et al.An introduction to deep reinforcement learning. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2018, 11(3-4), DOI: 10.1561/2200000071.
|
| [34] |
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al.Scikit-learn:Machine Learning in Python.Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2825-2830.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
Abadi M, Barham P, Chen Jianmin, et al.TensorFlow: A System for Large-scale Machine Learning//Proceedings of the 12th USENIX conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, 2016: 265-283.
|
| [37] |
Paszke A, Gross S, Chintala S, et al.Automatic Differentiation in PyTorch//31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 1-4.
|
| [38] |
Yin S, Ouyang P, Tang S, et al.A high energy efficient reconfigurable hybrid neural network processor for deep learning applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(4): 968-982. DOI: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2778281
|
| [39] |
Vazhkudai S, Supinski B R, Bland A S.The Design, Deployment, and Evaluation of the CORAL Pre-exascale Systems//The InternationalConference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, 2018: 661-672.
|
| [40] |
Reichstein M, Camps-Valls G, Stevens B, et al.Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven earth system science. Nature, 2019, 566(7743): 195-204. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
Karpatne A, Atluri G, Faghmous J, et al.Theory-guided data science:A new paradigm for scientific discovery from data.IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering, 2017, 29(10): 2318-2331.
|
| [43] |
Berry T, Harlim J.Correcting biased observation model error in data assimilation. Mon Wea Re, 2017, 145(7): 2833-2853. DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-16-0428.1
|
| [44] |
安捷, 马尽文.基于全卷积网络的遥感图像自动云检测.信号处理, 2019, 35(4): 556-562.
An Jie, Ma Jinwen.Automatic cloud segmentation based on the fully convolutional neural networks.Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(4): 556-562.
|
| [45] |
Chang Nibin, Bai Kaixu, Chen Chifarn.Smart information reconstruction via time-space-spectrum continuum for cloud removal in satellite images. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(5): 1898-1912. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2400636
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
Cintra R, de Campos Velho H, Cocke S.Tracking the Model: Data Assimilation by Artificial Neural Network//2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks(IJCNN), 2016: 403-410.
|
| [48] |
Lee Y J, Hall D, Stewart J, et al.Machine learning for targeted assimilation of satellite data.Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, 2018, 11053: 53-68.
|
| [49] |
Scher S.Toward data-driven weather and climate forecasting approximating a simple general circulation model with deep learning. Geophys Res Lett, 2018, 45(22): 12616-12622. DOI: 10.1029/2018GL080704
|
| [50] |
Brenowitz N D, Bretherton C S.Prognostic validation of a neural network unified physics parameterization. Geophys Res Lett, 2018, 45: 6289-6298. DOI: 10.1029/2018GL078510
|
| [51] |
Pan B, Hsu K, AghaKouchak A, et al.Improving precipitation estimation using convolutional neural network. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(3): 2301-2321. DOI: 10.1029/2018WR024090
|
| [52] |
O'Gorman P A, Dwyer J G.Using machine learning to parameterize moist convection:Potential for modeling of climate, climate change, and extreme events. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2018, 10(10): 2548-2563. DOI: 10.1029/2018MS001351
|
| [53] |
Rasp S, Pritchard M S, Gentine P.Deep learning to represent subgrid processes in climate models. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 115(39): 9684-9689. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1810286115
|
| [54] |
Xu H, Zhang T, Luo Y, et al.Parameter calibration in global soil carbon models using surrogate-based optimization. Geoscientific Model Development, 2018, 11(7): 3027-3044. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-11-3027-2018
|
| [55] |
Wu L, Zhang T, Qin Y, et al.An effective parameter optimization with radiation balance constraint in CAM5.Geophys Res Lett, 2020, 13: 41-53.
|
| [56] |
Burke A.Calibration of machine learning-based probabilistic hail predictions for operational forecasting.Bull Amer Meteor Soc, 2020, 35: 149-168.
|
| [57] |
Taillardat M.Calibrated ensemble forecasts using quantile regression forests and ensemble model output statistics. Mon Wea Rev, 2016, 144(6): 2375-2393. DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-15-0260.1
|
| [58] |
Rasp S, Lerch S.Neural networks for postprocessing ensemble weather forecasts. Mon Wea Rev, 2018, 146(11): 3885-3900. DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-18-0187.1
|
| [59] |
Scher S, Messori G.Predicting weather forecast uncertainty with machine learning. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc, 2018, 144(717): 2830-2841. DOI: 10.1002/qj.3410
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
Ham Y G, Kim J H, Luo J J.Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 568-572. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1559-7
|
| [62] |
Zhou K, Zheng Y, Li B, et al.Forecasting different types of convective weather:a deep learning approach. J Meteor Res, 2019, 33(5): 797-809. DOI: 10.1007/s13351-019-8162-6
|
| [63] |
Kurth T, Treichler S, Romero J, et al.Exascale Deep Learning for Climate Analytics//Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, 2018: 1-12.
