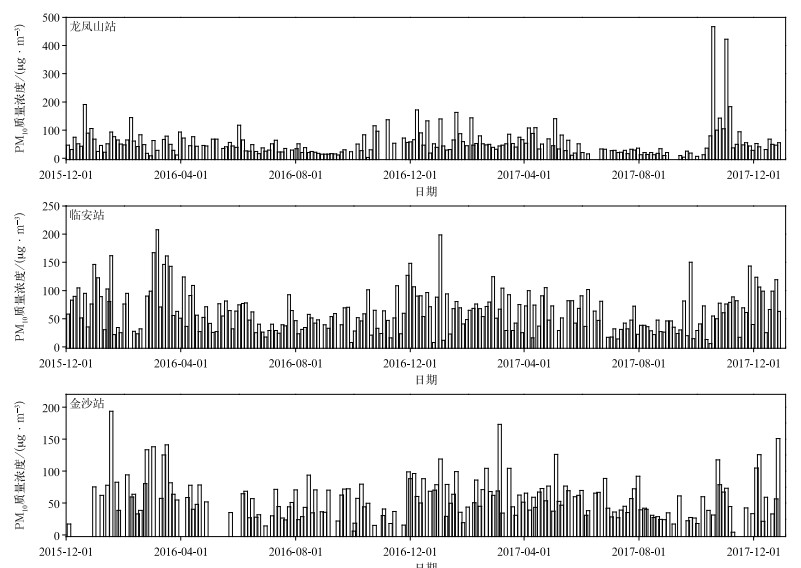
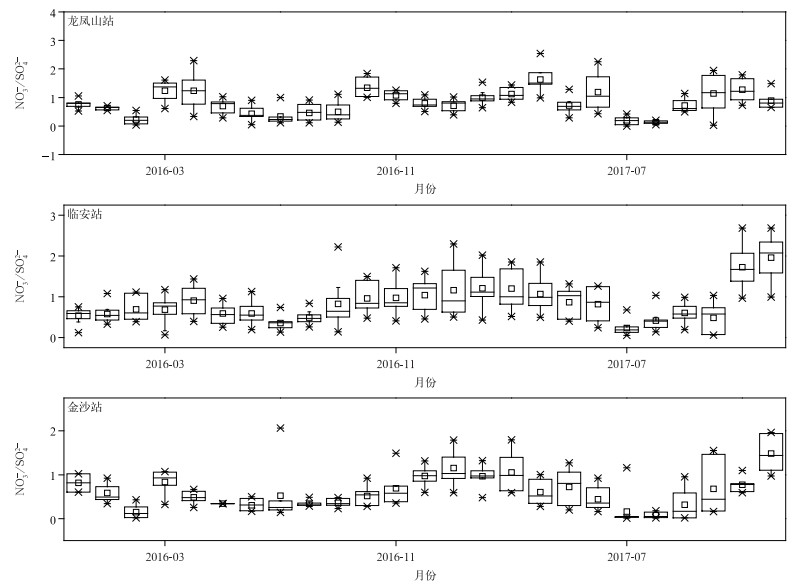
|
[1]
|
Molnár A, Mészáros E, Hansson H C, et al.Importance of organic and elemental carbon in the fine atmospheric aerosol particles.Atmos Environ, 1999, 17(33): 2745-2750.
|
|
[2]
|
Li D P, Cheng X H, Sun Z A, et al.Radiative effects of aerosols in different areas of Beijing. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(5): 609-618. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180509 |
|
[3]
|
Ma X L, Gao X N, Liu Y, et al.Simulations of aerosol influences on the East Asian winter monsoon. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2018, 29(3): 333-343. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20180307 |
|
[4]
|
Liang Y X, Che H Z, Wang H, et al.Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects during a pollution episode in Beijing. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(5): 583-594. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200506 |
|
[5]
|
Heintzenberg J.Fine particles in the global troposphere-A review.Tellus, 1989, 41B: 149-160.
|
|
[6]
|
Xu J, Bergin M H, Yu X, et al.Measurement of aerosol chemical, physical, and radiative properties in the Yangtze delta region of China. Atmos Environ, 2002, 36: 161-173. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00455-1 |
|
[7]
|
Matta E, Facchini M C, Decesari S, et al.Mass closure on the chemical species in size-segregated atmospheric aerosol collected in an urban area of the Po Valley, Italy. Atmos Chem Phys, 2003, 3(3): 623-637. doi: 10.5194/acp-3-623-2003 |
|
[8]
|
Fridlind A M, Jacobson M Z.A study of gas-aerosol equilibrium and aerosol pH in the remote marine boundary layer during the First Aerosol Characterization Experiment (ACE 1). J Geophys Res Atmos, 2000, 105(D13): 17325-17340. doi: 10.1029/2000JD900209 |
|
[9]
|
Svenningsson B, Hansson H C, Wiedensohler A, et al.Hygroscopic growth of aerosol particles and its influence on nucleation scavenging in cloud:Experimental results from Kleiner Feldberg.J Atmos Chem, 1994, 19(1): 129-152.