|
| [64] |
Rojek K.Machine learning method for energy reduction by utillzing dynamic mixed precision on GPU-based supercomputers.Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience, 2019, 31(6):e4644.1-e4644.12.
|
| [65] |
Manandhar S, Dev S, Lee Y H, et al.A data-driven approach for accurate rainfall prediction. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 2019, 57(11): 9323-9331. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2926110
|
| [66] |
Gagne D, Haupt S, Nychka D, et al.Interpretable deep learning for spatial analysis of severe hailstorms. Mon Wea Rev, 2019, 147(8): 2827-2845. DOI: 10.1175/MWR-D-18-0316.1
|
| [67] |
Karevan Z, Suykens J.Transductive LSTM for time-series prediction:An application to weather forecasting. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 1-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.12.030
|
| [68] |
Qiu M, Zhao P, Zhang K, et al.A Short-term Rainfall Prediction Model Using Multi-task Convolutional Neural Networks//2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, 2017: 395-404.
|
| [69] |
Yuan M, Ji X, Lu T, et al.A Novel Two-Factor Attention Encoder-Decoder Network through Combining Temporal and Prior Knowledge for Weather Forecasting//2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019: 1-8.
|
| [70] |
Prasetya E P, Djamal E C.Rainfall Forecasting for the Natural Disasters Preparation Using Recurrent Neural Networks//2019 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 2019: 52-57.
|
| [71] |
Tan C, Feng X, Long J, et al.FORECAST-CLSTM: A New Convolutional LSTM Network for Cloudage Nowcasting//2018 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, 2018: 1-4.
|



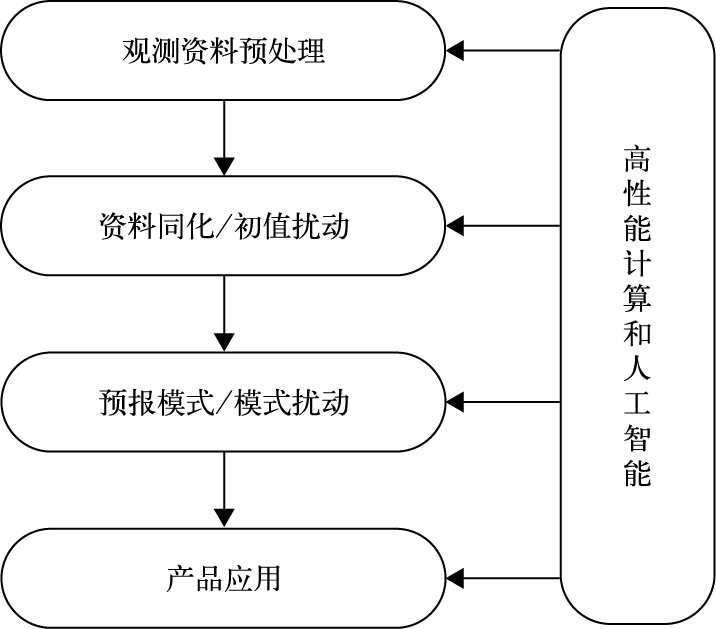
 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
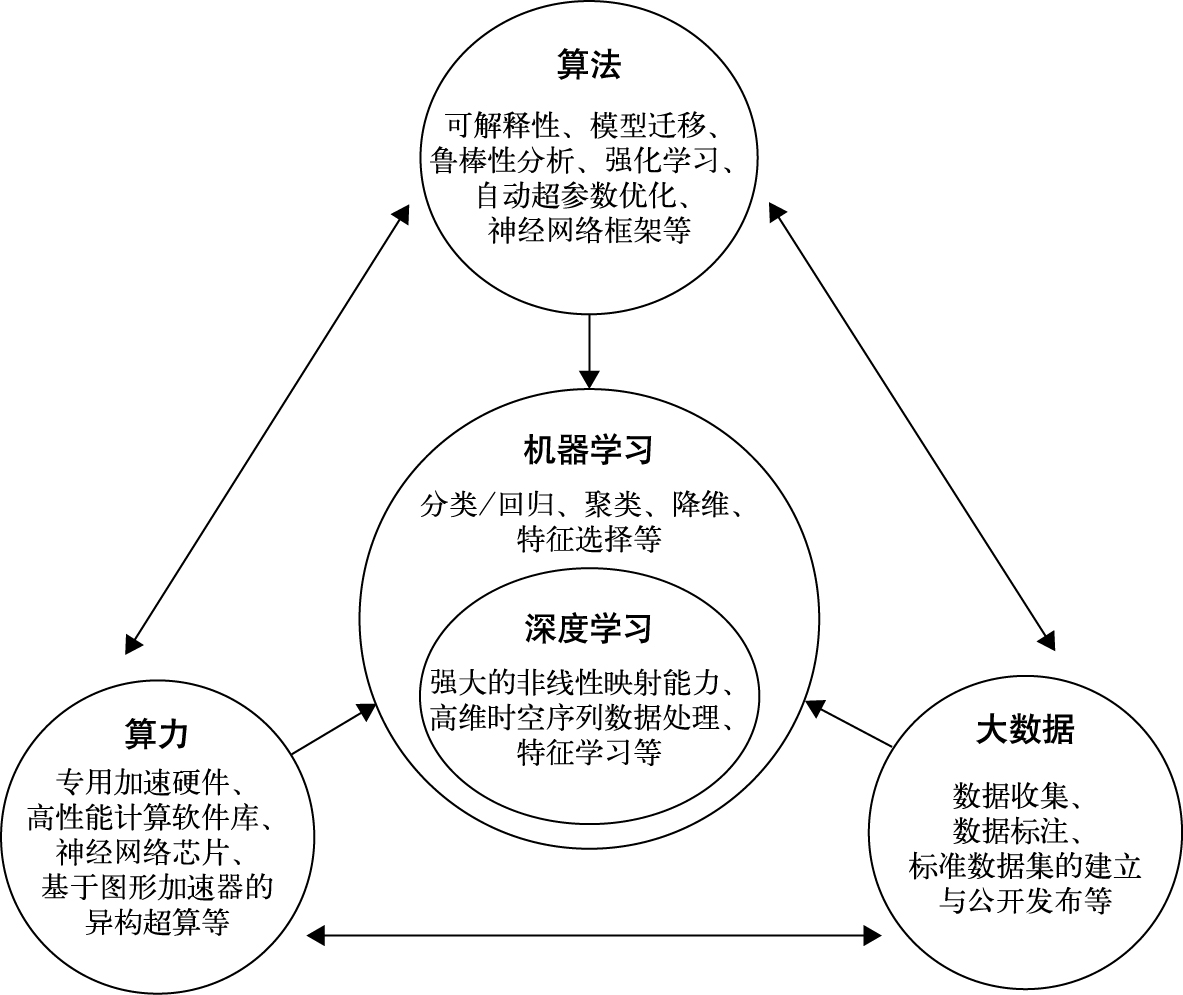
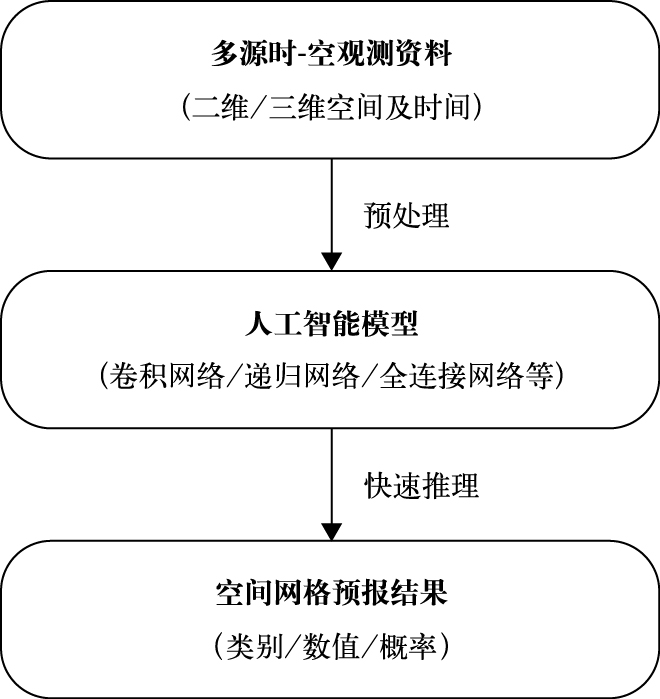
 本站查看
本站查看