|
|
[10]
|
Tao J, Ho K F, Chen L G, et al.Effect of chemical composition of PM 2.5 on visibility in Guangzhou, China, 2007 spring. Particuology, 2009, 7(1): 68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2008.11.002 |
|
[11]
|
Offenberg J H, Baker J E.Aerosol size distributions of elemental organic carbon in urban and over-water atmosphere. Atmos Environ, 2000, 34(10): 1509-1517. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00412-4 |
|
[12]
|
Zheng B, Tong D, Li M, et al.Trends in China's anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos Chem Phys, 2018, 18(19): 14095-14111. doi: 10.5194/acp-18-14095-2018 |
|
[13]
|
Zhao S P, Yin D Y, Yu Y, et al.PM 2.5 and O 3 pollution during 2015-2019 over 367 Chinese cities:Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ Pollut, 2020, 264: 114694. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114694 |
|
[14]
|
Wang Y S, Li W J, Gao W K, et al.Trends in particulate matter and its chemical compositions in China from 2013-2017. Sci China Earth Sci, 2019, 62: 1857-1871. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9373-1 |
|
[15]
|
Zhang Y M, Vu V T, Sun J Y, et al.Significant changes in chemistry of fine particles in wintertime Beijing from 2007 to 2017:Impact of clean air actions.Environ Sci Technol, 2019, 54: 1344-1352.
|
|
[16]
|
Zhang Y M, Yan P, Yang D Z, et al.Seasonal physical and chemical features variation of ambient aerosol in Lin'an. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2007, 18(5): 635-644. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2007.05.008 |
|
[17]
|
Zhang X Y, Wang Y Q, Niu T, et al.Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China:Spatial/Temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos Chem Phys, 2012, 12(2): 779-799. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-779-2012 |
|
[18]
|
Luan T, Guo X L, Zhang T H, et al.The scavenging process and physical removing mechanism of pollutant aerosols by different precipitation intensities. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(3): 279-291. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190303 |
|
[19]
|
Zhang X Y, Wang J Z, Wang Y Q, et al.Changes in chemical components of aerosol particles in different haze regions in China from 2006 to 2013 and contribution of meteorological factors. Atmos Chem Phys, 2015, 15(22): 12935-12952. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-12935-2015 |
|
[20]
|
Wang Y H, Gao W, Wang S, et al.Contrasting trends of PM 2.5 and surface-ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2017. National Science Review, 2020, 7(8): 1331-1339. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa032 |
|
[21]
|
Ke H B, Gong S L, He J J, et al.Assessment of open biomass burning impacts on surface PM 2.5 concentration. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(1): 105-116. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200110 |
|
[22]
|
Zhang F J, Xu J, Ma J Z, et al.Impact of crop residue burning on PM 2.5 inorganic components in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding areas. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(4): 467-478. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190407 |
|
[23]
|
Yan P, Zhang R J, Huan N, et al.Characteristics of aerosols and mass closure study at two WMO GAW regional background stations in eastern China. Atmos Environ, 2012, 60: 121-131. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.05.050 |
|
[24]
|
Yan P, Mao J T, Yang D Z, et al.The characterization of aerosol physical and chemical properties at Lin'an station during the transport of a sandstorm.Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(4): 437-446.
|
|
[25]
|
Zhang D W, Wang X J, Liu B X, et al.Characteristics of PM2.5 and its chemical composition in the urban area of Beijing.Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(8): 1186-1192.
|
|
[26]
|
Yang S X, Cao J J, Shen Z X, et al.Variations of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at Xi'an between summer and winter.Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(8): 1179-1188.
|
|
[27]
|
Zhang H, An Q, Zhao S Y, et al.Advances in the research of optical properties and radiative forcing of nitrate aerosols.Acta Meteor Sinica, 2017, 75(4): 539-551.
|
|
[28]
|
Zhou L, Wang W, Hou S, et al.Heterogeneous uptake of nitrogen dioxide on Chinese mineral dust.J Environ Sci, 2015(36): 110-118.
|
|
[29]
|
|
|
[30]
|
Jia X F, Yan P, Meng Z Y, et al.Characteristics of PM 2.5 in heavy pollution events in Beijing and surrounding areas from November to December in 2016. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(3): 302-315. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190305 |
|
[31]
|
|




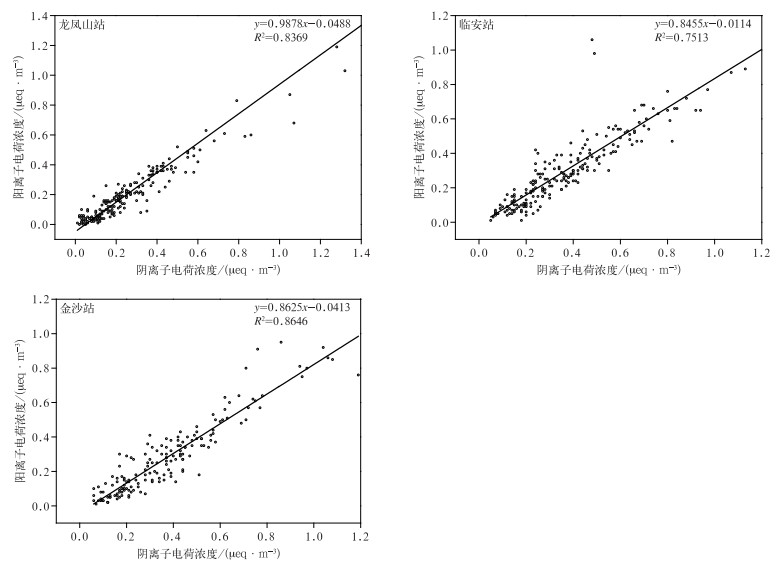
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: